
Experts Warn About 5 Can.cer Warning Signs Many People Overlook
5 subtle cancer warning signs experts say you should never ignore
Ginger has long been celebrated as a natural remedy for nausea, inflammation, and digestive discomfort. From herbal teas to supplements and cooking ingredients, this spicy root has earned a reputation as a powerful superfood. However, despite its many benefits, ginger is not always suitable for everyone. For some individuals, consuming ginger regularly or in large amounts may actually lead to unwanted side effects or health risks.
Health experts suggest that people with certain medical conditions should be cautious when including ginger in their diets. Understanding when ginger might do more harm than good can help individuals make safer dietary choices and protect their overall well-being.

Ginger is known for its natural blood-thinning properties. While this can be beneficial for improving circulation, it may pose risks for individuals with bleeding disorders such as hemophilia or those prone to excessive bleeding. Consuming ginger in large quantities may increase the likelihood of bruising or prolonged bleeding.
Additionally, people who are taking blood-thinning medications like aspirin or anticoagulants should be particularly cautious. Combining ginger with these medications could enhance their effects and raise the risk of internal bleeding. Consulting a healthcare professional before consuming ginger regularly is strongly recommended for individuals in this group.
Because ginger can slow blood clotting, doctors often advise patients to avoid it before surgical procedures. Consuming ginger in the days or weeks leading up to surgery may increase bleeding during and after the operation, potentially complicating recovery.
Most medical professionals recommend discontinuing ginger supplements and limiting ginger intake at least one to two weeks before surgery. This precaution helps reduce the risk of excessive bleeding and ensures safer surgical outcomes.
Ginger may stimulate bile production, which can aid digestion for many people. However, for those with gallstones or gallbladder disease, this stimulation may trigger discomfort or complications. Increased bile flow could potentially worsen symptoms such as abdominal pain or nausea.
Individuals with a history of gallbladder problems should consult their doctors before adding significant amounts of ginger to their diet. In some cases, avoiding ginger altogether may be the safest option.
Ginger is sometimes praised for its ability to help lower blood pressure naturally. While this can be beneficial for people with hypertension, it may not be suitable for those who already have low blood pressure. Consuming ginger regularly could cause blood pressure to drop further, leading to dizziness, fainting, or weakness.
People who frequently experience lightheadedness or have been diagnosed with hypotension should monitor their ginger intake carefully. If symptoms worsen after consuming ginger, reducing or eliminating it from the diet may help.

Ginger is often used to relieve morning sickness during pregnancy, and in small amounts, it is generally considered safe for many expectant mothers. However, excessive ginger consumption may carry potential risks. Because ginger can influence blood clotting and hormone levels, high doses may not be advisable for all pregnancies.
Pregnant women with a history of miscarriage, bleeding disorders, or high-risk pregnancies should consult their healthcare providers before consuming ginger regularly or taking ginger supplements. Personalized medical advice ensures both mother and baby remain safe.
For most healthy individuals, moderate ginger consumption is unlikely to cause harm and may even offer several health benefits. However, as with any natural remedy or supplement, more is not always better. Consuming large amounts without understanding personal health conditions can lead to unintended consequences.
Experts recommend using ginger in reasonable quantities and paying attention to how the body responds. Those with existing health concerns or who are taking medications should always seek professional medical guidance before making significant dietary changes.
Ginger remains a valuable ingredient in many cuisines and traditional healing practices. Its anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits are well documented, making it a popular choice for maintaining overall health. Still, recognizing that certain individuals may need to limit or avoid ginger is essential.

5 subtle cancer warning signs experts say you should never ignore
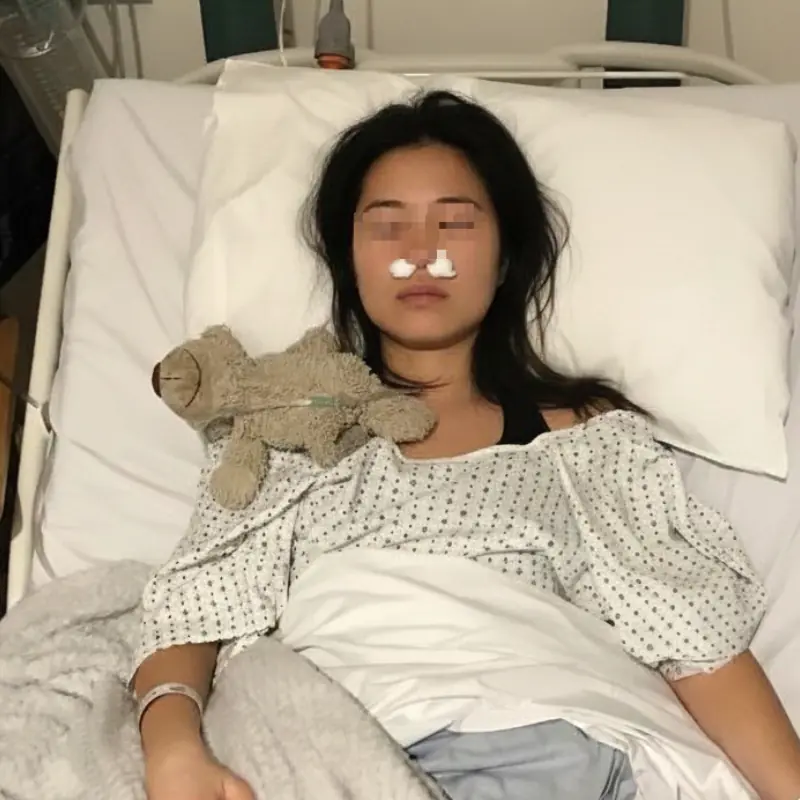
Hidden daily habit leads to serious nasal fungal infection case
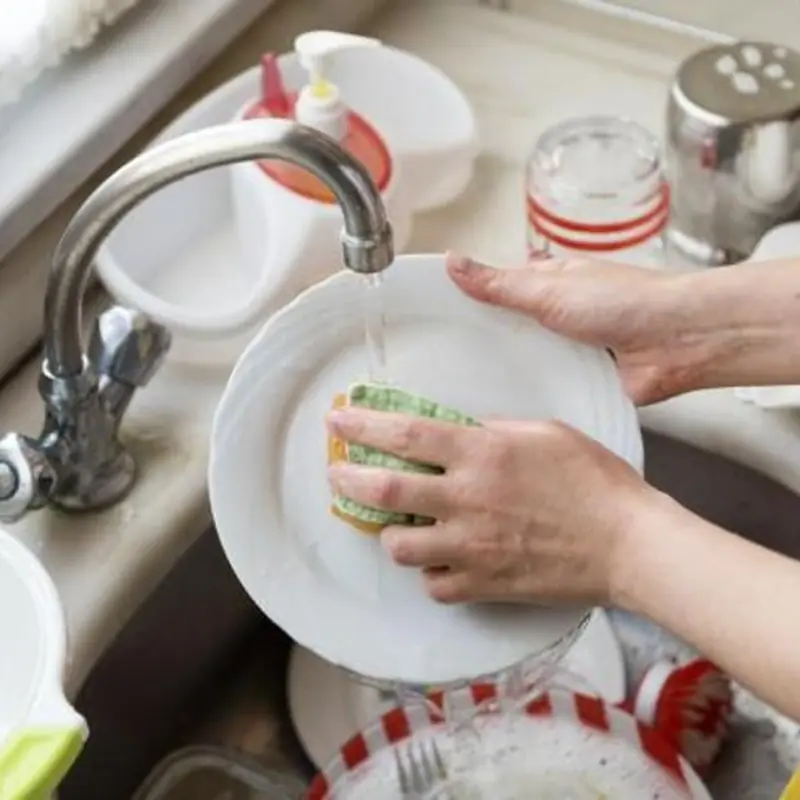

A simple dishwashing habit may pose hidden health risks at home.

Sweet Potatoes: A Nutritious Food for Health and Taste
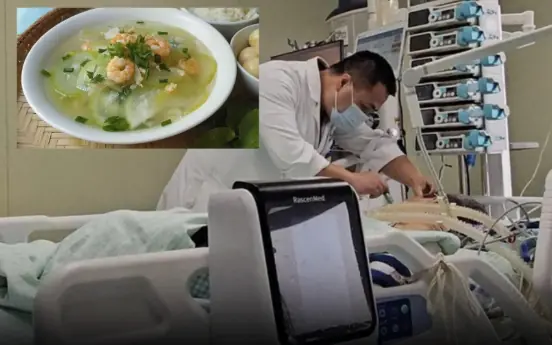
According to Mrs. Wang's account, before being hospitalized, she ate a bowl of bitter gourd soup.
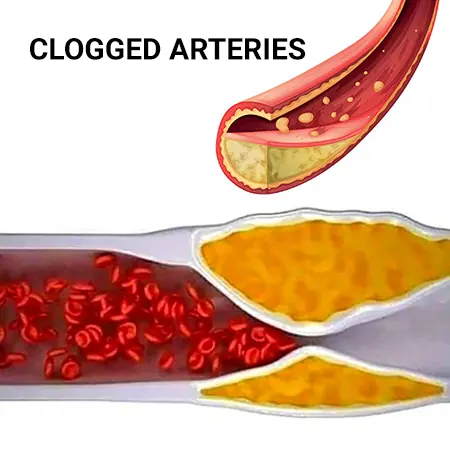
Clogged arteries rarely happen overnight. Instead, they develop slowly as fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up inside blood vessels, a process known as atherosclerosis.

Broccoli has earned its place as one of the healthiest vegetables on the planet — and for good reason.

When you have to be at work bright and early the next morning, it’s extremely unpleasant to wake up at an ungodly hour and find yourself unable to get back to sleep.
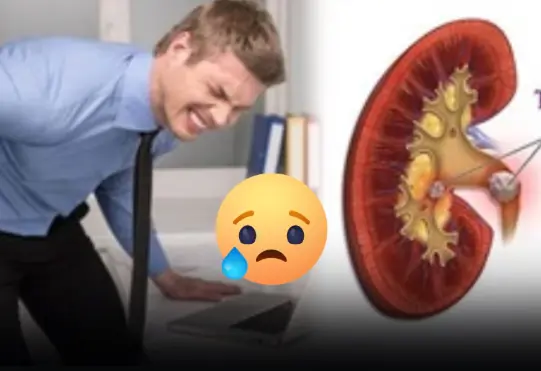
Kidney stones are one of the most common urinary stone disorders, especially among middle-aged men.

Guava leaves are not only an ingredient in cooking but also have many wonderful uses for health and beauty. Here are some of the outstanding benefits of guava leaves:

Here are 4 best vegetables that can help prevent cancer due to their rich content of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals:
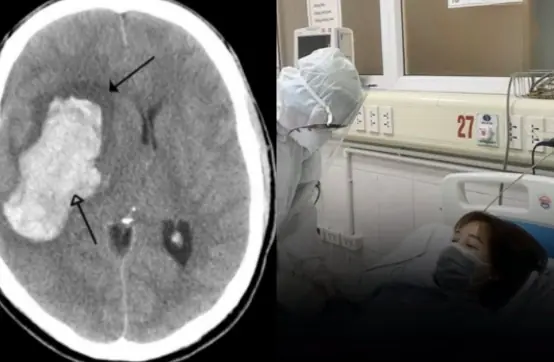
Even young individuals can experience strokes

It’s fragrant, refreshing, and a staple in many Southeast Asian kitchens

Oregano may seem like just another kitchen herb, but this small, fragrant leaf carries a surprising amount of medicinal power.

Boiled eggs are one of the most common and convenient foods in everyday life.

Although often praised as a “golden beverage” for its benefits to cardiovascular health, brain function, and energy metabolism, coffee is not always good for the body if consumed at the wrong time.
8 foods that are incompatible with tumors, remind each other to eat them regularly
Hidden bedroom pollutants may quietly threaten lung health
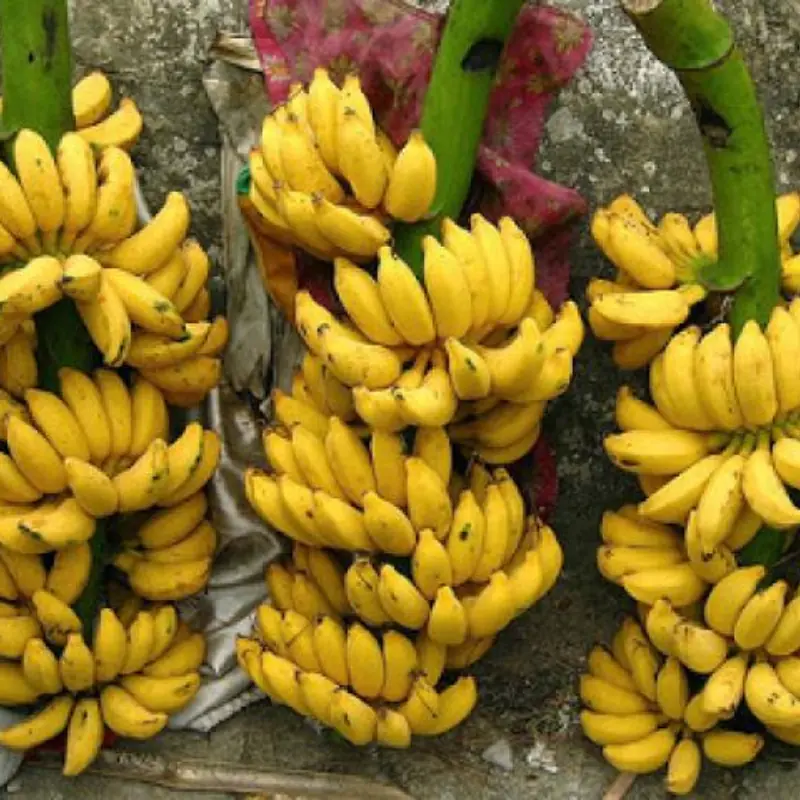

Why a simple banana at night may change how you sleep

5 subtle cancer warning signs experts say you should never ignore

Hidden daily habit leads to serious nasal fungal infection case

A simple dishwashing habit may pose hidden health risks at home.

Sweet Potatoes: A Nutritious Food for Health and Taste




According to Mrs. Wang's account, before being hospitalized, she ate a bowl of bitter gourd soup.

Home remedies to remove tartar dental

Clogged arteries rarely happen overnight. Instead, they develop slowly as fat, cholesterol, and other substances build up inside blood vessels, a process known as atherosclerosis.

10 signs that a man shows when he's in love
I was ashamed of my mom’s old car until the night it saved my dad

I almost sold my late father’s house to a stranger — until my son asked me one question that changed everything

The empty chair at the table said more than words ever could

We pretended everything was fine until it wasn’t

I thought my parents were strong until i saw them break

Managing blood sugar does not have to rely solely on medication or strict dietary deprivation.

Broccoli has earned its place as one of the healthiest vegetables on the planet — and for good reason.