
Is It Safe to Sleep with a Fan On? Here’s What Happens to Your Body
What Happens to Your Body When You Sleep with a Fan Running?

Tomatoes are colorful, delicious, and packed with essential nutrients. Often celebrated as a “superfood,” tomatoes are used in countless dishes—from salads and sauces to juices and stir-fries. They’re rich in vitamin C, potassium, antioxidants like lycopene, and various other nutrients that promote heart health, improve skin, and fight inflammation.
However, despite their health benefits, not everyone should include tomatoes in their diet without caution. For certain individuals, eating tomatoes may lead to unpleasant or even harmful health effects. Here are six groups of people who should consider avoiding or limiting their tomato intake to prevent adverse symptoms.
Tomatoes are naturally acidic, containing high levels of citric acid and malic acid. These compounds can stimulate the stomach to produce more gastric acid. For people suffering from acid reflux or gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), this can aggravate symptoms like heartburn, chest discomfort, or regurgitation.
Even cooked tomatoes—like those in pasta sauces or soups—can trigger these symptoms. If you’re prone to acid reflux, it's wise to monitor your body's reaction to tomatoes and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized dietary guidance.
IBS is a chronic gastrointestinal disorder that causes symptoms like bloating, gas, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. People with IBS often have sensitivities to certain foods, particularly those that are high in fiber or certain sugars.
Tomatoes, especially their skins and seeds, can irritate the gut lining and worsen IBS symptoms. Some people also experience allergic-like reactions or digestive discomfort after eating large quantities of tomatoes. If you suffer from IBS, consider tracking your symptoms and reducing or avoiding tomato-based foods as necessary.
Histamine intolerance occurs when the body is unable to break down histamine efficiently, often due to a deficiency of the enzyme diamine oxidase (DAO). Since tomatoes are considered a high-histamine food, consuming them can cause unpleasant symptoms such as:
Headaches
Skin rashes or hives
Nasal congestion
Digestive issues
If you’ve experienced these reactions and suspect histamine intolerance, speak with a medical professional. Avoiding tomatoes may help alleviate symptoms significantly.
Tomatoes are high in potassium, which is essential for healthy nerve and muscle function. However, for individuals with chronic kidney disease, excess potassium can lead to hyperkalemia—a potentially life-threatening condition that affects heart rhythm.
In addition, tomato sauces and processed tomato products are rich in oxalates, compounds that can contribute to kidney stone formation, particularly in those already at risk. People with kidney issues or a history of stones should limit tomato intake or avoid it entirely, depending on medical advice.
Although relatively rare, some people are allergic or sensitive to tomatoes. Allergic reactions can range from mild to severe and may include:
Skin itching, hives, or eczema
Sneezing, coughing, or runny nose
Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
Nausea or stomach upset
In some cases, touching raw tomatoes can also cause allergic contact dermatitis, resulting in itchy, swollen, or inflamed skin. If you experience any of these symptoms, it's best to get tested and avoid tomato exposure altogether.
Gout is a type of arthritis caused by high levels of uric acid in the blood. This acid forms crystals in the joints, leading to sudden and intense pain. Tomatoes contain purines—organic compounds that break down into uric acid. Additionally, the vitamin C in tomatoes can react with uric acid in a way that triggers crystallization, worsening gout attacks.
While the purine content in tomatoes is moderate compared to meats or alcohol, even small amounts can trigger symptoms in sensitive individuals. People living with gout should consult a doctor before adding tomatoes back into their diet.
If you fall into one of the categories above, don’t worry—there are several delicious and nutritious substitutes for tomatoes that offer similar taste and color:
Red bell peppers – Sweet and rich in vitamin C, perfect for salads or cooking
Ripe tamarind or lemon juice – A tangy alternative for soups and sauces
Pumpkin or butternut squash – For a sweeter, creamy texture in stews
Carrots and beets – Naturally sweet with a vibrant hue
These ingredients can often mimic the role of tomatoes in cooking while being easier on your system.
Tomatoes are undeniably healthy for most people, offering powerful antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals. However, they can pose health risks for individuals with acid reflux, IBS, histamine intolerance, kidney problems, allergies, or gout.
As always, listen to your body. If tomatoes make you feel unwell, don’t ignore the symptoms. Consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and explore alternative foods that nourish you without causing harm.
Remember: “Healthy food” isn’t one-size-fits-all—what works for many may not work for you.

What Happens to Your Body When You Sleep with a Fan Running?

Why Do Your Legs Often Feel Numb? Common Causes and Conditions

Stop the Pain: 3 Powerful Home Remedies for Canker Sores

Some common foods may contain parasites if poorly handled or cooked.
Kidney Red Flags: Warning Signs Your Body Is Trying to Tell You

Peanuts offer nutrients but may affect health in certain cases.
Some morning eating habits may affect long-term stomach health.
4 morning foods to eat on an empty stomach for a healthier gut and better digestion
Drinking Lemon Peel Water Daily: 5 Powerful Health Benefits You Should Know
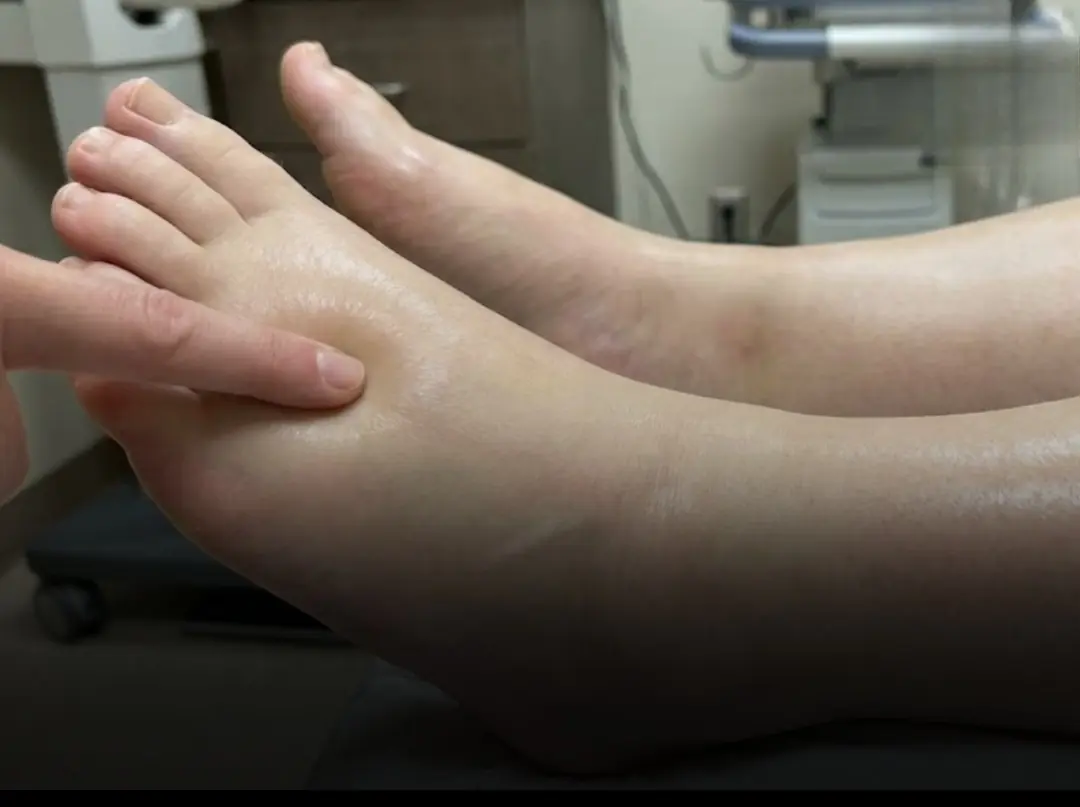
Effective Ways to Reduce Water Retention Naturally

If your legs cramp at night, you need to know this immediately

No more night cramps — here’s how to avoid them
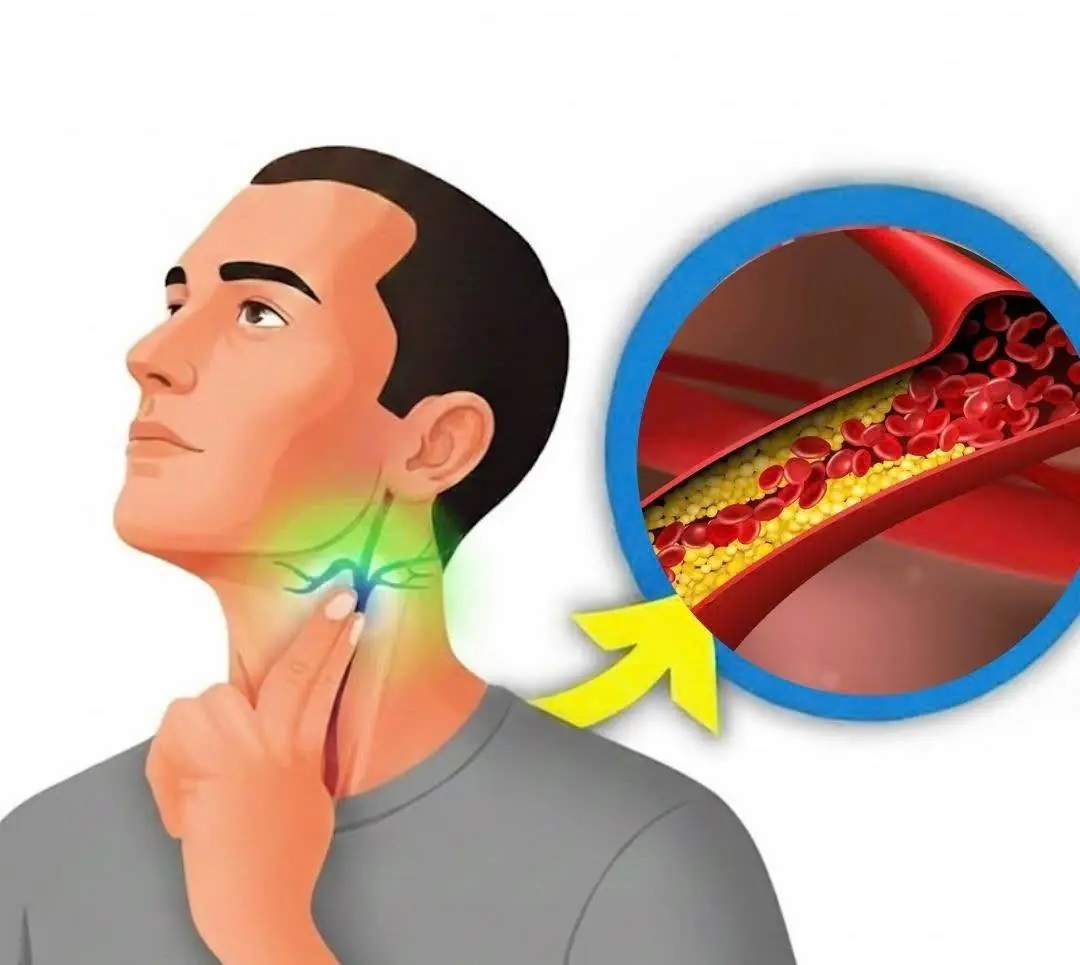
6 Best Remedies That May Help Keep Your Arteries Healthy and Improve Circulation
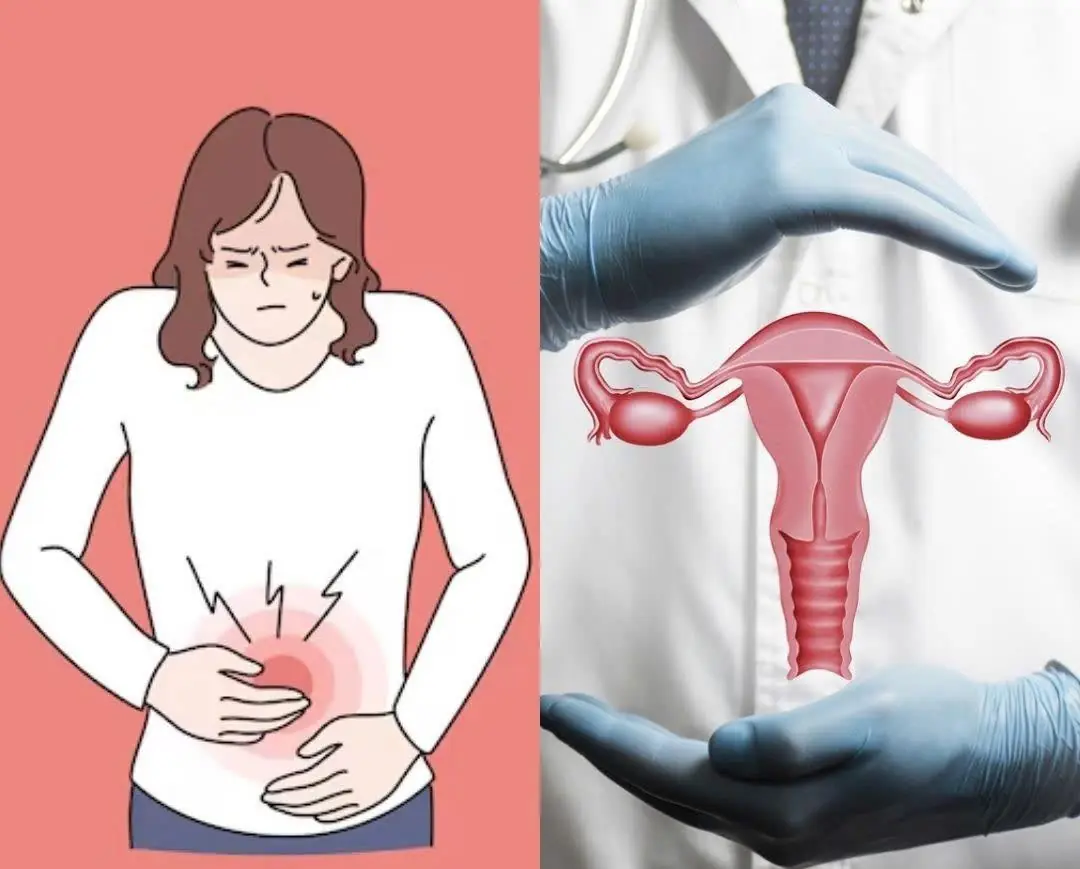
8 Early Warning Signs of Ovarian Cancer That Many Women Ignore
Pay attention to the following 3 areas
3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cer:vical C.a.n.c.e.r
These are the symptoms nearly half of str:oke patients feel days before the att:ack

Just as your body is finally surrendering to sleep, it happens.:

Avoid These 5 Foods in the Morning for Better Health

What Happens to Your Body When You Sleep with a Fan Running?

Why Do Your Legs Often Feel Numb? Common Causes and Conditions

What Happens When You Put Peppercorns Under Your Bed?

Stop the Pain: 3 Powerful Home Remedies for Canker Sores

Some common foods may contain parasites if poorly handled or cooked.

Kidney Red Flags: Warning Signs Your Body Is Trying to Tell You

One Natural Ingredient That Can Transform Your Skin

Thick ice in your fridge can be removed quickly with this trick.

Peanuts offer nutrients but may affect health in certain cases.

Some morning eating habits may affect long-term stomach health.

4 morning foods to eat on an empty stomach for a healthier gut and better digestion

Drinking Lemon Peel Water Daily: 5 Powerful Health Benefits You Should Know

Effective Ways to Reduce Water Retention Naturally

If your legs cramp at night, you need to know this immediately

No more night cramps — here’s how to avoid them

6 Best Remedies That May Help Keep Your Arteries Healthy and Improve Circulation

8 Early Warning Signs of Ovarian Cancer That Many Women Ignore

Pay attention to the following 3 areas


3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cer:vical C.a.n.c.e.r