Why Do Healthy People Suddenly Die After Being Diagnosed with Can.cer? Doctors Explain the Reasons
Why Do Healthy People Suddenly Die After Being Diagnosed with Can.cer? Doctors Explain the Reasons
There are individuals who seem perfectly healthy for years but cannot survive after being diagnosed with can.cer. Why does this happen?

Many people have wondered: why do some individuals appear to be in good health, yet rapidly deteriorate and even pass away shortly after receiving a cancer diagnosis?
In reality, this is not uncommon. It vividly reflects how cancer progresses in many patients. Before being diagnosed, they may live a normal life, feel optimistic, and show no obvious symptoms. Even with a tumor developing inside, their physical condition remains relatively stable.
However, everything can change dramatically the moment they hear the words “you have cancer.” No matter how strong or resilient a person may be, it’s hard to avoid both physical and emotional decline. The transformation can be visibly drastic: hair loss, sunken face, weakened body, and eventually struggling to walk.
Why Do Some People Die Soon After Being Diagnosed with Cancer?
-
Late Detection
Most cancers develop silently and show little to no symptoms in the early stages, making early diagnosis extremely difficult. Many people only discover the disease when the tumor is already advanced and has spread, making treatment less effective.
A prime example is pancreatic cancer — often called the “king of cancers” due to its difficult-to-access location and vague early symptoms. Most patients are already in the late stage when diagnosed, with cancer having metastasized to other organs.
Therefore, if you notice unexplained rapid weight loss, prolonged fever, dull pain, or declining body functions, do not delay seeking medical advice.
-
High Malignancy and Rapid Progression
Some types of cancer grow very quickly and are highly aggressive, such as pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, bile duct cancer, or small-cell lung cancer. Even with modern treatments like chemotherapy, radiation, or targeted therapies, these high-grade cancers often respond poorly, and survival rates remain low.
For instance, more than 50% of pancreatic cancer patients die within six months of diagnosis.
-
Severe Psychological Shock
Many individuals experience intense psychological shock immediately after being told they have cancer. The perception of cancer as a “death sentence” can lead to depression, anxiety, insomnia, and rapid mental decline. This mental collapse often affects physical health, reduces treatment effectiveness, and in some cases, hopelessness accelerates the progression of the disease.
-
Genetic Mutations and Drug Resistance
Cancer is closely linked to genetic disorders. Cancer cells can mutate and “evolve,” making them resistant to treatment — especially targeted drugs or chemotherapy. Once drug resistance develops, treatment becomes significantly less effective and the disease progresses more quickly.
-
Weakened Overall Health
Many cancer patients already suffer from underlying conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, or heart disease. Cancer treatments like chemotherapy and radiation place an extra burden on the body. If the patient’s overall health is not strong enough, they may become too weak to endure the harsh treatment process.
-
Emergency Complications from Tumors
Cancer not only silently damages the body but can also cause sudden, life-threatening complications. For example:
-
Colon or stomach cancer can cause gastrointestinal perforation.
-
Liver cancer or large tumors may rupture and cause internal bleeding.
-
Lung cancer may lead to massive coughing up of blood, blocking airways and causing death within minutes.
The “Gold Standard” in Cancer Screening: Essential Tests to Be Done Regularly
Early detection of cancer plays a vital role in improving treatment outcomes and survival rates. Below are the gold-standard screening methods for various common cancers, especially recommended for high-risk groups.
-
Stomach Cancer: Gastroscopy combined with biopsy is the most effective method to diagnose and prevent stomach cancer. This type of cancer is one of the few that can be effectively prevented if detected early through routine endoscopy.
-
Lung Cancer: Low-dose spiral CT scan is considered the best option for lung cancer screening. According to official screening guidelines, high-risk individuals should undergo this scan to detect abnormalities early.
-
Colorectal Cancer: Colonoscopy is the gold standard for detecting colorectal cancer. Screening is recommended starting at age 45, including an annual fecal occult blood test and colonoscopy every 10 years up to age 75.
-
Liver Cancer: Screening should include both an alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) blood test and liver ultrasound. For high-risk individuals, doctors recommend screening every six months.
-
Cervical Cancer: Most cervical cancer cases are linked to high-risk HPV infections. The most effective screening method is a combination of HPV testing and Pap smear (TCT), widely used around the world.
-
Breast Cancer: The most common cancer among women. High-risk individuals should start screening at age 25. Mammography or regular breast ultrasound are prioritized methods for early detection.
-
Esophageal Cancer: For the general population, screening should begin at age 55. For high-risk groups (such as smokers, heavy drinkers, or those with acid reflux disease), screening is recommended from age 40. Gastroscopy is the chosen method for early esophageal cancer detection.
-
Prostate Cancer: Men aged 50 and older should undergo routine prostate cancer screening. The PSA (Prostate-Specific Antigen) test is simple, sensitive, and convenient for early detection.
Proactive screening and regular health check-ups help detect cancer at an early stage, increasing the chances of successful treatment and extending life expectancy. People — especially those in high-risk groups — should follow these screening recommendations as advised by healthcare professionals.
News in the same category


Can.cer often shows no pain early on. If you notice these 8 signs in the bathroom, don’t ignore them

Raw Veggies Might Be Hiding Worms: 5 Types You Shouldn’t Eat Uncooked
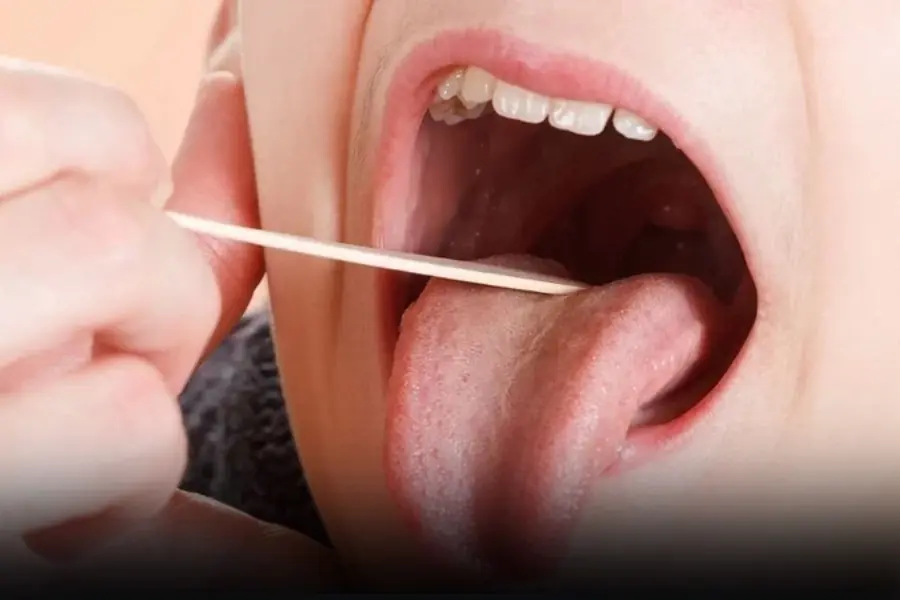
Mouth ulcers that did not heal for three months, went to the hospital for examination and discovered can.cer
These are the symptoms nearly half of str:oke patients feel days before the att:ack 👇
10 Warning Signs of Stroke One Month Before - Unbelievable Signs... Revealed!
Your Body May Be Whispering About Diabetes — Watch for These 10 Symptoms
If You Keep Noticing These 5 Strange Symptoms, Diabetes Might Be the Reason

Pay attention to the following 3 areas

Did You Know Waking Up at 3 or 4 A.M. Could Be a Clear Warning Sign of Something Serious?
Experts Warn to Avoid Them Now!

If you often feel a dull ache in your abdomen or around your navel, it may be your body signaling a potential problem.
If someone has prominent veins, share these important tips

Don’t ignore these 5 strange symptoms frequent signs may point to diabetes

3 Types of Pain That Could Be an Early Warning Sign of Can.cer
A small mistake led to a serious eye complication: Doctors warn of signs that may require can.cer screening

The risk of liver fluke infection from eating habits that many people have

No one would dare reheat cold rice to eat if they knew this terrible truth

A cup of hot water can cure 6 common dis.eases, simple but few people pay attention
Most stomach can.cers are detected late: Doctors say there are 5 symptoms after meals so you should have an early endoscopy
News Post

Surprising causes of hives revealed - What may be triggering your skin

Can.cer often shows no pain early on. If you notice these 8 signs in the bathroom, don’t ignore them

Raw Veggies Might Be Hiding Worms: 5 Types You Shouldn’t Eat Uncooked

Mouth ulcers that did not heal for three months, went to the hospital for examination and discovered can.cer

These are the symptoms nearly half of str:oke patients feel days before the att:ack 👇

10 Warning Signs of Stroke One Month Before - Unbelievable Signs... Revealed!

Your Body May Be Whispering About Diabetes — Watch for These 10 Symptoms

If You Keep Noticing These 5 Strange Symptoms, Diabetes Might Be the Reason

Pay attention to the following 3 areas

Did You Know Waking Up at 3 or 4 A.M. Could Be a Clear Warning Sign of Something Serious?

Experts Warn to Avoid Them Now!

If you often feel a dull ache in your abdomen or around your navel, it may be your body signaling a potential problem.

If someone has prominent veins, share these important tips

Spicy Braised Squid with Chili Oil and Sesame Eggs

Don’t ignore these 5 strange symptoms frequent signs may point to diabetes

3 Types of Pain That Could Be an Early Warning Sign of Can.cer

Crispy Sweet and Sour Chicken

Creamy Spicy Shrimp with Broccoli

A small mistake led to a serious eye complication: Doctors warn of signs that may require can.cer screening
