Are Green Tomatoes Toxic?
Are Green Tomatoes Toxic?
Some people believe green tomatoes should not be consumed due to their high toxicity levels. Is this true?

1. Nutritional Value of Green (Unripe) Tomatoes
Green tomatoes, which are not yet ripe, contain a variety of vitamins, minerals, and beneficial compounds that contribute to overall health. According to Master of Science and Traditional Medicine Practitioner Nguyen Dinh Thuc, Vice President and General Secretary of the Vietnam Association of Traditional Medicine, studies have shown that green tomatoes are rich in antioxidants. These antioxidants can reduce inflammation, repair tissue, prevent scarring, and promote smoother skin.
Unripe tomatoes are particularly rich in vitamin C, an essential nutrient for immune function and skin health. They also provide significant amounts of potassium, which supports heart health and muscle function.
Green tomatoes contain more calcium and magnesium than ripe tomatoes, both of which are crucial for bone health and other bodily functions.
Additionally, they are a good source of dietary fiber, promoting digestive health and helping regulate blood sugar levels. Chlorophyll, present in green tomatoes, also exhibits potential antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
While green tomatoes have lower lycopene levels than ripe ones, they still provide other antioxidants like beta-carotene and vitamin E, which protect cells from oxidative stress.
They also contain tomatine and solanine, plant chemicals that may offer health benefits in moderate amounts, including antibacterial and anticancer properties.
Certain culinary traditions even appreciate the unique flavor of green tomatoes in dishes like fried green tomatoes or green tomato salsa.
2. Compounds in Green Tomatoes That May Cause Toxicity
Green tomatoes contain solanine and tomatine, natural glycoalkaloids found in the nightshade family. These compounds act as the plant’s natural defense mechanisms against pests and fungi.
For humans, solanine and tomatine can be toxic when consumed in large quantities. Adults eating approximately 625 grams of green tomatoes might experience symptoms of poisoning.
The levels of these compounds decrease as tomatoes ripen, making ripe tomatoes safer to eat. Consuming small amounts of unripe green tomatoes is unlikely to harm most people. However, some individuals may experience digestive discomfort or gastrointestinal issues.
Common symptoms of solanine poisoning include:
- Nausea and vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Abdominal cramps
- Headaches
- Dizziness
People with sensitive digestive systems or pre-existing gastrointestinal conditions may be more susceptible to these effects.
To reduce the risk, cook green tomatoes, as heat can help lower solanine levels. If you experience persistent digestive issues after consuming green tomatoes, consult a healthcare provider.
3. Groups That Should Be Cautious with Green Tomatoes
While small amounts of green tomatoes are generally safe for most people, some groups should exercise caution:
- Pregnant women
- Young children
- Individuals with sensitive digestive systems
These groups are more vulnerable to potential adverse effects from solanine and tomatine.
Though unripe tomatoes typically contain relatively low levels of these compounds, minimizing consumption can reduce potential risks.
Conclusion
Eating green tomatoes in small amounts is not toxic, and they are still used in some culinary traditions. However, ripe tomatoes are a better choice, as they usually contain more lycopene and are safer for consumption. Whenever possible, choose ripe tomatoes for better nutritional benefits and reduced risk of adverse effects.
News in the same category


5 common foods that ha.rm your li.ver

5 Eye Symptoms That May Signal Your Li.ver Is Crying for Help – Women, Don’t Ignore These if You Want to Stay Healthy Every Day

Dried fruit becomes "tonic" Drink water every day to live healthy and long

Ca.nc.er cells destroyed in 42 days with a glass of juice has been successful

Himalayan fungus compound tweaked for 40x anti-c.a.n.cer boost, Scientists Say
8 Early Warning Signs of Sto.mach Can.cer: See a Doctor If You Have Even One

101-Year-Old Nutrition Professor Shares 7 Rules for Longevity and Health — Still Drives Around the World by Himself

The More You Drink, the Weaker Your Bones: 3 “Silent Kil.lers” That Drain Calcium from Your Body
The Hidden Culprits Behind Osteoporosis: 3 Popular Beverages You Should Watch Out For

9 drinks that can naturally reduce liver fat in just 2 weeks

Prevent Bad Blood Fats from ‘Flooding’ Your Bloodstream by Drinking This Highly Beneficial Beverage

Doctors Warn of Alarming Health Risks of Sleeping with a Fan On During Hot Weather

Reheating These 6 Dishes Could Turn Them into "Poison"
The Silent Threat: A Dangerous Disease Affecting 1 in 3 Asian Adults
Don’t Wait Until You’re Hospitalized to Regret It: Your Fingernails Have Been Warning You of a Serious Illness for Months!

More and More People Are Suffering From Cere.bral Infar.ction – Doctors Warn: Avoid These 3 Post-Meal Habits That Can Accelerate the Risk

A Sincere Warning: Always Wear Gloves When Doing These 7 Things—Or Risk Har.ming Your Health

51-Year-Old Man Shoc.ked to Discover Brain Dam.age: The “Culprit” Is 4 Favorite Dishes Many People Love

Women Who Do These 3 Things in the Morning Tend to Accumulate Less “To.xins,” Stay Younger, and Maintain a Great Figure
News Post

The Vegetable Dubbed the “King” of Cancer Prevention: Prepare It Right, and Its Benefits Multiply

Eating These 4 Fruits Regularly Can Harm Your Liver Even More Than Alcohol — But Many People Don’t Know It!

Why do flight attendants like to bring a banana on the plane?

What are the symptoms of no.seble.eds and when should you see a doctor?

Here's What Eating Blueberries Every Day Does to Your Body, Says a Registered Dietitian

No matter how delicious they are, don't eat these 5 parts of the pig or you'll get si.ck

5 common foods that ha.rm your li.ver

Tips to fix food that is too spicy when cooking

Adding only water when cooking rice is a big mistake. I will share with you the secret that hotels use

Cardinal Robert Francis Prevost elected as 267th pope, takes name Leo XIV

Take These 5 Items Out of Your Fridge Now One Day They Could Actually "Explode"

This type of leaf contains calcium

Is it right to close the door tightly when using the air conditioner

How to chase away a bunch of rats with just a handful of rice, without using toxic baits

5 Eye Symptoms That May Signal Your Li.ver Is Crying for Help – Women, Don’t Ignore These if You Want to Stay Healthy Every Day
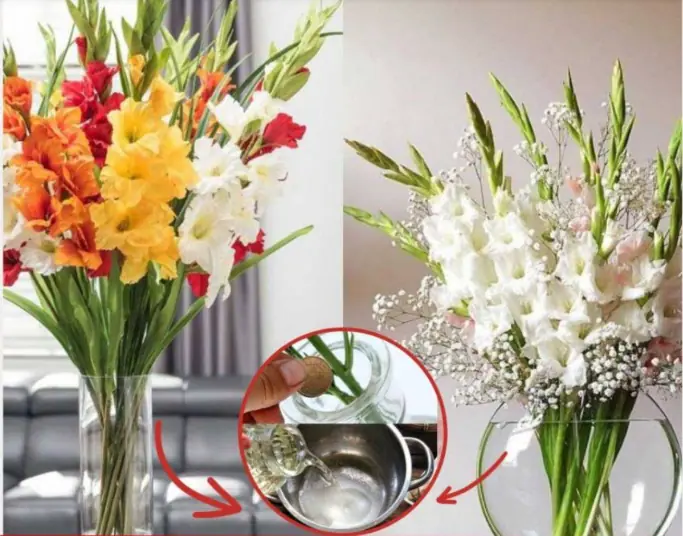

Tips to keep your flowers fresh
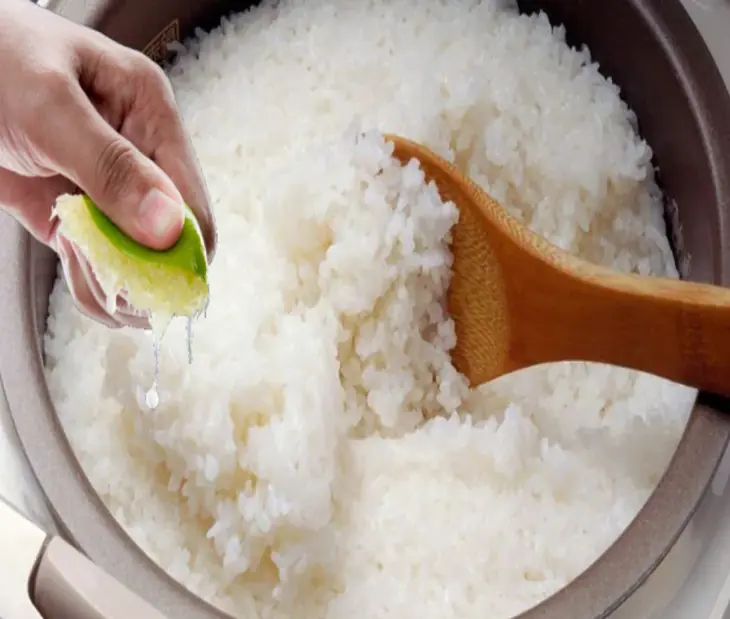

Tips to make rice more delicious that not everyone knows
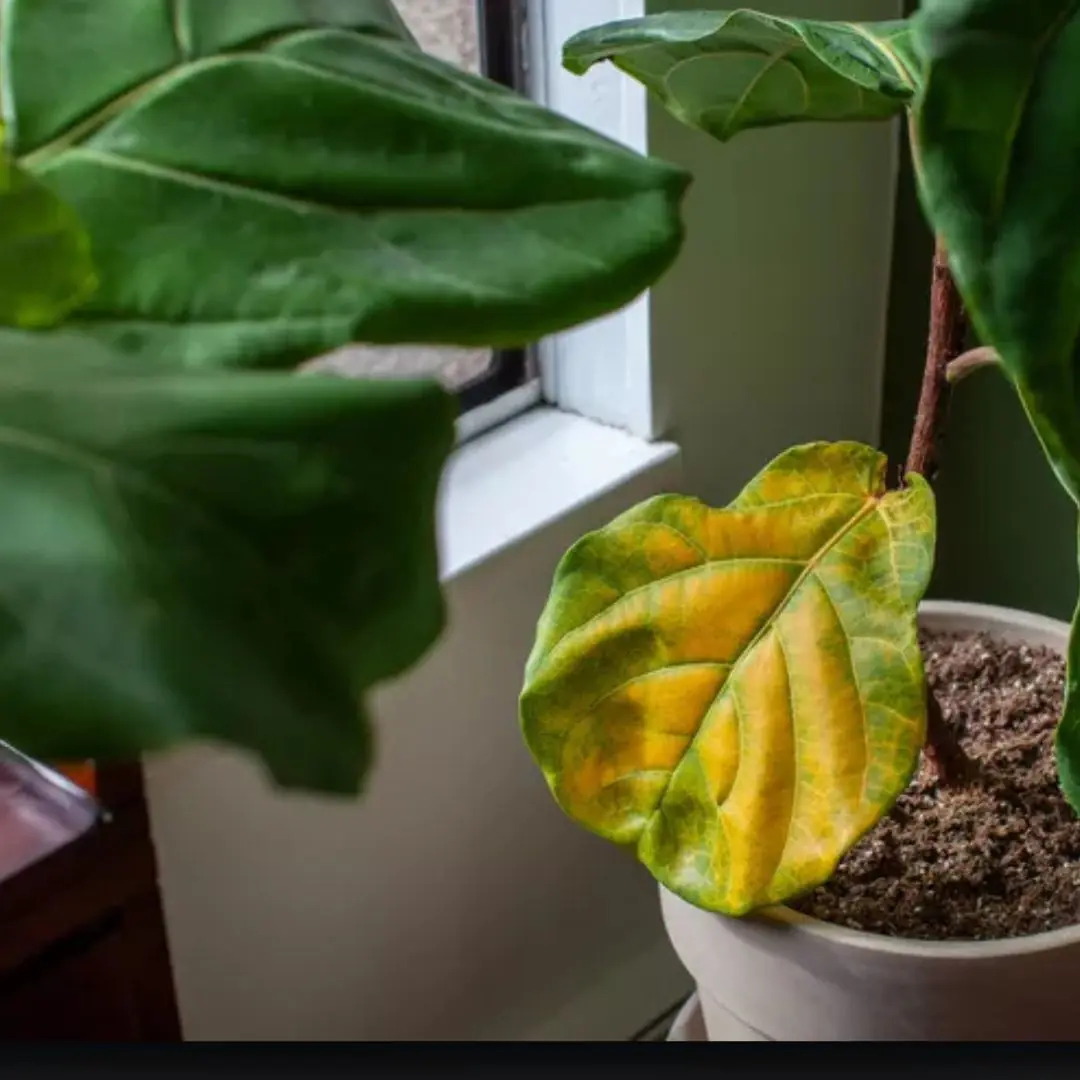

8 Plants You Should Never Grow Indoors—and What You Should Plant Instead
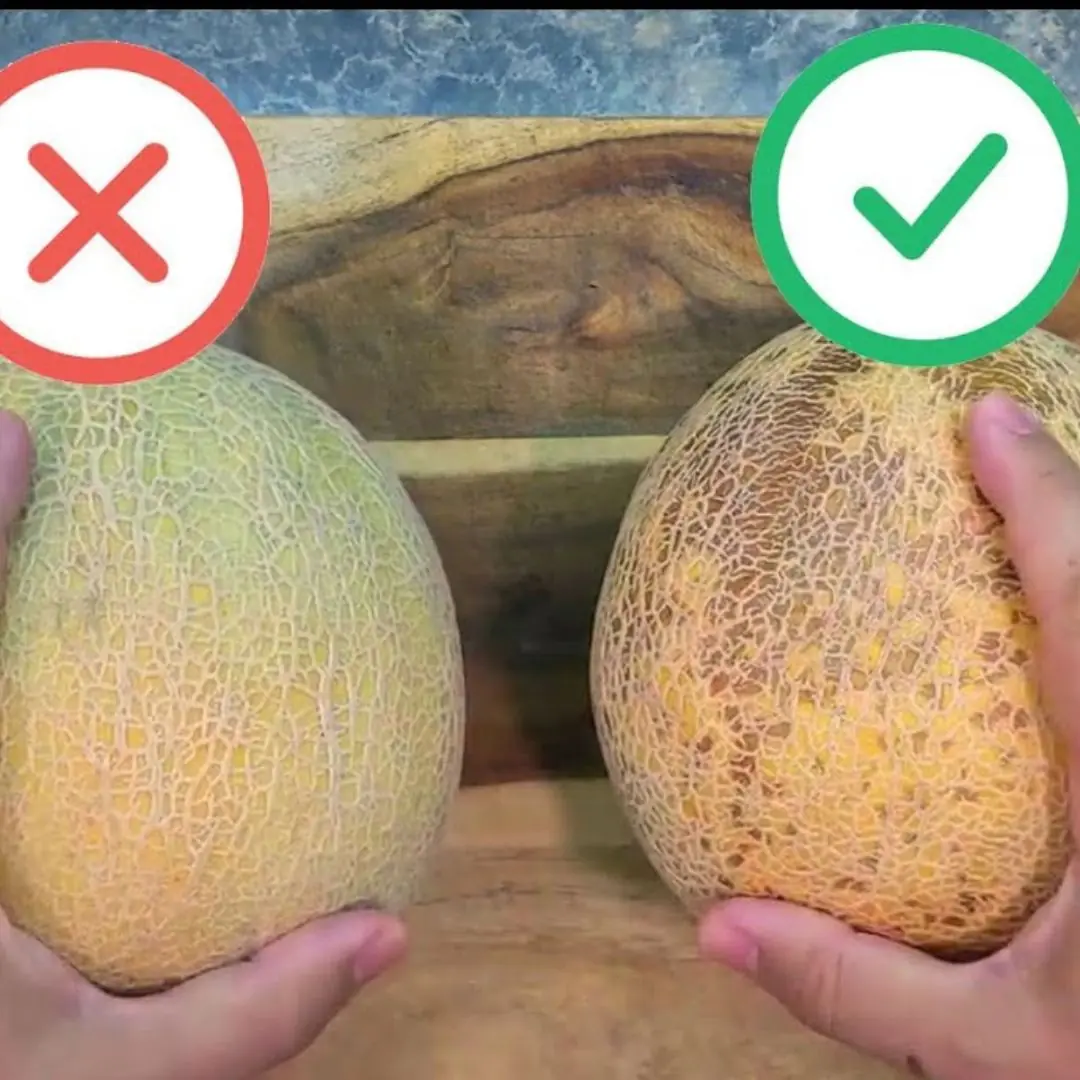

How to pick a sweet and juicy cantaloupe melon
