10 signs of coronary heart disease you must never ignore
Symptoms of coronary artery disease often begin silently but may be the very first warning of a life-threatening heart attack. Even a brief episode of chest pain or an unusual moment of breathlessness can be an emergency signal that patients frequently overlook. More concerning, many symptoms are atypical—especially in the elderly, women, and people with diabetes. Early and accurate recognition of cardiovascular symptoms is the key to protecting the heart before it’s too late. Do not ignore the following 10 warning signs, as they may represent the most critical window to save a life.
1. What you need to know about coronary artery disease
Symptoms of coronary artery disease typically result directly from the narrowing or blockage of the coronary arteries—the vessels that supply blood to the heart muscle. When blood and oxygen cannot reach the heart adequately, the cardiac muscle gradually weakens, leading to dangerous complications such as angina, heart attack, or heart failure.
1.1 What is coronary artery disease?
Coronary artery disease (also known as coronary heart disease) develops as a result of plaque buildup on the arterial walls. These plaques consist of cholesterol, inflammatory cells, and fats, which gradually narrow the vessel lumen and restrict blood flow. This process progresses silently for many years before producing noticeable cardiovascular symptoms.
Coronary artery disease forms due to the buildup of atherosclerotic plaque in artery walls. (Image: ADAM)
Notably, in some individuals—particularly women and people with diabetes—symptoms may be atypical, making diagnosis more challenging.
1.2 Causes of coronary artery disease
The causes include non-modifiable factors such as age, sex, and genetics. So, is heart disease hereditary? The answer is yes. If your family has a history of early cardiovascular disease, your risk is significantly higher. However, the most common causes are the modifiable risk factors: smoking, hypertension, dyslipidemia, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle.

1.3 Treatment of coronary artery disease
Treatment depends on severity and may involve lifestyle changes, medication, and coronary interventions. In severe cases or acute myocardial infarction, timely intervention during the “golden window” can save lives. What should you do when experiencing heart attack symptoms? Seek emergency medical care immediately—do not self-medicate or delay, as this can result in irreversible heart muscle damage.
Regular health checkups, controlling underlying conditions such as hypertension and diabetes, maintaining a healthy diet, and exercising consistently are essential measures for preventing coronary artery disease.
2. The 10 most common symptoms of coronary artery disease
Coronary artery disease is the leading cause of death among cardiovascular disorders. Yet many individuals are unaware of their condition until a serious event such as a heart attack occurs. Recognizing symptoms early is critical to timely treatment and reducing life-threatening complications.
Below are 10 common symptoms that should never be overlooked:
2.1 Chest pain (angina)
This is the classic sign of myocardial ischemia. Patients often feel pressure, heaviness, or tightness in the center of the chest. The pain may radiate to the jaw, neck, left shoulder, or arm, especially during exertion or emotional stress. It usually improves with rest or nitroglycerin.
2.2 Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath occurs when the heart muscle does not receive sufficient oxygen. Patients may feel breathless even during light activity or when lying down. This symptom is often overlooked, especially among older adults and diabetics.
2.3 Persistent fatigue
Reduced cardiac output (the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute) can make individuals feel weak and drained of energy even without significant exertion. This fatigue develops gradually, often mistaken for stress or general tiredness.
2.4 Dizziness or lightheadedness
Dizziness, faintness, or a floating sensation can occur when insufficient blood reaches the brain. This is commonly associated with low cardiac output or arrhythmias. Atrial fibrillation—a common arrhythmia—is a serious risk factor. It causes blood to pool inside the heart, increasing the risk of clots that can travel to the brain and cause ischemic stroke. Statistics show that 1 in 4 strokes is related to atrial fibrillation.
Dizziness and lightheadedness may also indicate coronary artery disease. (Image: Heart Foundation)
Blood clots may also block the pulmonary artery, leading to pulmonary embolism. Therefore, unexplained dizziness—especially if accompanied by palpitations—should not be ignored.
2.5 Palpitations
Rapid, irregular, or skipped heartbeats may indicate arrhythmias secondary to myocardial ischemia. These may occur alone or along with chest pain, causing persistent episodes of heart pounding.
2.6 Dull or sharp chest discomfort
Not all chest pain is severe. Some experience mild, intermittent, or dull chest discomfort. If such pain persists or recurs frequently, a cardiac evaluation is necessary.
2.7 Indigestion, bloating, or nausea
Unexplained indigestion, bloating, or nausea—especially with fatigue or chest discomfort—may be subtle signs of heart disease. In women, gastrointestinal symptoms often replace classic chest pain.
2.8 Excessive sweating
Cold or excessive sweating unrelated to exertion or heat is a warning sign of a potential heart attack. It is triggered by the sympathetic nervous system in response to severe oxygen deprivation in the heart.
2.9 Persistent high blood pressure
Chronic high blood pressure is both a risk factor and a symptom associated with coronary artery disease. If hypertension is prolonged and resistant to treatment, it may indicate vascular damage or evolving heart failure.
2.10 Swelling of the legs, ankles, or face
Fluid retention is a common sign of late-stage heart failure. Swelling of the lower legs, feet, or face accompanied by fatigue and shortness of breath suggests that the heart is no longer pumping effectively. This is a serious condition requiring immediate medical attention.
Swelling in the lower legs may indicate coronary artery disease. (Image: Times of India)
(Note: These symptoms may occur individually, progress silently, or appear together. Some patients may have no clear symptoms until a heart attack occurs.)
3. Who should pay special attention to heart symptoms?
The following groups should be particularly vigilant, as they are at higher risk of progressing to a heart attack if symptoms are missed:
-
Older adults: Risk increases with age as arteries lose elasticity.
-
Those with a family history of early cardiovascular disease: If parents or siblings developed heart disease early (before age 55 in men, 65 in women), your risk is higher. Heart disease can be hereditary, especially early-onset coronary disease.
-
Individuals with clear risk factors: Smoking, hypertension, diabetes, high cholesterol, obesity, chronic stress, and inactivity accelerate atherosclerosis.
-
People already experiencing symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, or palpitations but have not undergone cardiac evaluation.
These groups should undergo regular screening and seek medical advice promptly when abnormalities arise to prevent severe complications.
4. Cardiovascular treatment and monitoring at FV Hospital help reduce complications
4.1 Experienced coronary specialists
When symptoms of heart disease appear, it means the heart has already suffered from coronary narrowing. At FV Hospital, Dr. Hồ Minh Tuấn—Head of the Cardiology and Interventional Cardiology Department with 30 years of experience—leads the application of advanced techniques such as TAVI, OCT, IVUS, ROTApro, and the latest IVL (intravascular lithotripsy), along with AI-integrated 3mensio software for minimally invasive, highly effective coronary treatment. He is also a pioneer in implementing the “70-minute golden window” (compared to the international standard of 90 minutes) in emergency myocardial infarction care, saving many critical cases.
4.2 Advanced technology and techniques
FV follows a personalized treatment approach at every stage—from screening and diagnosis to treatment and follow-up:
-
Cathlab operates 24/7 to treat emergency cases such as acute chest pain, heart attacks, and complex arrhythmias. Under the policy “save the patient first—fees processed later,” emergency cardiac patients receive 100% health insurance benefits without transfer paperwork.
-
Accurate, advanced diagnostics: 3D echocardiography with AI, high-resolution coronary imaging such as OCT and IVUS allow detailed assessment of artery structure and plaque severity, helping physicians determine the most appropriate intervention.
-
Optimal, minimally invasive interventions: Stent placement, plaque modification using ROTApro, or TAVI for valve disease enable quick recovery and reduced complications.
-
Comprehensive risk-factor management: Along with interventions, patients receive guidance on lifestyle changes, blood pressure, glucose, and lipid control, exercise programs, and routine follow-ups with cardiology specialists.
Thanks to strong expertise and modern technology, FV has helped many patients survive acute phases, avoid heart attacks, and significantly improve long-term quality of life. When you or a loved one develops symptoms such as chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or persistent fatigue, do not hesitate—visit the Cardiology and Interventional Cardiology Department at FV Hospital for timely evaluation and treatment.
News in the same category

If you see these 3 signs every night before going to bed, be careful that c.a.ncer cells are being "raised" in your body
The X-ray of a Young Woman’s Stru.ggle with Ch.ronic Constipation
3 eye warning signs that signal an incoming stro.ke or cancer — ignore them at your own risk!

3 foods that become highly to.xic after mold appears - What you must know to protect your health

5 special health benefits your body gets when eating black sesame every day

7 health benefits of drinking lemon water you may not know
A 38-year-old female patient with gastric ulcer could not have imagined that just because of a familiar daily hobby

Doctor Issues Urgent Warning: Stop Eating These 4 Foods Immediately They Contain High Levels of Parasites

4 types of nuts are silently destr.oying the liver, causing can.cer if eaten a lot
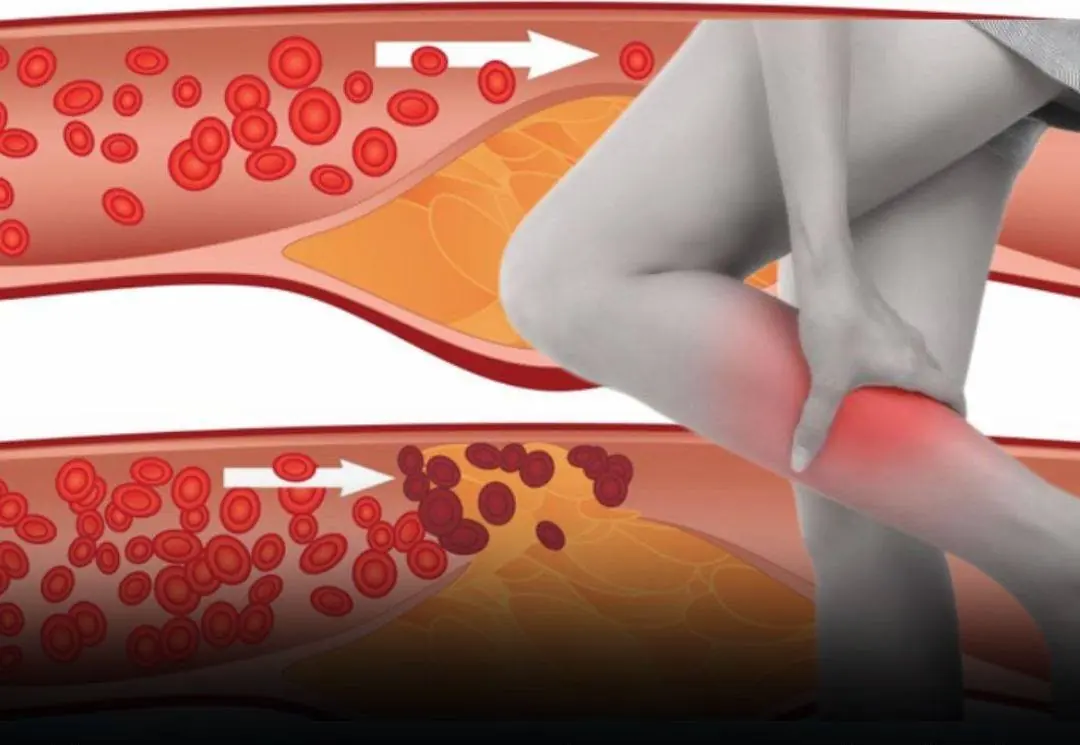
Few people recognize the warning signs of circulation problems that may appear in the feet and legs at night

If you notice these three nighttime signs before going to sleep, it may indicate that your body is under stress
The number of people experiencing kidney issues has been rising each year. Doctors warn that these four types of beverages should be limited to support kidney health.
Consume these 4 morning foods on an empty stomach to support intestinal cleansing, improve digestion, and promote overall health.
7 Foods That May Help Your Body Fight Can.cer Add Them to Your Diet Today

4 abdominal changes that may signal an underlying condition and shouldn’t be ignored.

People who regularly eat cucumbers may experience 3 remarkable changes over time
Dull abdominal pain, abdominal pain around the navel, be careful because you may have this disease
News Post

What does the half moon at the base of the nails mean?

If you see these 3 signs every night before going to bed, be careful that c.a.ncer cells are being "raised" in your body

Creamy Garlic Shrimp with Rice

The X-ray of a Young Woman’s Stru.ggle with Ch.ronic Constipation

3 eye warning signs that signal an incoming stro.ke or cancer — ignore them at your own risk!

3 foods that become highly to.xic after mold appears - What you must know to protect your health

Never leave a charger in an outlet without your phone: I'll expose the three major reasons

The Sho.cking Truth Behind Your Ankle Bracelet And What It Reveals About You - It’s More Than Just Jewelry

Cheesy Ham Puff Pastry Stacks

5 special health benefits your body gets when eating black sesame every day

7 health benefits of drinking lemon water you may not know

A 38-year-old female patient with gastric ulcer could not have imagined that just because of a familiar daily hobby

Creamy Swedish Meatballs with Mashed Potatoes

Doctor Issues Urgent Warning: Stop Eating These 4 Foods Immediately They Contain High Levels of Parasites

4 types of nuts are silently destr.oying the liver, causing can.cer if eaten a lot

Few people recognize the warning signs of circulation problems that may appear in the feet and legs at night

Delicious Fresh Peach Fritters

If you notice these three nighttime signs before going to sleep, it may indicate that your body is under stress
