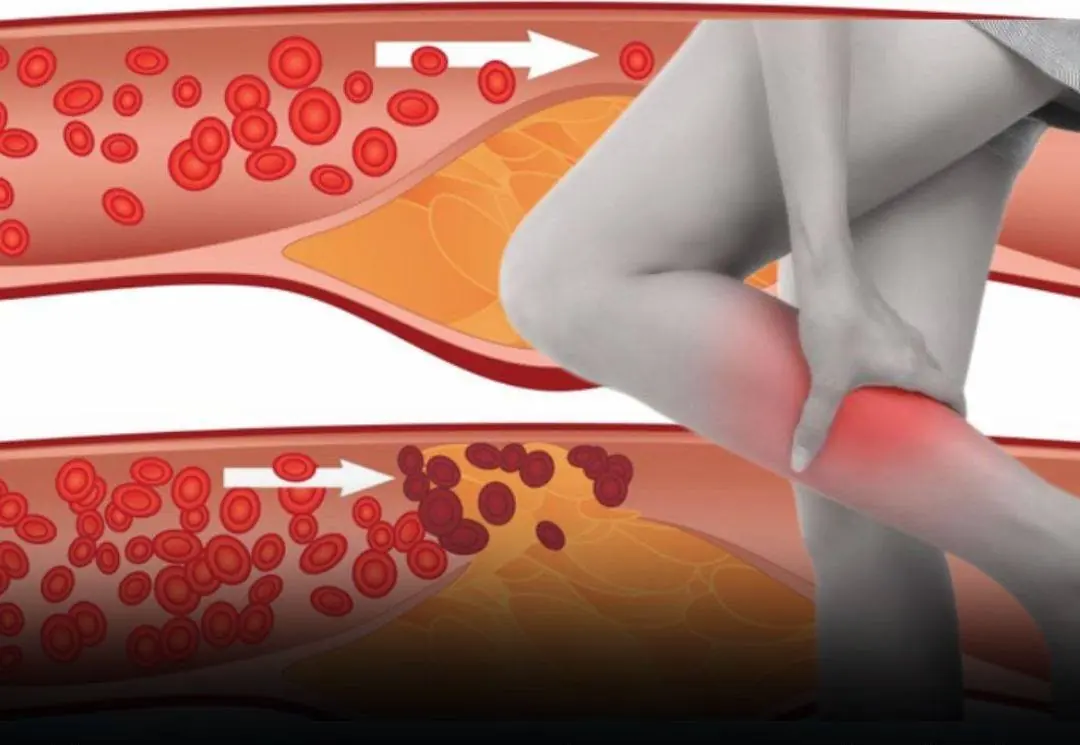
The number of people experiencing kidney issues has been rising each year. Doctors warn that these four types of beverages should be limited to support kidney health.
4 Types of Beverages You Should Limit to Support Kidney Health
Kidney health is essential for maintaining the balance of fluids, electrolytes, and waste removal in the body. These organs work nonstop to filter the bloodstream, regulate blood pressure, and keep the body’s internal environment stable. However, modern dietary habits—especially the excessive consumption of certain beverages—can place unnecessary stress on the kidneys over time. While no single drink directly causes kidney disease on its own, frequent or heavy intake of specific types of beverages may contribute to dehydration, metabolic imbalance, and increased kidney workload. Below are four beverages that health professionals commonly advise limiting to support long-term kidney function.
1. Sugary Soft Drinks and Sweetened Beverages
Sugary drinks remain one of the most common contributors to metabolic stress. Regular consumption of sodas, sweetened teas, flavored juices, and energy drinks has been linked to higher rates of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. These conditions place significant strain on the kidneys because they interfere with blood sugar control and increase inflammation in blood vessels, including those that supply the kidneys.
High sugar intake may also increase the risk of kidney stones by altering how the body processes minerals such as calcium and oxalate. Additionally, the phosphorus additives found in many soft drinks may contribute to mineral imbalance when consumed excessively. While occasional sugary drinks are not harmful for most people, consistently substituting them for water or healthier alternatives can negatively impact kidney function over time. Moderation is essential, and reducing intake significantly benefits overall metabolic health.
2. High-Sodium Packaged Drinks and Instant Soups
Many instant beverages—such as packaged broths, instant noodles, powdered soups, and canned drinks—contain extremely high sodium levels. Excess sodium forces the kidneys to work harder to maintain electrolyte balance. Over time, chronic high sodium intake can increase blood pressure, one of the leading risk factors for kidney damage worldwide.
Even drinks marketed as “savory” or “nutrient-rich” may contain more sodium than the recommended daily limit. Because sodium is often hidden in processed foods and beverages, people may consume far more than they realize. Limiting these products and choosing low-sodium alternatives can significantly reduce pressure on the kidneys and support cardiovascular health at the same time.
3. Excessive Coffee or Highly Caffeinated Drinks
Coffee can offer health benefits when consumed in moderation. However, excessive caffeine intake—from coffee, strong teas, energy drinks, or concentrated caffeine beverages—may lead to dehydration because caffeine has mild diuretic effects. When the body loses more fluid than it takes in, the kidneys must filter more concentrated blood, which increases their workload.
High caffeine consumption can also temporarily elevate blood pressure and heart rate. For individuals with existing kidney concerns, hypertension, or sensitivity to stimulants, these changes may be problematic. The key is balance: moderate coffee intake is typically safe, but relying on multiple caffeinated drinks per day to maintain energy may stress the kidneys unnecessarily.
4. Alcohol When Consumed Frequently or in Large Amounts
Alcohol affects several organ systems, including the kidneys. When consumed in large quantities or on a regular basis, alcohol can disrupt the body’s fluid balance and promote dehydration. It also interferes with hormone regulation related to kidney function, making it harder for the kidneys to maintain proper hydration and filtration.
Excessive alcohol consumption may also raise blood pressure and impair liver function. Since the kidneys and liver work closely to filter toxins and regulate metabolism, damage to one organ affects the other. While moderate alcohol intake may not pose risks for healthy individuals, heavy or frequent use is associated with reduced kidney efficiency over time. Hydration and moderation remain essential guidelines.
A Balanced Approach to Kidney Health
No single beverage guarantees harm or protection, but habits matter. The kidneys are resilient, yet they function best when supported by adequate hydration, balanced electrolytes, and minimal exposure to excess sugar, sodium, stimulants, or alcohol. Choosing water, herbal teas, natural fruit-infused water, or low-sugar beverages can help maintain healthy kidney function.
Monitoring how your body responds to different drinks and staying aware of long-term habits are key steps in preventing unnecessary kidney strain. When symptoms such as fatigue, swelling, changes in urination, or persistent discomfort arise, seeking medical evaluation ensures early detection and appropriate care.
Supporting kidney health is ultimately about consistency—small daily choices that reduce stress on the body and promote long-term wellness.
News in the same category


If you notice these three nighttime signs before going to sleep, it may indicate that your body is under stress
Consume these 4 morning foods on an empty stomach to support intestinal cleansing, improve digestion, and promote overall health.
7 Foods That May Help Your Body Fight Can.cer Add Them to Your Diet Today

4 abdominal changes that may signal an underlying condition and shouldn’t be ignored.

People who regularly eat cucumbers may experience 3 remarkable changes over time

4 habits that are quietly dam.aging your immune system
Dull abdominal pain, abdominal pain around the navel, be careful because you may have this disease

What happens to your body if you regularly drink ginger and red date tea in the morning?

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...
8 signs you may be experiencing kid.ney fai.lure
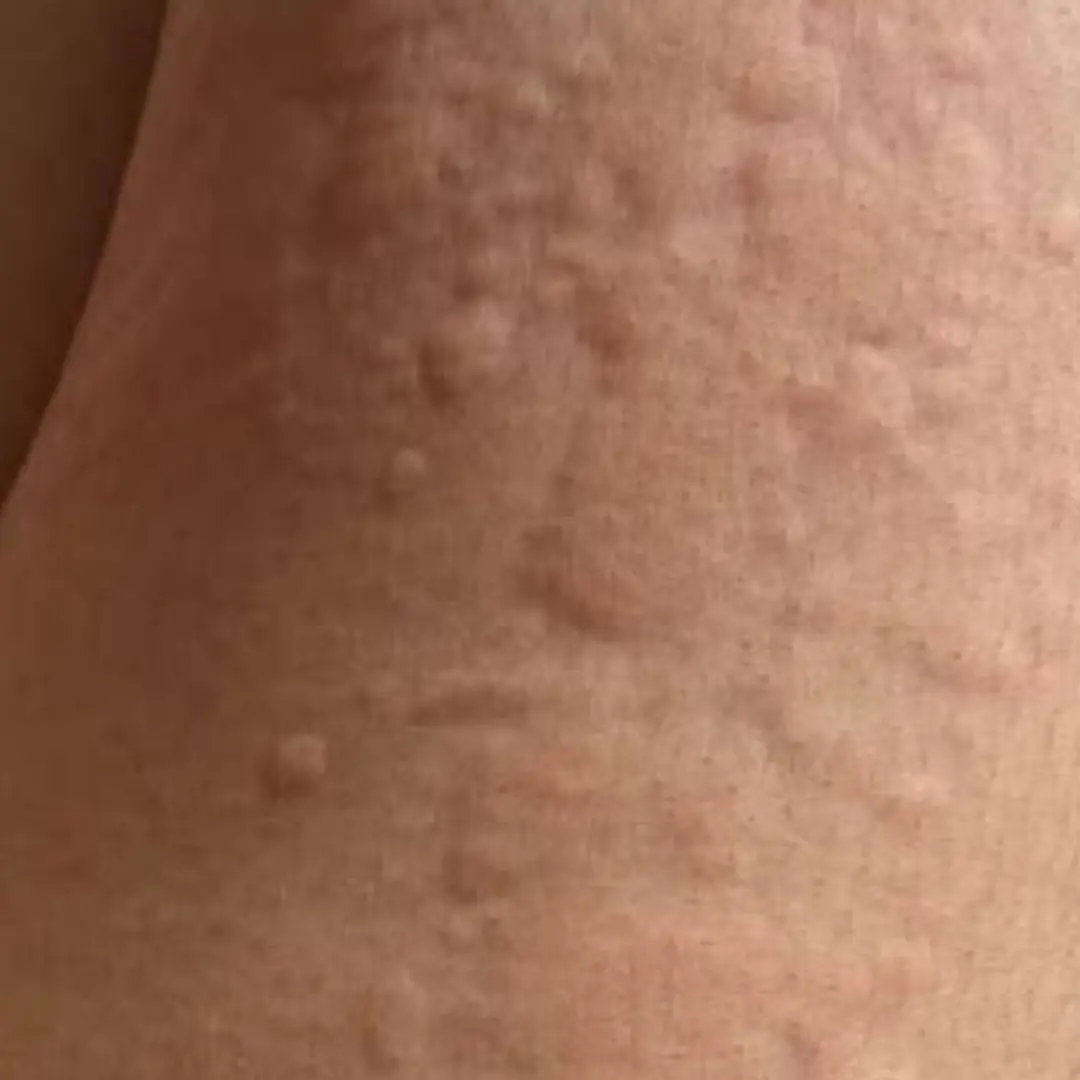
Her Whole Body Was Itchy: What She Thought Was a Common Allergy Was Hiding Something More Serious

Avoid these 4 drinks before going to bed

What really happens when you sleep with socks on?

Eating steamed sweet potatoes every day, woman panicked when receiving liver test results: How could this be?

Don’t Ignore These 4 Finger Changes — They Might Point to Lung Can.cer

Doctors Warn: It’s Better to Eat More Meat Than to Overindulge in These 3 Foods

Acute Li.ver Failure With Li.ver Enzymes Rising 250 Times Caused by Eating a Single Part of Fish

8 low-sugar fruits experts love and why they’re actually elite for your health
News Post

Few people recognize the warning signs of circulation problems that may appear in the feet and legs at night

Delicious Fresh Peach Fritters

If you notice these three nighttime signs before going to sleep, it may indicate that your body is under stress

Consume these 4 morning foods on an empty stomach to support intestinal cleansing, improve digestion, and promote overall health.

Red wax keeps appearing on my daughter-in-law’s door lock, even after she removes it. She’s been living alone ever since my son died. Is this a warning?

7 Foods That May Help Your Body Fight Can.cer Add Them to Your Diet Today

4 abdominal changes that may signal an underlying condition and shouldn’t be ignored.

People who regularly eat cucumbers may experience 3 remarkable changes over time

3 Simple and Effective Ways to Keep Your Home Completely Mouse-Free

“I Replaced Your Blood Pressure Pills with Chalk!” — Said My Mother-in-Law, Not Knowing I’d Set Up a Camera and She Was Headed for Criminal Charges

4 habits that are quietly dam.aging your immune system

“Mommy, we love you so much!” the children said at the table. But that night, I overheard them arguing over who would get my country house

Dull abdominal pain, abdominal pain around the navel, be careful because you may have this disease

What happens to your body if you regularly drink ginger and red date tea in the morning?

Raspberry Cream Layer Cake (No-Bake Style)

Doctors reveal that eating beets causes...

8 signs you may be experiencing kid.ney fai.lure

Spicy Garlic Shrimp with Avocado Tomato Salad
