Avoid these 4 drinks before going to bed

Heart attacks remain one of the leading causes of death worldwide, especially among older adults. Recently, the sudden passing of a 65-year-old man at 11 p.m. has renewed public attention on nighttime habits that may influence cardiovascular risk. Following the incident, medical professionals issued an important reminder: no matter how thirsty you feel before going to bed, certain types of drinks may provoke stress on the heart and should be avoided.
This article explores why the elderly are more vulnerable to heart attacks, which nighttime drinking habits may contribute to cardiovascular strain, and the early warning signs everyone should know.
(Information here is for educational purposes only and not a substitute for medical advice.)
Why Older Adults Are More Prone to Heart Attacks
A heart attack occurs when blood supply to a part of the heart muscle becomes blocked, causing tissue damage or necrosis. Because the heart cannot regenerate efficiently, this event can quickly become life-threatening.
Aging naturally increases cardiovascular risk for several reasons:
1. Degeneration of Blood Vessels
As people age, arteries tend to stiffen and accumulate plaque. Narrower or less flexible blood vessels make it easier for blockages to occur.
2. Weakened Physical Resilience
Older adults typically have lower muscle mass, reduced immune function, and diminished cardiac output. These factors reduce the heart’s ability to withstand sudden stress.
3. Greater Likelihood of Chronic Diseases
Conditions such as:
-
hypertension
-
diabetes
-
osteoporosis
-
kidney dysfunction
-
arrhythmia
…are more common in older adults and can indirectly influence heart health.
In particular, osteoporosis and age-related bone weakening may affect posture, breathing mechanics, and even circulation. When circulation is compromised, the heart may struggle to receive sufficient oxygen, raising the risk of a heart attack.
4. Reduced Nighttime Autonomic Stability
During sleep, the body undergoes natural changes in heart rate and blood pressure. In older adults, these regulatory systems may be less stable, making them more vulnerable during nighttime hours.
If You’re Thirsty at Night, Avoid Drinking These 4 Types of Liquids
Doctors emphasize that the type of drink consumed before bedtime can influence cardiovascular stress, especially for individuals with underlying heart conditions. Below are four types of beverages that may increase physiological strain and should generally be avoided at night.
1. Ice-Cold Water
On hot evenings, many people reach for a glass of ice water. While refreshing, extremely cold water can cause blood vessels to constrict suddenly.
Why this may be risky:
-
Cold temperature causes rapid vasoconstriction
-
Blood pressure may fluctuate
-
The heart must work harder to stabilize circulation
This sudden change in vascular tone may trigger discomfort or, in rare cases, contribute to cardiovascular events in vulnerable individuals.:quality(75)/2024_6_5_638532030774184406_nuoc-ngot-co-ga-avt.jpg)
2. Concentrated or Strong Tea
Some people enjoy strong tea before bed to relax, but this habit may backfire.
Potential issues:
-
Strong tea contains high levels of caffeine and theobromine
-
Both stimulate the nervous system and raise heart workload
-
They may increase heart rate or trigger palpitations
For individuals with heart disease or arrhythmia, drinking strong tea late at night may disrupt sleep and increase cardiovascular stress.
3. Coffee
Coffee is a well-known stimulant. Even a single cup can increase alertness - which is the exact opposite of what the body needs before bedtime.
Why doctors advise against it at night:
-
Caffeine excites the brain and sympathetic nervous system
-
Heart rate and blood pressure may rise temporarily
-
It can interfere with natural nighttime recovery processes
-
Individuals with cardiovascular or neurological sensitivity may react more strongly
Health experts generally recommend avoiding coffee at least 2–3 hours before sleeping.
4. Fruit Juice
Fruit juice may seem harmless, but its high fructose content can thicken the blood slightly and increase metabolic load.
Possible effects:
-
Increased blood viscosity
-
Sudden rise in blood sugar
-
Digestive discomfort during sleep
-
Extra strain on metabolic and cardiovascular systems
These effects are not severe for everyone, but they may contribute to nighttime instability for individuals with heart disease, diabetes, or circulation issues.

Temperature Matters: Avoid Liquids That Are Too Hot or Too Cold
The esophagus can tolerate temperatures around 40°C (104°F), but extreme heat or cold can irritate its lining. Long-term repeated irritation may contribute to inflammation, discomfort, or in rare cases, structural damage.
Additionally:
-
Very hot drinks may injure mucosal tissue
-
Very cold drinks may trigger muscle spasms or sudden vascular constriction
Over time, these irritations may lead to ulcers or increase susceptibility to infections.
Why Drinking Too Much Liquid Before Bed Can Be Harmful
Nighttime hydration should be moderate. Excessive fluid intake before bedtime may lead to:
-
waking up frequently to urinate
-
disrupted sleep cycles
-
sudden changes in heart rhythm when waking abruptly
-
increased stress on the cardiovascular system
Frequent nighttime awakenings may also increase fall risk among older adults.
How to Reduce the Risk of Heart Attacks
Prevention is key. Although no method can fully eliminate risk, several lifestyle practices may help support heart health.
1. Exercise Wisely - Not Excessively
Moderate daily movement strengthens the heart, but overexertion - especially in cold weather - can increase heart strain. Sudden intense activity may lead to dangerous spikes in blood pressure.
2. Maintain a Balanced Work–Rest Cycle
Overwork and chronic stress can elevate stress hormones, increasing cardiovascular risk. Adequate sleep, relaxation, and emotional support help maintain long-term heart health.
A positive mindset also contributes significantly to cardiovascular resilience.
Early Warning Signs of a Possible Heart Attack
The body may show warning signs hours, days, or even weeks before a major event. Recognizing these signals can be life-saving.
Warning Sign 1: Chest Pain or Shortness of Breath
Discomfort may feel like:
-
tightness
-
pressure
-
heaviness
-
burning sensation
Pain often centers behind the breastbone and may radiate to the left arm, shoulder, jaw, or back.
Warning Sign 2: Angina During Sleep
If chest pain occurs at night or awakens you from sleep, this may indicate unstable angina - a potential precursor to a heart attack.
Warning Sign 3: Unexplained Abdominal Pain
Some patients mistake heart-related discomfort for stomach pain. If abdominal pain appears 1–2 hours after eating, especially with nausea or sweating, it should not be ignored.
Warning Sign 4: Irregular Heartbeat at Night
Sudden arrhythmias or palpitations around 3–4 a.m. may signal instability in heart function.
Final Thoughts
Preventing heart attacks requires awareness, healthy habits, and prompt attention to warning signs. Avoiding certain types of beverages before bedtime - especially extremely cold drinks, strong tea, coffee, and high-sugar fruit juice - may help reduce unnecessary nighttime stress on the heart. While these precautions cannot eliminate risk, they contribute to a safer and healthier routine, particularly for older adults or individuals with cardiovascular concerns.
Listening to your body, adopting moderate lifestyle habits, and seeking medical evaluation when symptoms appear are essential steps in supporting long-term heart health.
News in the same category


Eating steamed sweet potatoes every day, woman panicked when receiving liver test results: How could this be?
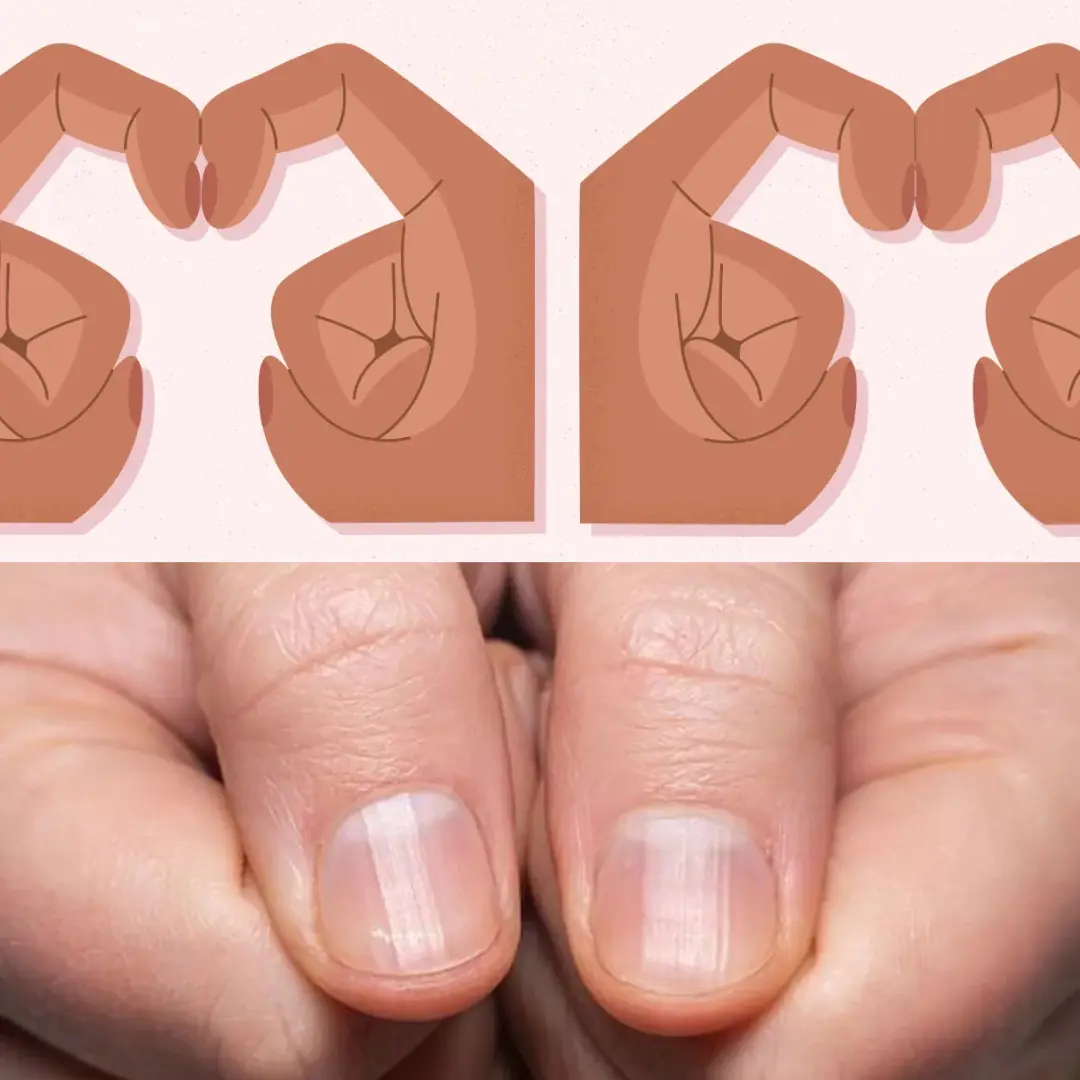

Don’t Ignore These 4 Finger Changes — They Might Point to Lung Can.cer

Doctors Warn: It’s Better to Eat More Meat Than to Overindulge in These 3 Foods

Acute Li.ver Failure With Li.ver Enzymes Rising 250 Times Caused by Eating a Single Part of Fish

8 low-sugar fruits experts love and why they’re actually elite for your health

All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying
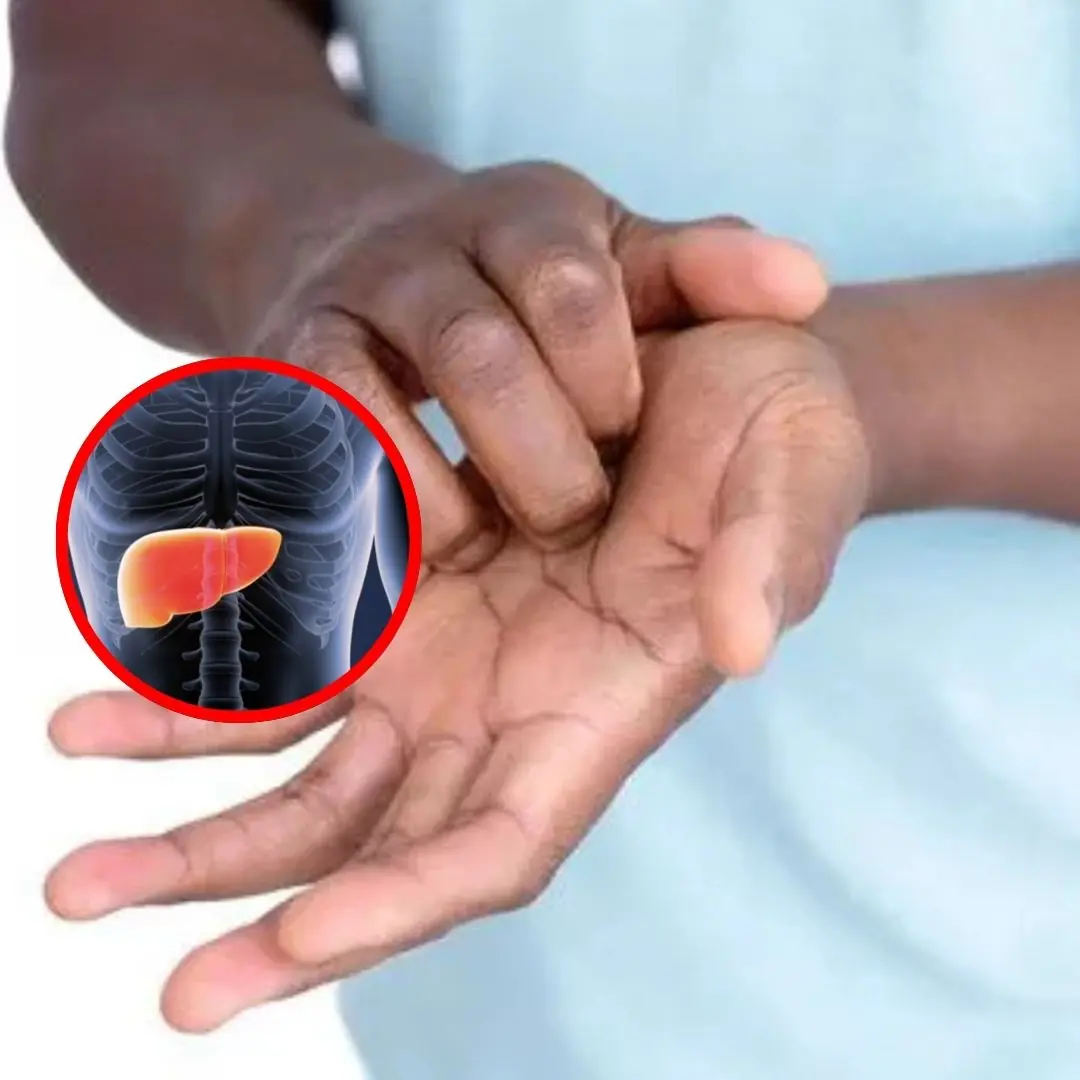
People with liver failure often have 3 characteristics on their hands, if you have 1 you should see a doctor soon.

Stomach Can-cer: The “Silent Disease” You Shouldn’t Ignore
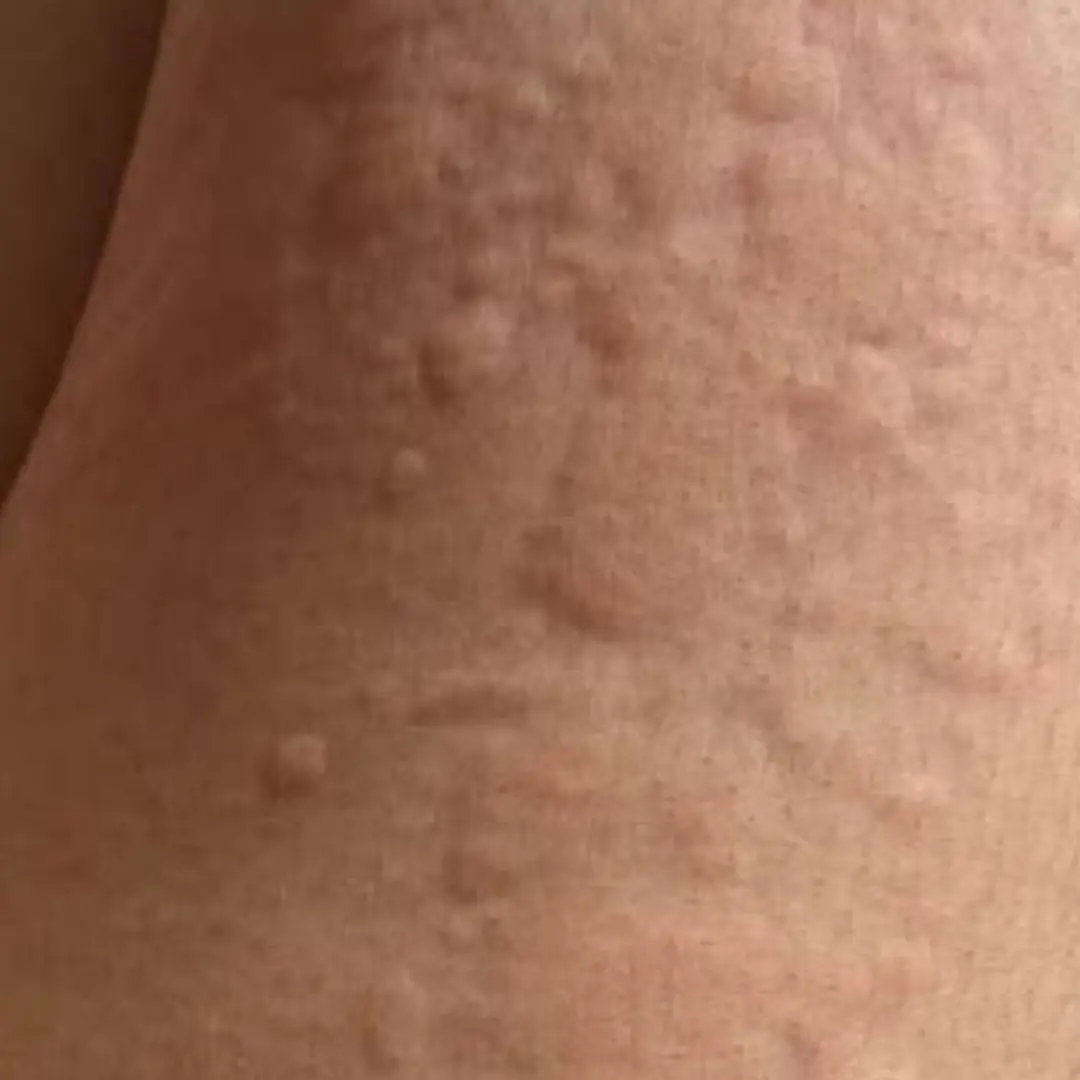
Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Nearly died from septic shock due to ureteral stones, doctor warns of fatal complications

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath
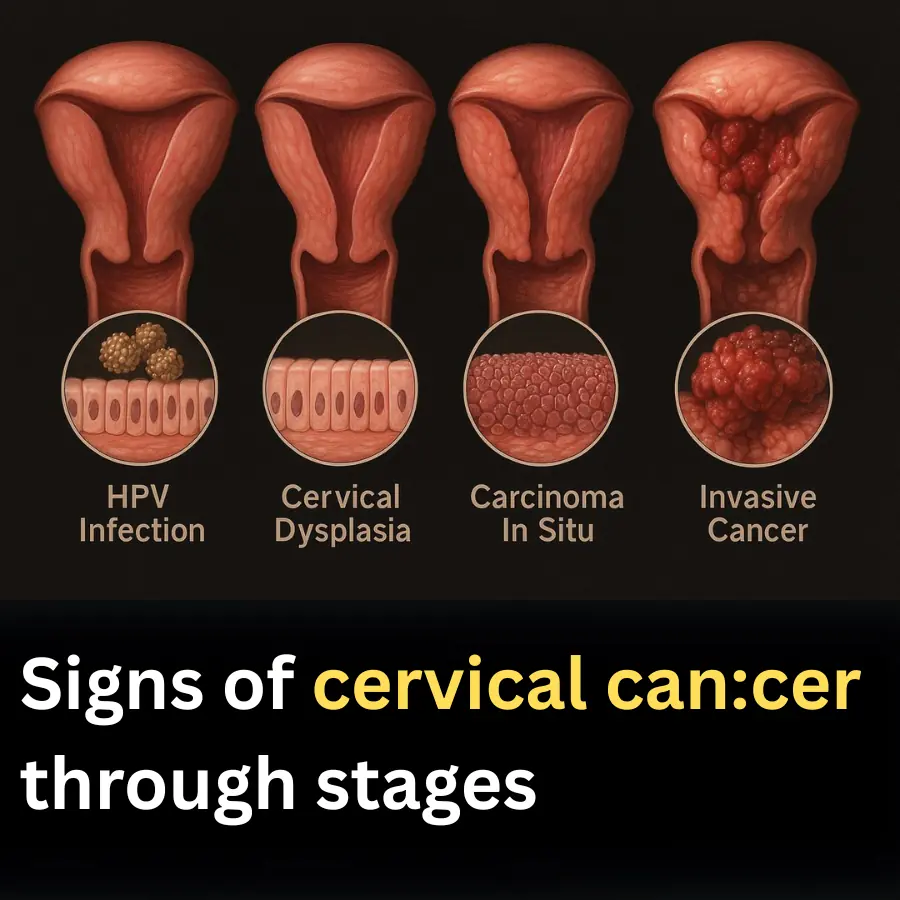
Signs of cervical can:cer through stages
36-Year-Old Teacher Dies From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods

7 Reasons You Should Be Adding Sweet Potatoes to Your Diet

The Startling Revelation from My Daughter-in-Law’s Phone
5 Alarming Stroke Warning Signs to Watch for in Young People

5 signs of suspected cervical can:cer that women need to know
News Post

Her Whole Body Was Itchy: What She Thought Was a Common Allergy Was Hiding Something More Serious

Beef Stew

What really happens when you sleep with socks on?

Eating steamed sweet potatoes every day, woman panicked when receiving liver test results: How could this be?

Don’t Ignore These 4 Finger Changes — They Might Point to Lung Can.cer

Doctors Warn: It’s Better to Eat More Meat Than to Overindulge in These 3 Foods

Acute Li.ver Failure With Li.ver Enzymes Rising 250 Times Caused by Eating a Single Part of Fish

8 low-sugar fruits experts love and why they’re actually elite for your health

Creamy Black Pepper Chicken Bowl – Clean, Bold & Comforting!

All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying

People with liver failure often have 3 characteristics on their hands, if you have 1 you should see a doctor soon.

Stomach Can-cer: The “Silent Disease” You Shouldn’t Ignore

Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Nearly died from septic shock due to ureteral stones, doctor warns of fatal complications

The reason why many people pour salt into clogged toilets

My Daughter Keeps Drawing a Woman in Our Attic—But We Don’t Even Have One

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

Signs of cervical can:cer through stages
