
Signs of cervical can:cer through stages
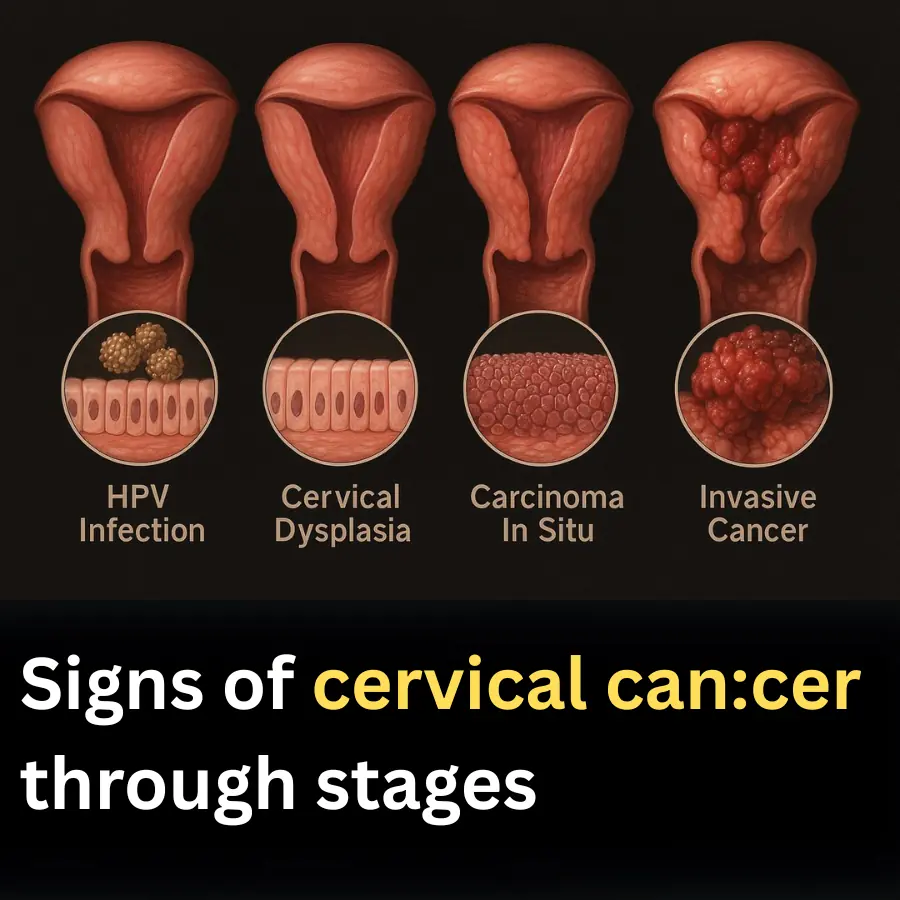
Cervical Cancer Symptoms and Stages
Cervical cancer often begins with vague and silent symptoms, making it difficult to detect early. When clear signs appear, cancer cells may have already spread to other organs. Although treatment can still be effective at this stage, interventions become more complex and costly. In severe cases, women may face the risk of complete removal of the uterus, ovaries, and surrounding lymph nodes, seriously affecting fertility.
Symptoms of Cervical Cancer
-
Pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse.
-
Abnormal vaginal bleeding: after sexual activity, between periods, post-menopause, or after gynecological exams.
-
Unusual vaginal discharge: grayish and foul-smelling.
-
Urinary discomfort or frequent urination.
-
Blood in urine or stool (indicating invasion into the bladder or rectum).
-
Irregular or prolonged menstrual periods.
-
Unexplained weight loss and fatigue.
If these symptoms occur, especially in combination, women should seek medical attention immediately. Early diagnosis is crucial, as similar symptoms can also occur in other conditions.
Types of Cervical Cancer
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
-
Arises from thin, flat cells on the cervix surface.
-
Most common type (80–85%), often caused by HPV infection.
-
-
Adenocarcinoma
-
Occurs in glandular cells in the upper cervix.
-
Accounts for 10–20% of cases.
-
-
Other types
-
Small cell carcinoma, adenosquamous carcinoma, lymphoma, melanoma.
-
Less common, not typically HPV-related, and harder to prevent.
-
Cervical Cancer Stages
-
Stage 0: Pre-cancerous changes; abnormal cells may develop into cancer.
-
Stage I: Cancer confined to the cervix.
-
Stage II: Cancer spreads beyond the cervix but not to pelvic lining or lower vagina.
-
Stage III: Cancer invades the lower vagina and pelvic lining.
-
Stage IV: Cancer metastasizes to other organs like intestines, bladder, or lungs.
Potential Complications
-
Infertility: Tumor invasion can impair conception. Radical treatment may require removal of the uterus and ovaries, leading to early menopause.
-
Psychological impact: Emotional distress, depression, and disruption of family life.
-
Abnormal bleeding: Tumor invasion of the vagina, bladder, or rectum can cause bleeding.
-
Kidney damage: Tumor pressure on the ureters can obstruct urine flow, causing kidney swelling and impaired function.
Preventive Advice
-
HPV vaccination is the most effective prevention.
-
Delay sexual activity until the reproductive system is fully developed.
-
Practice safe sex and limit the number of sexual partners.
-
Maintain genital hygiene, especially during menstruation and after sexual activity.
-
Seek medical attention promptly for any abnormal symptoms.
News in the same category

People with liver failure often have 3 characteristics on their hands, if you have 1 you should see a doctor soon.

Stomach Can-cer: The “Silent Disease” You Shouldn’t Ignore
Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Nearly died from septic shock due to ureteral stones, doctor warns of fatal complications

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath
36-Year-Old Teacher Dies From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods

The Startling Revelation from My Daughter-in-Law’s Phone
5 Alarming Stroke Warning Signs to Watch for in Young People

5 signs of suspected cervical can:cer that women need to know
Statins warning: new research confirms these harmful side effects

Silent warning signs of head and neck can:cer

8 of the Best Anti-Cancer Foods. It’s Time to Start Adding them to Your Diet

How Your Feet Could Be Signaling Heart Problems and Clogged Arteries

Distinguishing between pharyngitis and nasopharyngeal can:cer

Your Feet May Be a “Blood Sugar Monitor”
Lymphoma Survivors Share Six Symptoms They Experienced Before Being Diagnosed

6 warning signs that your intestinal condition may be serious
News Post

Creamy Black Pepper Chicken Bowl – Clean, Bold & Comforting!

All The Things You Need to Know About Nighttime Urination And When To Start Worrying

People with liver failure often have 3 characteristics on their hands, if you have 1 you should see a doctor soon.

Stomach Can-cer: The “Silent Disease” You Shouldn’t Ignore

Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common

Nearly died from septic shock due to ureteral stones, doctor warns of fatal complications

The reason why many people pour salt into clogged toilets

My Daughter Keeps Drawing a Woman in Our Attic—But We Don’t Even Have One

Say Goodbye to Joint and Foot Pain with a Relaxing Rosemary Bath

36-Year-Old Teacher Dies From Diabetes Doctors Say Was Triggered By Everyday Foods

7 Reasons You Should Be Adding Sweet Potatoes to Your Diet

My Husband’s Work Badge Logged In at 9PM—But He Was Home with Me

The Startling Revelation from My Daughter-in-Law’s Phone

5 Alarming Stroke Warning Signs to Watch for in Young People

5 signs of suspected cervical can:cer that women need to know

Savory Oven-Roasted Chicken Drumsticks with Rustic Potatoes & Sweet Peppers

Statins warning: new research confirms these harmful side effects

The Shocking Betrayal: A Christmas Dinner to Remember
