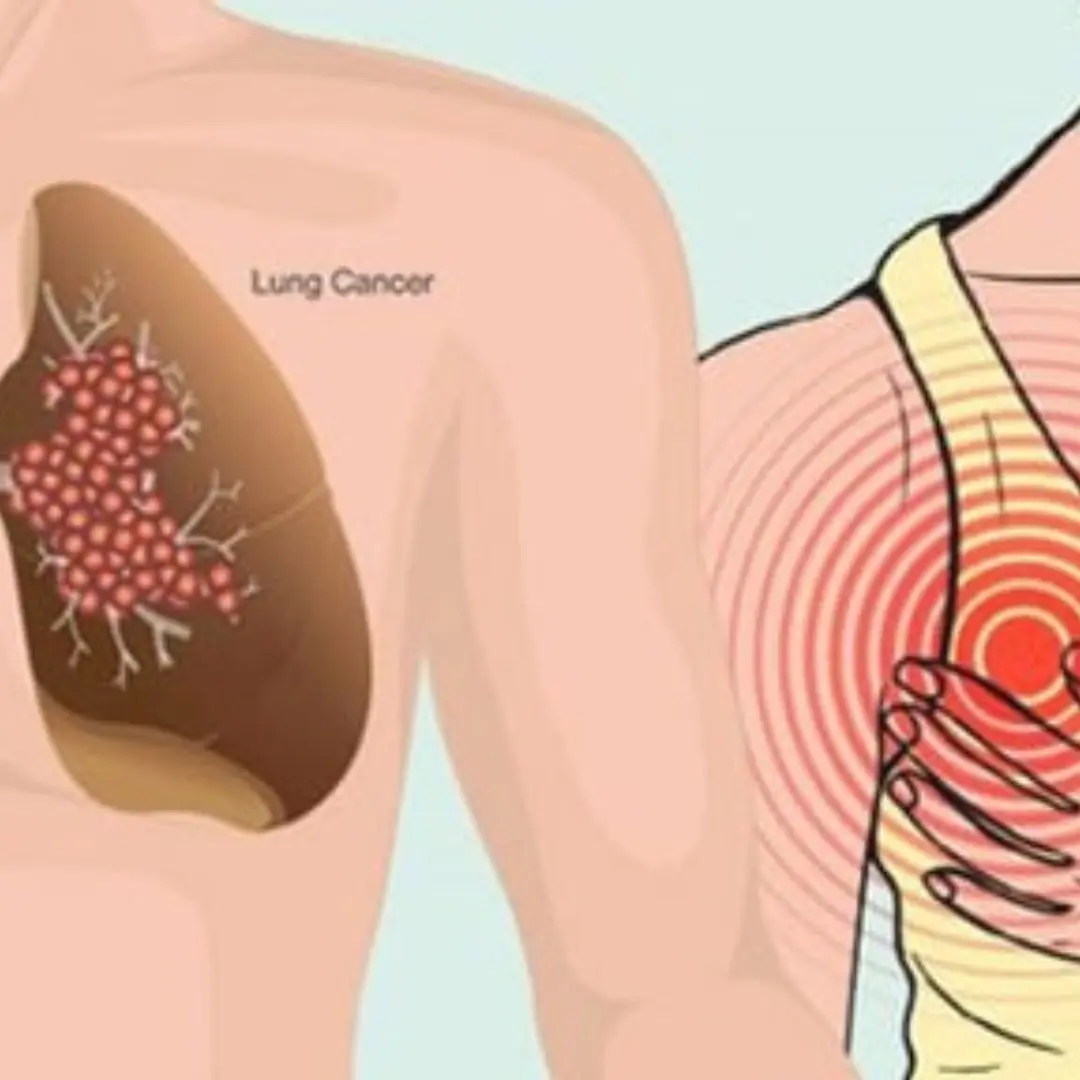
5 Early Signs of Lung C.an.cer You Need to Know

If people can recognize the signs of lung cancer at an early stage, the survival rate and treatment effectiveness will improve significantly. This article provides detailed information about the warning signs to watch for, helping patients monitor their health and seek timely medical care.
This article was reviewed by Dr. Tô Kim Sang, Oncology Center, Vinmec Central Park International General Hospital.
1. Recognizing Early Signs of Lung Cancer
Lung cancer symptoms are often non-specific and subtle, with most patients only being diagnosed at an advanced stage. Therefore, people at high risk (such as smokers, those exposed to secondhand smoke, or individuals over 50) should undergo low-dose CT scans to screen for lung cancer.
When lung cancer progresses, more noticeable symptoms may appear, such as back pain, headaches, weight loss, and fatigue. Bone pain is also common, as lung cancer often metastasizes to the bones.
Although most patients with lung cancer do not have clear symptoms in the early stages, some may recognize early warning signs. However, it is important to remember that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, not just lung cancer.
Below are 5 early signs of lung cancer that everyone should know for timely checkups and treatment:
1.1 Persistent Cough
A chronic cough is often the earliest sign of lung cancer.
While coughing is a common symptom of colds or flu, a cough that persists after other symptoms (like a runny nose) have gone away should be considered abnormal.
If a cough continues for 2–3 weeks without being linked to a viral or bacterial infection, patients should see a doctor immediately.
1.2 Shortness of Breath
According to the American Cancer Society, unexplained shortness of breath is a warning sign of lung cancer. While this symptom usually appears in later stages, it can also occur when a tumor blocks the airways. Any unexplained difficulty breathing requires medical evaluation.
1.3 Coughing Up Blood
Some patients may cough up blood if the tumor is located near the bronchial tubes. Even small amounts of reddish-brown sputum should not be ignored. Patients experiencing coughing up blood—especially when accompanied by dizziness or shortness of breath—should seek urgent medical care.
1.4 Chest Pain
Lung cancer can cause chest pain due to large tumors pressing on surrounding tissues, metastasis to the bones, or fluid accumulation in the pleura. Chest pain typically worsens when coughing, laughing, or breathing deeply.
Because chest pain can signal other serious conditions, any persistent or unexplained chest discomfort should be reported to a doctor for proper evaluation.
Patients experiencing chest tightness, sweating, nausea, dizziness, or shortness of breath should seek medical attention immediately.
1.5 Other Symptoms of Lung Cancer
Additional signs may include:
-
Unexplained weight loss, declining overall health, and fatigue
-
Voice changes or persistent hoarseness due to effects on the vocal cords
-
Coughing up sputum that is tinged with blood
2. Causes of Lung Cancer
Understanding the causes and risk factors not only raises awareness but also helps individuals reduce exposure to potential risks:
-
Tobacco exposure: Both active smoking and secondhand smoke damage lung tissue and cause genetic mutations in lung cells.
-
Environmental and occupational exposure: Air pollutants such as vehicle exhaust, fine dust, and industrial chemicals increase lung cancer risk.
-
Genetic and family factors: A family history of lung cancer raises the likelihood of developing the disease due to inherited genetic mutations.
-
Toxic substances: Radon, asbestos, welding fumes, nickel, and other industrial chemicals are known carcinogens.
-
Air pollution: Industrial pollutants, fine particulate matter, and chemical exposure can damage the lungs and increase cancer risk.
3. Methods of Early Lung Cancer Diagnosis
To detect lung cancer early, doctors may use the following:
-
Physical examination: Assessing respiratory function and medical history to identify suspicious signs.
-
Imaging tests: Low-dose CT scans for screening; chest X-rays, ultrasound, PET-CT, or MRI for detailed evaluation.
-
Blood tests: Including tumor markers, liver and kidney function tests, and respiratory assessments.
-
Cytology tests: Analyzing sputum or bronchial fluid to detect cancer cells.
-
Prognostic tests: Identifying cancer cell type and assessing the extent of metastasis.
4. Treatment Options
There is a significant difference in survival rates between early and late detection. The 5-year survival rate for late-stage lung cancer is below 10%, but when detected early, treatment success rates increase greatly.
Treatment depends on the tumor’s location, size, spread, and the patient’s overall health. Options include:
-
Surgery: Open or laparoscopic procedures to remove the tumor and nearby tissue.
-
Chemotherapy: Administered before or after surgery to shrink tumors or destroy remaining cancer cells. Modern therapies include immunotherapy and targeted therapy, which improve survival and reduce recurrence risk.
-
Radiation therapy: High-energy rays used to kill cancer cells, either alone or combined with surgery/chemotherapy for better outcomes.
-
Supportive care: Symptom management (pain, shortness of breath, fatigue) through medication, nutrition counseling, and palliative care methods.
👉 If you experience early signs of lung cancer, you can visit Vinmec International General Hospital for examination and treatment. Vinmec provides comprehensive cancer care, including surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and pain management through physiotherapy, nerve blocks, and other advanced methods.
News in the same category


Just one glass of sugarcane juice, taken at the perfect time, can unlock countless benefits for your body
7-year-old boy mo.cked by classmates for bad smell, mother stunned by what doctor removed from his mouth
Signs and treatment of early stage nasopharyngeal cancer
4 Oral Abnormalities That Are EARLY WARNINGS When Can.cer Targets You as Its “Prey”
Peeing in the shower: harmless habit or hidden danger? Experts explain
People with healthy kidneys will not have these 3 signs on their skin: If you don't have all of them, congratulations!
70% of Ova.rian Can.cer Cases Are Diagnosed at a Late Stage
The Habit That Puts Millions at Risk of Pancreatic Can.cer

5 Types of “Chemical-Soaked” Produce You’ll Find at the Market

Tragedy Strikes: One Dead, Three Fighting for Life After Eating Leftover Meat Stored in a Freezer

A 33-Year-Old Woman Ate Lettuce at Every Meal—Three Months Later
7 Foods That Can Turn He.art Medications into a “De.adly Poi.son”
Catching Nasopharyngeal Cancer in Its Early Stages May Offer a 72% Survival Rate

Doctor Reveals 5 Dangerous Mistakes You Must Avoid Right After Eating
"7 Silent Habits That Wreck Your Bones and Joints — Quit Them Now or Face Pain in Old Age

Night Sweats Explained: 7 Surprising Facts
Warning: 10 Overlooked Symptoms That Could Signal Blood Cancer

4 Abnormal Signs in the Abdomen That May Seem “Minor” but Could Indicate Can.cer
News Post

This morning symptom should never be ignored: it may signal cancer, seek medical attention immediately

Just one glass of sugarcane juice, taken at the perfect time, can unlock countless benefits for your body

7-year-old boy mo.cked by classmates for bad smell, mother stunned by what doctor removed from his mouth

Signs and treatment of early stage nasopharyngeal cancer

The Strange Fruit That’s Sweet When Bitten Lengthwise but Astringent When Bitten Crosswise

4 Oral Abnormalities That Are EARLY WARNINGS When Can.cer Targets You as Its “Prey”

No Matter How Cheap It Is, Never Buy These 3 Types of Chicken Meat

Peeing in the shower: harmless habit or hidden danger? Experts explain

Using a rice scoop for decades, but not everyone knows what this small dot does

“Black Bean Bugs Uncovered: The Dangers They Pose and How to Get Rid of Them Fast!

People with healthy kidneys will not have these 3 signs on their skin: If you don't have all of them, congratulations!
Place a Piece of Ginger by Your Bedside

70% of Ova.rian Can.cer Cases Are Diagnosed at a Late Stage
5-Year-Old Boy’s Sto.mach Pain Leads to Shocking Discovery

Once Used as Pig Feed, Now a Luxury Delicacy Worth $3 Million per Kilogram

The Overlooked ‘Ginseng for the Poor’ Growing Wild in the Countryside

The Habit That Puts Millions at Risk of Pancreatic Can.cer

5 Types of “Chemical-Soaked” Produce You’ll Find at the Market
