Doctors Warn: 3 Nail Symptoms That May Indicate Underlying Health Issues
Doctors Warn: 3 Nail Symptoms That May Indicate Underlying Health Issues
Brain hemorrhage, also known as intracerebral hemorrhage, is a serious and life-threatening medical condition caused by bleeding inside the
brain. It can lead to sudden neurological damage, long-term disability, or even death if not treated immediately. While brain hemorrhage can
occur unexpectedly, medical research shows that certain moments and conditions significantly increase the risk.
Understanding these high-risk periods can help people recognize warning signs early, manage risk factors, and take preventive measures -
especially those with hypertension, cardiovascular disease, or a history of stroke.
Below are five critical times when brain hemorrhage is more likely to occur.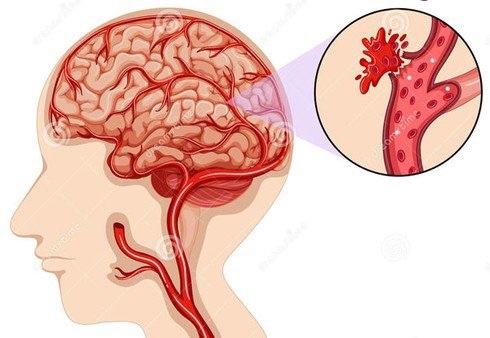
One of the most dangerous periods for brain hemorrhage is the early morning, typically between 4 a.m. and 8 a.m.
During this time, the body undergoes natural physiological changes:
Blood pressure rises rapidly after waking
Heart rate increases
Stress hormones such as cortisol surge
For people with high blood pressure or weakened blood vessels, this sudden spike can cause fragile arteries in the brain to rupture.
Blood vessels that have already been damaged by long-term hypertension may not withstand the sharp increase in pressure that occurs upon
waking.
Avoid jumping out of bed suddenly
Wake up slowly and calmly
Take blood pressure medication consistently as prescribed
Monitor morning blood pressure regularly
Moments of extreme stress - whether physical or emotional are another high-risk trigger for brain hemorrhage.
Examples include:
Heavy lifting or intense exercise
Sudden anger, fear, or emotional shock
Prolonged mental stress or anxiety
Stress causes blood pressure and heart rate to rise sharply, increasing pressure on cerebral blood vessels.
Sudden spikes in blood pressure can overwhelm weakened or narrowed arteries, leading to rupture.
Avoid sudden strenuous activity, especially if you are not physically conditioned
Practice stress management techniques such as deep breathing or meditation
Maintain regular physical activity at a moderate level rather than sporadic intense workouts
Alcohol has a direct impact on blood pressure and blood vessel stability. Heavy drinking - especially binge drinking significantly increases
the risk of brain hemorrhage.
Alcohol-related risks include:
Sudden increases in blood pressure
Impaired blood clotting
Weakened vessel walls over time
Alcohol dilates blood vessels initially, then causes rebound constriction, which can trigger vessel rupture—especially in people with hypertension.
Limit alcohol intake
Avoid binge drinking
Stay well-hydrated
People with high blood pressure or stroke history should avoid alcohol altogether
Sudden exposure to very cold or very hot temperatures can increase the risk of brain hemorrhage.
Examples include:
Stepping into cold weather suddenly in winter
Taking very hot baths or saunas
Rapid temperature changes between environments
Cold causes blood vessels to constrict, raising blood pressure. Heat can lead to dehydration, thickened blood, and unstable circulation—both
of which strain cerebral vessels.
Dress appropriately for weather conditions
Avoid sudden temperature changes
Stay hydrated in hot environments
Limit time in saunas or hot baths
Many people assume sleep is a “safe” time, but brain hemorrhages can and do occur during the night.
Possible contributing factors:
Poorly controlled nighttime blood pressure
Sleep apnea
Missed or improperly timed medication
Blood pressure does not drop normally in some individuals (known as “non-dippers”), increasing nighttime stroke risk. Symptoms may go
unnoticed until the person wakes with severe neurological deficits.
Take medications exactly as prescribed
Manage sleep apnea if present
Monitor blood pressure patterns, including nighttime readings
Brain hemorrhage often occurs suddenly. Seek emergency care immediately if any of the following symptoms appear:
Sudden, severe headache (“worst headache of your life”)
Loss of consciousness
Weakness or numbness on one side of the body
Slurred speech or difficulty understanding speech
Vision problems
Seizures
Sudden confusion or dizziness
Time is critical. Early treatment can save lives and reduce permanent damage.
Certain individuals face a higher risk of brain hemorrhage, including those who:
Have high blood pressure
Smoke
Drink alcohol excessively
Have diabetes
Take blood-thinning medications
Have a history of stroke or vascular disease
Brain hemorrhage is a medical emergency that often strikes without warning - but it is not entirely unpredictable. Early morning hours, intense
stress, alcohol consumption, extreme temperature exposure, and nighttime blood pressure instability are five particularly dangerous moments
when risk increases.
By understanding these high-risk periods, managing blood pressure, reducing stress, and maintaining healthy habits, individuals can
significantly lower their risk.
Awareness saves lives. Paying attention to timing, lifestyle, and early warning signs may make the difference between rapid treatment and
irreversible damage.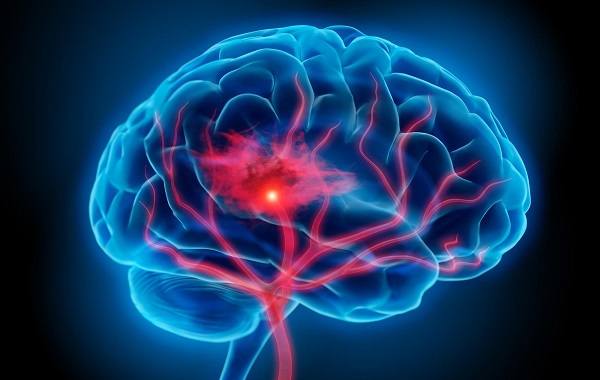

Doctors Warn: 3 Nail Symptoms That May Indicate Underlying Health Issues

Doctors were confused when a strange growth was found in a 9-month-old ba.by’s mouth
Warning: A Bleach - Like Stain in Your Underwear May Be Trying to Tell You Something
Two Warning Signs Of Silent Kil:ler That You Might Spot In Your Feet
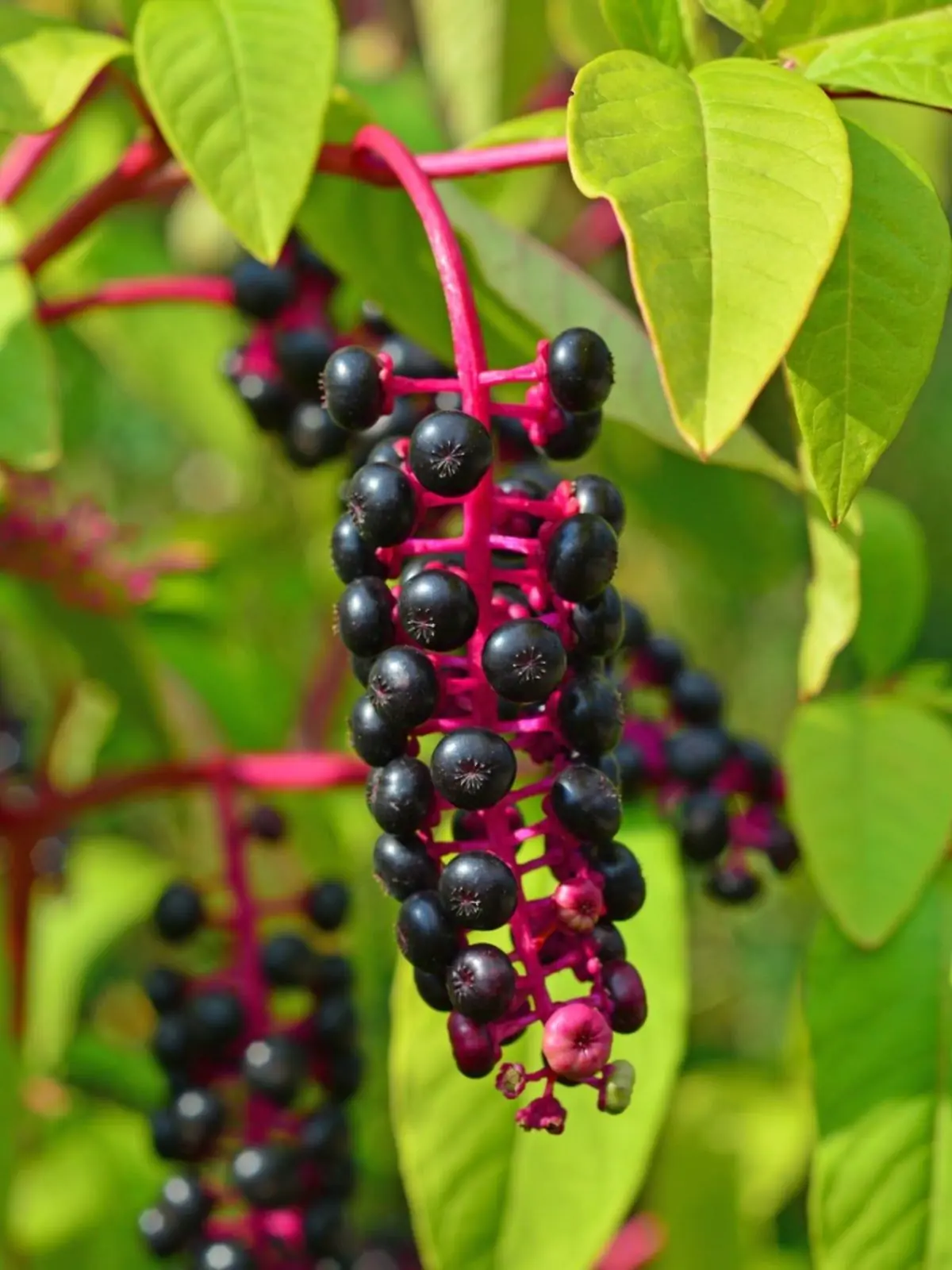

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): Beautiful to Look At, Dan.gerous to Touch
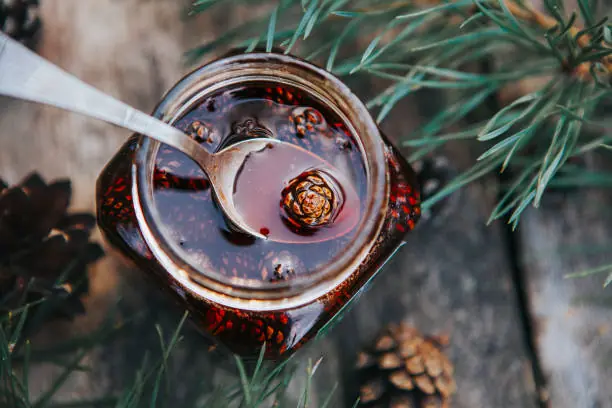

Discover Pine Cone Syrup: Benefits, Easy Recipe, and Creative Everyday Uses
Woman Di:es of Stomach Can:cer; Doctor Reveals 3 Bedtime Habits That Silent Harmed Her Health
Older people may experience issues with blood circulation more often than the younger population.

Tofu is Nutritious but These 5 Groups Should Avoid It
7 Possible Brain Cancer Symptoms Every Woman Should Be Aware Of
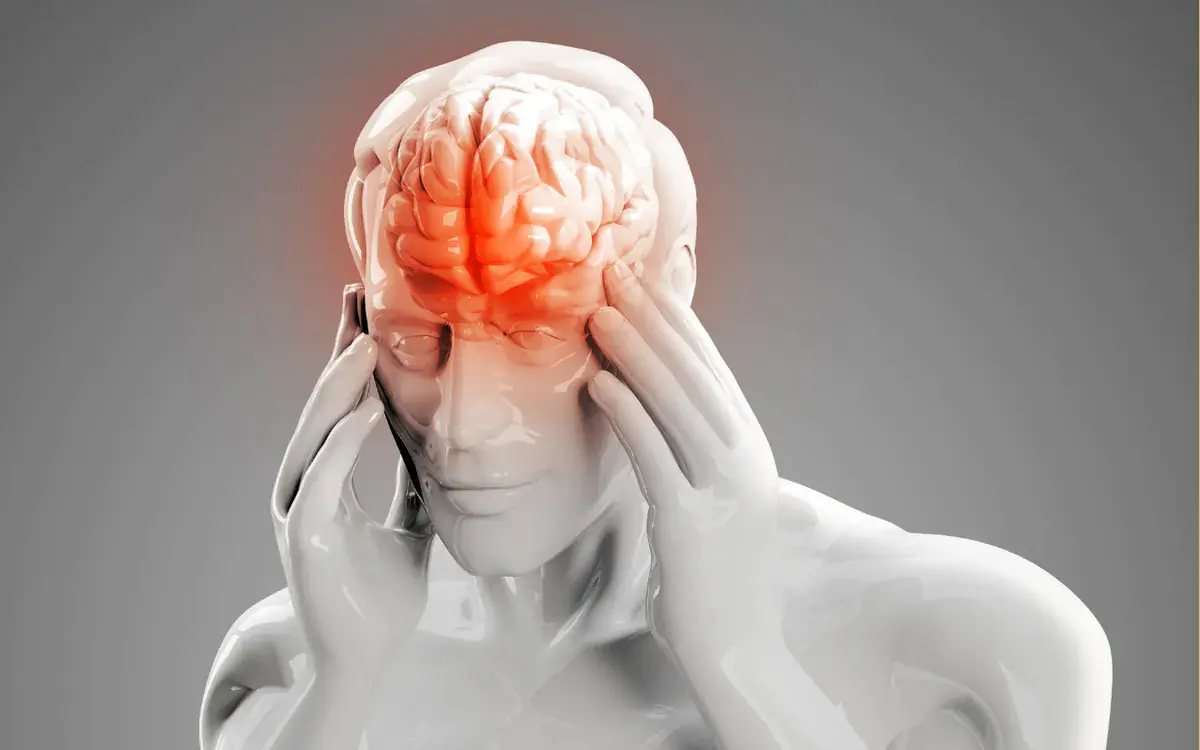

Cold weather often brings complaints of headaches and dizziness, especially in the early morning or late at night.
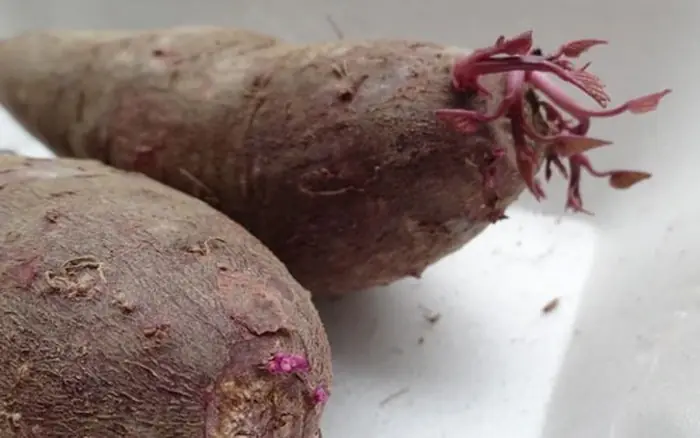

Sweet potatoes are truly a gift from nature—affordable, filling, and nutritious. But for them to be genuinely good for your health, careful selection is essential.

Certain intimate habits in men may silently increase women’s cancer risk.

A tragic case highlights the hidden dangers of improperly stored leftovers.
Warn:ing Symptoms of Heart Blockage In Legs And Feet At Night

A child’s death prompts doctors to warn parents about unhealthy diets.
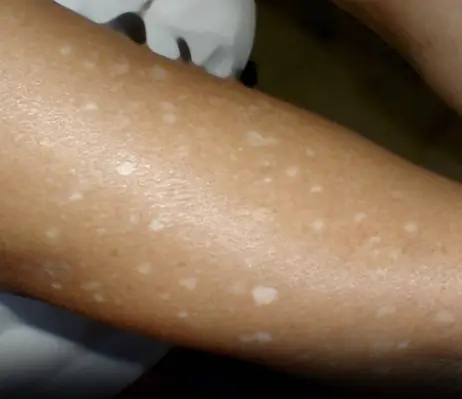
As the last traces of a summer tan begin to fade, many people notice small, pale dots appearing on their legs and arms. These
Keeping food fresh and flavorful isn’t just about buying quality ingredients —it also depends on how you store them.


Doctors Warn: 3 Nail Symptoms That May Indicate Underlying Health Issues

Doctors were confused when a strange growth was found in a 9-month-old ba.by’s mouth

Warning: A Bleach - Like Stain in Your Underwear May Be Trying to Tell You Something

Two Warning Signs Of Silent Kil:ler That You Might Spot In Your Feet

Pokeweed (Phytolacca americana): Beautiful to Look At, Dan.gerous to Touch

Discover Pine Cone Syrup: Benefits, Easy Recipe, and Creative Everyday Uses

Woman Di:es of Stomach Can:cer; Doctor Reveals 3 Bedtime Habits That Silent Harmed Her Health

A crave-worthy fusion that combines tacos with classic cheeseburgers.
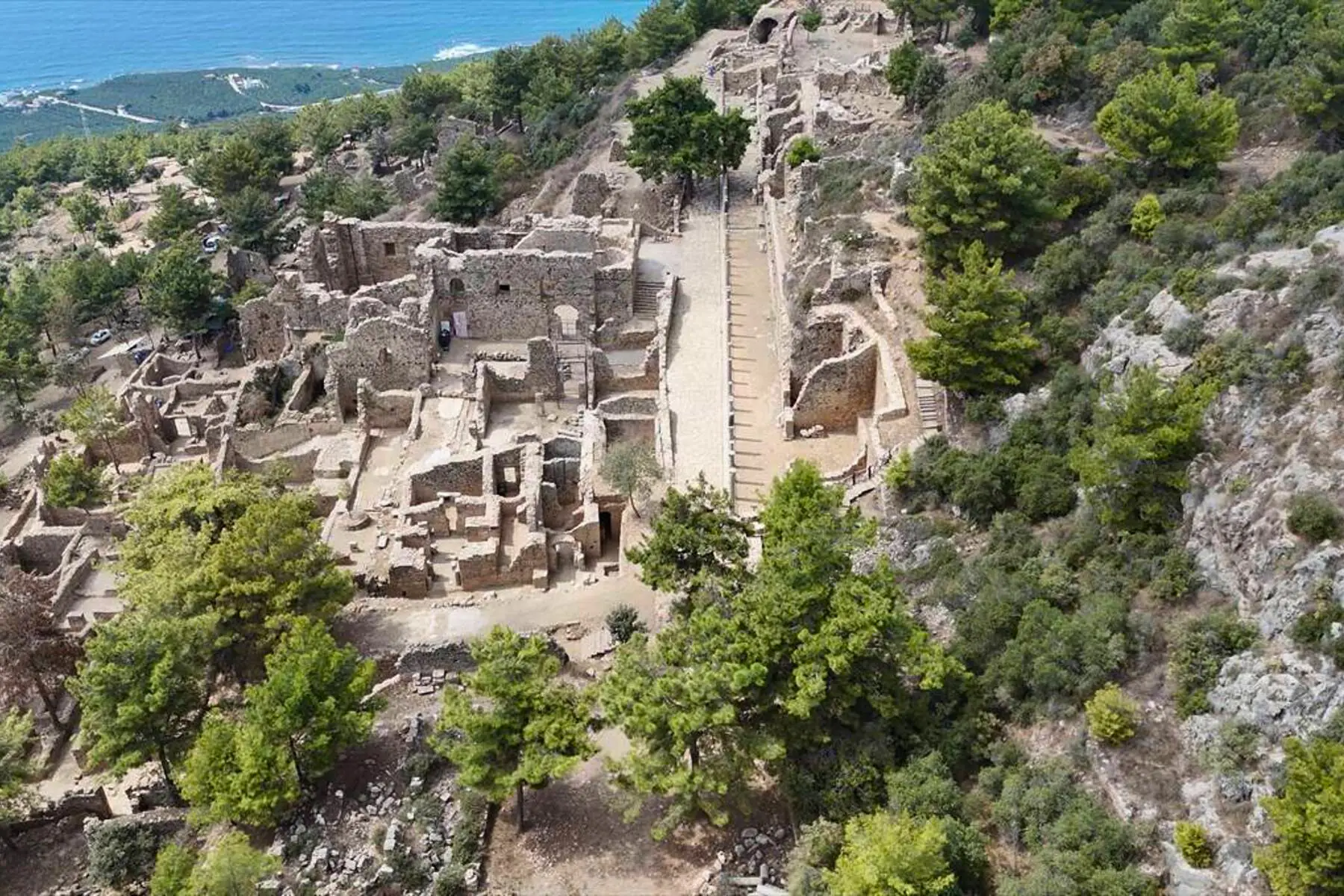

Researchers say the findings indicate Syedra was not only a regional producer but one of the Mediterranean’s key suppliers in antiquity, challenging earlier assumptions about the city’s economic role.

We all know that food consumption habits vary greatly among countries.

Typically, hotel beds come with at least four pillows

Older people may experience issues with blood circulation more often than the younger population.

Tofu is Nutritious but These 5 Groups Should Avoid It

7 Possible Brain Cancer Symptoms Every Woman Should Be Aware Of

Plants that should not be planted because they attract snakes into the house, including very familiar types

Cold weather often brings complaints of headaches and dizziness, especially in the early morning or late at night.

When this habit intrudes into face-to-face conversations, a serious question emerges:

Sweet potatoes are truly a gift from nature—affordable, filling, and nutritious. But for them to be genuinely good for your health, careful selection is essential.