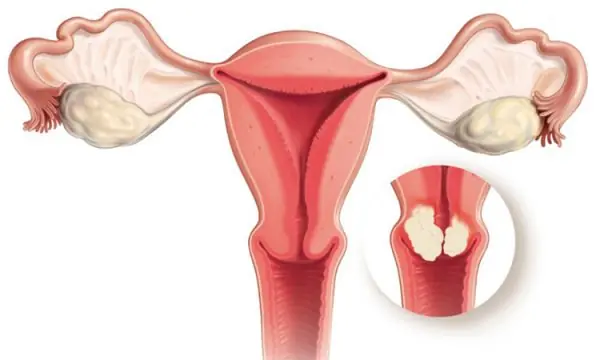
5 common foods that may negatively affect ute.rine health in women
Many women eat these 5 foods without knowing they can harm their ute.rus
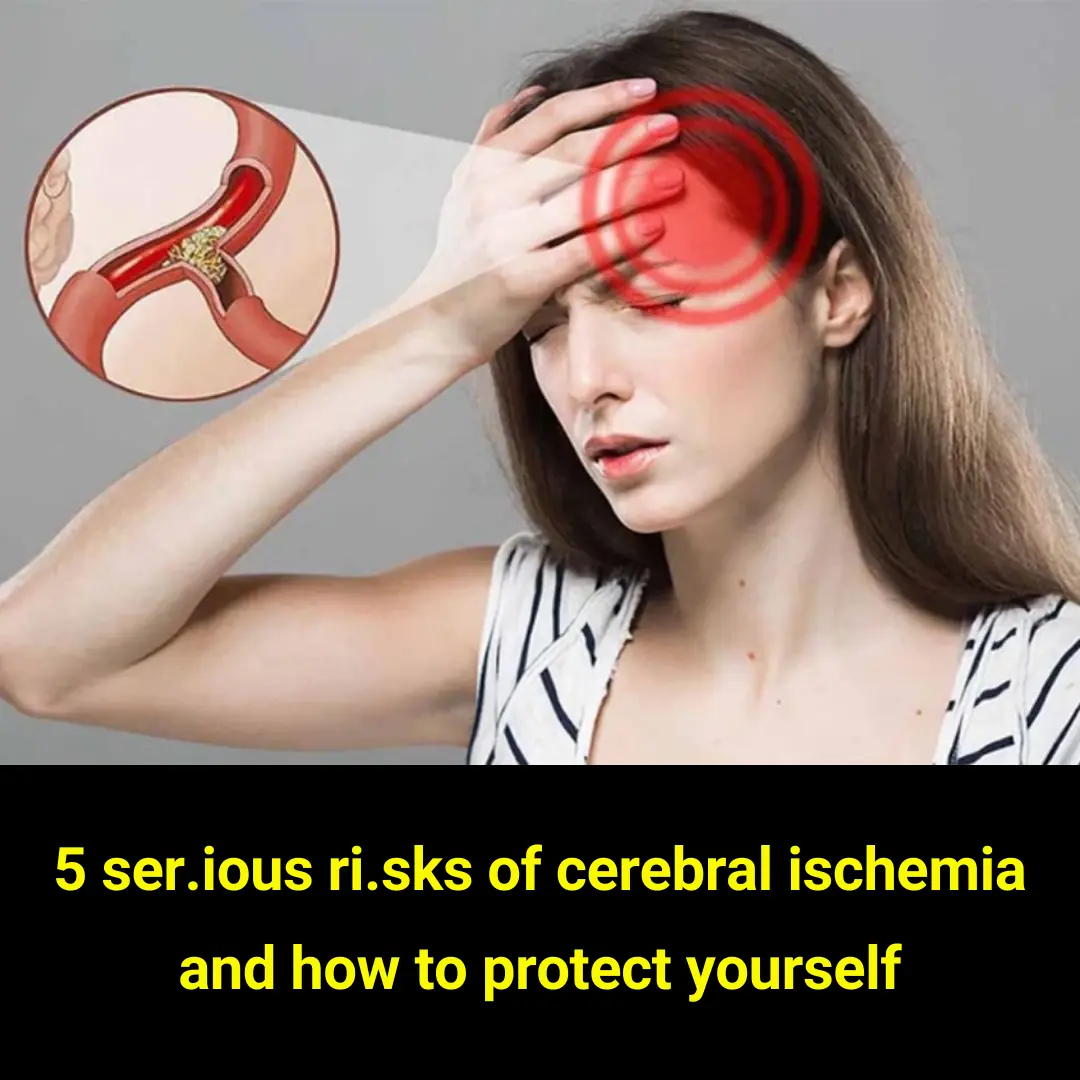
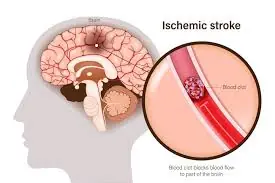
Cerebral ischemia, often referred to as reduced blood flow to the brain, is a serious medical condition that can quietly damage brain tissue
over time or trigger sudden, life-threatening events such as stroke. The brain depends on a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients delivered
through the bloodstream. When that supply is disrupted even briefly brain cells can begin to suffer irreversible damage.
Understanding the risks associated with cerebral ischemia and knowing how to prevent or reduce those risks is essential for protecting
long-term brain health. Below are five major dangers of cerebral ischemia, along with practical prevention strategies.
One of the most serious risks of cerebral ischemia is ischemic stroke, which occurs when a blood vessel supplying the brain becomes blocked
by a clot or narrowed by plaque buildup. Prolonged or repeated episodes of reduced blood flow significantly increase the likelihood of a
major stroke.
A stroke can result in:
Paralysis or weakness on one side of the body
Difficulty speaking or understanding language
Vision loss
Permanent disability or death
Control blood pressure and cholesterol levels
Avoid smoking and limit alcohol intake
Maintain a heart-healthy diet rich in vegetables, fruits, and whole grains
Seek medical evaluation for symptoms such as sudden dizziness, slurred speech, or numbness
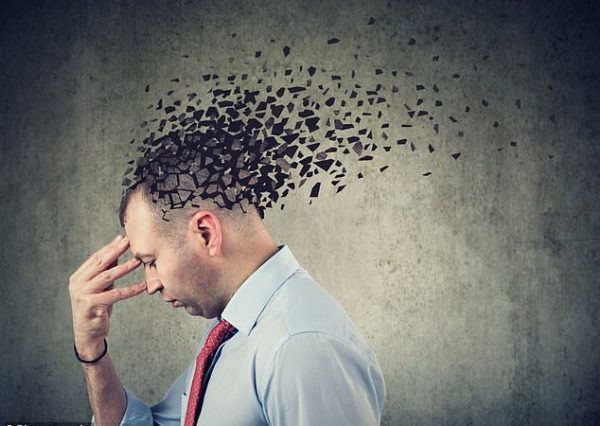
Chronic cerebral ischemia may not cause dramatic symptoms at first, but over time it can impair cognitive function. Reduced blood flow
deprives brain cells of oxygen, affecting areas responsible for memory, concentration, and decision-making.
This condition may contribute to:
Forgetfulness
Difficulty concentrating
Slower thinking
Increased risk of vascular dementia
Engage in regular mental stimulation such as reading or problem-solving
Exercise regularly to improve circulation
Manage chronic conditions such as diabetes and hypertension
Ensure adequate sleep and stress management

When parts of the brain responsible for balance and coordination receive insufficient blood supply, physical stability may be affected. People
with cerebral ischemia often experience dizziness, weakness, or unsteady movement.
These issues can lead to:
Frequent falls
Injuries such as fractures
Reduced independence in daily activities
Perform balance and strength exercises
Rise slowly from sitting or lying positions
Stay hydrated to maintain healthy blood circulation
Regularly monitor blood pressure, especially in older adults

The brain regulates emotions as well as physical functions. Reduced blood flow can disrupt neurotransmitter balance, increasing the risk of
mood changes.
Common emotional effects include:
Anxiety
Depression
Irritability
Emotional instability
These symptoms are often overlooked or mistaken for stress or aging, delaying proper care.
Maintain social connections and emotional support
Practice stress-reducing activities such as meditation or gentle exercise
Seek professional help if mood changes persist
Treat underlying vascular or metabolic conditions
If cerebral ischemia remains untreated, repeated episodes can lead to permanent brain damage. This may result in long-term disability,
reduced independence, and a significant decline in overall quality of life.
Severe outcomes may include:
Loss of speech or movement
Difficulty performing basic daily tasks
Dependence on long-term care
Attend regular health checkups, especially for cardiovascular health
Follow prescribed treatments for heart and blood vessel conditions
Adopt a physically active lifestyle appropriate for age and health status
Respond promptly to warning signs such as sudden confusion, vision changes, or weakness

In addition to addressing specific risks, the following habits can greatly reduce the likelihood of cerebral ischemia:
Maintain a healthy weight
Eat a balanced, low-salt, low-fat diet
Exercise at least 30 minutes most days of the week
Manage chronic conditions such as diabetes and high cholesterol
Avoid prolonged sitting and remain physically active
Cerebral ischemia is a serious condition with far-reaching consequences if left unaddressed. The risks range from stroke and cognitive decline
to emotional disturbances and long-term disability. However, many of these dangers are preventable with early awareness, healthy lifestyle
choices, and proper medical care.
Protecting brain health starts with protecting blood flow. By taking preventive steps today, individuals can reduce their risk of cerebral
ischemia and preserve cognitive and physical function well into the future.

Many women eat these 5 foods without knowing they can harm their ute.rus
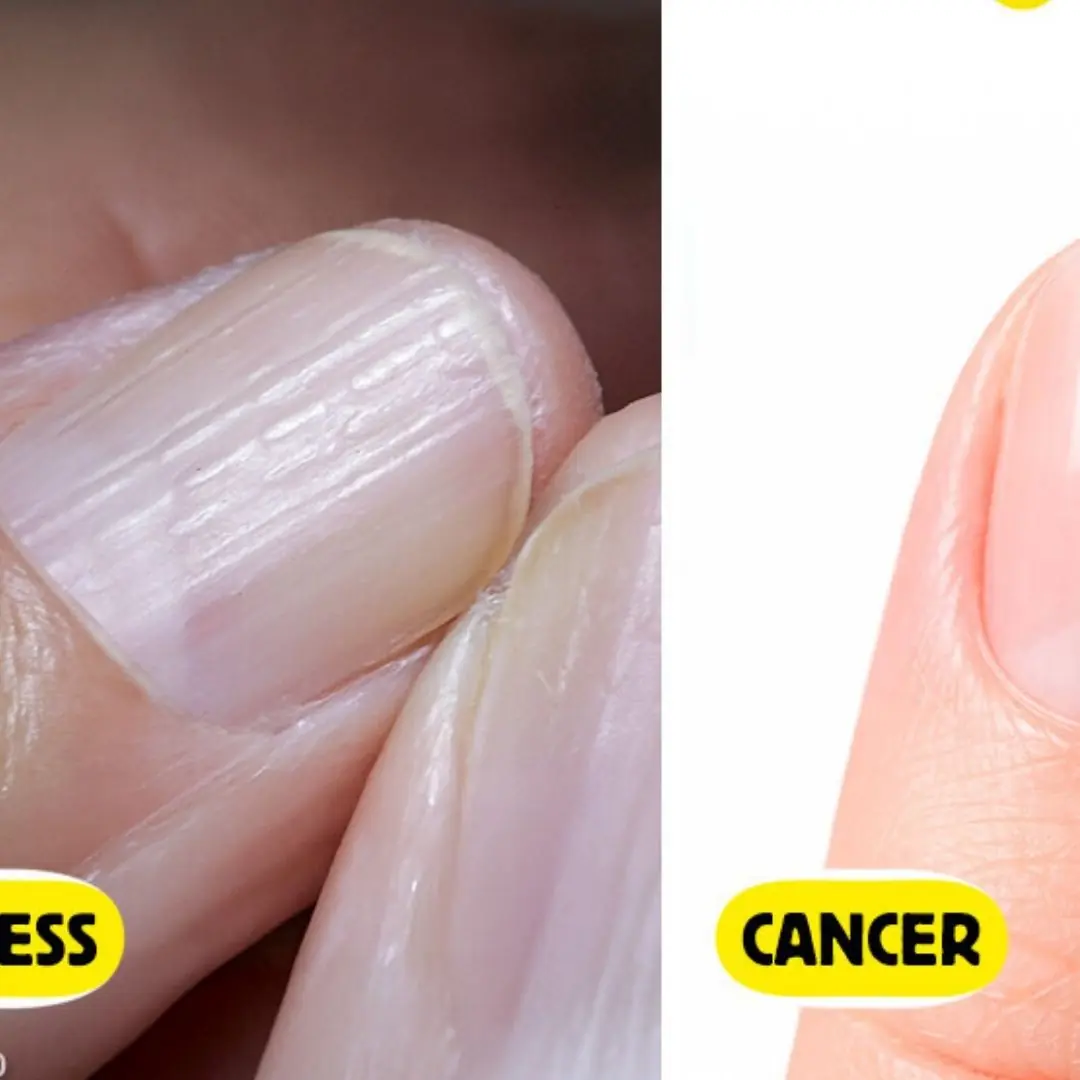
5 Serious Health Issues Your Nails Might Be Warning You About
A recent tragic case involving a 50-year-old man has once again raised public awareness about the hidden dangers of consuming refrigerated leftovers.

A hospital in Sydney has recently unveiled an innovative medical device that is transforming the way cancer and chronic pain are treated.

Papaya Seeds: A Powerful Remedy for Liver Health and How to Use Them as a Pepper Substitute
Did you know that the main cause of death in the US are heart attacks?

Are you noticing that your vision isn’t as sharp as it used to be?

Yevgeniy Chazov — legendary physician, world-renowned cardiologist

Yet across the UK, a growing number of middle-aged women are quietly walking away from marriages that, from the outside, look perfectly stable.
4 Real Reasons Your Vagina May Smell Sour (And What It Means)
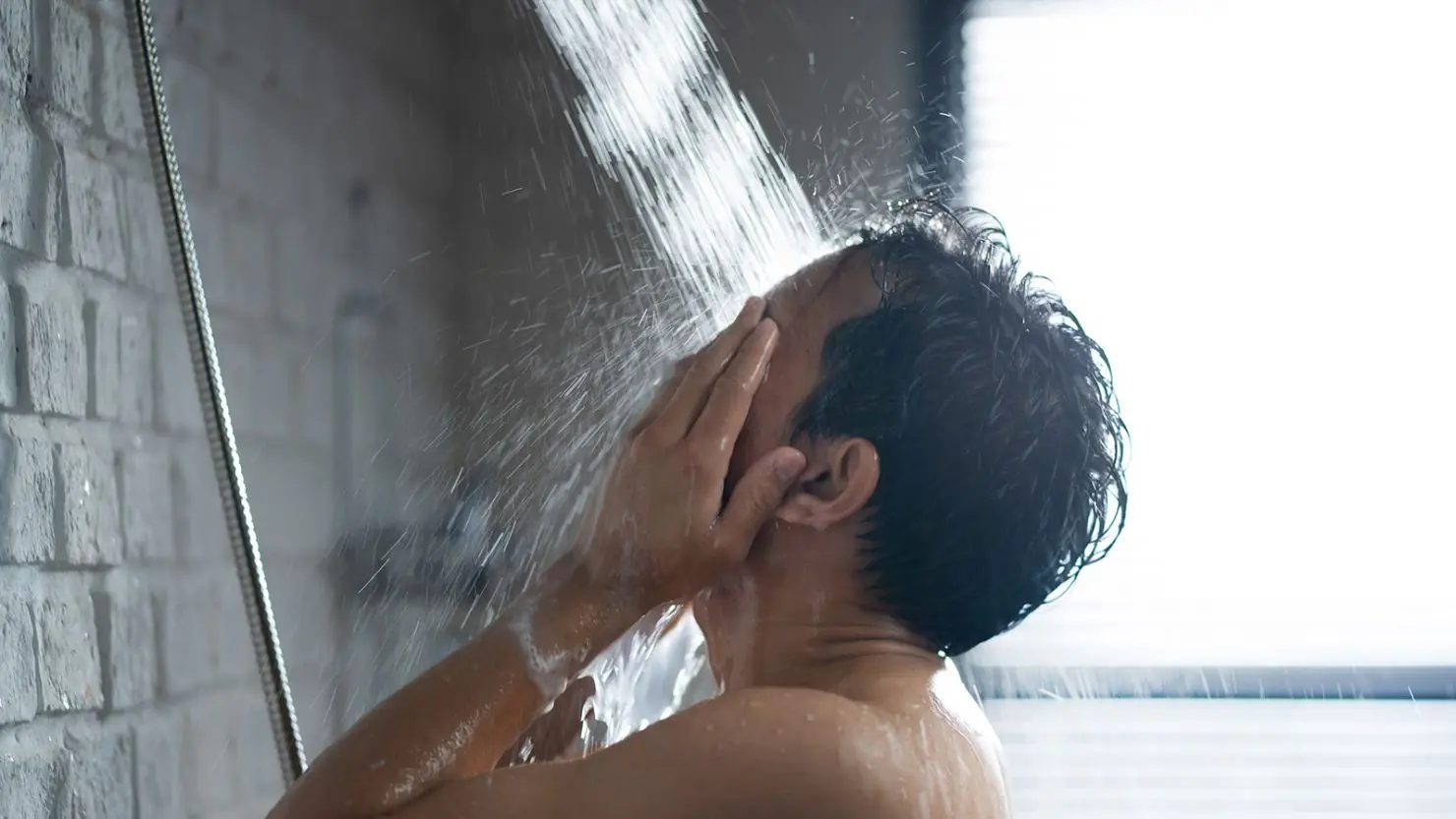

In recent years, the number of strokes and sudden medical emergencies occurring during or immediately after bathing among middle-aged and older adults has been rising.
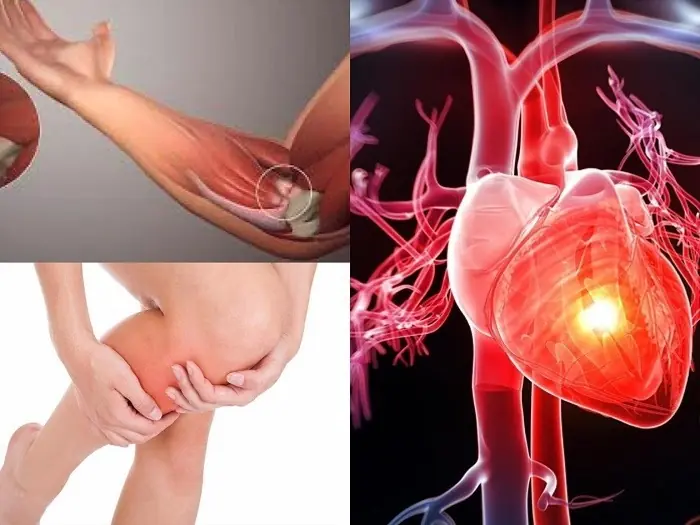
Heart attacks rarely strike without warning.
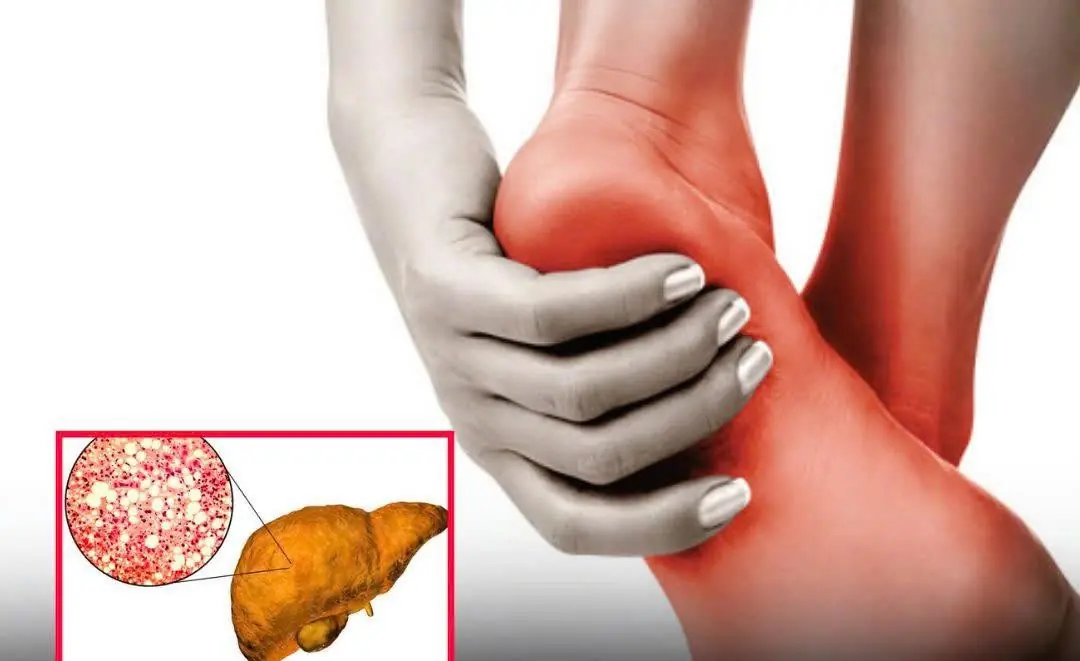
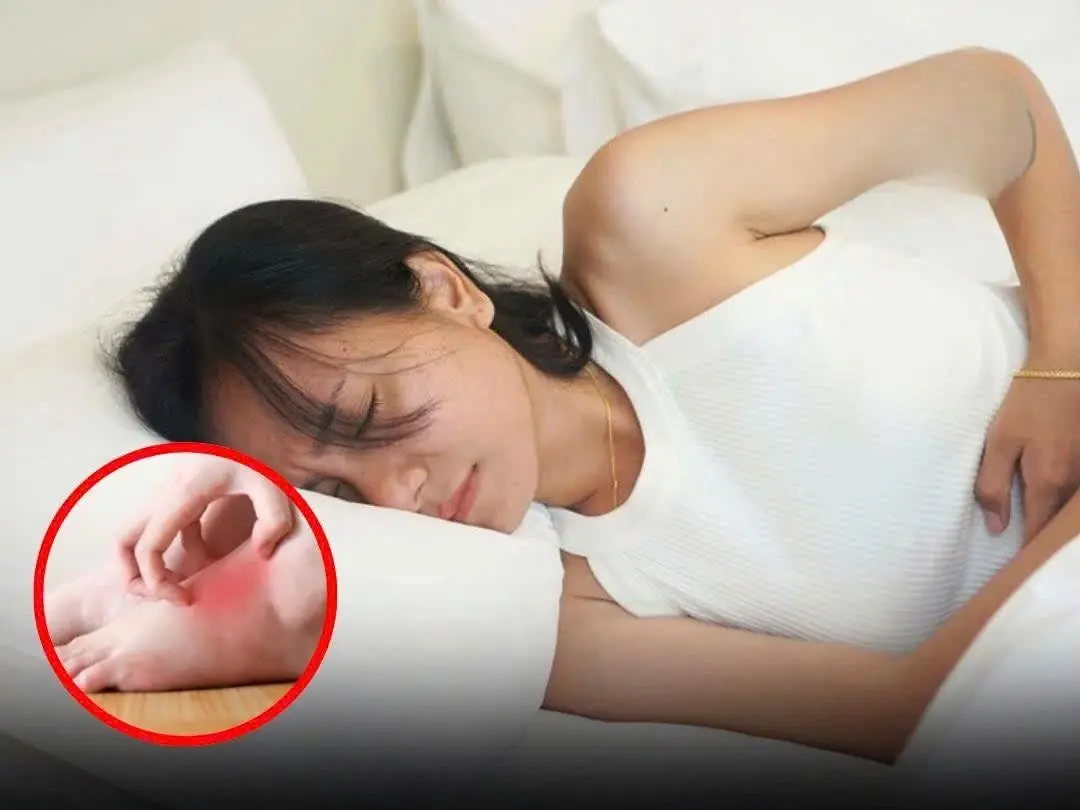
If You Notice This Change in Your Feet, Your Fat:ty Liver May Be Beyond Repair
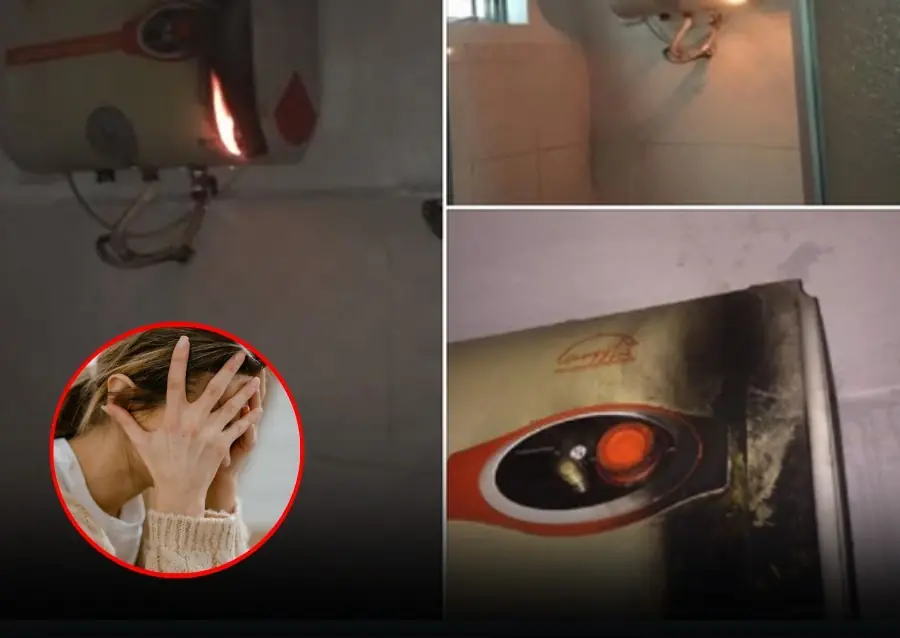

the truth no homeowner should ignore:
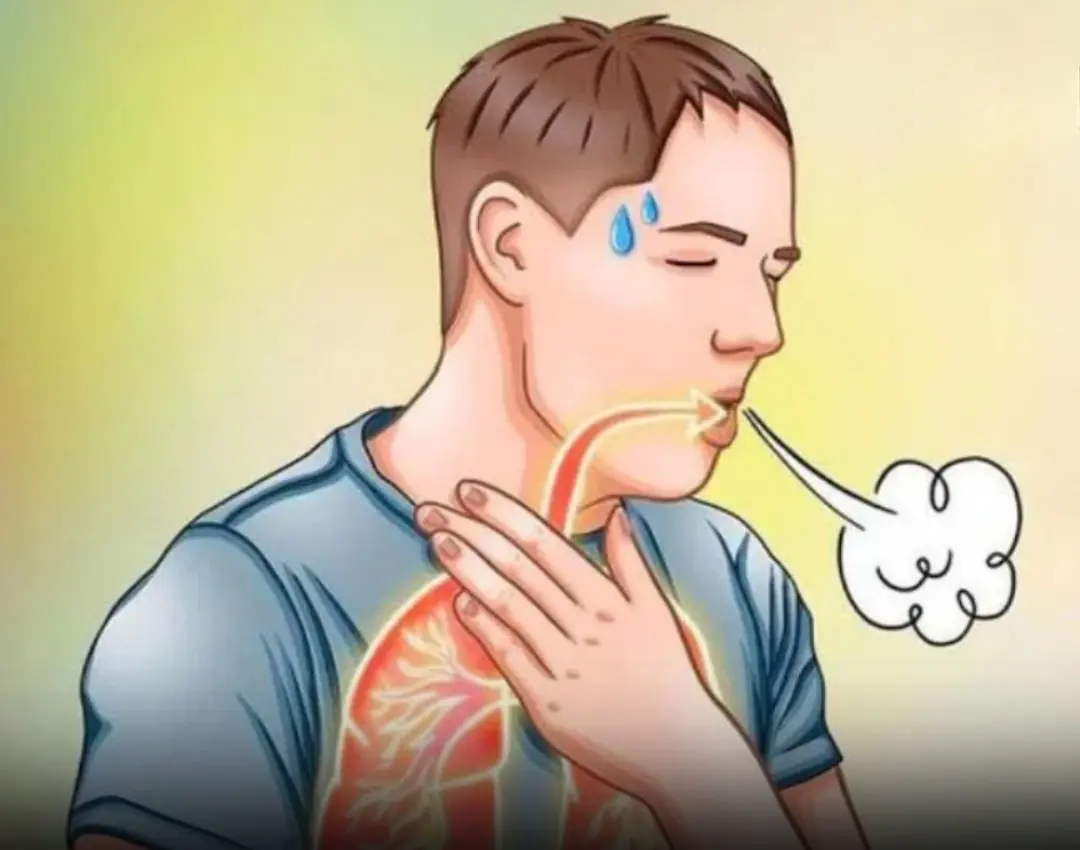
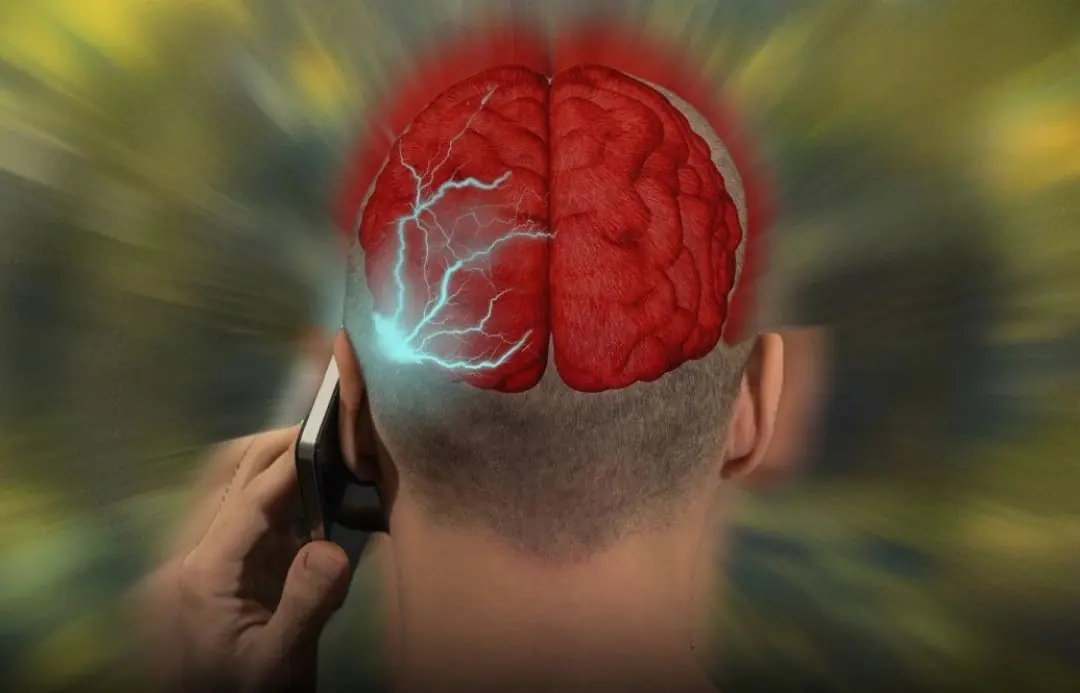
Something many people don’t realize

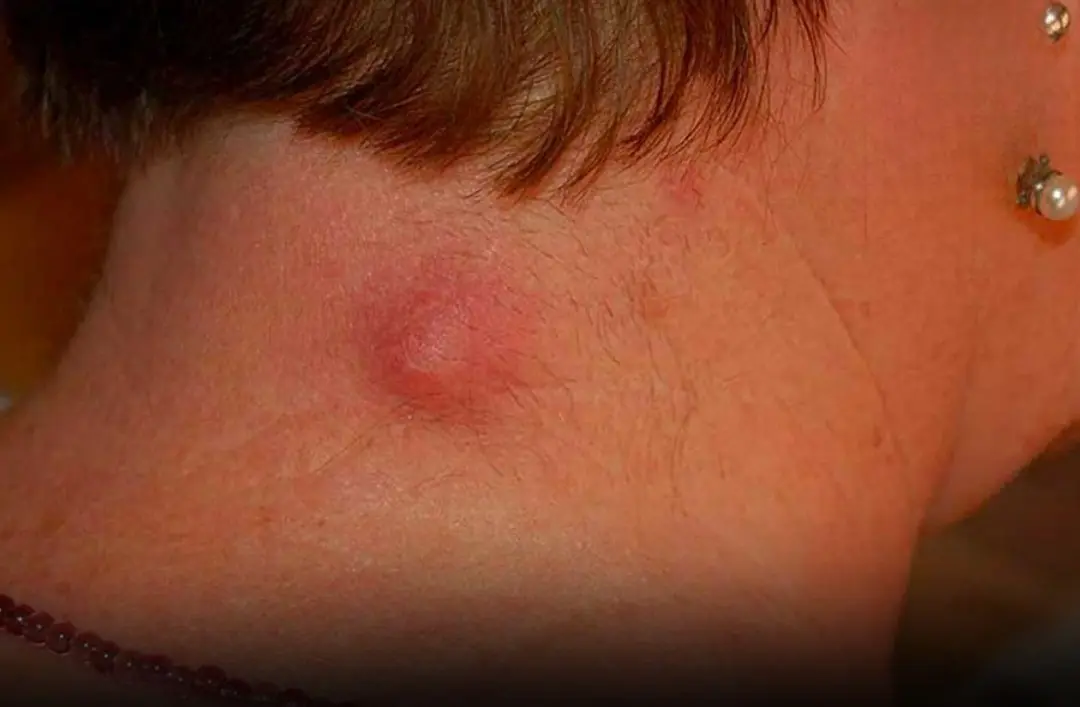
Lumps in the neck, back, or behind the ear can have several causes — early checks matter
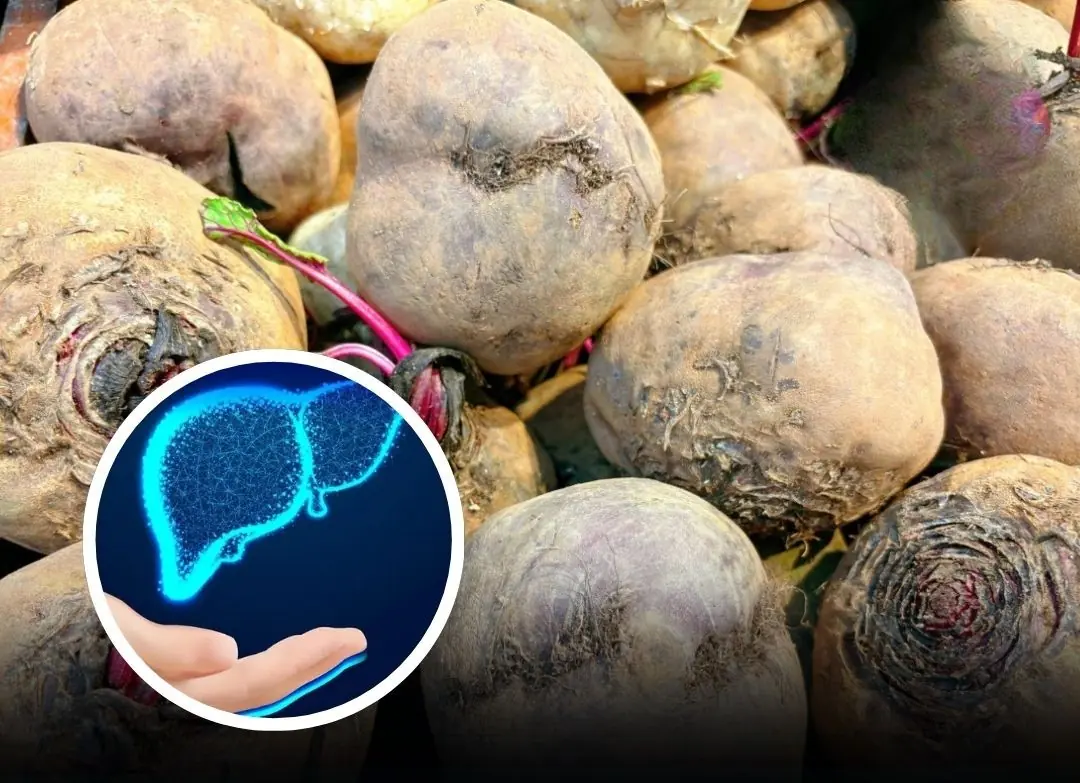

Nutritionists Reveal 5 Vegetables That Help Protect and Support Your Liver
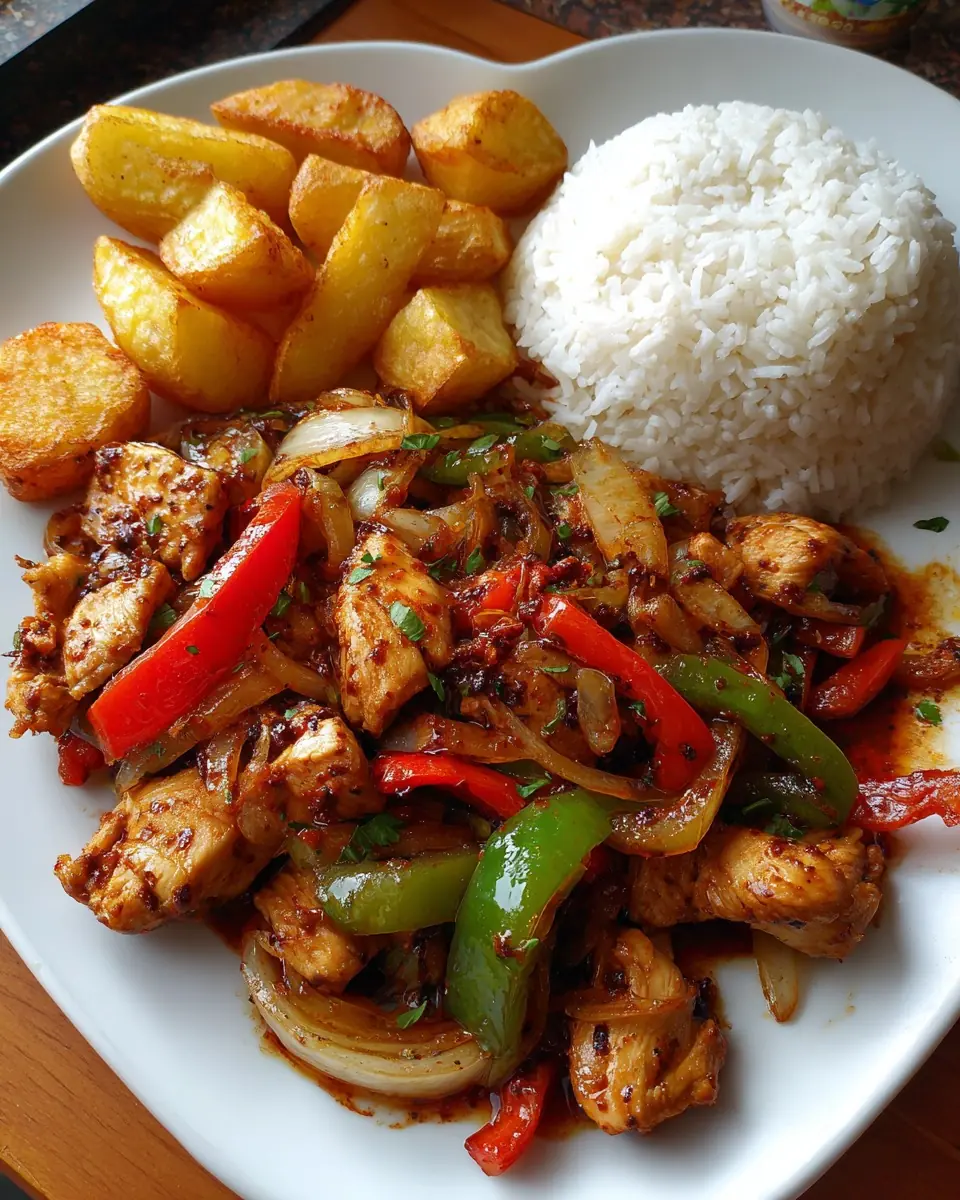

Spicy Chicken Stir-Fry with Bell Peppers, Roast Potatoes & Steamed Rice
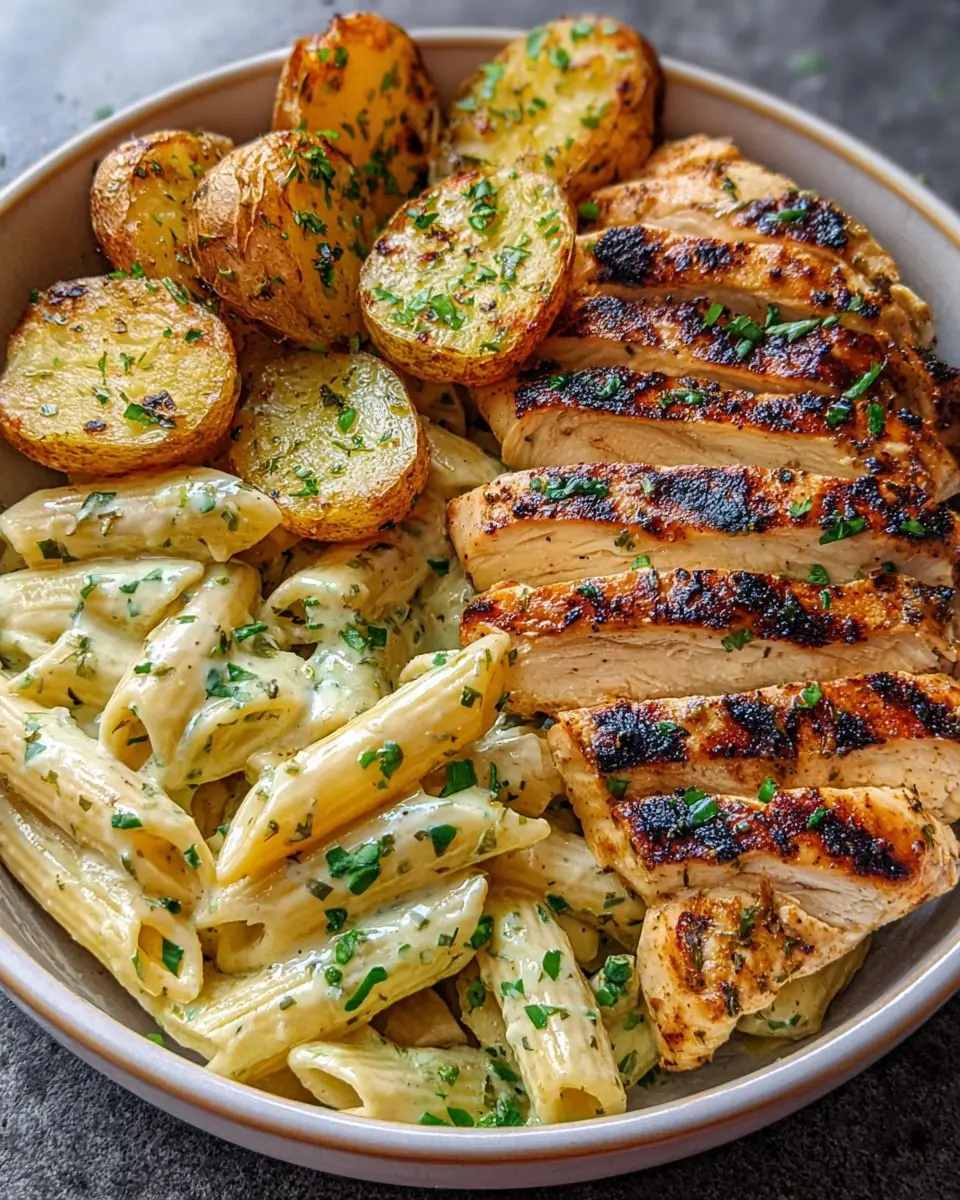

Creamy Herb Penne with Grilled Chicken & Garlic Roasted Potatoes

Many women eat these 5 foods without knowing they can harm their ute.rus

5 Serious Health Issues Your Nails Might Be Warning You About


A recent tragic case involving a 50-year-old man has once again raised public awareness about the hidden dangers of consuming refrigerated leftovers.

A hospital in Sydney has recently unveiled an innovative medical device that is transforming the way cancer and chronic pain are treated.

Papaya Seeds: A Powerful Remedy for Liver Health and How to Use Them as a Pepper Substitute

Did you know that the main cause of death in the US are heart attacks?
The Kingdom of Benin was an important African kingdom that flourished between the 13th and 19th centuries AD.
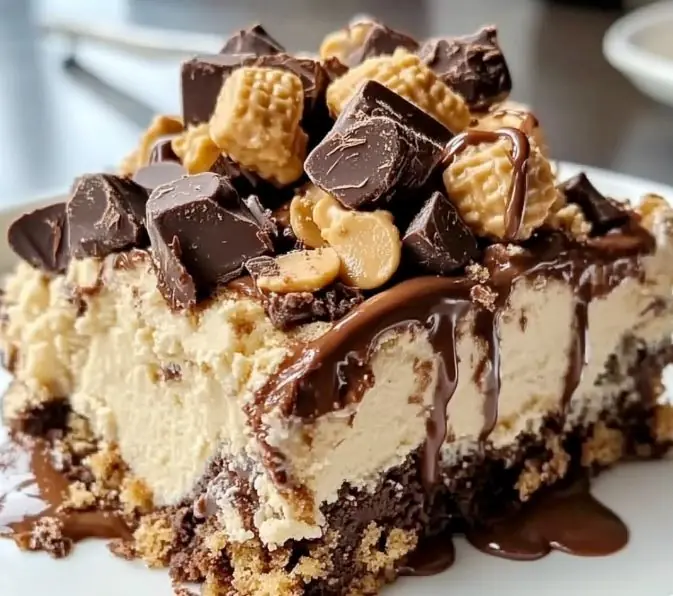

Serve with ice cream, whipped cream, or a drizzle of chocolate or peanut butter.

Are you noticing that your vision isn’t as sharp as it used to be?

Yevgeniy Chazov — legendary physician, world-renowned cardiologist

Yet across the UK, a growing number of middle-aged women are quietly walking away from marriages that, from the outside, look perfectly stable.
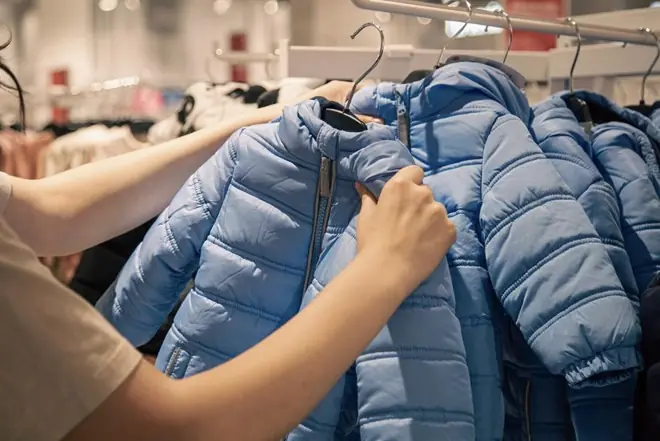

Just one careless step can cause the filling to collapse, distort the shape, and reduce its ability to retain heat.

4 Real Reasons Your Vagina May Smell Sour (And What It Means)

In recent years, the number of strokes and sudden medical emergencies occurring during or immediately after bathing among middle-aged and older adults has been rising.

Heart attacks rarely strike without warning.

If You Notice This Change in Your Feet, Your Fat:ty Liver May Be Beyond Repair

the truth no homeowner should ignore: