Common Reasons You Get Mucus in Your Throat
Feeling like you constantly have mucus stuck in your throat can be annoying, uncomfortable, and sometimes even worrying. Many people describe it as a “lump” sensation, a need to clear the throat often, or sticky phlegm that won’t go away. The good news is that, in most cases, this problem has common causes—many of which are treatable with simple changes.
Below are the most frequent reasons you may experience throat mucus, along with symptoms and practical solutions.
1. Postnasal Drip (The Most Common Cause)
Postnasal drip happens when mucus from your nose and sinuses flows down the back of your throat. Your body normally produces mucus to trap dust and germs, but when production increases, it becomes noticeable.
Common signs include:
-
Frequent throat clearing
-
A dripping sensation in the throat
-
Cough that worsens at night
-
Bad breath or a hoarse voice
Why it happens: allergies, colds, sinus infections, or irritants like smoke.
What helps: staying hydrated, using saline nasal sprays, and avoiding allergens.
2. Allergies and Sensitivities
Allergic rhinitis (hay fever) can trigger excess mucus production. Even mild allergies—dust, pet dander, pollen, mold—can cause chronic mucus in the throat.
Symptoms may include:
-
Sneezing and itchy eyes
-
Runny or blocked nose
-
Throat tickle and cough
-
Mucus that is clear or slightly white
What helps: antihistamines, nasal corticosteroid sprays, and reducing exposure to triggers (air purifier, cleaning dust, washing bedding).
3. Sinus Infections and Chronic Sinusitis
When your sinuses are inflamed or infected, mucus can become thicker and drain into your throat. Chronic sinusitis can last weeks or months.
Clues it may be sinus-related:
-
Facial pressure or headache
-
Thick yellow/green mucus
-
Stuffy nose
-
Reduced smell or taste
What helps: warm steam, saline rinses, and medical treatment if symptoms persist or worsen.
4. Acid Reflux (GERD or “Silent Reflux”)
Acid reflux can irritate the throat and trigger mucus production. Many people don’t feel typical heartburn, especially with silent reflux (LPR), where acid reaches the throat.
Possible symptoms:
-
Constant throat clearing
-
Hoarseness, especially in the morning
-
Sour taste or burning sensation
-
Feeling of something stuck in your throat
What helps: avoiding spicy/fatty foods, eating smaller meals, not lying down after eating, and consulting a doctor if frequent.
5. Dehydration and Dry Air
When you don’t drink enough fluids—or when the air is dry—mucus becomes thick and sticky, making it feel like it’s trapped in your throat.
Signs include:
-
Dry mouth and lips
-
Thick, hard-to-clear phlegm
-
Scratchy throat
What helps: drink more water, use a humidifier, and limit caffeine/alcohol (they can dry you out).
6. Respiratory Infections (Cold, Flu, or COVID-19)
Viral infections often increase mucus production as your body fights illness. Mucus may drip into your throat and cause coughing.
What to watch for:
-
Fever, fatigue, body aches
-
Sore throat
-
Mucus changing color over time
What helps: rest, hydration, warm drinks, and monitoring symptoms. Seek help if breathing becomes difficult.
7. Smoking, Pollution, and Irritants
Smoke and pollutants irritate the airways and can cause chronic mucus as the body attempts to protect itself.
Common triggers:
-
Cigarettes or vaping
-
Dusty environments
-
Chemical fumes
-
Air pollution
What helps: avoiding irritants, improving indoor air quality, and quitting smoking for long-term relief.
8. When to See a Doctor
Most cases of throat mucus improve with home care, but you should get medical advice if you experience:
-
Mucus lasting more than 3–4 weeks
-
Blood in mucus
-
Severe sore throat, trouble swallowing
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Shortness of breath or chest pain
-
Persistent fever
These may signal infections, chronic reflux, or other conditions that require professional evaluation.
Practical Tips to Reduce Throat Mucus
Here are quick, effective habits you can start today:
-
Drink warm water or herbal tea
-
Gargle with salt water
-
Use saline nasal rinse regularly
-
Avoid dairy if it worsens symptoms (for some people)
-
Elevate your head during sleep
-
Limit smoking and strong fragrances
Final Thoughts
Mucus in the throat is usually your body’s natural response to irritation, infection, or inflammation. By identifying the cause—such as postnasal drip, allergies, sinus problems, or acid reflux—you can choose the right approach and feel better faster. If symptoms persist or worsen, don’t hesitate to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
News in the same category


5 War.ning Signs Your Body Is Overloaded with Sugar

Dry mouth at night could be a warning sign: Don’t ignore these 8 reasons
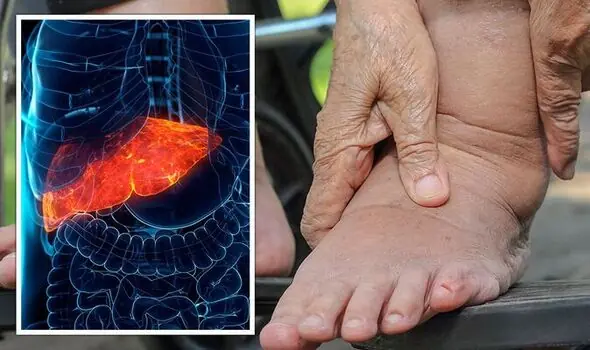
Fatty liver disease: The sign in your feet that means the condition is irreversible
Your feet may be warning you about diabetes: Don’t ignore these 5 strange signs

Not every fruit or vegetable peel is safe to eat. Continuing to eat certain peels may be harmful to your health
Why Do Red Dots Appear on Your Skin? Causes and What They Could Mean
Up to 3 months before a heart att.ack, the body often sends out 5 critical warning signs but many people ignore them

3 morning habits young people often do that harm their kidneys; anyone doing them should stop immediately

Office Worker’s Buttock and Back Pain Turns Out to Be a Serious Disease

Scientists May Have Actually Found One Of The Causes Of Autism
24-Year-Old Woman Suffers Stomach Perforation Due to One Common Morning Coffee Mistake
One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs

This One Superfood Could Tackle Major Health Issues—Here’s What You Need To Know

Anyone with high blo.od fat should use this seed: just about $0.20 per handful, and every part—from leaves to roots—is medicinal

Why Your Hard-Boiled Eggs Have That Weird Green Ring
Itching in 9 Areas: A Warning Sign of Malignant Tumors, Number 7 Is the Most Common
Eating Just One Bite is Already Harmful, But Many Still Eat It Without Worry

A 4-Year-Old Girl Nearly Lost Her Life to Diabetes — Parents in Tears: “I Spoiled Her Too Much!”
3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead
News Post

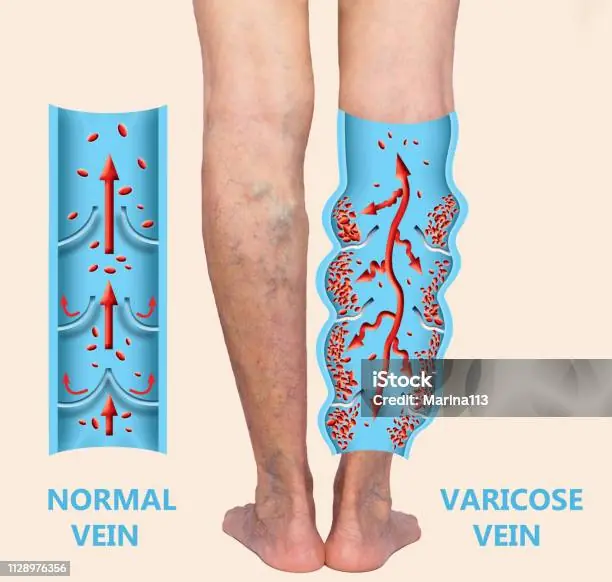
If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things

5 War.ning Signs Your Body Is Overloaded with Sugar

Dry mouth at night could be a warning sign: Don’t ignore these 8 reasons

Fatty liver disease: The sign in your feet that means the condition is irreversible

Your feet may be warning you about diabetes: Don’t ignore these 5 strange signs

Green Pandan Rice Noodles in Coconut Milk with Mango

Salmon Mango Poke Bowl

Not every fruit or vegetable peel is safe to eat. Continuing to eat certain peels may be harmful to your health

Strawberry Mille Crêpe Cake

Why Do Red Dots Appear on Your Skin? Causes and What They Could Mean

Coconut Panna Cotta with Mango & Passion Fruit

Up to 3 months before a heart att.ack, the body often sends out 5 critical warning signs but many people ignore them

3 morning habits young people often do that harm their kidneys; anyone doing them should stop immediately

Office Worker’s Buttock and Back Pain Turns Out to Be a Serious Disease

Here's how to choose delicious, sweet mangosteens – all 10 of them are perfect

Scientists May Have Actually Found One Of The Causes Of Autism

24-Year-Old Woman Suffers Stomach Perforation Due to One Common Morning Coffee Mistake

One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs

This One Superfood Could Tackle Major Health Issues—Here’s What You Need To Know
