
Few people truly understand what a ring on the right hand represents
The meaning of a ring worn on the right hand is not widely known

Biosynthesis of proteins and nucleic acid require nitrogen however atmospheric nitrogen is not available to eukaryotes for organic synthesis. Only few prokaryotes (such as cyanobacteria, clostridia, archaea etc) have the ability to fix the molecular nitrogen abundantly available in the atmosphere. Some nitrogen-fixing bacteria live inside eukaryotic cells in symbiotic relation as endosymbionts. For example, the cyanobacteria Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa (UCYN-A) is an endosymbiont of the of the unicellular microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii in marine systems. Such natural phenomenon is thought to have played a crucial role in evolution of eukaryotic cell organelles mitochondria and chloroplasts through integration of endosymbiotic bacteria to the eukaryotic cell. In a recently published study, researchers found that the cyanobacteria “UCYN-A” had closely integrated with the eukaryotic microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii and evolved from an endosymbiont to nitrogen-fixing eukaryotic cell organelle named nitroplast. This made microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii the first known nitrogen-fixing eukaryote. This discovery has expanded the function of fixation of atmospheric nitrogen from prokaryotes to eukaryotes.
Symbiosis i.e., organisms of different species sharing habitat and living together, is a common natural phenomenon. The partners in the symbiotic relationship may benefit from each other (mutualism), or one may benefit while the other remain unaffected (commensalism) or one benefits while the other is harmed (parasitism). The symbiotic relationship is called endosymbiosis when one organism lives inside the other, for example, a prokaryotic cell living inside a eukaryotic cell. The prokaryotic cell, in such situation, is called endosymbiont.
Endosymbiosis (i.e., internalization of prokaryotes by an ancestral eukaryotic cell) played a crucial role in evolution of mitochondria and chloroplasts, the cell-organelles characteristic of more complex eukaryotic cells, which contributed in proliferation of eukaryotic life forms. An aerobic proteobacterium is thought to have entered ancestral eukaryotic cell to become an endosymbiont at a time when the environment was increasingly becoming oxygen rich. The ability of the endosymbiont proteobacterium to use oxygen to make energy allowed the host eukaryote to thrive in the new environment while the other eukaryotes became extinct due to negative selection pressure imposed by the new oxygen-rich environment. Eventually, the proteobacterium integrated with the host system to become a mitochondrion. Similarly, some photosynthesising cyanobacteria entered the ancestral eukaryotes to become endosymbiont. In due course, they assimilated with the eukaryotic host system to become chloroplasts. Eukaryotes with chloroplasts acquired the ability to fix atmospheric carbon and became autotrophs. Evolution of carbon-fixing eukaryotes from the ancestral eukaryotes was a turning point in the history of life on earth. 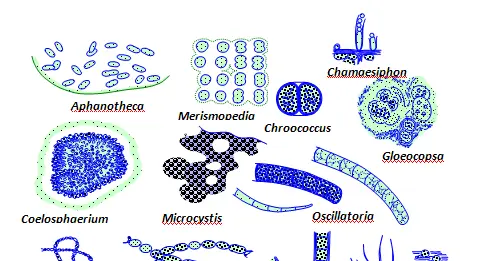
Nitrogen is required for organic synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids however the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen is limited only to few prokaryotes (such as some cyanobacteria, clostridia, archaea etc). No known eukaryotes can independently fix atmospheric nitrogen. Mutualistic endosymbiotic relationships between nitrogen-fixing prokaryotes and carbon-fixing eukaryotes that need nitrogen to grow are seen in nature. One such instance is the partnership between the cyanobacteria Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa (UCYN-A) and the unicellular microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii in marine systems.
In a recent study, the endosymbiotic relationship between the cyanobacteria Candidatus Atelocyanobacterium thalassa (UCYN-A) and the unicellular microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii was investigated using soft x-ray tomography. Visualisation of cell morphology and division of the alga revealed a coordinated cell cycle in which the endosymbiont cyanobacteria divided evenly just the way chloroplasts and mitochondria in a eukaryote divide during cell division. Study of proteins involved in the cellular activities revealed that a sizable fraction of them were encoded by the genome of algae. This included proteins essential for biosynthesis, cell growth, and division. These findings suggest that the endosymbiont cyanobacteria had closely integrated with the host cellular system and transitioned from an endosymbiont to a full-fledged organelle of the host cell. As a consequence, the host algal cell acquired the ability to fix atmospheric nitrogen for synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids required for growth. The new organelle is named nitroplast because of its nitrogen fixing ability.
This makes the unicellular microalgae Braarudosphaera bigelowii the first nitrogen-fixing eukaryote.This development may have implications for agriculture and chemical fertiliser industry in the long run.
References:

The meaning of a ring worn on the right hand is not widely known

Most people THROW IT AWAY — but this tiny metal ring on sausages is actually saving your health!
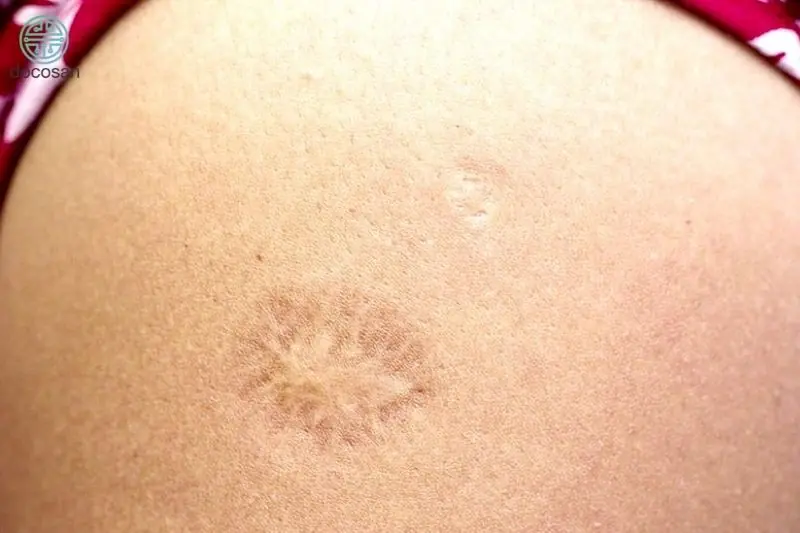
Do you know why there’s a small scar on the upper left arm and what it means?

Using an electric kettle daily? Here are 4 errors you should watch out for

If a millipede crawls indoors, don’t eliminate it immediately

If You Don’t Unplug These 5 Electrical Devices at Home, Your Electricity Bill Could Skyrocket!

Don’t rush to call a technician — just do this simple fix to keep your fridge running smoothly
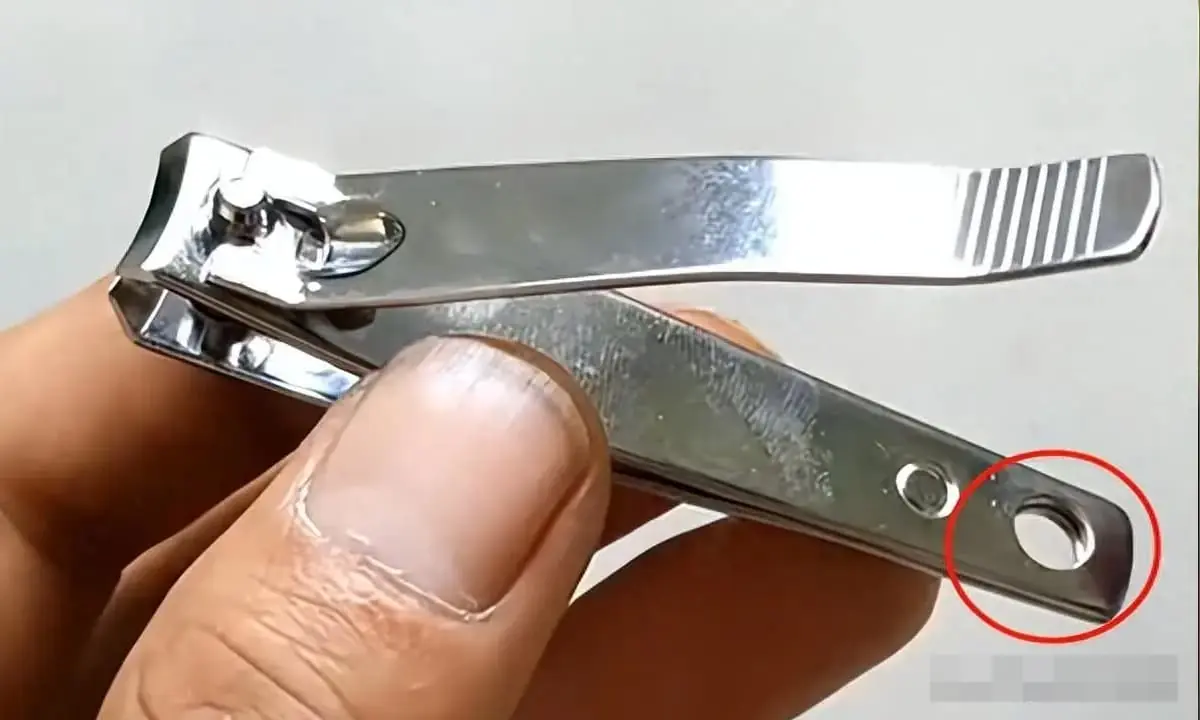

Why do nail clippers include a small hole? The hidden reason revealed

Nothing drains your energy more than the battles you fight inside your own mind. Release what is beyond your control

The Truth about Sleepwalking

The surprising reasons why your cat loves sleeping in your bed
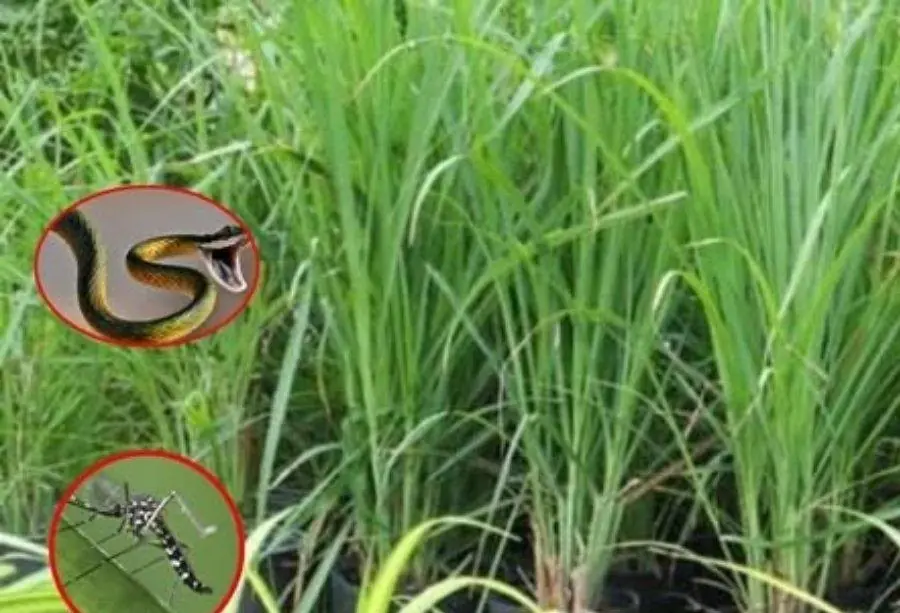

Mosquitoes and snakes avoid this plant. Do you have it in your yard?

Why people in Japan sleep on the floor: tradition and everyday practicality explained

4 raw foods that may offer significant health benefits

5 countries introducing stricter policies affecting Americans living and working there
Your Brain Uses About 20% of Your Body’s Total Energy — Even at Rest

Everyone deserves the chance to experience love, no matter what stage of life they are in.

Abandoned Baby Macaque Punch At Ichikawa Zoo Wins Hearts Worldwide After Viral

Why do dogs often sniff people when they meet them?

Many people don’t know what its purpose is used for

What Frequent Nighttime Urination Might Say About Your Health

Possible Heart Attack Symptoms? Here’s Why Immediate Medical Help Matters

Discover the simple drink that may improve blood circulation in your legs fast.

Exploring the power of Xanthium strumarium: from traditional medicine to contemporary applications
7 foods with anticancer effects you probably didn’t know about.

Struggling with low energy or constant fatigue? While many factors can contribute to feeling this way, certain natural ingredients may support your daily energy levels.

Rice Water: How to Turn Cloudy Rinse Water into a Natural Beauty Boost for Skin and Hair

Yellow teeth? Try this viral hack before your next dental visit.
Ectomorph, Mesomorph, or Endomorph? Discover Your True Body Type
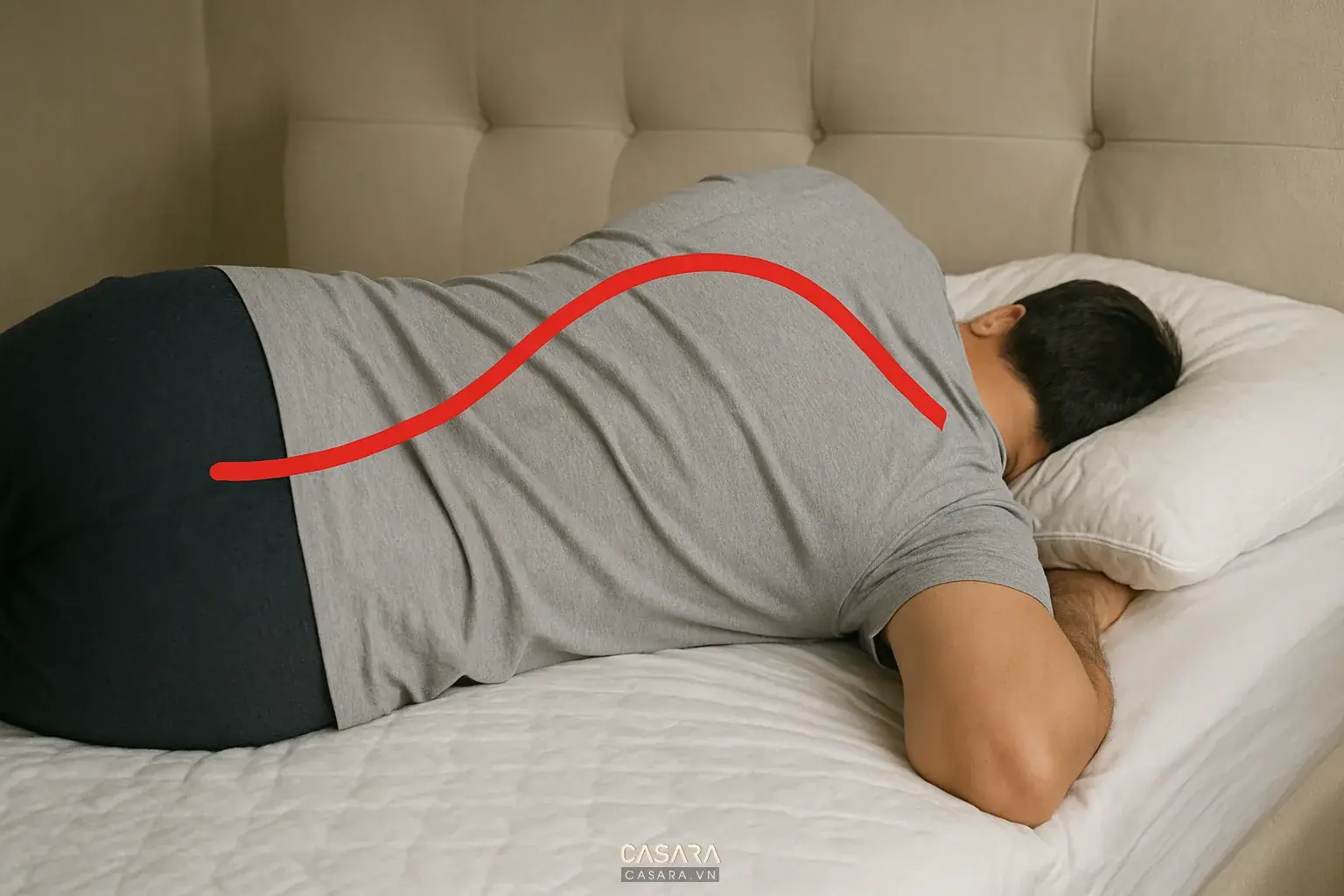

The Hidden Health Risks of Poor Sleep Posture (And How to Correct Them)

7 must-know tips for using cloves effectively
Researchers outline 7 hidden health problems your nails might suggest
For many people, simply hearing the word “colonoscopy” is enough to cause immediate fear or discomfort.

Peanuts, also known as groundnuts, are rich in vitamins and nutrients, often hailed as a "longevity nut" that is highly beneficial for health.
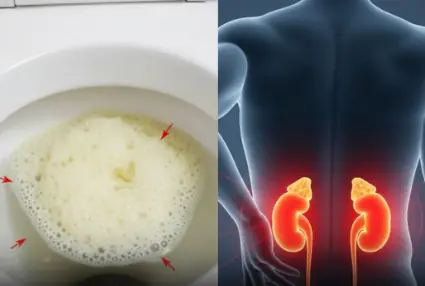
Occasionally noticing foamy urine is usually harmless and not a cause for concern.

Heart disease does not always announce itself with dramatic chest pain during the day. In many cases, the heart sends subtle warning signals at night, when the body is at rest and symptoms become more noticeable.
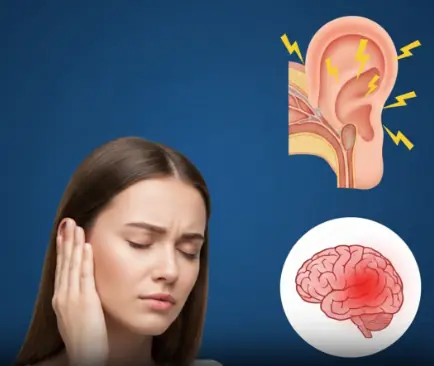
Have you ever noticed a faint hum, buzz, or ringing in your ear — especially when everything around you is silent?

When our skin becomes itchy, we often attribute the discomfort to external factors such as sweat, hygiene products, laundry detergents, or the fabric of our clothing.
tching is a common condition that everyone experiences, and it is usually not a serious sign.