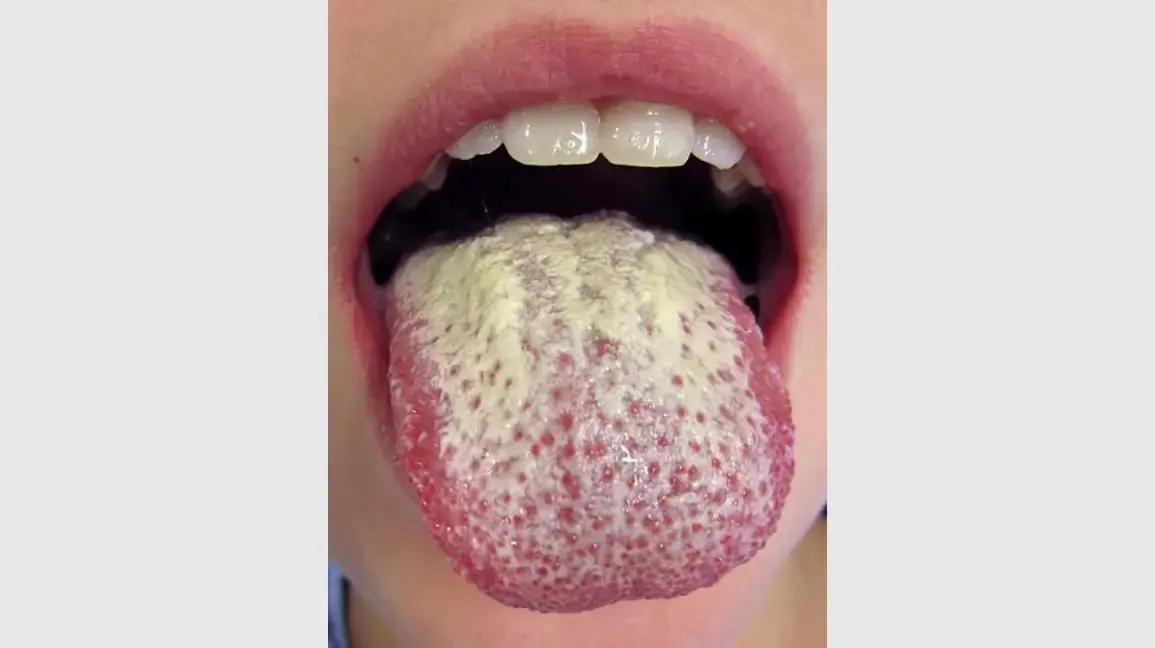
Why Is Your Tongue White? What It Says About Your Health
White Coating on Your Tongue? Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You
Stroke remains one of the leading causes of death and long-term disability worldwide. Despite advances in medical technology, many stroke cases still occur suddenly, leaving patients and families shocked and unprepared. However, doctors emphasize that strokes rarely happen without warning. In fact, studies and clinical observations suggest that nearly 90 percent of stroke patients displayed certain behaviors or symptoms in the days leading up to the event.
Medical experts now warn that recognizing these early signs could save lives. In the three days before a stroke, the body often sends subtle but critical signals—signals that many people overlook or dismiss as harmless.
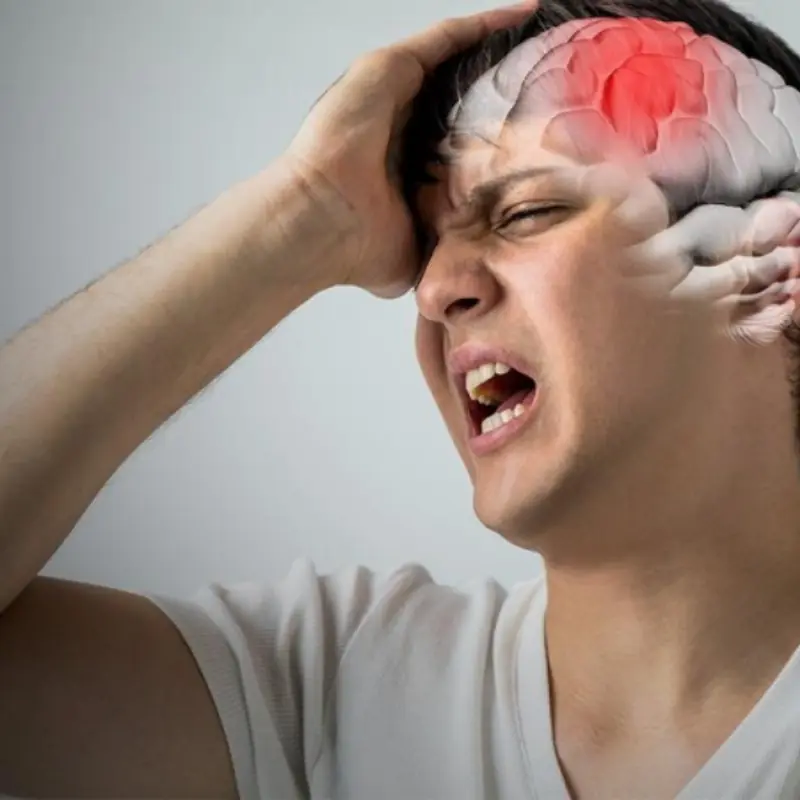

One of the most common warning signs reported by stroke patients is a sudden, unusual headache. Unlike regular tension headaches, these headaches often appear abruptly and may be accompanied by dizziness, nausea, or confusion. Some patients describe the pain as intense or unfamiliar, while others experience pressure or heaviness in the head.
Doctors explain that these symptoms can indicate changes in blood flow to the brain or the formation of blood clots. Unfortunately, many people choose to ignore the discomfort, attributing it to stress, lack of sleep, or dehydration. This delay in seeking medical attention can have devastating consequences.
The second behavior—one that many people may be doing right now—is chronic sleep deprivation combined with excessive physical or mental stress. In the days before a stroke, many patients reported staying up late, working long hours, or experiencing extreme fatigue.
Lack of sleep significantly affects blood pressure, heart rhythm, and brain function. When combined with stress, it increases the risk of blood vessel damage and clot formation. Doctors warn that consistently ignoring the body’s need for rest places enormous strain on the cardiovascular system, making a stroke more likely—especially in individuals with high blood pressure, diabetes, or a history of smoking.

Another overlooked warning sign is sudden emotional instability. Patients and their families often recall unusual irritability, anxiety, or mood swings in the days before a stroke. Some individuals became unusually quiet, withdrawn, or emotionally sensitive without a clear reason.
Neurologists explain that emotional changes can be linked to reduced blood flow in certain areas of the brain. When the brain is under stress or oxygen-deprived, emotional regulation can be affected. These signs are often subtle, making them easy to miss.
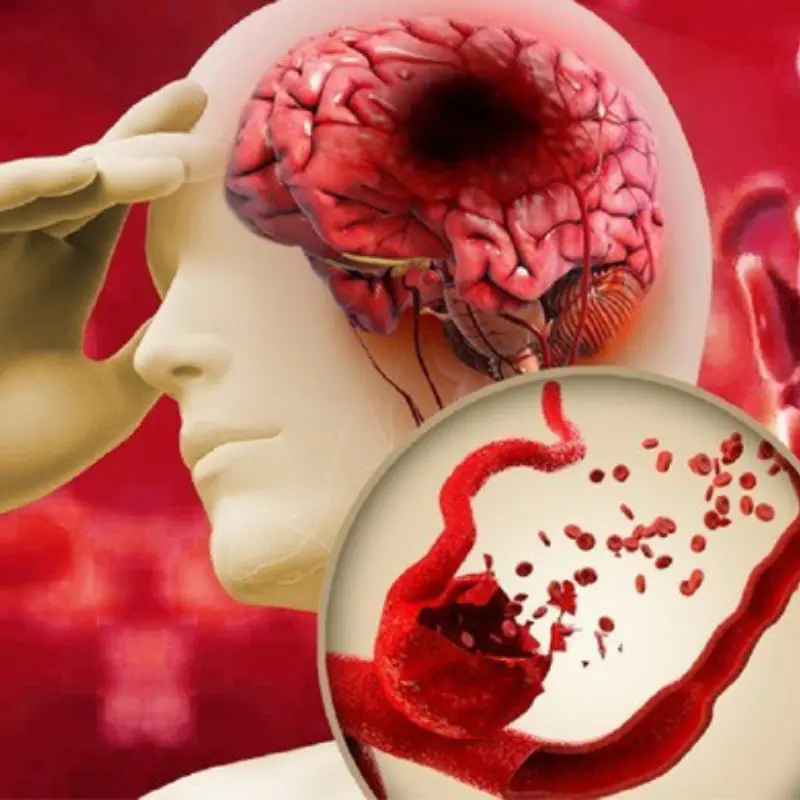
The image accompanying this report illustrates the severity of a stroke—showing bleeding or blockage in the brain and the intense pain experienced by patients. It serves as a powerful reminder that strokes are medical emergencies, not sudden accidents without cause.
Doctors emphasize that early intervention can dramatically reduce the severity of a stroke. Seeking medical attention at the first sign of unusual headaches, extreme fatigue, or neurological symptoms can make the difference between recovery and permanent damage.

While strokes are more common among older adults, doctors warn that younger people are increasingly affected. Poor lifestyle habits, chronic stress, lack of exercise, and unhealthy diets are contributing to this alarming trend. People with high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes, obesity, or a family history of stroke should be especially cautious.
Medical professionals urge the public to take warning signs seriously and adopt healthier daily habits. Prioritizing sleep, managing stress, maintaining a balanced diet, and undergoing regular health checkups can significantly reduce stroke risk.
Ultimately, a stroke does not happen overnight. The body often provides warning signals—signals that should never be ignored. Understanding and responding to these signs may help prevent one of the most dangerous medical emergencies of our time.

White Coating on Your Tongue? Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You

3 overlooked spousal habits that may put wives at greater risk for cer.vical can.cer - awareness matters

The 3-Hour Rule Before Bed: A Simple Habit for Better Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar

These 5 strange signs could be warning signals of dia.betes - don’t ignore them

Why People in Japan Sleep on the Floor and 5 Reasons to Give It a Try
7 Important Signs Your Body Is Crying Out for Help

Taro: The Underrated Superfood That Could Transform Your Energy, Digestion, and Overall Wellness
At just 20 years old, Linh Nguyen (name changed), a young and passionate teacher at a local elementary school, passed away from liver cancer — a disease typically associated with older individuals or those with long-term health issues.

Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but the good news is that certain foods contain powerful compounds that may help prevent and even fight cancer.

Magnesium is an essential mineral in the human body, playing a critical role in over 300 enzymatic processes.

Three Morning Habits Young People Often Ignore That Can Seriously Dam:age Their Kidneys — Quit These Now

If Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, It May Be Time to Prepare
7 Signs Your Kidneys Are Working Well — Check Yourself

Have you ever been drifting off to sleep when suddenly your body jolts as if you’re falling?
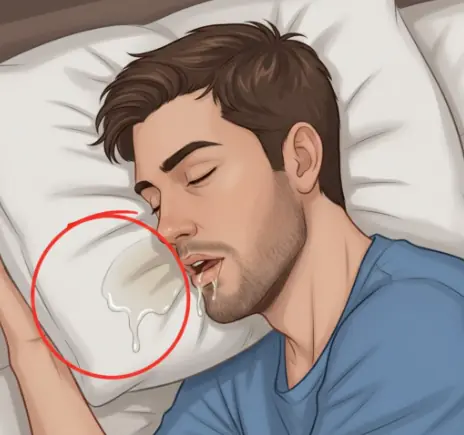
The problem of drooling while sleeping should not be ignored, as it may be a sign of some diseases.
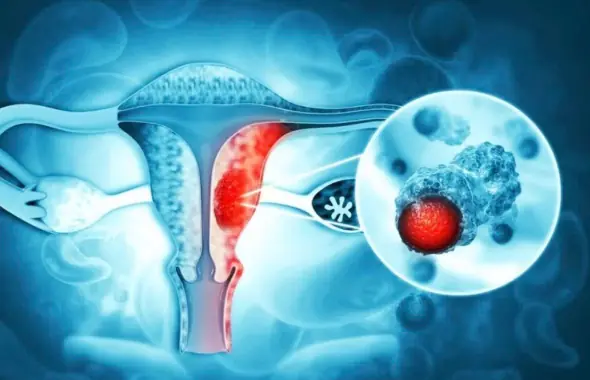
3 Intimate Habits of Husbands That May Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer — What Every Couple Should Know
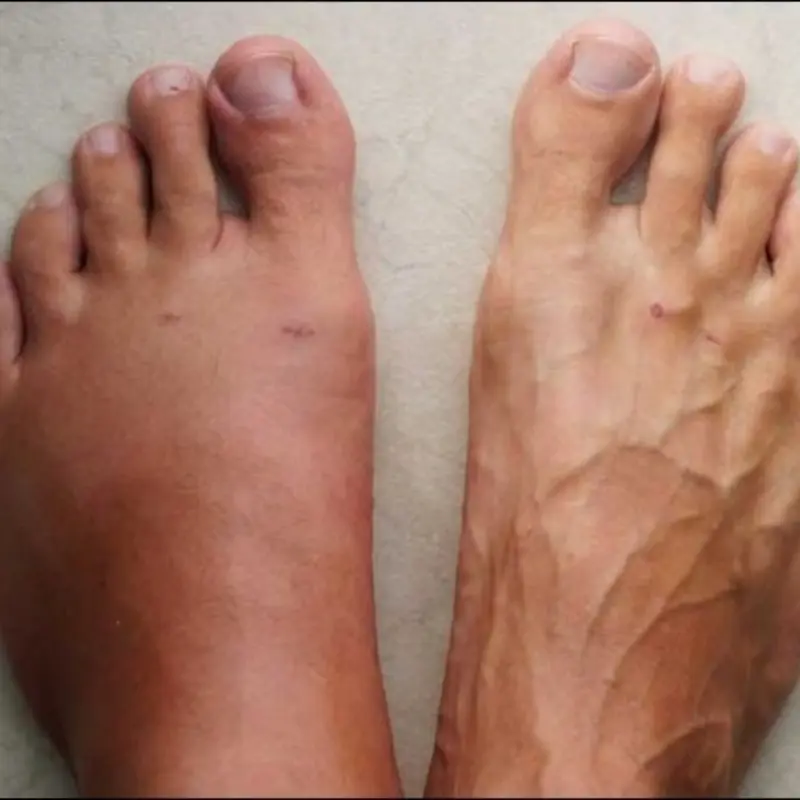
Swollen hands and feet? Know the warning signs

Understanding feminine odor: causes every woman should know

Bananas may seem small, but the impact on your heart is BIG!

Is tilapia really good for you? Some facts might make you think twice

White Coating on Your Tongue? Here’s What Your Body Might Be Telling You

3 overlooked spousal habits that may put wives at greater risk for cer.vical can.cer - awareness matters

The 3-Hour Rule Before Bed: A Simple Habit for Better Blood Pressure and Blood Sugar

These 5 strange signs could be warning signals of dia.betes - don’t ignore them

Why People in Japan Sleep on the Floor and 5 Reasons to Give It a Try

7 Important Signs Your Body Is Crying Out for Help

Taro: The Underrated Superfood That Could Transform Your Energy, Digestion, and Overall Wellness

At just 20 years old, Linh Nguyen (name changed), a young and passionate teacher at a local elementary school, passed away from liver cancer — a disease typically associated with older individuals or those with long-term health issues.

Cancer is one of the leading causes of death worldwide, but the good news is that certain foods contain powerful compounds that may help prevent and even fight cancer.

Magnesium is an essential mineral in the human body, playing a critical role in over 300 enzymatic processes.

Three Morning Habits Young People Often Ignore That Can Seriously Dam:age Their Kidneys — Quit These Now

If Your Parent Shows These 4 Signs, It May Be Time to Prepare

7 Signs Your Kidneys Are Working Well — Check Yourself

Have you ever been drifting off to sleep when suddenly your body jolts as if you’re falling?

The problem of drooling while sleeping should not be ignored, as it may be a sign of some diseases.

3 Intimate Habits of Husbands That May Increase Their Wives’ Risk of Cervical Cancer — What Every Couple Should Know

Swollen hands and feet? Know the warning signs

Boiling garlic at home may freshen air naturally

Understanding feminine odor: causes every woman should know