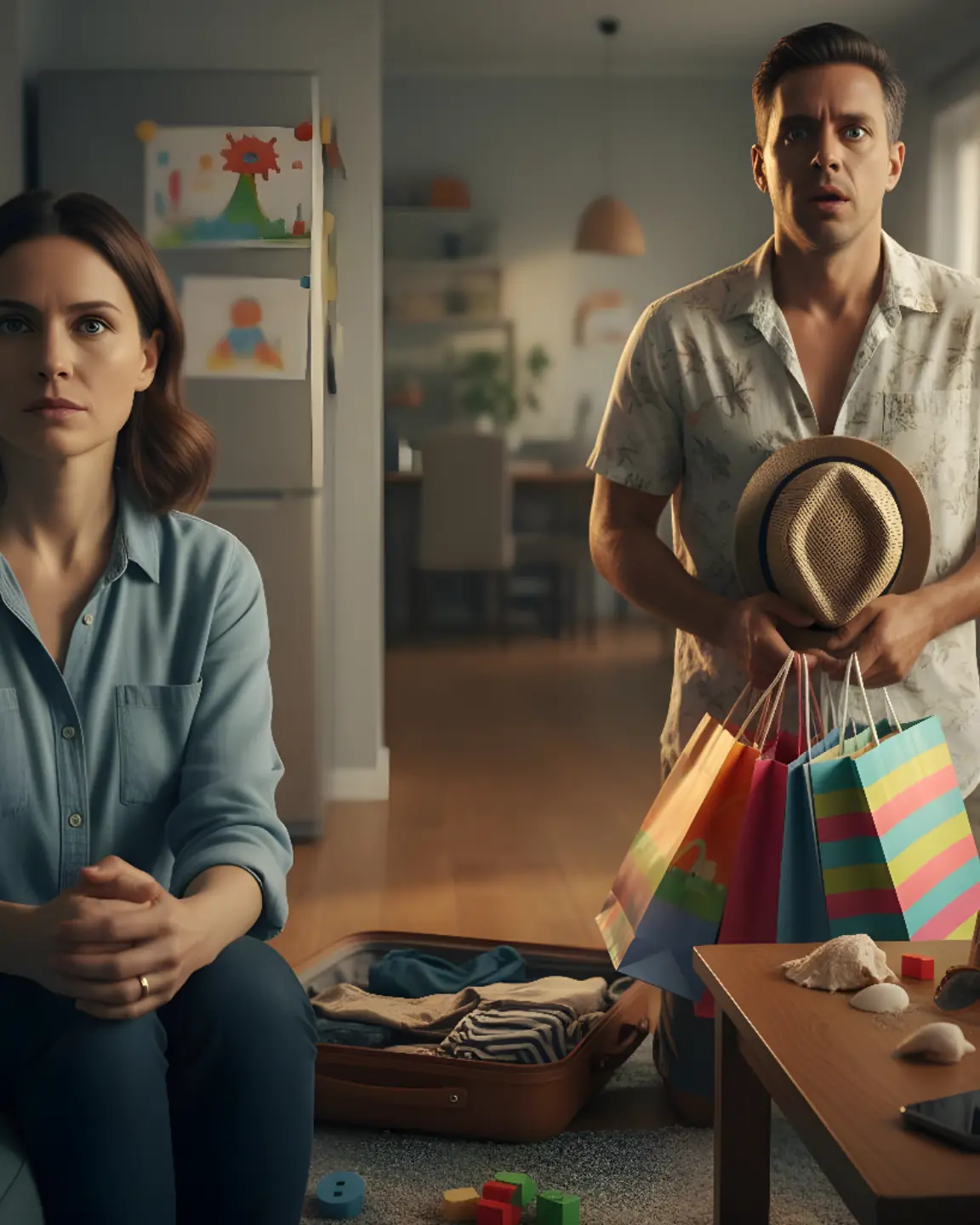
My Husband Took a Secret 15-Day Trip With His “Best Friend”—When He Came Back, I Asked One Question That Stopped Him Cold
My Husband Took a Secret 15-Day Trip With His “Best Friend”—When He Came Back, I Asked One Question That Stopped Him Cold
Every day, you make thousands of decisions — what to wear, when to respond to messages, how to structure your work, what to eat.
If your brain had to consciously evaluate every one of these choices from scratch, you’d be mentally exhausted before noon.
This is why the brain relies heavily on habits.
Habits are automated behavioral patterns stored primarily in the basal ganglia — brain structures that help convert repeated actions into efficient routines.
Once a behavior becomes habitual, it requires far less cognitive effort.
In essence, habits act as energy-saving shortcuts.
The brain is an energy-intensive organ, consuming roughly 20% of the body’s fuel. Efficiency is therefore a priority. Automating predictable behaviors frees mental resources for more complex tasks like problem-solving and creativity.
Imagine driving a familiar route. Early on, it required full attention. But after repetition, you can navigate it with minimal conscious thought.

That’s your brain conserving energy.
This efficiency also explains why routines often feel comfortable. Predictability reduces cognitive load, allowing the nervous system to operate with less friction.
But habits are neutral tools — they reinforce whatever is repeated, whether beneficial or not.
Formation follows a simple loop:
Cue → Behavior → Reward
Over time, the brain begins anticipating the reward as soon as it detects the cue, making the behavior feel almost automatic.
Importantly, building habits is less about motivation and more about repetition.

Small, consistent actions tend to outlast bursts of enthusiasm.
For example:
Individually, these seem minor. Collectively, they reduce daily decision fatigue.
There is also psychological relief in structure. When certain parts of your day run on autopilot, the mind experiences fewer micro-stresses.
However, flexibility remains important. The brain benefits from novelty too — new experiences stimulate neural connections and support adaptability.
The goal isn’t rigid routine, but supportive rhythm.
Think of habits as the brain’s way of budgeting energy.

By automating the predictable, it preserves capacity for what truly requires thought.
So if you’ve ever wondered why routines feel grounding…
It’s because your brain is quietly thanking you for making its job easier.
After all, the less energy spent on repetition, the more remains for awareness, creativity, and growth.

My Husband Took a Secret 15-Day Trip With His “Best Friend”—When He Came Back, I Asked One Question That Stopped Him Cold









A simple banana a day could support energy and heart health.



This common backyard plant may hold surprising health benefits.
Small white bumps on lips or private areas? Know the real causes.

Foot symptoms may signal deeper health issues you shouldn’t ignore

How Does Eating Bananas Every Day Affect Your Blo.od Pressure?

Marrying Kavita: The Choice Everyone Fought—And the Truth I Didn’t Expect

A Father’s Instinctive Dash to Protect His Daughter

My Husband Took a Secret 15-Day Trip With His “Best Friend”—When He Came Back, I Asked One Question That Stopped Him Cold












A simple banana a day could support energy and heart health.



