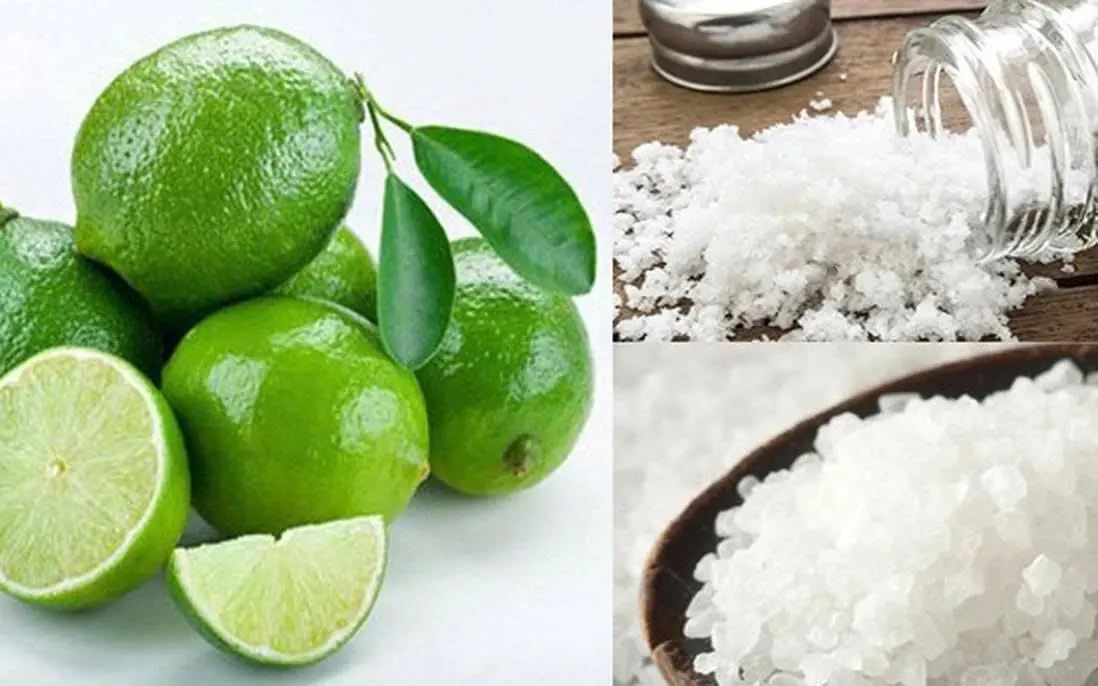

Why Many People Put Lemon with Salt in Their Room – A Little-Known Trick
The Surprising Benefits of Placing Lemon with Salt in Your Room
One common piece of advice from nutrition experts is to avoid storing tomatoes in the refrigerator.

Tomatoes are a staple in daily meals, rich in nutrients, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants. However, improper storage can reduce their quality.
One primary reason not to refrigerate tomatoes is that low temperatures can negatively affect their flavor and texture. According to a study published in the Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, storing tomatoes in the refrigerator can cause them to lose freshness and flavor due to the slowed oxidation process at low temperatures. Cold temperatures reduce the activity of enzymes responsible for developing the natural taste of tomatoes, making them bland and less sweet.
Additionally, refrigeration can alter the texture of tomatoes. The cold damages their cell structure, making them soft, mushy, and more prone to rotting. Refrigerated tomatoes often develop thicker skins and wrinkled surfaces, leading to spoilage once removed from the fridge.
Cold temperatures can also reduce the lycopene content in tomatoes. Lycopene is a powerful antioxidant that protects cells and lowers the risk of chronic diseases. However, storing tomatoes in the fridge can degrade this compound, diminishing their nutritional benefits.
Instead of refrigerating, tomatoes should be stored at room temperature in a dry, well-ventilated place, away from direct sunlight. This helps maintain their natural flavor and preserve their nutritional value for a longer time.
Although refrigeration may extend the shelf life of tomatoes, it negatively impacts their taste and nutrient content. To enjoy the best flavor and health benefits, it is best to store tomatoes at room temperature and avoid exposing them to cold temperatures.

The Surprising Benefits of Placing Lemon with Salt in Your Room

5 Plants That Might Bring Snakes Into Your Garden – Many People Still Grow Number 1
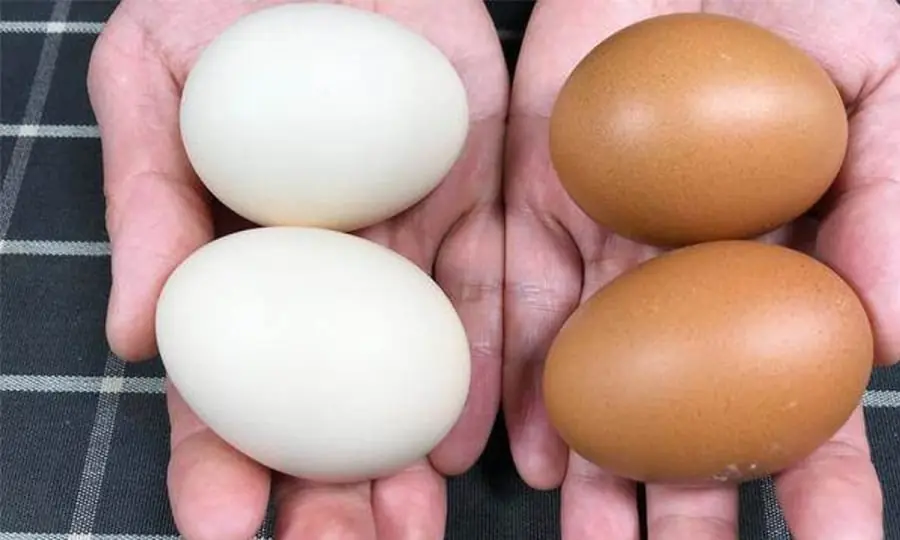

When Buying Eggs, Should You Pick Red or White Ones?
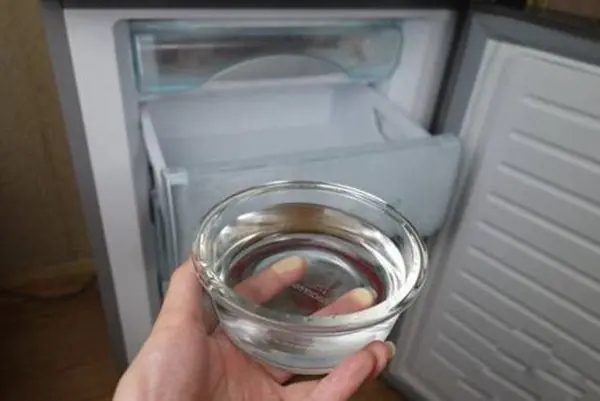

How a Bowl of Water Can Help Your Refrigerator Save Electricity
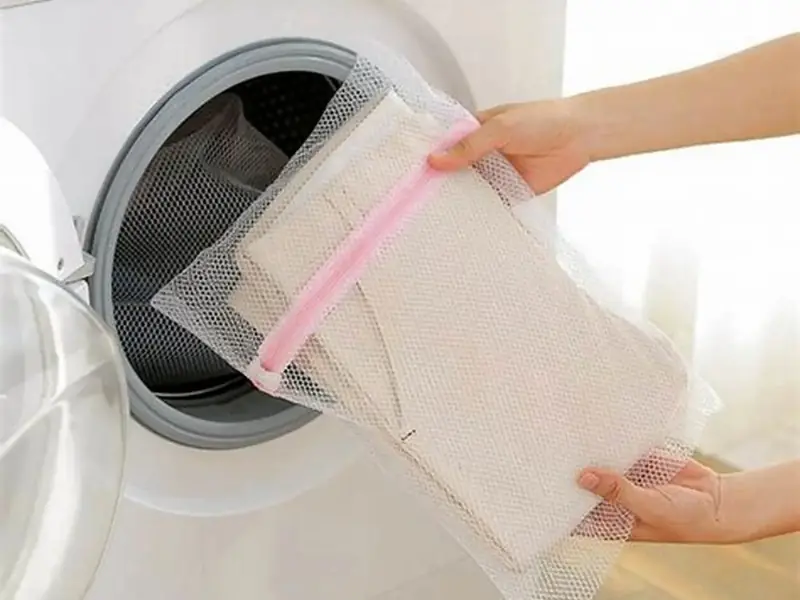

Do This Before Washing to Keep Clothes Smooth Without Ironing

What Happens When You Put Peppercorns Under Your Bed?
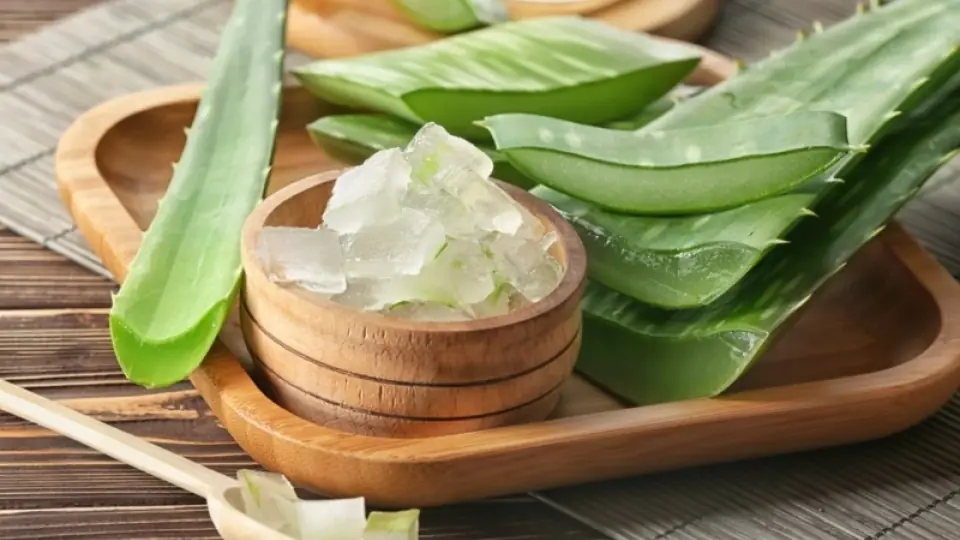

One Natural Ingredient That Can Transform Your Skin
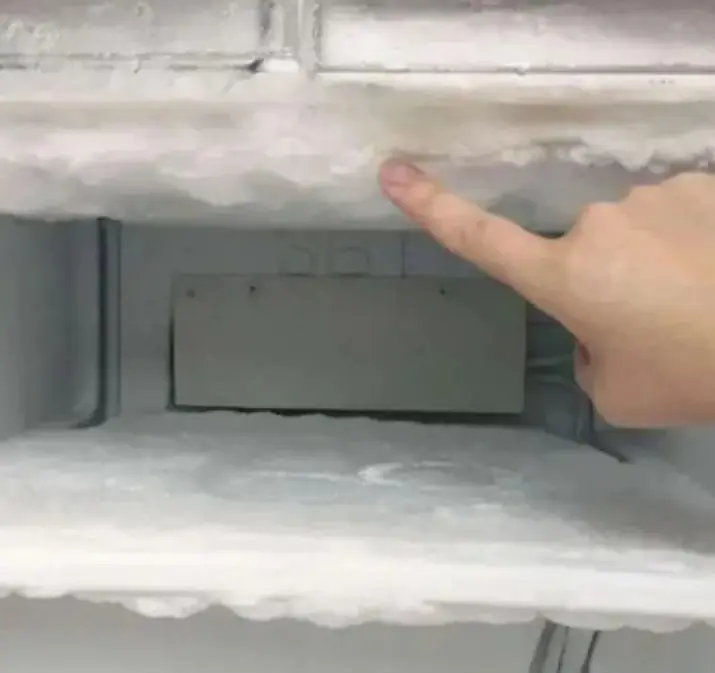

Thick ice in your fridge can be removed quickly with this trick.
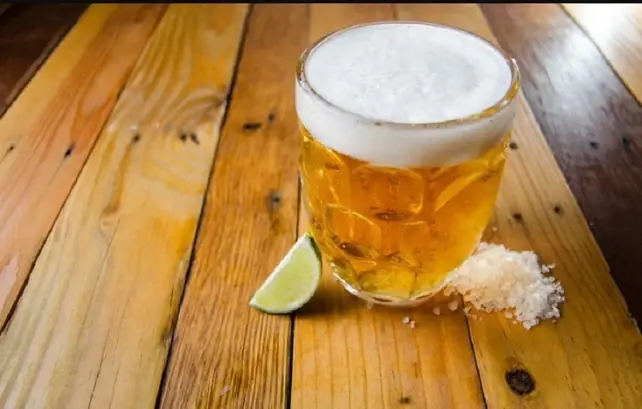

Beer and Salt: The Little-Known Home Trick That Can Be Surprisingly Useful

Why Some People Put Ginger Next to Their Pillow at Night?
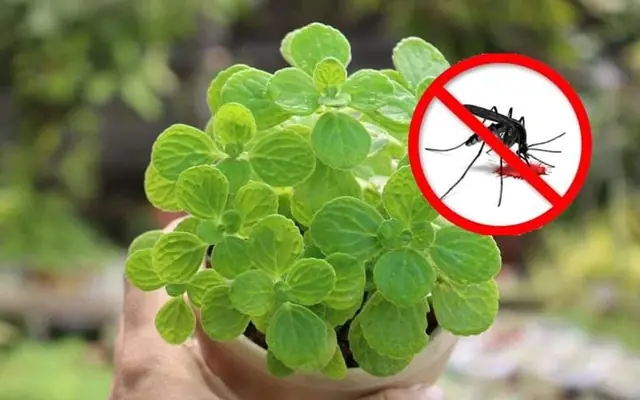

7 Beautiful Plants That Not Only Smell Good but Also Repel Mosquitoes
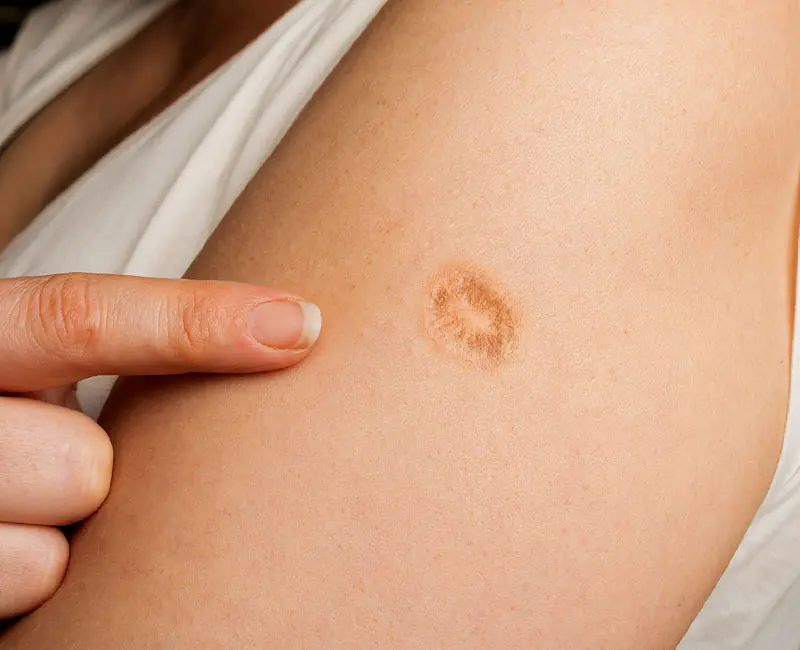
We got it when we were children; nobody asked, nobody explained. Today, few know the truth behind this mark that so many of us have
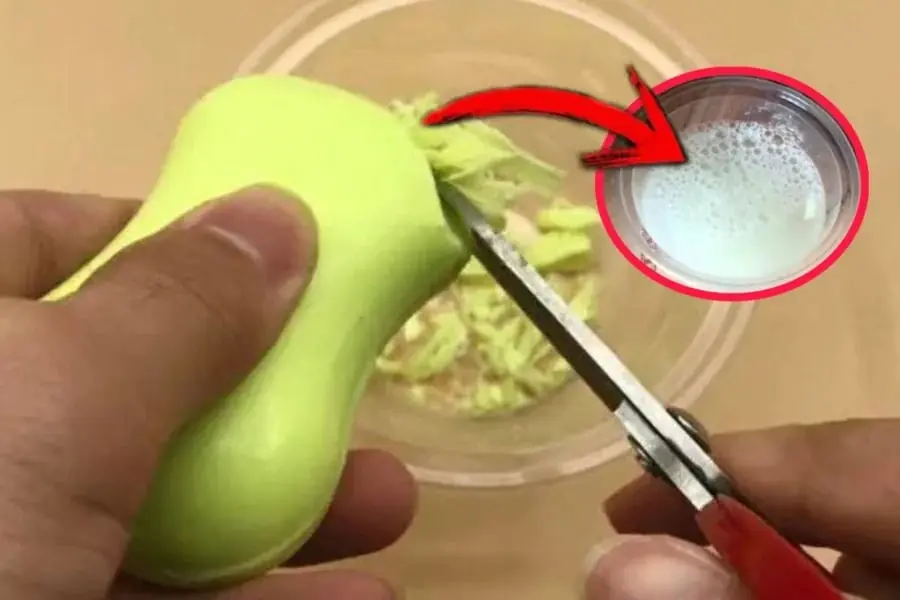

This Simple Kitchen Trick May Help Get Rid of Cockroaches and Rats
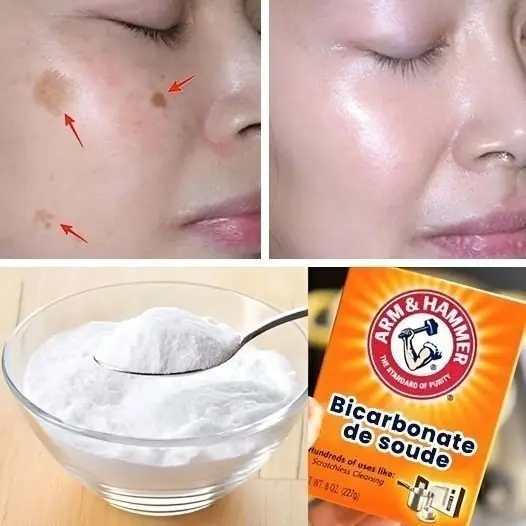

Dark Spots on Your Face? Try These Simple Baking Soda Tricks

The Best Methods to Get Rid of the Wax Coating on Apples
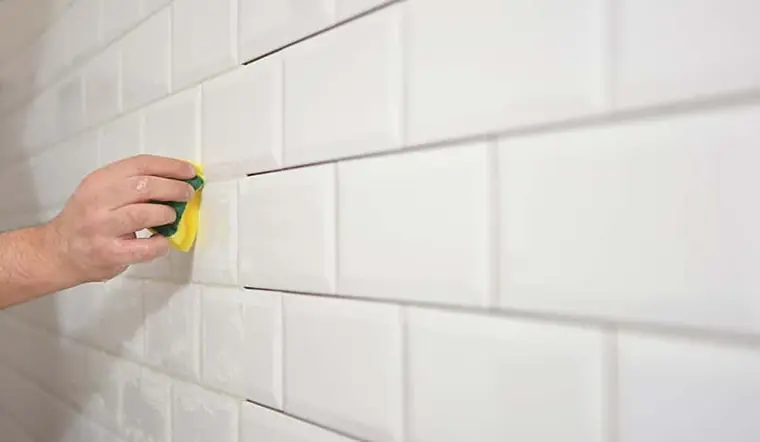

Make Your Tiles Look Brand New with These Free Home Cleaning Tips
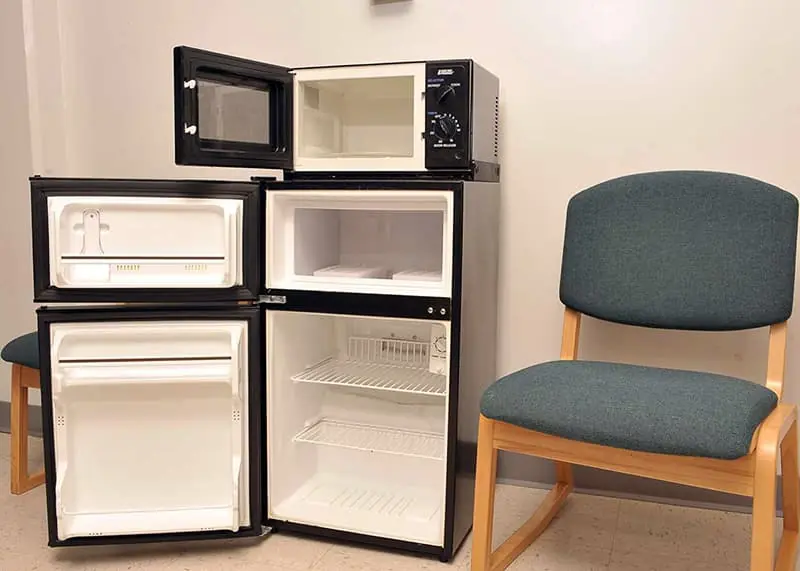

One Common Kitchen Habit Could Be Secretly Raising Your Power Bill
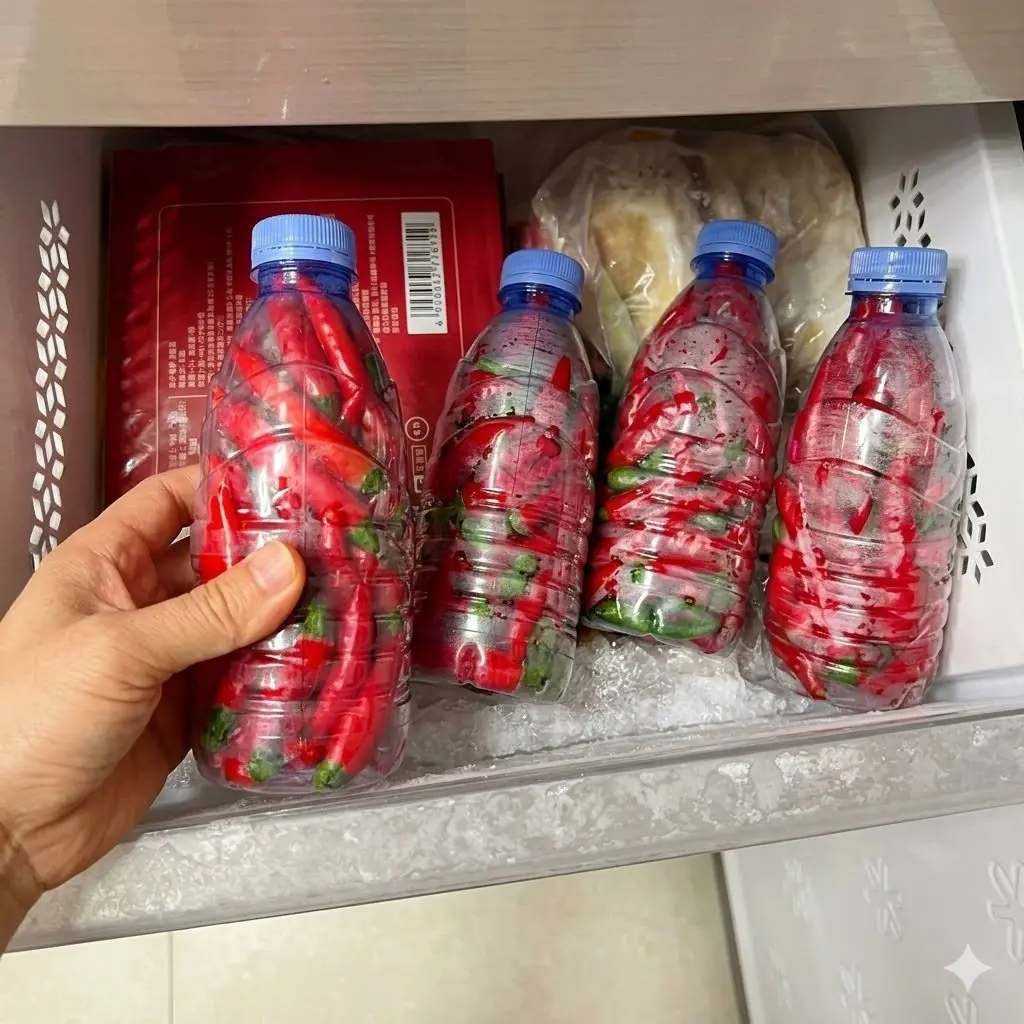

A simple storage trick can keep fresh chilies usable for months.
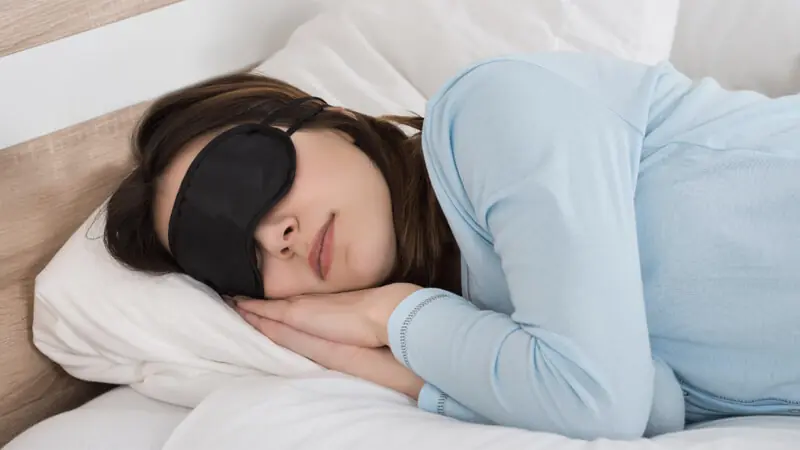

The 2-Minute Military Sleep Method Many People Use to Fall Asleep Faster

Unhealthy Eating Habits That Could Be Harming Your Liver Without You Realizing
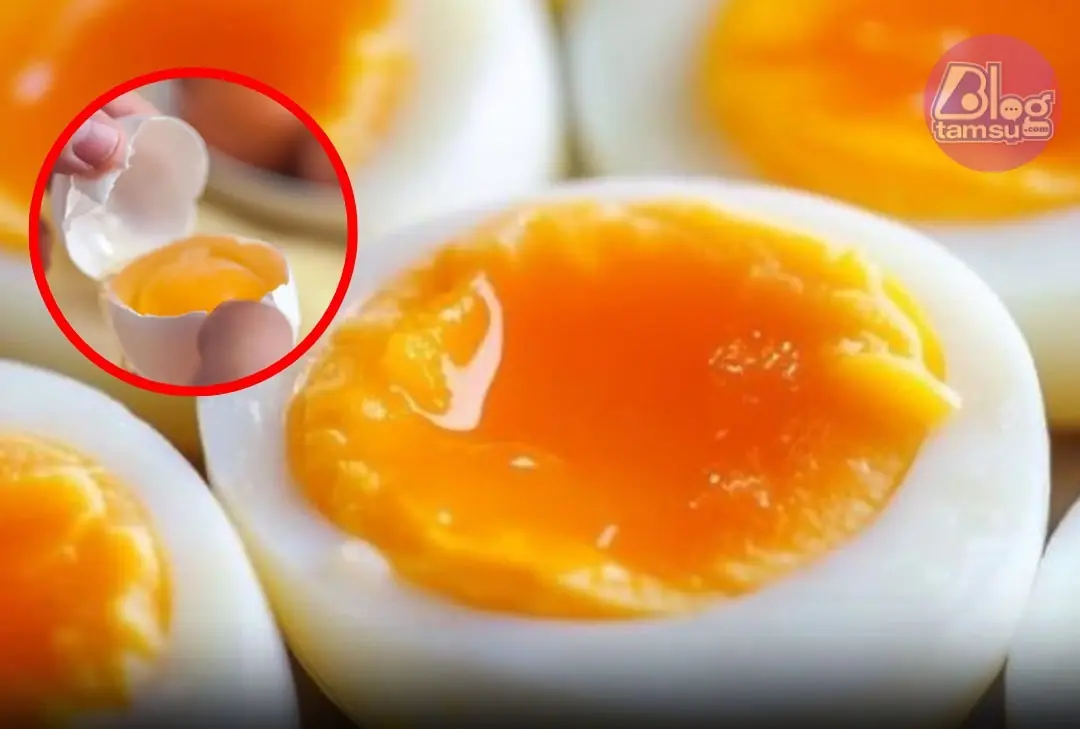

Medical Warning: How Many People Eat Boiled Eggs May Increase Artery Blockage Risk
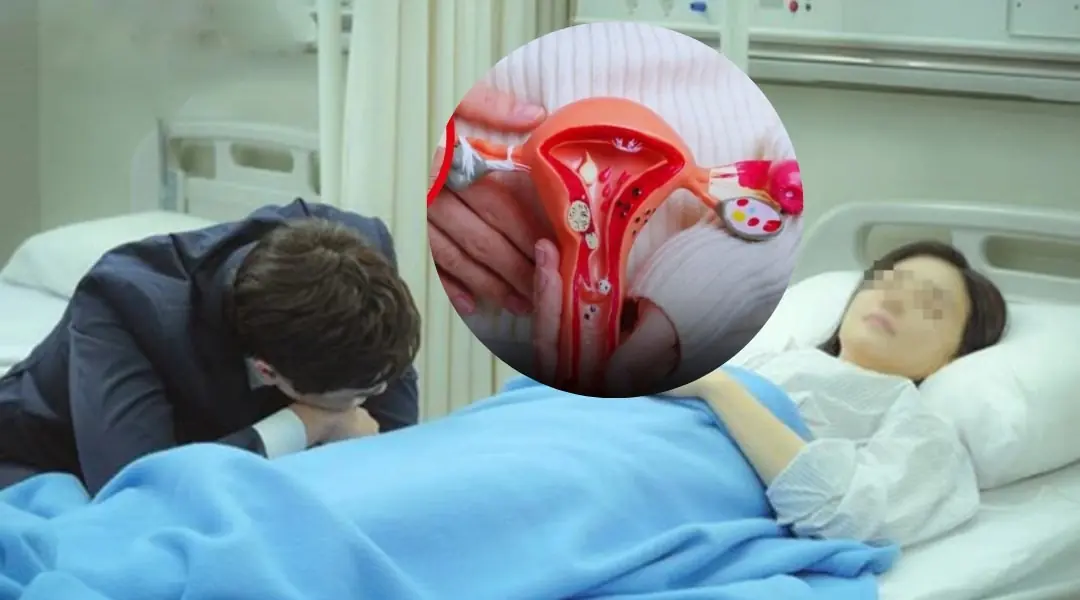
Some selfish and unhealthy habits from a husband can directly increase the risk of cer.vical can.cer in their wife.
They can creep up on you!
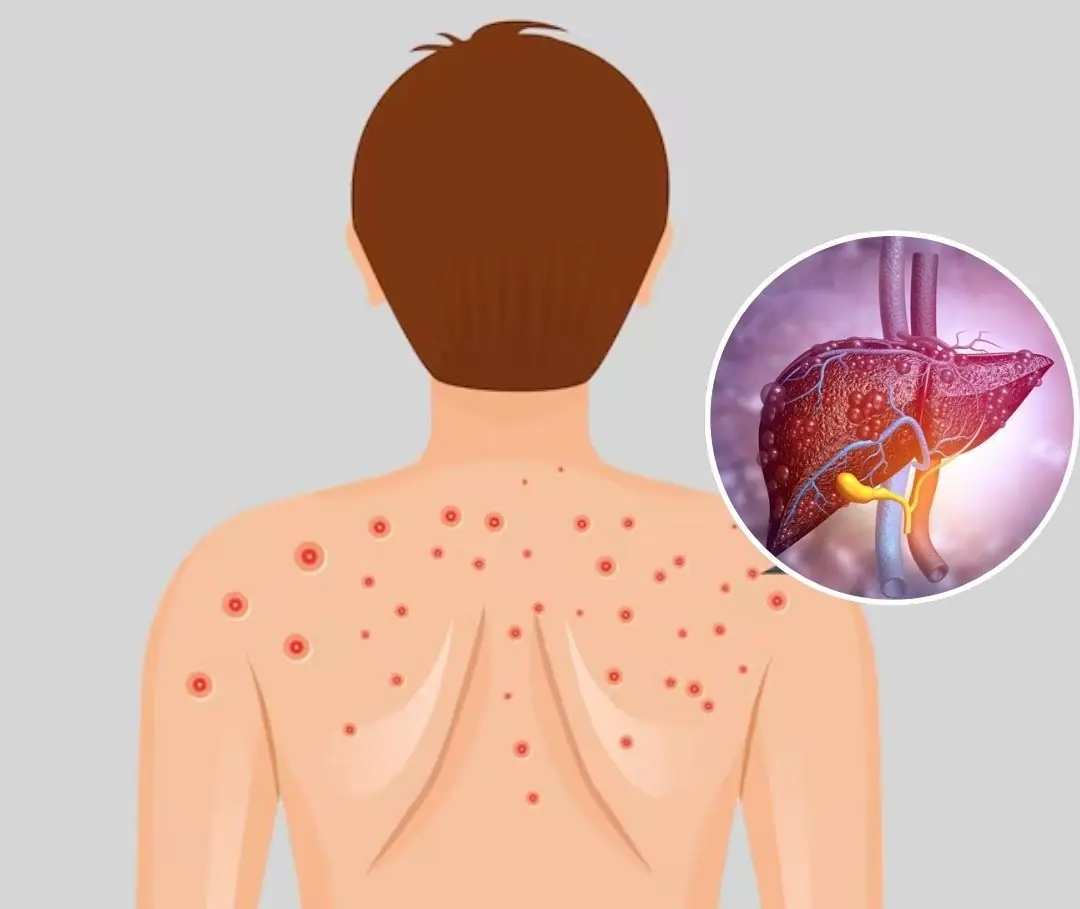
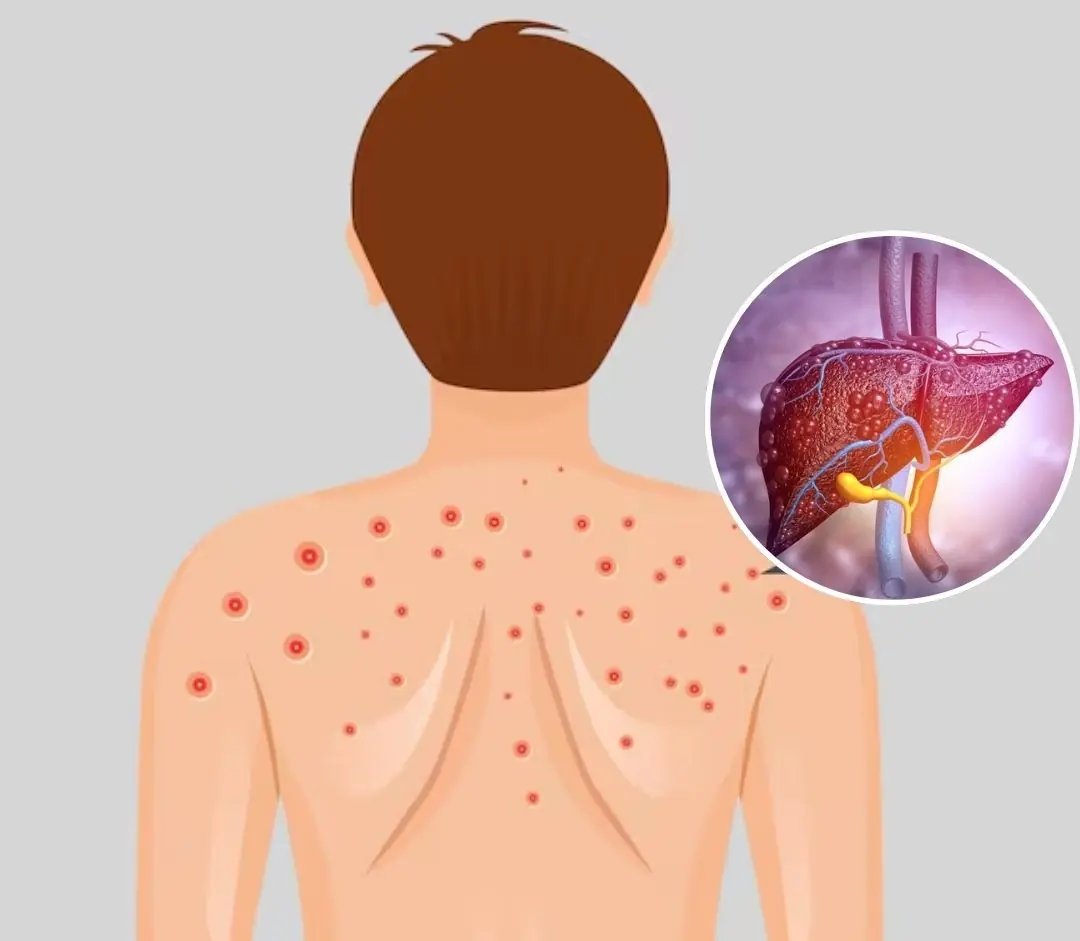
A Common Sign That May Be Linked to Fatty Liver Disease
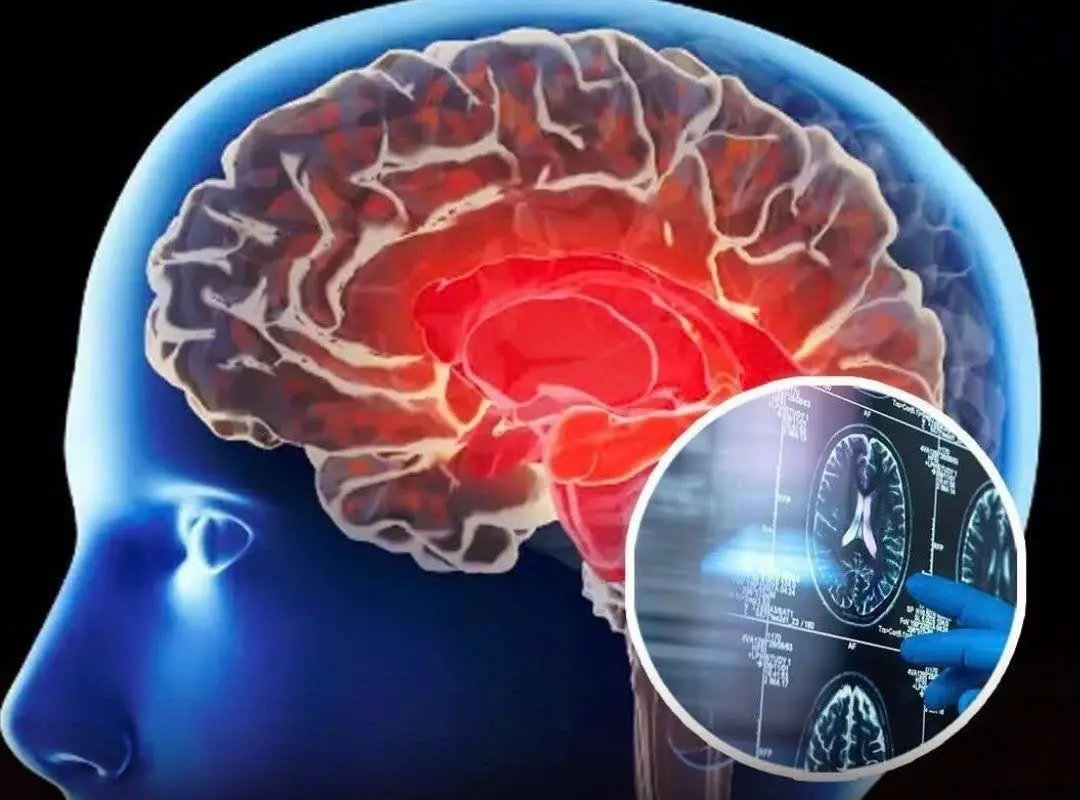
4 Red Flags Your Brain May Be in Trouble — Scientists Say Alzheimer’s Can Begin Decades Earlier
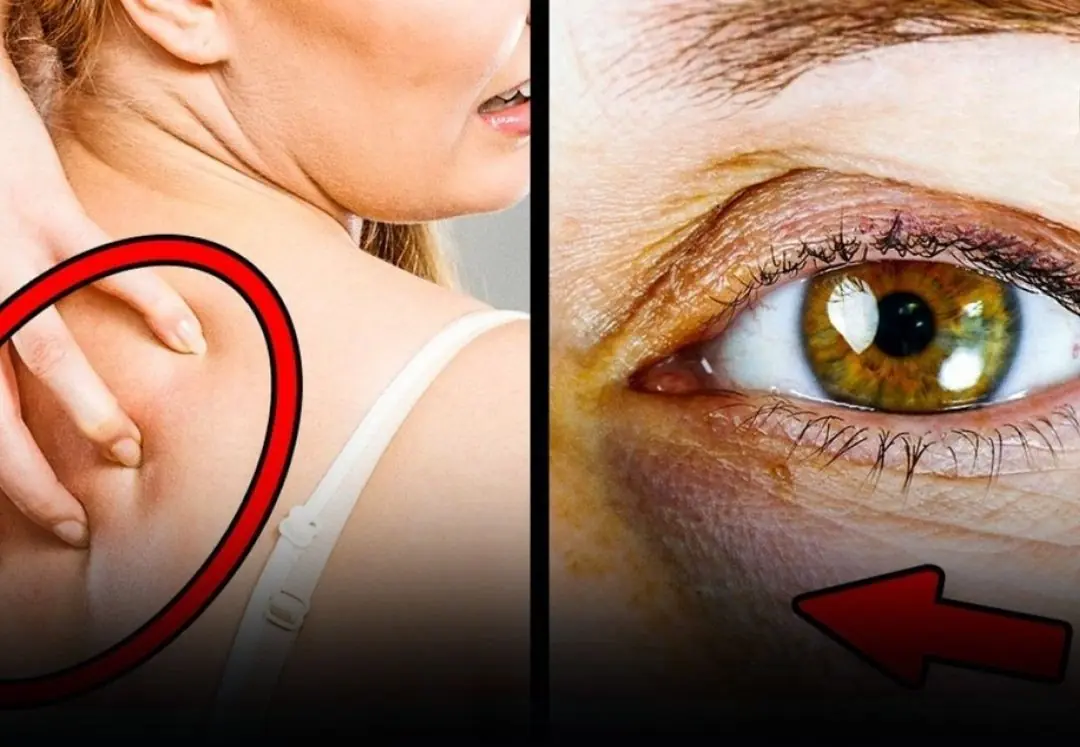
5 Signs Your Body May Be Warning You That You’re Consuming Too Much Sugar
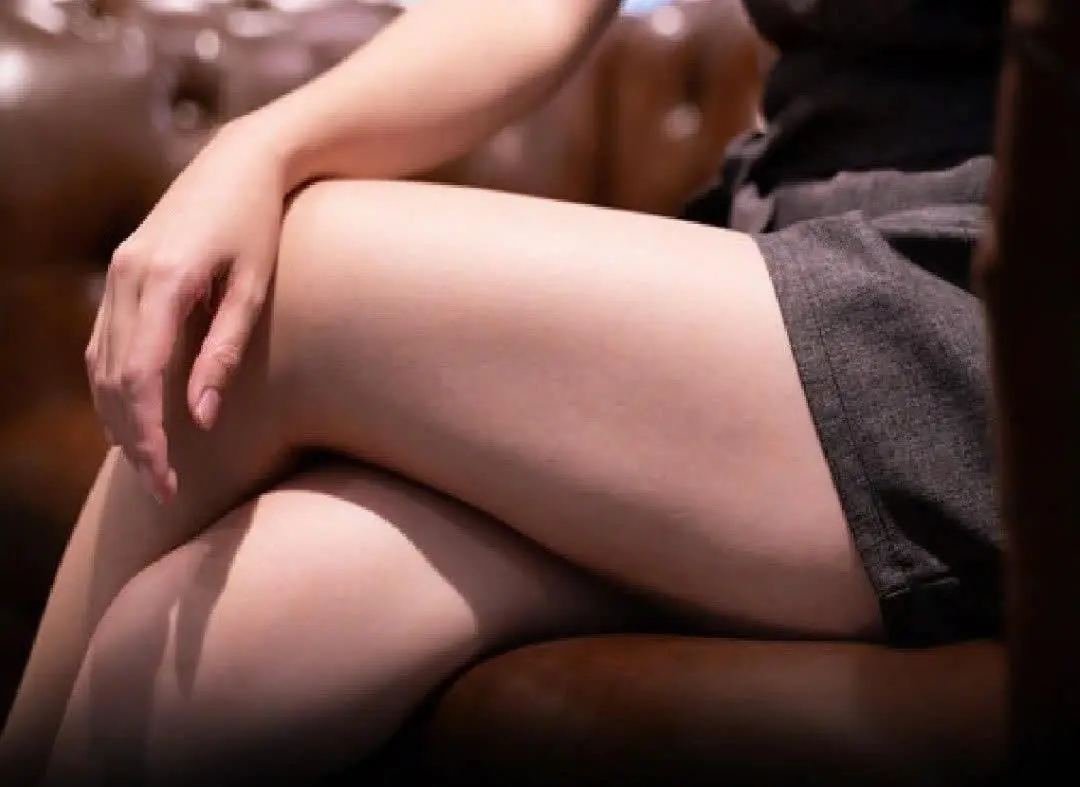

The Hidden Psychology Behind Women Crossing Their Legs
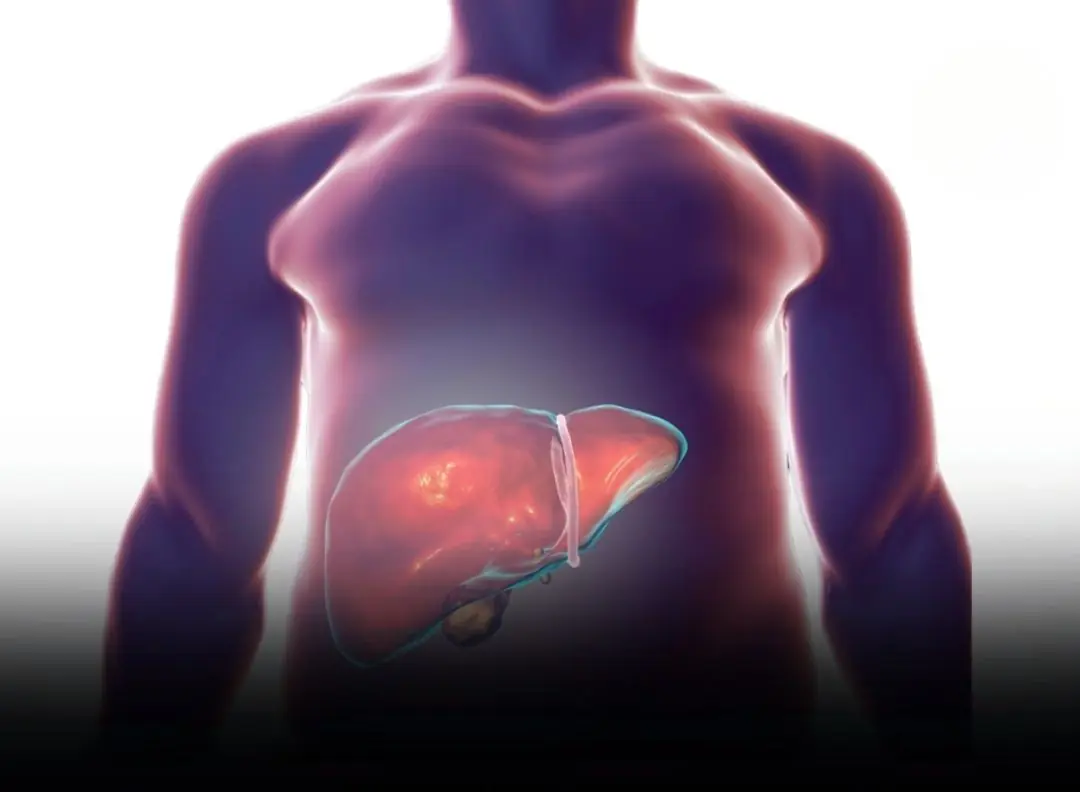
How to Know Whether a Protruding Belly Is Fat or a Sign of Liver Problems
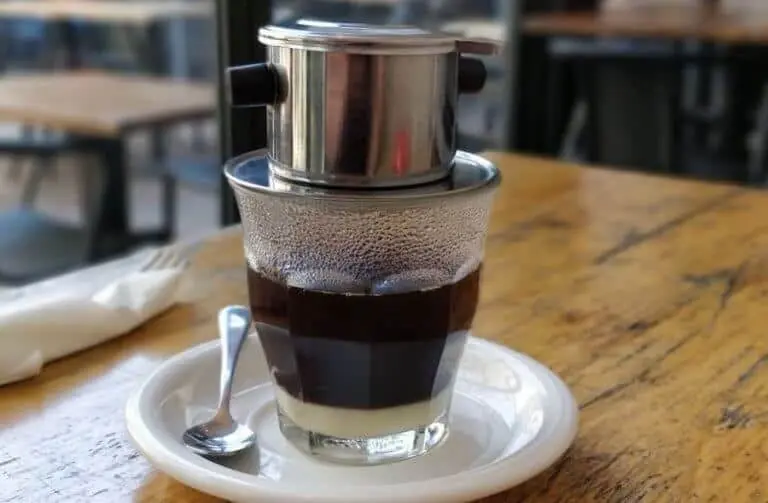

Drink Coffee Daily? Here’s What Doctors Say Happens to Your Body
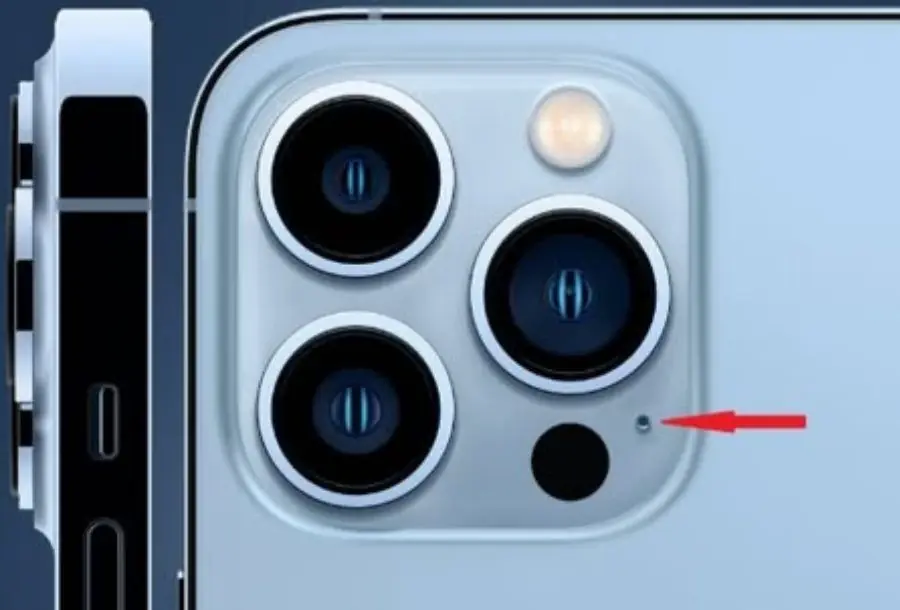

More Than 90% of iPhone Users:
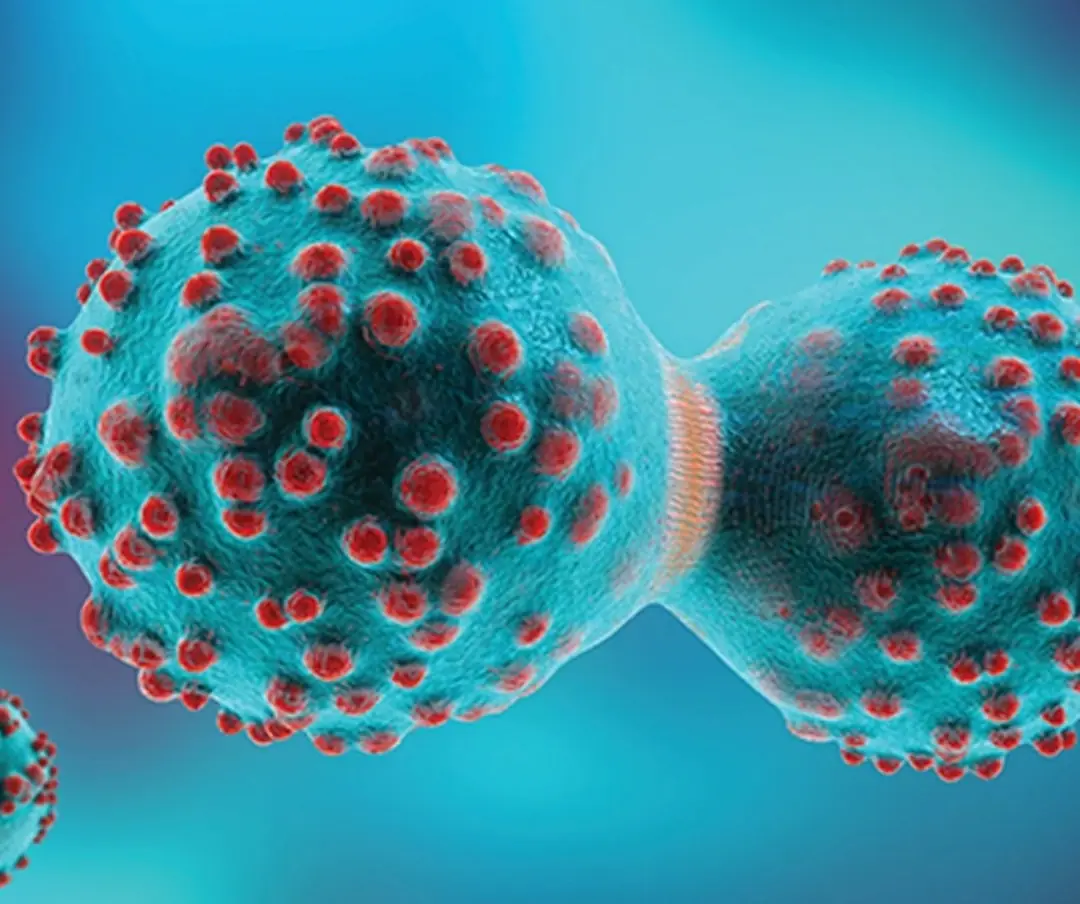
Rapamycin Reduces Lung Tumor Count by Up to 90% in Tobacco-Exposed Models....
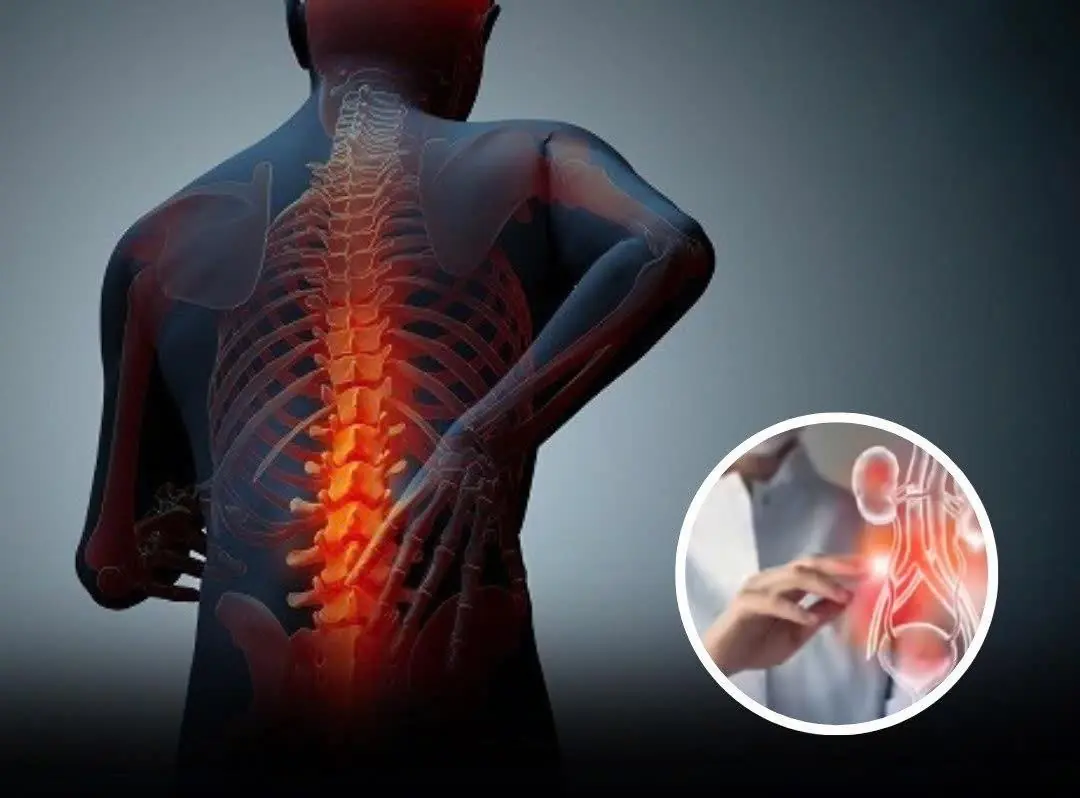
Your Body May Be Signaling Kidney Weakness—Here’s What to Look For
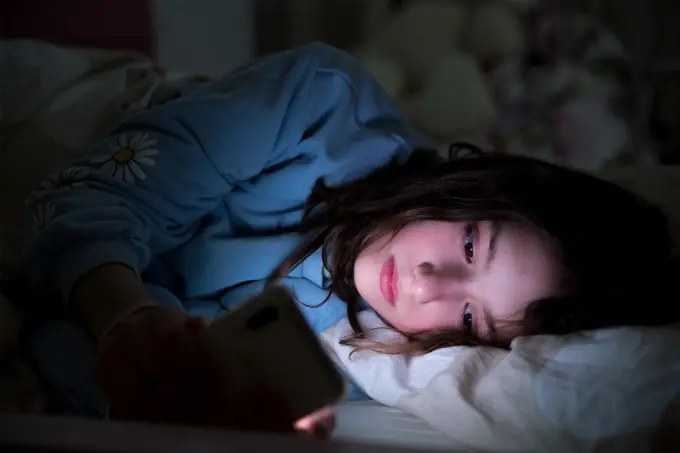

How Does Staying Up Late Often Affect Your Body?
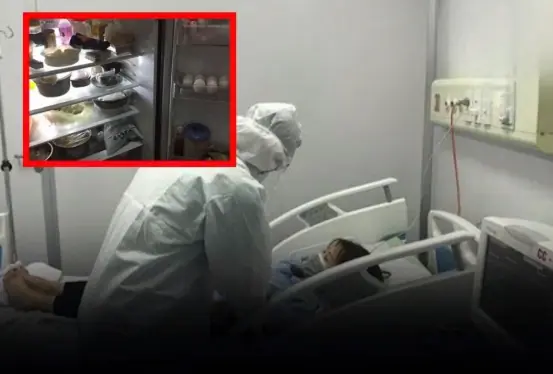
A recent tragic case involving a 50-year-old man has once again raised public awareness about the hidden dangers of consuming refrigerated leftovers.
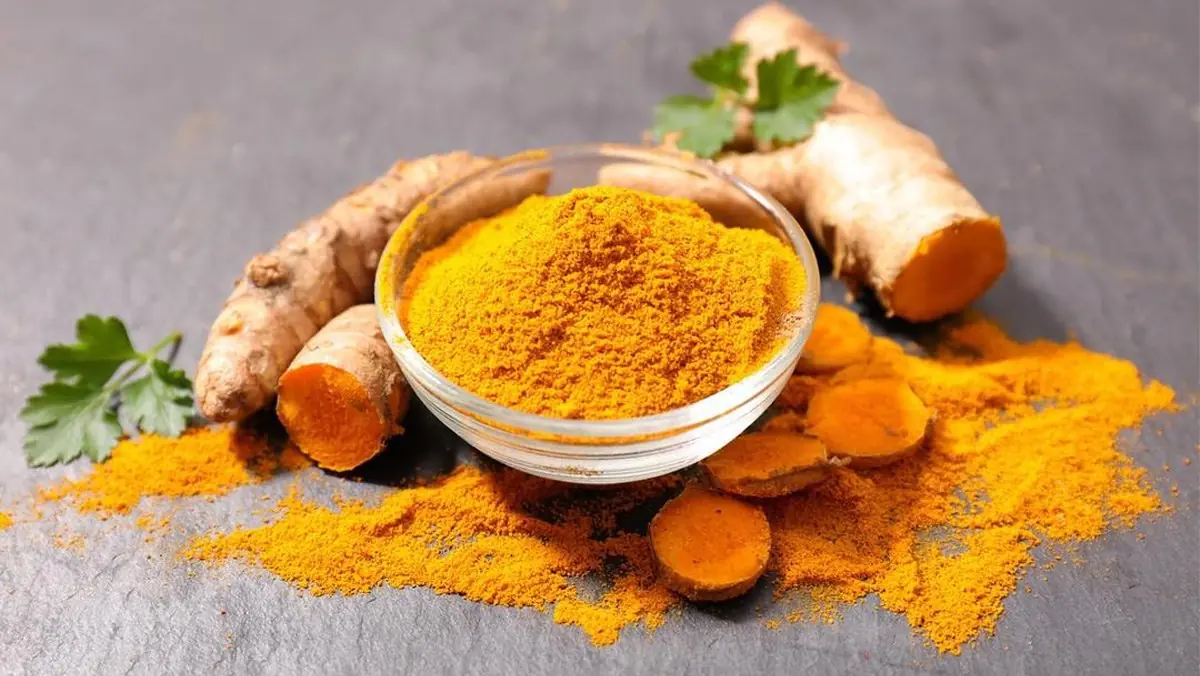

Turmeric: A Natural Spice with Powerful Health Benefits

Words matter most in grief: four things never to say at a funeral
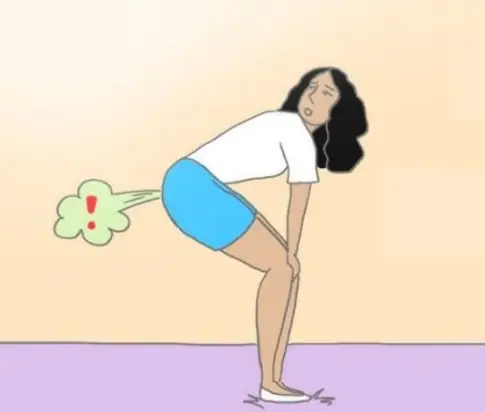
Passing gas is a normal part of digestion. In fact, healthy people release gas between 14 and 23 times a day on average, according to the American College of Gastroenterology.

Her secrets to a long and healthy life have garnered widespread interest, blending a disciplined lifestyle with a meticulous diet.

The Surprising Benefits of Placing Lemon with Salt in Your Room