Most stomach can.cers are found too late. Doctors warn of five post-meal symptoms that signal the need for early endoscopy
Doctors warn five post-meal symptoms may signal stomach cancer early.
Many people start their mornings with unhealthy habits that unknowingly increase their risk of stroke. A stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, leading to serious complications like paralysis, brain damage, or even death.
Morning is a high-risk time for strokes, as the body undergoes sudden changes in blood pressure, heart rate, and circulation after waking up. If you want to reduce your risk, you should avoid these 4 common morning habits that may be putting you closer to a stroke.
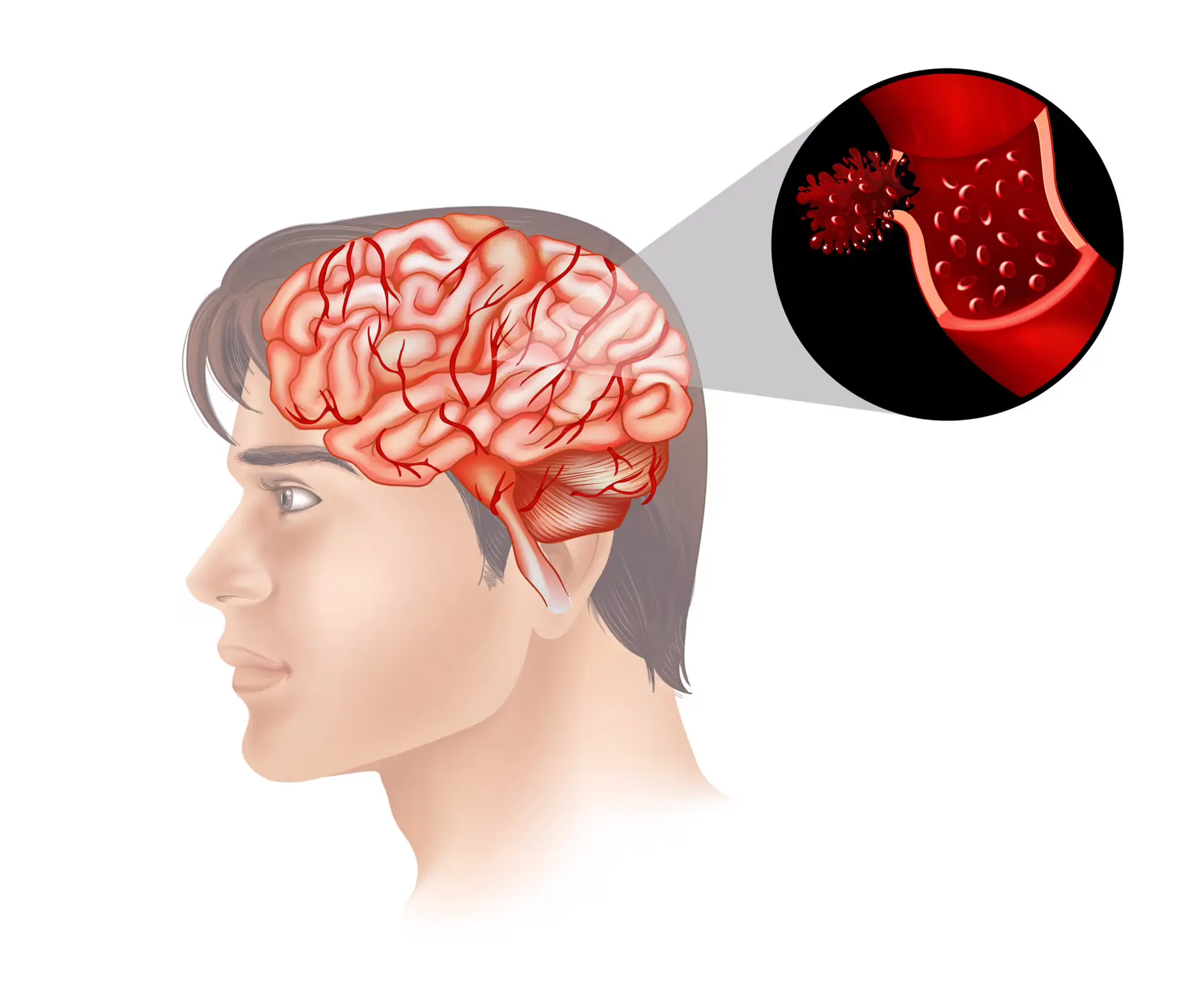
Many people jump out of bed immediately after waking up, but this can be dangerous for your heart and brain.
✔ Why It Increases Stroke Risk:
🚨 Signs You’re Moving Too Fast:
💡 What to Do Instead:
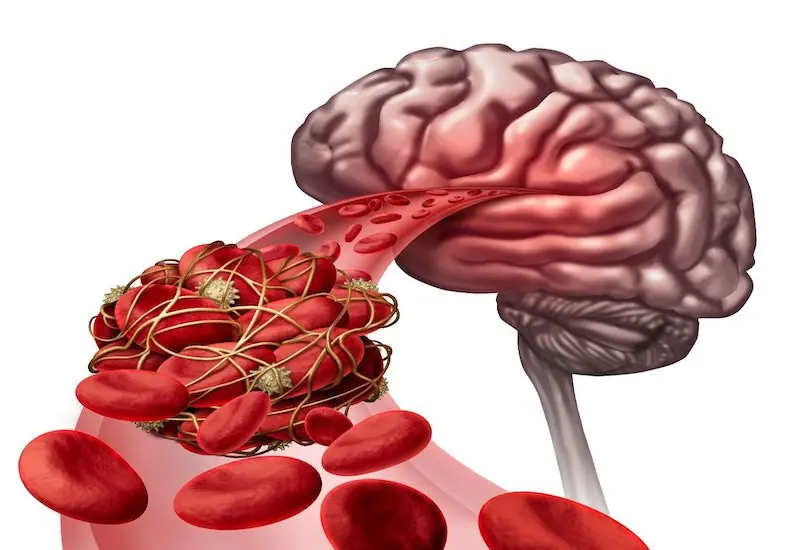
Breakfast is the first meal of the day, and what you eat can impact blood flow, blood pressure, and brain function.
✔ Why It Increases Stroke Risk:
🚨 Unhealthy Breakfast Foods to Avoid:
❌ Processed meats (bacon, sausage, ham) – High in salt and cholesterol.
❌ Sugary pastries and cereals – Cause blood sugar spikes and crashes.
❌ Too much coffee on an empty stomach – Raises blood pressure suddenly.
💡 What to Eat Instead:
Many people forget to drink water after waking up, but morning dehydration can increase the risk of stroke.
✔ Why It Increases Stroke Risk:
🚨 Signs of Morning Dehydration:
💡 What to Do Instead:
Some people ignore the urge to urinate in the morning, but this puts stress on the heart and blood vessels, increasing the risk of stroke.
✔ Why It Increases Stroke Risk:
🚨 Signs You’re Holding It Too Long:
Doctors warn five post-meal symptoms may signal stomach cancer early.
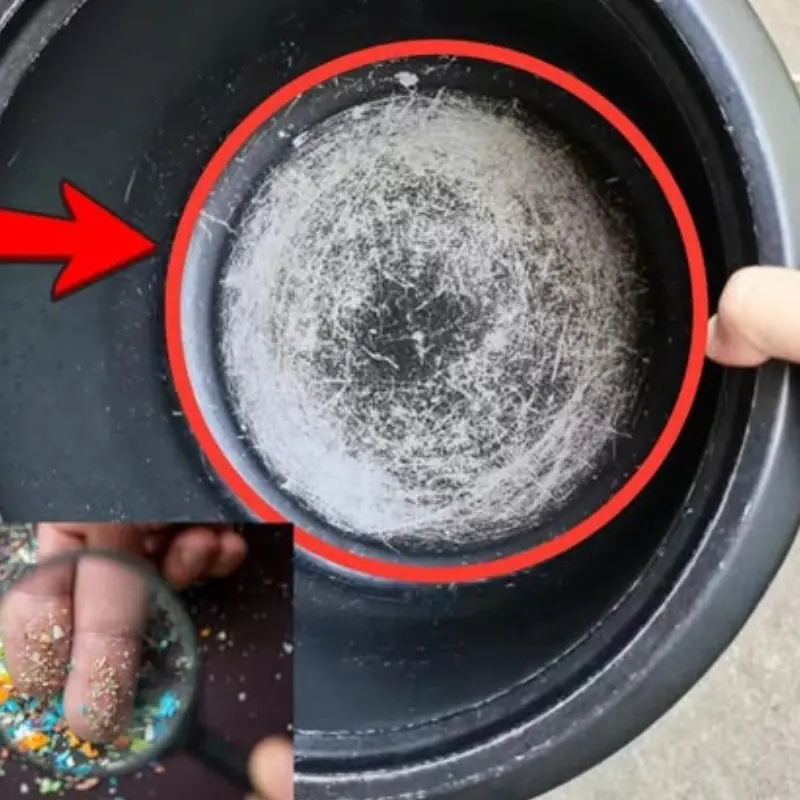

Scratched cookware could silently add thousands of microplastics to meals.

Drooling While You Sleep? Here Are 6 Possible Causes
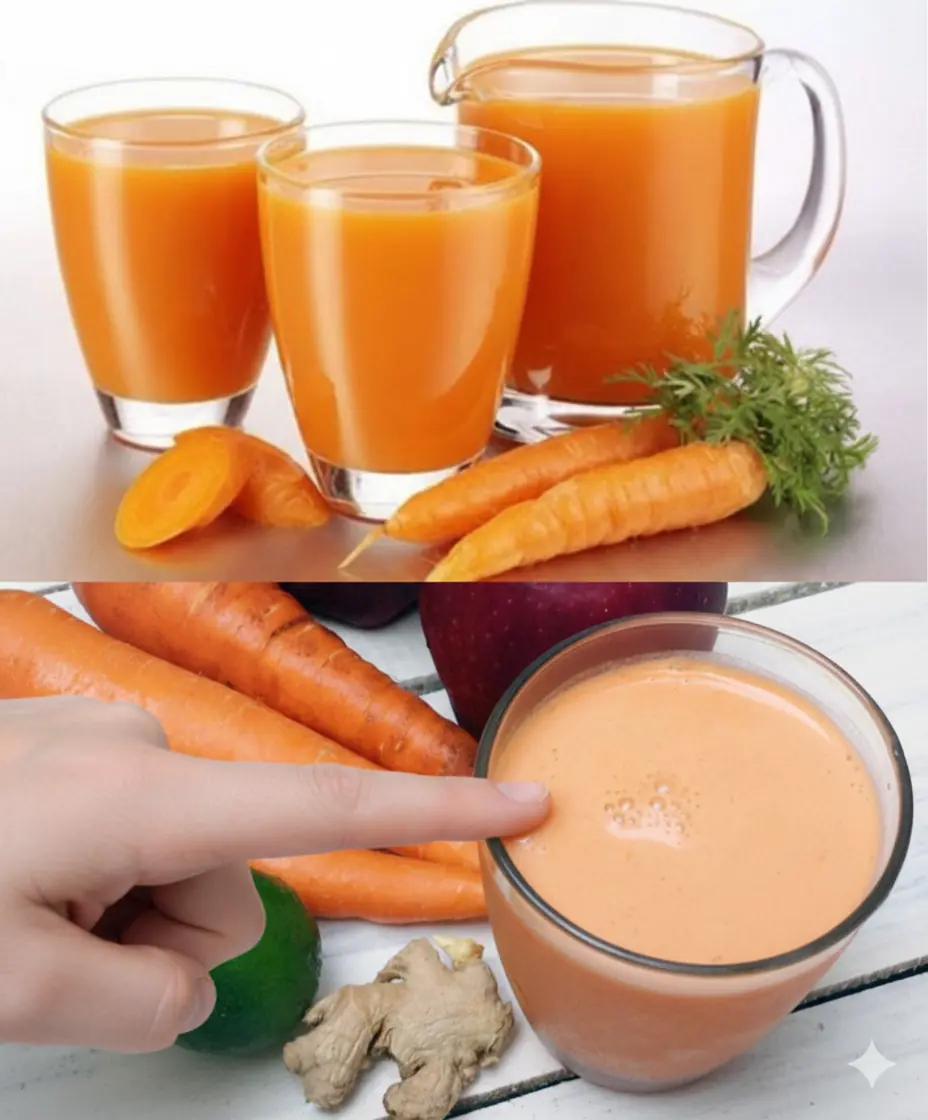

How carrot juice supports skin health and eye function
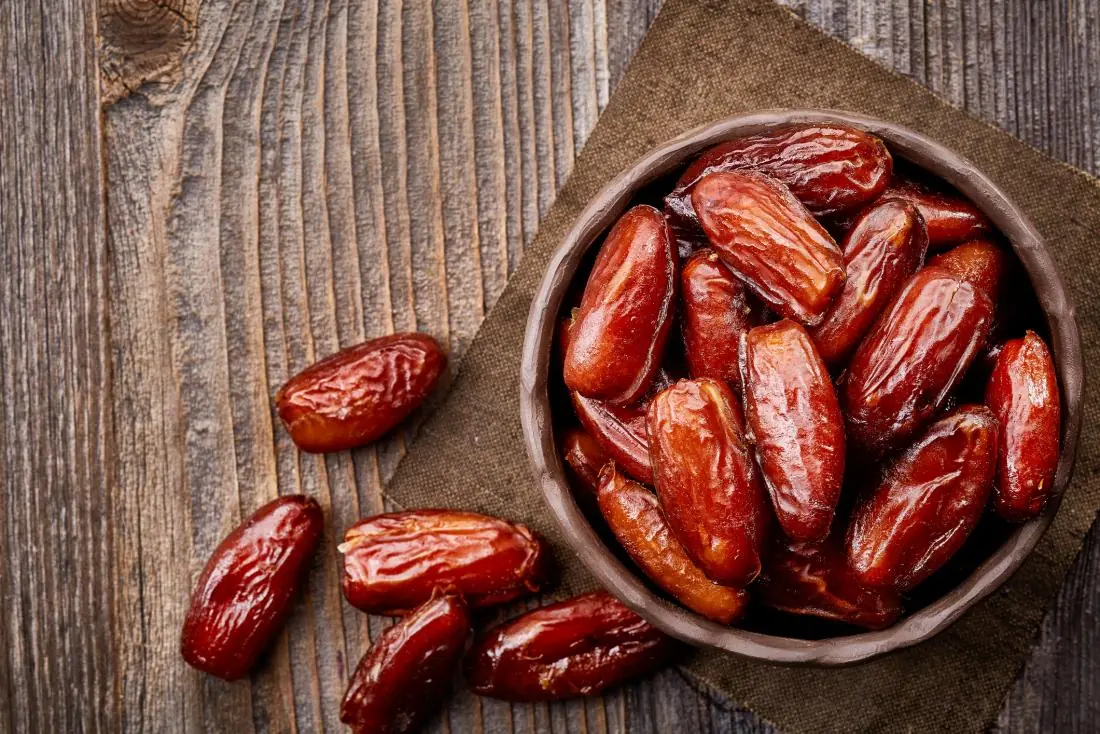

Surprising benefits of dates most people overlook
Kidney Health Alert: Key Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
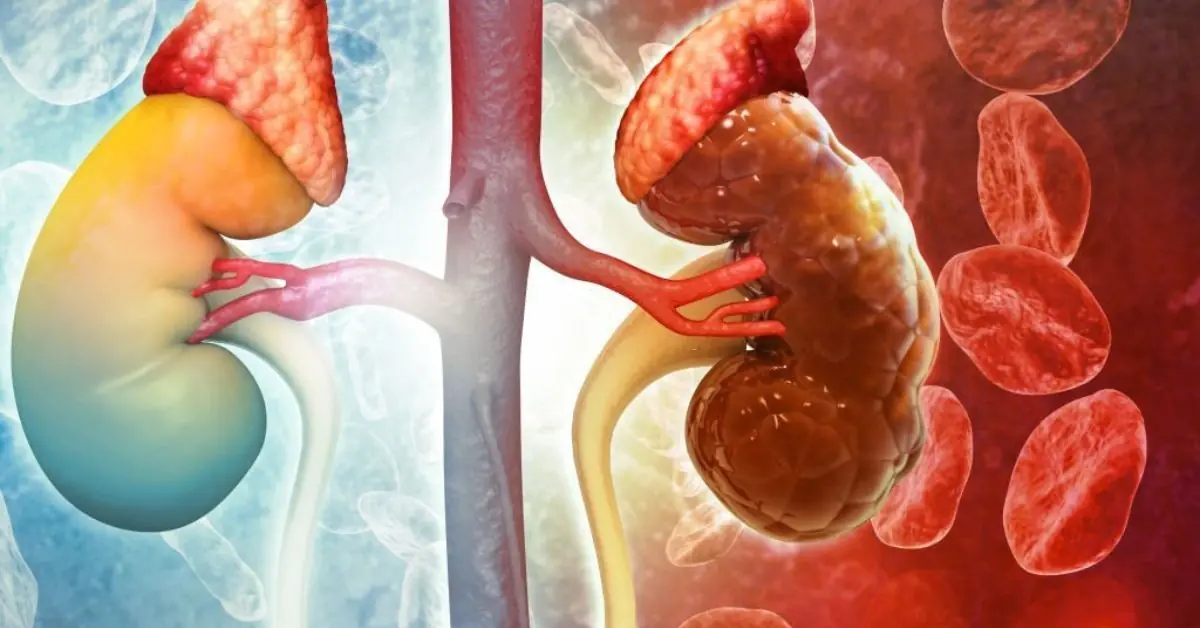
Why kidney problems are appearing before age 30: 2 habits doctors warn against
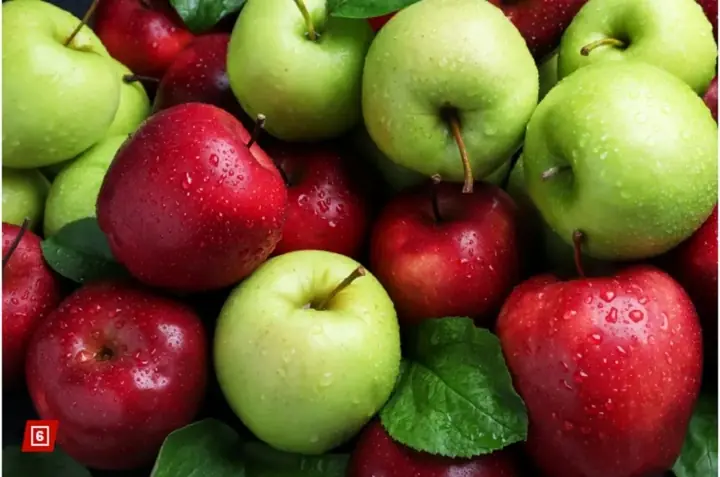

Support liver health: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits to include daily
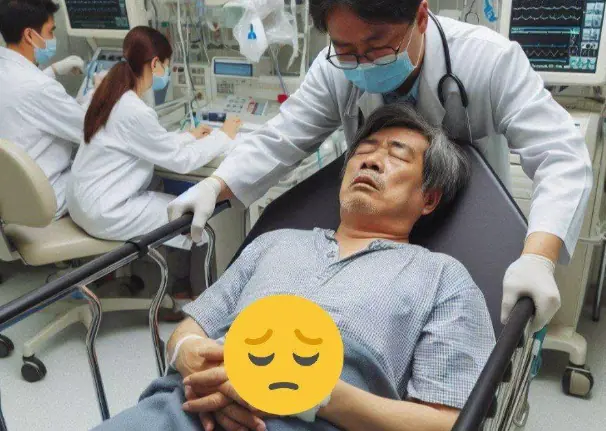
Mr. Tran Vu, 56 years old, living in China, has been diagnosed with diabetes for more than ten years.
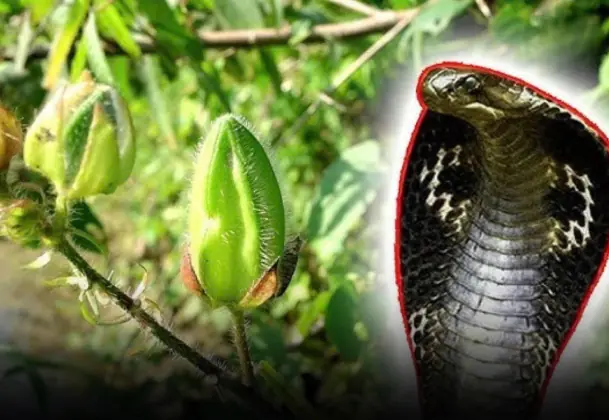

Most people feel unsettled at the thought of snakes wandering too close to their balcony, garden, or home.

Her secrets to a long and healthy life have garnered widespread interest, blending a disciplined lifestyle with a meticulous diet.
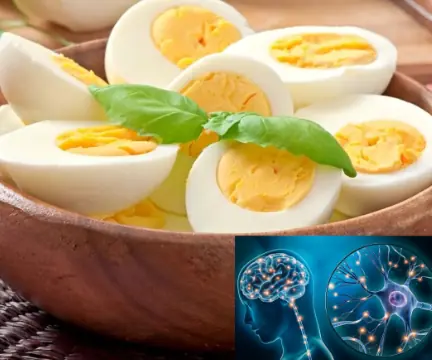
The benefits of eggs are sometimes overshadowed by mainstream media attention to their potential drawbacks.
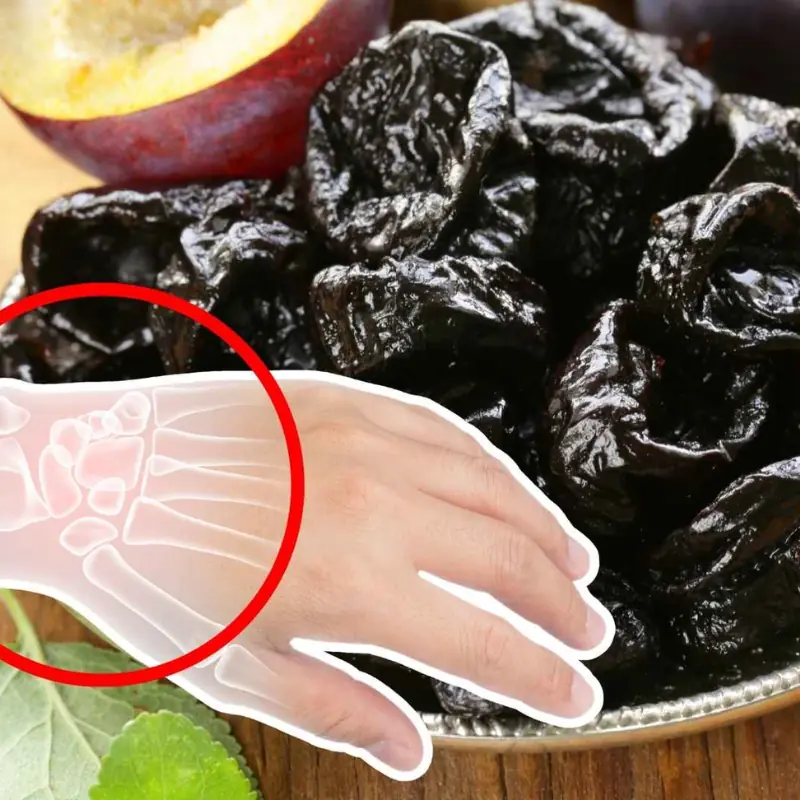
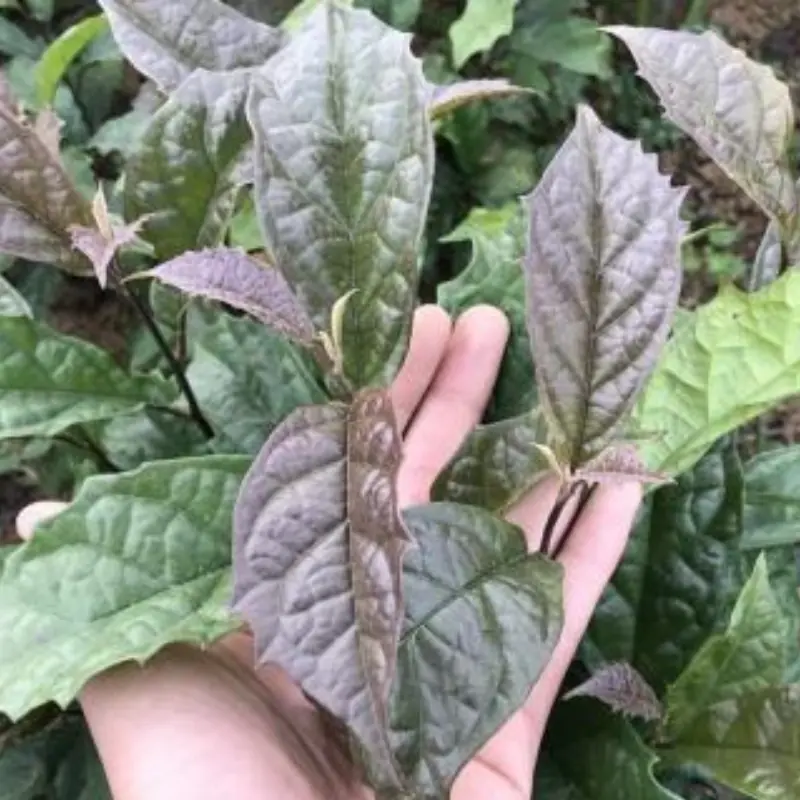



Doctors highlight plant compounds that may help support cancer prevention.
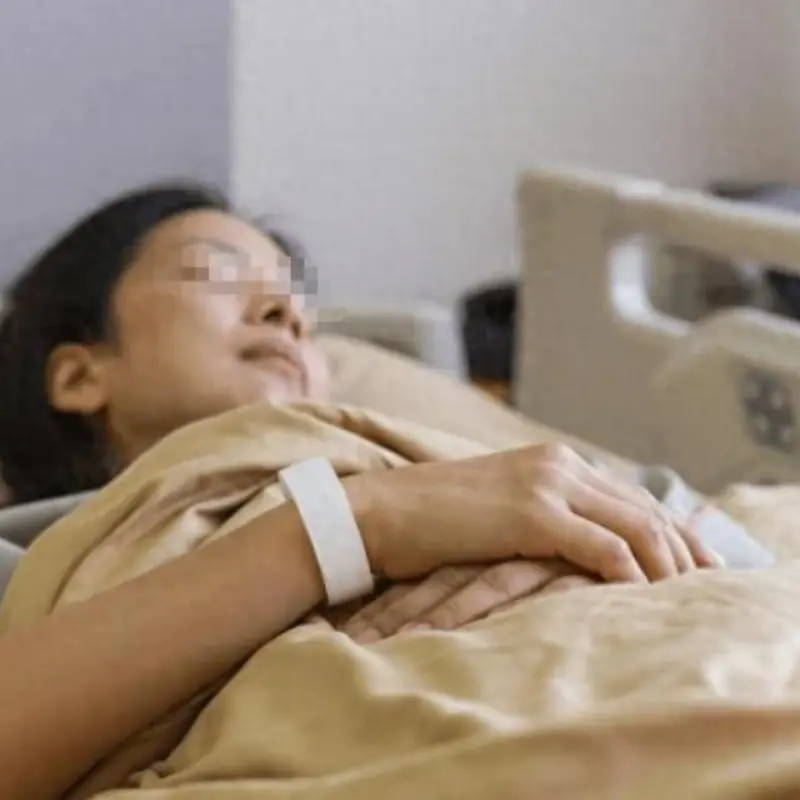
A tragic case highlights everyday habits that may silently harm the pancreas.
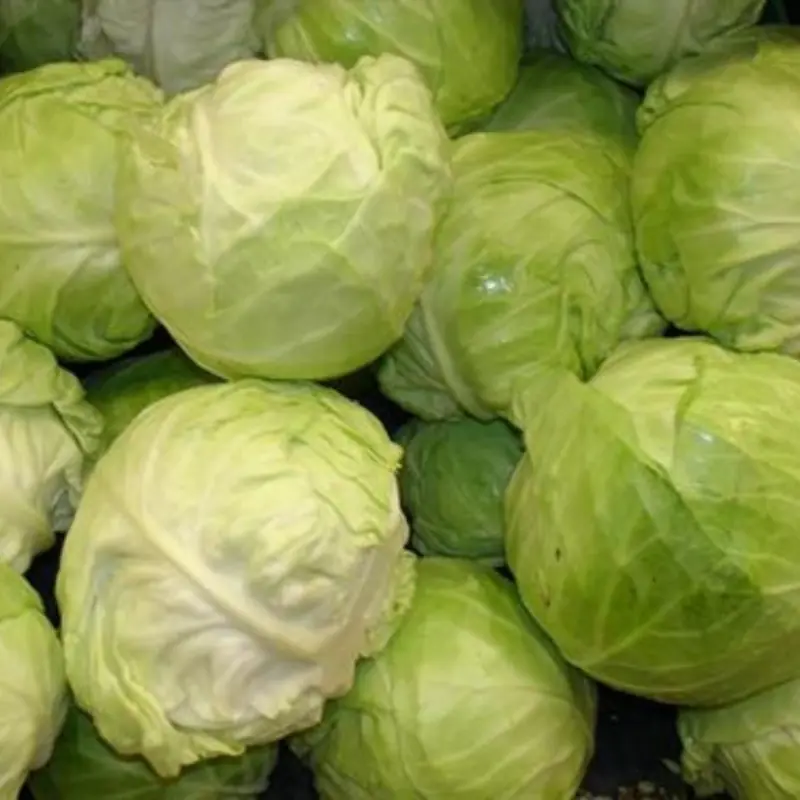

Cabbage is nutritious, but for some people it may pose health risks.

For centuries, rosemary has held a special place in Mediterranean kitchens
Doctors warn five post-meal symptoms may signal stomach cancer early.

Scratched cookware could silently add thousands of microplastics to meals.

Drooling While You Sleep? Here Are 6 Possible Causes


How carrot juice supports skin health and eye function

Surprising benefits of dates most people overlook

Kidney Health Alert: Key Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention

Why kidney problems are appearing before age 30: 2 habits doctors warn against

Support liver health: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits to include daily

These 5 plants in your garden could make it more appealing to snakes

Mr. Tran Vu, 56 years old, living in China, has been diagnosed with diabetes for more than ten years.

Most people feel unsettled at the thought of snakes wandering too close to their balcony, garden, or home.

Her secrets to a long and healthy life have garnered widespread interest, blending a disciplined lifestyle with a meticulous diet.

The benefits of eggs are sometimes overshadowed by mainstream media attention to their potential drawbacks.
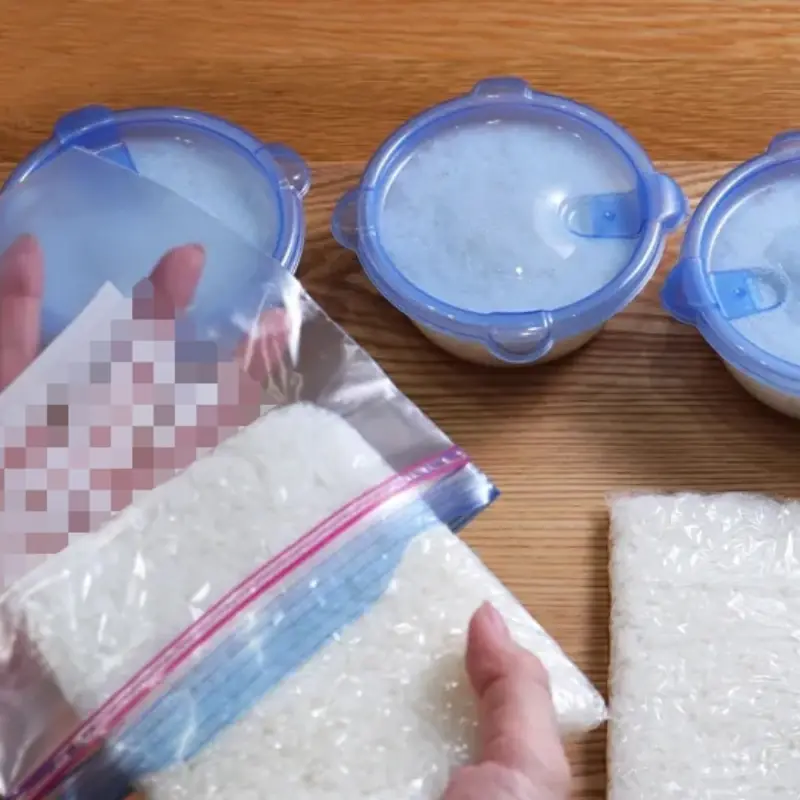

A simple Japanese food hack keeps leftover rice soft, fresh, and tasty.


Infidelity doesn’t always end intimacy — and the reasons are complex.

It’s not about looks. These women leave a lasting mark on men’s minds.
