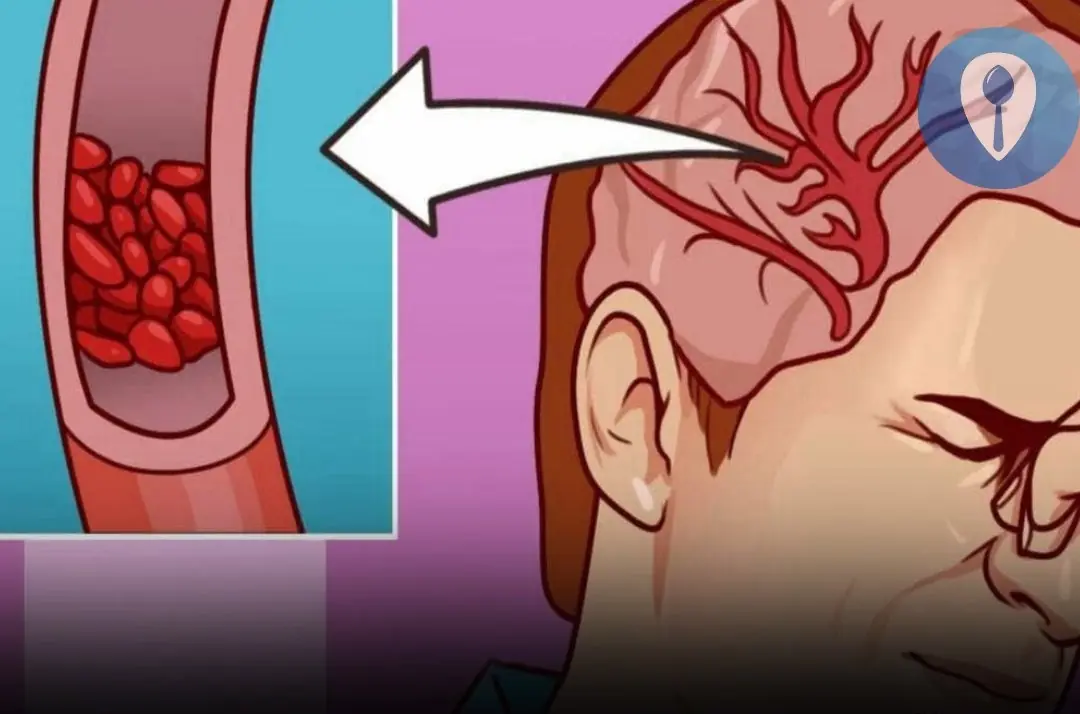
Hidden risk factors inside the home
A Mother and Her Two Sons All Developed Lung Cancer — Even Though No One Smoked
When people hear the words lung cancer, the first assumption is almost always smoking. While smoking remains the leading risk factor, medical reality is far more complex. A growing number of lung cancer cases occur in people who have never smoked a single cigarette.
The story shown in the image—a mother and her two sons all diagnosed with lung cancer despite being non-smokers—raises an uncomfortable but important question: what else could be responsible?
Lung Cancer Is Not Only a Smoker’s Disease
Medical research confirms that 10–20% of lung cancer cases worldwide occur in non-smokers. In some regions, especially among women and younger individuals, the proportion is even higher.
This means that while smoking dramatically increases risk, it is not the only cause.
The Unexpected Cause: Long-Term Environmental Exposure
In families where multiple non-smokers develop lung cancer, doctors often look beyond personal habits and examine shared environmental exposures.
Common hidden risk factors include:
-
Indoor air pollution
-
Poor ventilation in living spaces
-
Long-term exposure to toxic fumes
-
Contaminated household materials
These exposures may seem harmless at first, but chronic low-level inhalation over years can damage lung tissue.
Indoor Air Pollution: A Silent Threat
Many homes unknowingly contain harmful airborne substances.
Examples include:
-
Cooking fumes from gas stoves or coal
-
Smoke from burning incense or candles
-
Poorly ventilated kitchens
-
Heating systems that release pollutants
In enclosed spaces, these particles accumulate and are inhaled repeatedly, sometimes for decades.
Radon Gas: Invisible and Odorless
One of the most overlooked causes of lung cancer in non-smokers is radon gas.
What makes radon dangerous:
-
It is colorless and odorless
-
It seeps into homes from soil and building materials
-
Long-term exposure damages lung cells
Radon is now recognized as the second leading cause of lung cancer in many countries.
Genetic Susceptibility Combined With Environment
Genetics alone rarely cause lung cancer, but genetic vulnerability can amplify the effects of environmental exposure.
In families where several members are affected:
-
Shared genes may reduce the body’s ability to repair DNA damage
-
Combined exposure increases cumulative risk
Why Symptoms Often Appear Late
Lung cancer is especially dangerous because early stages often produce no symptoms.
When signs do appear, they may include:
This does not mean cancer is inevitable, but it does mean vigilance is essential.
A Mother and Her Two Sons All Developed Lung Cancer — Even Though No One Smoked
When people hear the words lung cancer, the first assumption is almost always smoking. While smoking remains the leading risk factor, medical reality is far more complex. A growing number of lung cancer cases occur in people who have never smoked a single cigarette.
The story shown in the image—a mother and her two sons all diagnosed with lung cancer despite being non-smokers—raises an uncomfortable but important question: what else could be responsible?
Lung Cancer Is Not Only a Smoker’s Disease
Medical research confirms that 10–20% of lung cancer cases worldwide occur in non-smokers. In some regions, especially among women and younger individuals, the proportion is even higher.
This means that while smoking dramatically increases risk, it is not the only cause.
The Unexpected Cause: Long-Term Environmental Exposure
In families where multiple non-smokers develop lung cancer, doctors often look beyond personal habits and examine shared environmental exposures.
Common hidden risk factors include:
-
Indoor air pollution
-
Poor ventilation in living spaces
-
Long-term exposure to toxic fumes
-
Contaminated household materials
These exposures may seem harmless at first, but chronic low-level inhalation over years can damage lung tissue.
Indoor Air Pollution: A Silent Threat
Many homes unknowingly contain harmful airborne substances.
Examples include:
-
Cooking fumes from gas stoves or coal
-
Smoke from burning incense or candles
-
Poorly ventilated kitchens
-
Heating systems that release pollutants
In enclosed spaces, these particles accumulate and are inhaled repeatedly, sometimes for decades.
Radon Gas: Invisible and Odorless
One of the most overlooked causes of lung cancer in non-smokers is radon gas.
What makes radon dangerous:
-
It is colorless and odorless
-
It seeps into homes from soil and building materials
-
Long-term exposure damages lung cells
Radon is now recognized as the second leading cause of lung cancer in many countries.
Genetic Susceptibility Combined With Environment
Genetics alone rarely cause lung cancer, but genetic vulnerability can amplify the effects of environmental exposure.
In families where several members are affected:
-
Shared genes may reduce the body’s ability to repair DNA damage
-
Combined exposure increases cumulative risk
Why Symptoms Often Appear Late
Lung cancer is especially dangerous because early stages often produce no symptoms.
When signs do appear, they may include:
This does not mean cancer is inevitable, but it does mean vigilance is essential.
News in the same category

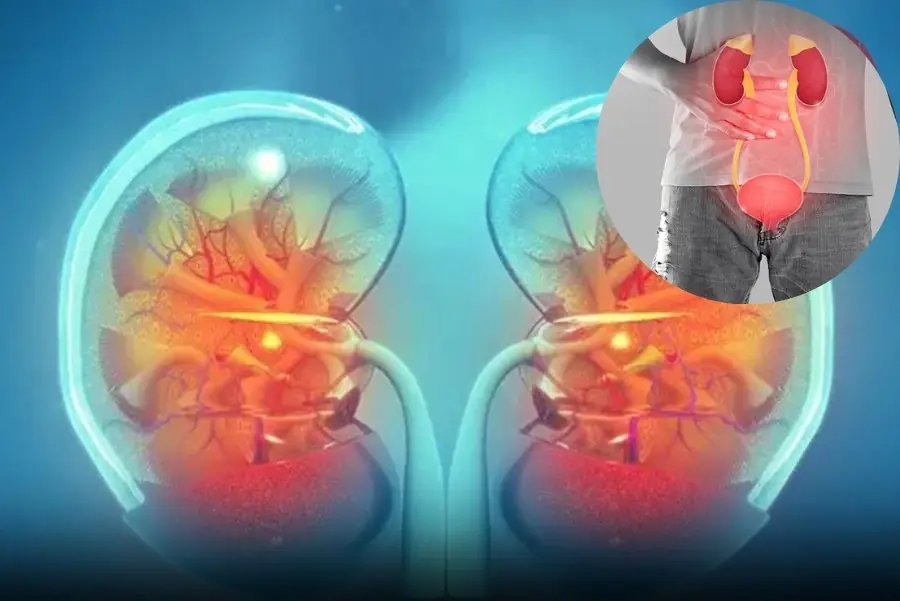
8 Silent Signs Your Kidneys Are Failing — Ignoring Them May Mean Dialysis for Life

Avoid these drinks before bedtime — they could cause problems

People with diabetes often make mistakes: Eating sweet potatoes must follow the “3 DON’Ts” to avoid blo.od sugar spikes
Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys
Hidden Ca.nc.er Ri.s.ks in Daily Life That People Keep Ignoring

If your veins are visible in your hand, it is a signal of...
The first sign is especially common in many households
I summarized the most interesting ones below

A silent stroke can strike when you least expect it — but these small habits could save your life

If you notice someone with bulging v.e.i.n.s, these are the crucial things you need to tell them

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to the …
The first food you eat in the morning plays a vital role in your health, especially your digestive system .....

Creamy Banana Colada Smoothie
Do Not Ignore These 10 Warning Signs That Your Kidneys May Be In Danger

13 Powerful Reasons Why Your Entire Family Should Drink Okra Water Every Day
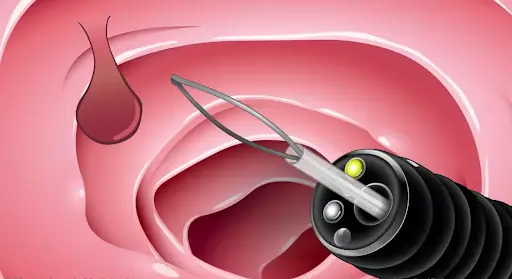
Spotting Colon Polyps Early: The Crucial Step in Preventing Colon Cancer
News Post

I experience 6 of these

8 Silent Signs Your Kidneys Are Failing — Ignoring Them May Mean Dialysis for Life

Avoid these drinks before bedtime — they could cause problems

People with diabetes often make mistakes: Eating sweet potatoes must follow the “3 DON’Ts” to avoid blo.od sugar spikes

Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Many people don’t know what its purpose is used for

FRESH SEA URCHIN (UNI) WITH IKURA

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

Hidden Ca.nc.er Ri.s.ks in Daily Life That People Keep Ignoring

Why should you avoid showering, washing dishes, and doing laundry during a thunderstorm?

If your veins are visible in your hand, it is a signal of...

The first sign is especially common in many households

I summarized the most interesting ones below

A silent stroke can strike when you least expect it — but these small habits could save your life

If you notice someone with bulging v.e.i.n.s, these are the crucial things you need to tell them

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to the …

The first food you eat in the morning plays a vital role in your health, especially your digestive system .....
