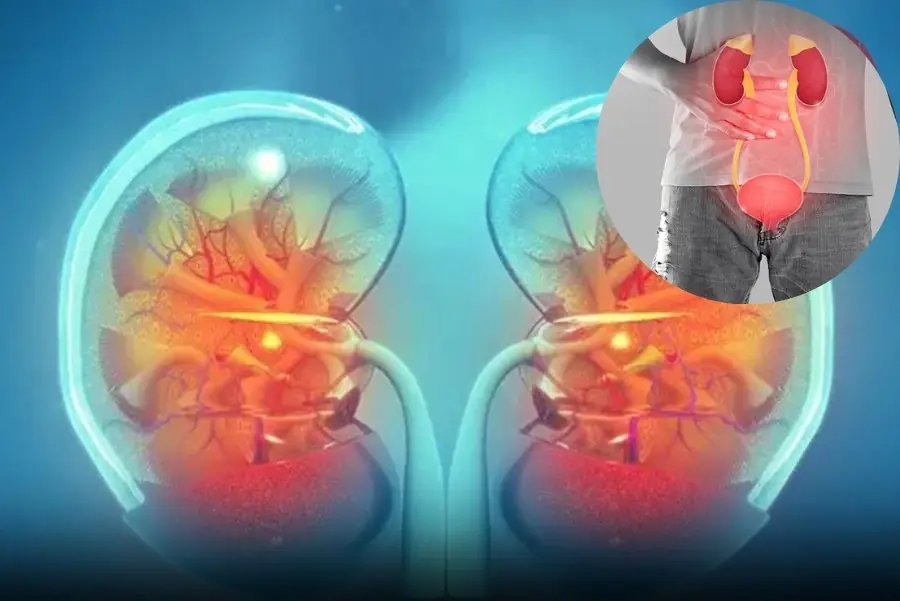
I experience 6 of these
32 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore
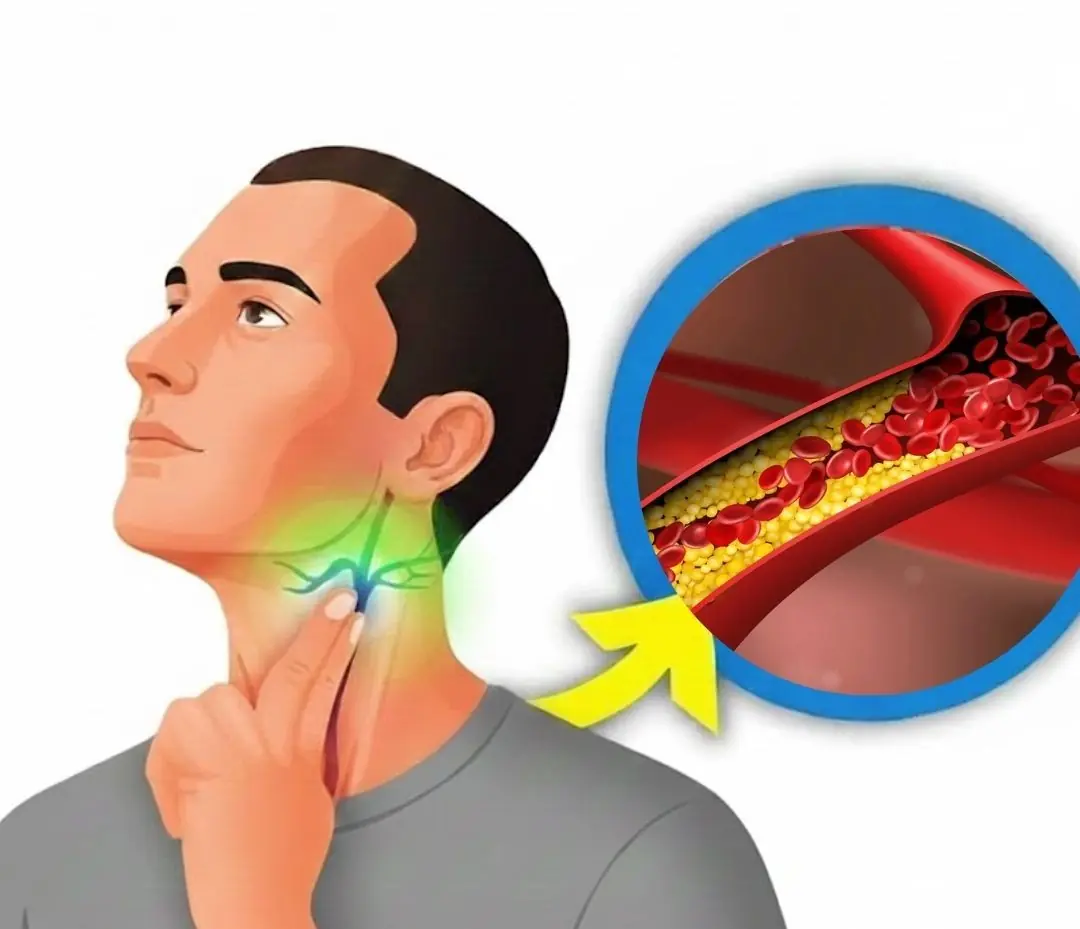
Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals in the human body, yet it is also one of the most commonly overlooked. The image above highlights the connection between blood vessel health and brain function, a reminder that magnesium plays a critical role in both circulation and neurological stability. When levels drop too low, the consequences can quietly build—sometimes until they become dangerous.
Many people live with magnesium deficiency without realizing it. The symptoms often appear vague, unrelated, or easy to dismiss. However, doctors warn that chronic magnesium deficiency can affect the heart, brain, muscles, and nervous system, increasing the risk of serious health events.\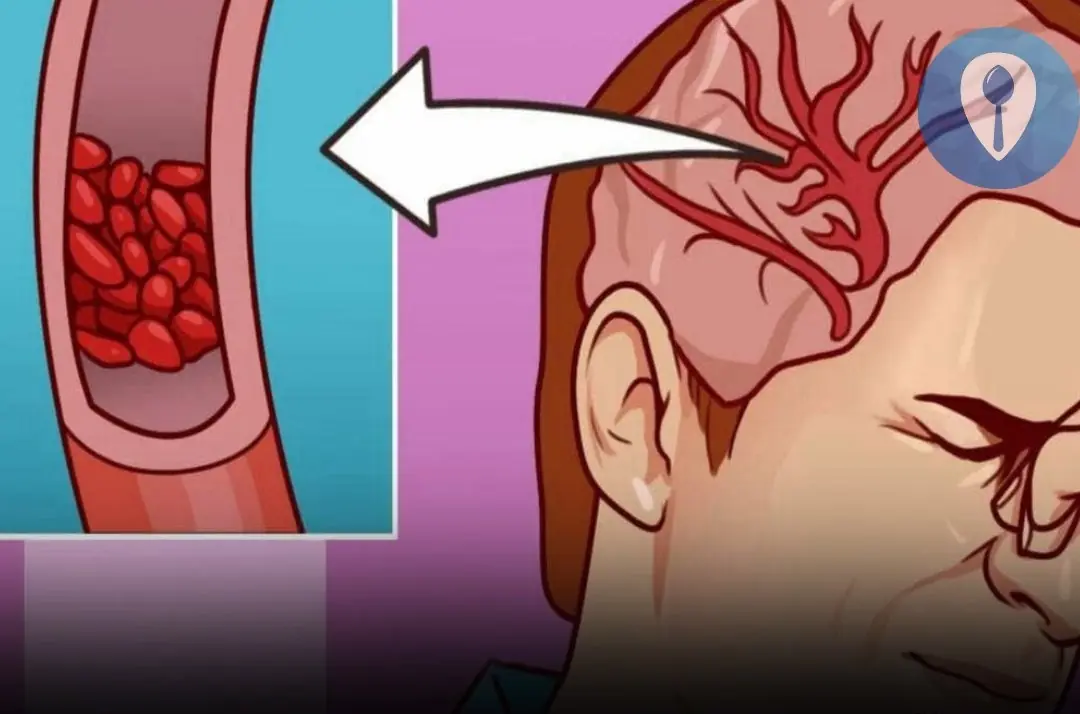
Why Magnesium Matters More Than You Think
Magnesium is involved in over 300 enzymatic reactions in the body. It helps regulate blood pressure, stabilize heart rhythm, control nerve impulses, and relax muscles after contraction. It also plays a key role in glucose metabolism and inflammation control.
When magnesium levels decline, the body struggles to maintain balance—especially in the cardiovascular and nervous systems, which are extremely sensitive to mineral imbalances.
Early Neurological and Mental Warning Signs
Some of the first symptoms affect the brain and nerves. These are often ignored or misattributed to stress or aging:
-
Frequent headaches or migraines
-
Brain fog or difficulty concentrating
-
Anxiety without a clear cause
-
Irritability or mood swings
-
Insomnia or restless sleep
-
Sensitivity to noise or light
-
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
-
Dizziness or lightheadedness
These signs reflect overactive nerve signaling, a common result of low magnesium.
Muscle and Physical Symptoms That Signal Deficiency
Magnesium is essential for proper muscle relaxation. Without it, muscles remain tense and unstable:
-
Muscle cramps, especially at night
-
Eye twitching
-
Muscle spasms or tremors
-
Weakness or fatigue
-
Tight neck and shoulder muscles
-
Restless legs syndrome
-
Reduced exercise tolerance
Persistent muscle symptoms are one of the clearest red flags of magnesium deficiency.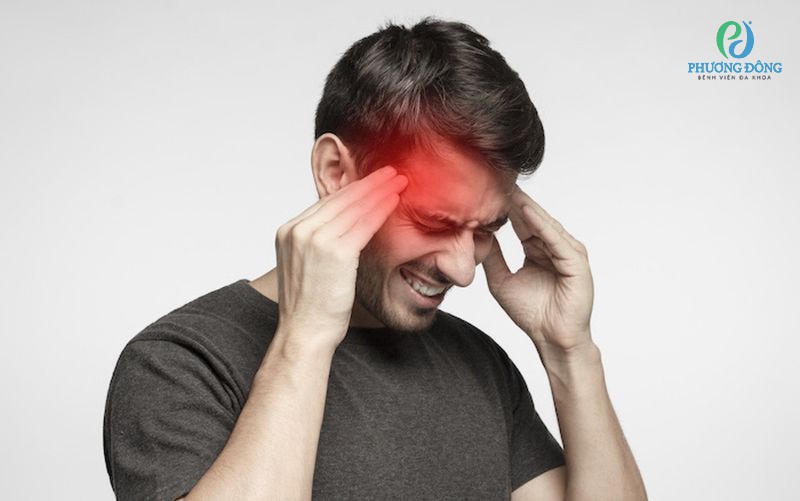
Cardiovascular Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore
The image’s focus on blood vessels is especially important. Magnesium helps prevent abnormal vessel constriction and irregular heart rhythms. Deficiency may cause:
-
Heart palpitations
-
Irregular heartbeat
-
Chest tightness
-
High blood pressure
-
Cold hands and feet
-
Sudden spikes in blood pressure
-
Increased risk of blood clots
In severe cases, low magnesium can contribute to arrhythmias, stroke, or cardiac arrest, particularly in older adults.
Metabolic and Digestive Red Flags
Magnesium also affects digestion and blood sugar regulation:
-
Constipation
-
Loss of appetite
-
Nausea
-
Sugar cravings
-
Insulin resistance
-
Difficulty controlling blood glucose
People with diabetes or metabolic syndrome are especially vulnerable to magnesium depletion.
Long-Term and Serious Consequences
If deficiency persists, more severe symptoms may appear:
-
Chronic inflammation
-
Osteoporosis or bone weakness
-
Depression
-
Increased risk of neurological disorders
At this stage, magnesium deficiency is no longer a minor nutritional issue—it becomes a systemic health threat.
Who Is Most at Risk
Certain groups are more likely to develop magnesium deficiency:
-
 Adults over 50
Adults over 50 -
People with high stress levels
-
Individuals consuming processed foods
-
Those with digestive disorders
-
People taking diuretics or acid-reducing medications
Modern diets are often low in magnesium-rich foods, making deficiency increasingly common.
How to Protect Yourself
Doctors recommend addressing magnesium deficiency through a combination of dietary intake and medical guidance. Foods rich in magnesium include leafy greens, nuts, seeds, whole grains, and legumes. Supplementation should only be considered after consulting a healthcare professional, especially for individuals with kidney or heart conditions.
Final Takeaway
Magnesium deficiency does not always announce itself loudly. Instead, it whispers through headaches, muscle tension, anxiety, and irregular heartbeats—until one day the damage becomes undeniable. The warning signs shown in the image are not random; they reflect the deep connection between minerals, blood vessels, and brain health.
Ignoring these signals can be costly. Recognizing them early can be life-saving.
News in the same category


Avoid these drinks before bedtime — they could cause problems
Hidden risk factors inside the home

People with diabetes often make mistakes: Eating sweet potatoes must follow the “3 DON’Ts” to avoid blo.od sugar spikes
Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys
Hidden Ca.nc.er Ri.s.ks in Daily Life That People Keep Ignoring

If your veins are visible in your hand, it is a signal of...
The first sign is especially common in many households
I summarized the most interesting ones below

A silent stroke can strike when you least expect it — but these small habits could save your life

If you notice someone with bulging v.e.i.n.s, these are the crucial things you need to tell them

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to the …
The first food you eat in the morning plays a vital role in your health, especially your digestive system .....

Creamy Banana Colada Smoothie
Do Not Ignore These 10 Warning Signs That Your Kidneys May Be In Danger

13 Powerful Reasons Why Your Entire Family Should Drink Okra Water Every Day
Spotting Colon Polyps Early: The Crucial Step in Preventing Colon Cancer
News Post
These 7 foods may help your body defend against can.cer, here’s why.

8 Silent Signs Your Kidneys Are Failing — Ignoring Them May Mean Dialysis for Life

Avoid these drinks before bedtime — they could cause problems

Hidden risk factors inside the home

People with diabetes often make mistakes: Eating sweet potatoes must follow the “3 DON’Ts” to avoid blo.od sugar spikes

Young and at Risk: Str.ok.e Strikes 19-Year-Old After Headache — 5 Symptoms You Shouldn’t Ignore

Many people don’t know what its purpose is used for

FRESH SEA URCHIN (UNI) WITH IKURA

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

The morning right after waking up is the time when the body most clearly reveals its health status, especially the kid.neys

Hidden Ca.nc.er Ri.s.ks in Daily Life That People Keep Ignoring

Why should you avoid showering, washing dishes, and doing laundry during a thunderstorm?

If your veins are visible in your hand, it is a signal of...

The first sign is especially common in many households

I summarized the most interesting ones below

A silent stroke can strike when you least expect it — but these small habits could save your life

If you notice someone with bulging v.e.i.n.s, these are the crucial things you need to tell them

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to the …
