How to Properly Wash a Puffer Jacket Without Flattening the Filling or Losing Its Shape
Just one careless step can cause the filling to collapse, distort the shape, and reduce its ability to retain heat.
HOW TO SAFELY AND QUICKLY REMOVE A FOREIGN OBJECT FROM YOUR EYE
There are several ways to remove a foreign object from your eye. It’s important to see a doctor to remove sharp objects, such as a glass or metal fragment.
A foreign object in the eye refers to anything from outside the body that gets into the eye. It can be lodged under the eyelid, stuck on the ocular surface, or penetrate the eye.
Commonly affected parts include:
Cornea: The clear dome covering the eye's front; it protects and helps focus light.
Conjunctiva: The thin membrane covering the sclera (white part) and lining under the eyelids.
Foreign objects cannot get lost behind the eyeball but may scratch the cornea.
Some injuries are minor, but others may cause infections or vision damage.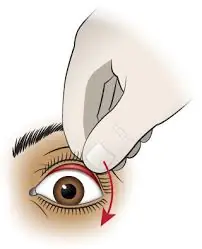
SYMPTOMS OF A FOREIGN OBJECT IN THE EYE
Pressure or discomfort
Sensation of something in the eye
Eye pain
Excessive tearing
Light sensitivity
Frequent blinking
Red or bloodshot eye
Less common but more severe: Intraocular foreign body — often caused by explosions or high-speed impacts (e.g., gunshots). Signs include fluid or blood discharge from the eye.
COMMON CAUSES
Everyday activities can result in:
Eyelashes
Dried mucus
Dirt or sand
Sawdust
Cosmetics
Contact lenses
Metal or glass particles
High-speed projectiles are most dangerous and can cause permanent vision loss.
WHEN TO GET EMERGENCY CARE
Seek immediate help if:
The object is sharp, rough, or large
It prevents the eye from closing
It contains chemicals
It’s embedded or caused bleeding
It was propelled at high speed
Until help arrives:
Limit eye movement
Bandage with clean cloth or gauze
Use a paper cup if the object is too large
Cover the uninjured eye to reduce movement
Even after removal, get medical attention if:
You still feel something in the eye
Vision or symptoms persist or worsen
Cloudiness appears on the cornea
HOME CARE STEPS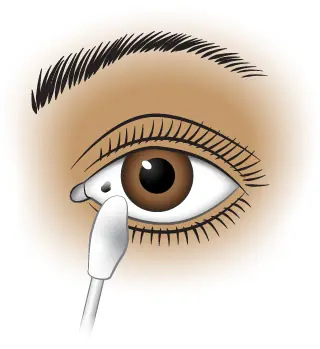
Don’t rub the eye or use tools like tweezers
Don’t remove contact lenses unless there’s swelling or chemical injury
Before starting care:
Wash your hands
Use bright light
Inspect the eye by manipulating eyelids:
Look up and pull down lower lid
Look down and flip upper lid
Techniques to remove the object:
Under upper eyelid:
Submerge face in water and blink several times
Use an eyecup to rinse
Pull upper lid over lower lid to dislodge
Under lower eyelid:
Pull lid down or press skin beneath to expose
Use a damp cotton swab if visible
Flush with water or use eyecup
For multiple small particles (e.g., sand):
Use wet cloth to wipe surrounding area
Submerge eye and blink repeatedly
For children: pour warm water into eye while holding lids open
WHEN TO SEEK MEDICAL HELP
If unable to remove the object
If vision is still abnormal
If tearing, swelling, or irritation persists
If symptoms worsen after removal
AT THE DOCTOR’S OFFICE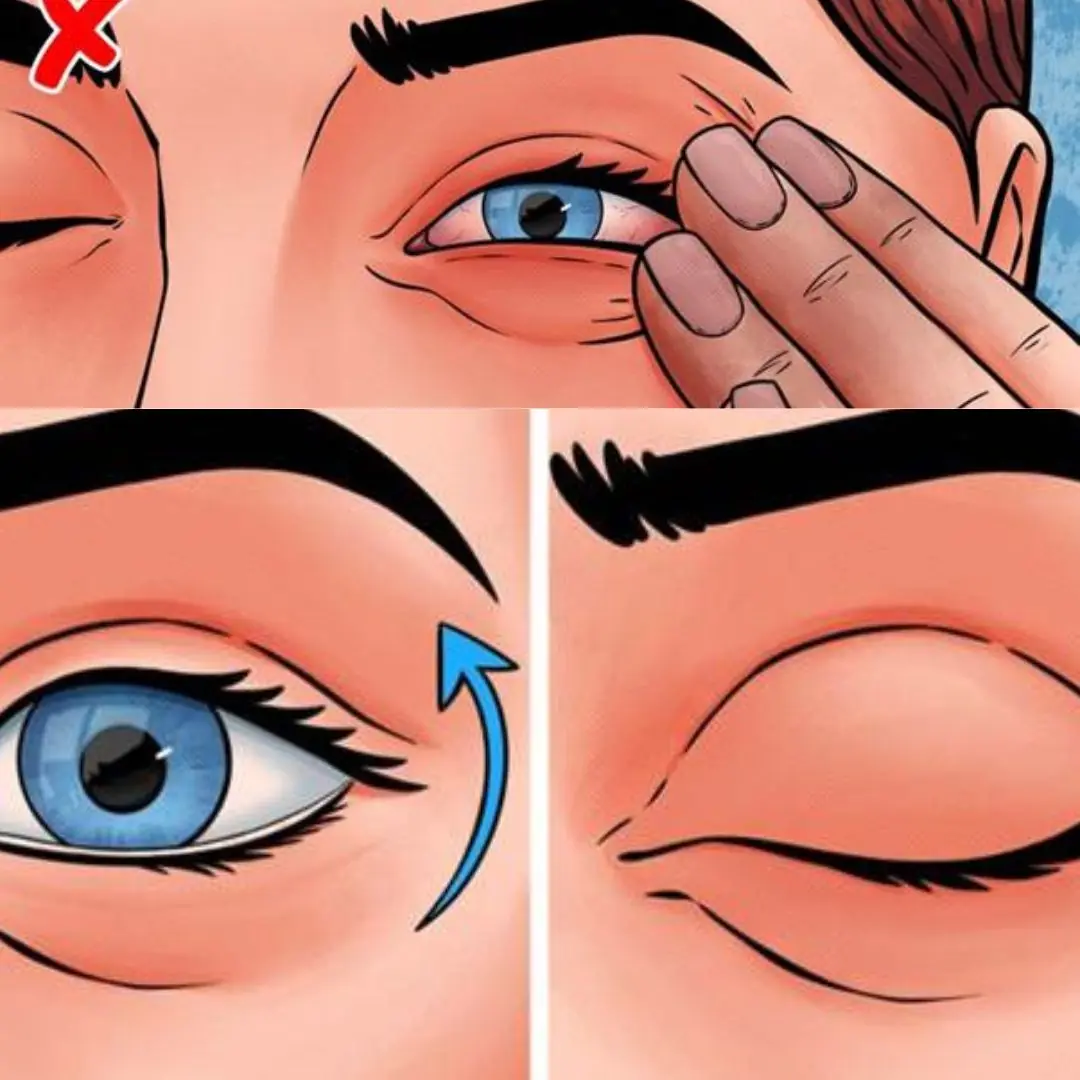
May use numbing drops and fluorescein dye
Tools: magnifier, cotton swab, tweezers, or water flush
In more severe cases: use of needles or surgical tools
If corneal abrasion:
Antibiotic ointment to prevent infection
Eye drops to keep pupil dilated (for large abrasions)
Pain relievers like acetaminophen
Imaging (CT scan) if intraocular damage suspected
Referral to ophthalmologist if necessary
RECOVERY
Minor cases heal in ~2 hours
Irritation may last 1–2 days
Corneal abrasions heal in 2–3 days
Higher infection risk with organic material (e.g., twigs, soil)
Intraocular injuries may cause permanent damage or endophthalmitis
PREVENTION
Use protective eyewear when:
Using tools (saws, hammers, grinders)
Working with chemicals
Mowing the lawn
Protecting your eyes during high-risk activities is the best way to prevent foreign objects from entering and causing harm.

Just one careless step can cause the filling to collapse, distort the shape, and reduce its ability to retain heat.

Noisy, shaking washer? Try these quick fixes before calling a technician

A simple trick: sprinkle everyday household ingredients in your garden to keep the soil warm and ensure healthy plant growth in spring

A simple fabric softener and salt trick that solves everyday household problems

What are those “Small bags” on the wall really?

The combined health and household benefits of clove, lemon and onion

Effective strategies for preventing motion sickness during vehicle travel












The liver loves these "4 vegetables - 2 fruits" Eat them regularly don't skimp
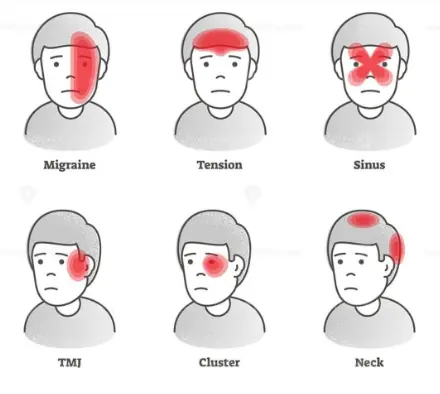
Headaches are the most common form of pain experienced worldwide, and they remain a leading cause of missed workdays, school absences, and doctor visits.

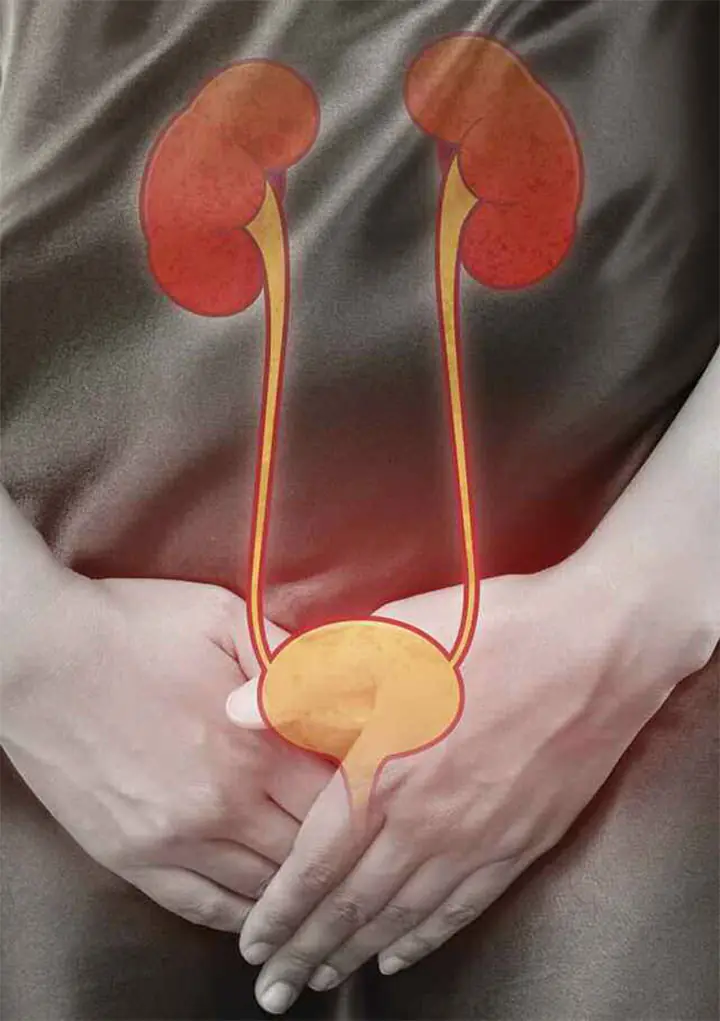
5 Common Signs of Bladder C.a.n.c.e.r That You May Ignore
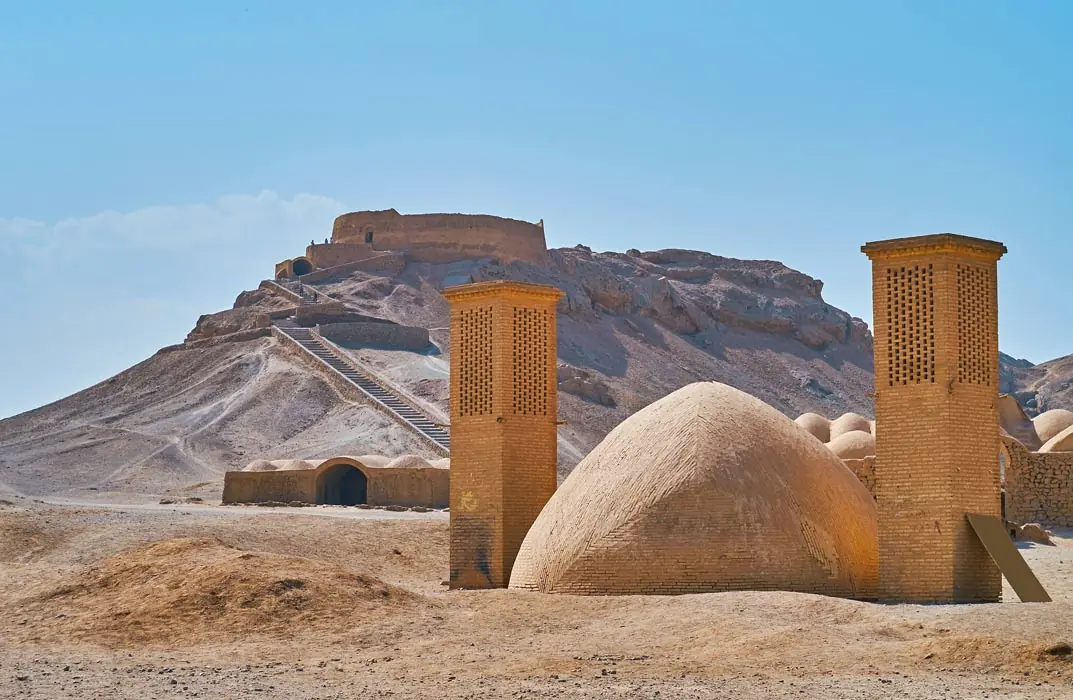


A tower of silence (known also as a ‘dakhma’) is a type of structure used for funerary purposes by adherents of the Zoroastrian faith.

For the Cake Layers

Cremation and faith: what scripture says and what truly matters after passing

When a married woman is attracted to another man, she does these 9 things

Hypertension — commonly known as high blood pressure — is one of the most prevalent health concerns globally

Why your stomach hurts after meals: 5 possible dis.eases

Why Do Women Cross Their Legs When Sitting?
Becoming an FBI agent isn’t simply about having brute strength or high academic achievements — it’s about training your mind to think differently, creatively, and strategically.
A man walks into his doctor’s office for a routine checkup. He feels fine—maybe just a little more tired than usual.

2 uncommon sleep-time signs that may indicate liver or kidney issues

The Incredible Health Benefits of Beets: A Nutrient Powerhouse

Passing gas is a normal part of digestion.
