5-Year-Old Passes Away from Late-Stage Cancer
The heartbreaking story of a 5-year-old child losing the battle against late-stage cancer has shaken many parents and health professionals.

Yes, while vitamins are essential for overall health, in some cases, taking certain vitamins in excess or inappropriately can make certain health conditions worse. Here are some examples of how vitamins can potentially worsen specific diseases or conditions:
Risk: Excessive vitamin A intake, particularly from supplements, can be toxic and lead to a condition called hypervitaminosis A. This can cause symptoms like nausea, dizziness, headaches, and in severe cases, liver damage.
Diseases that may worsen:
Liver disease: People with liver disorders (like cirrhosis) should be cautious with vitamin A supplements, as the liver struggles to process high levels of vitamin A.
Bone fractures: Excessive vitamin A may lead to a higher risk of fractures by interfering with vitamin D metabolism, which is crucial for bone health.
Risk: While vitamin D is vital for bone health and calcium absorption, too much vitamin D can cause hypercalcemia (high calcium levels in the blood), leading to nausea, vomiting, kidney stones, and even kidney failure in extreme cases.
Diseases that may worsen:
Kidney disease: In individuals with pre-existing kidney problems, excess vitamin D may worsen kidney function by increasing calcium levels, which can lead to further damage.
Sarcoidosis and Tuberculosis: These conditions can increase the conversion of vitamin D to its active form, leading to excessive calcium levels and worsening the disease.
Risk: High doses of vitamin E (more than 400 IU per day) can act as a blood thinner and interfere with clotting.
Diseases that may worsen:
Hemophilia and other bleeding disorders: Individuals with bleeding disorders or those on blood-thinning medications (like warfarin) should avoid high doses of vitamin E, as it can increase the risk of bleeding.
Heart disease: Some studies have suggested that high doses of vitamin E may increase the risk of heart failure in certain populations, though the evidence is still debated.
Risk: Vitamin K plays a crucial role in blood clotting, so taking large amounts of vitamin K supplements can interfere with the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications like warfarin (Coumadin).
Diseases that may worsen:
Blood clotting disorders: People on anticoagulant therapy need to maintain a consistent intake of vitamin K, as fluctuations can impact their medication’s effectiveness and lead to either excessive bleeding or clotting.
Risk: While vitamin B6 is essential for nerve function, excessive amounts (usually from supplements) can cause nerve damage (neuropathy).
Diseases that may worsen:
Neuropathy: High doses of vitamin B6 can aggravate or cause peripheral neuropathy, especially in individuals with a history of nerve damage, diabetes, or chronic alcoholism.
Risk: While folic acid is important for cell division and pregnant women, too much folic acid can mask symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency.
Diseases that may worsen:
Vitamin B12 deficiency: Excessive folic acid can mask the neurological symptoms of vitamin B12 deficiency, delaying diagnosis and potentially worsening nerve damage.
Cancer risk: Some studies suggest that high levels of folic acid could potentially fuel the growth of certain cancers, particularly colorectal cancer, by stimulating the growth of precancerous cells.
Vitamins are crucial for maintaining health, but it’s important to take them in the right amounts and in the right context. It’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any vitamin supplement, especially if you have an underlying health condition, to ensure that you're not inadvertently exacerbating an existing disease.

The heartbreaking story of a 5-year-old child losing the battle against late-stage cancer has shaken many parents and health professionals.

Japan Considers This the “Strongest Anti-Cancer Food”

Magnesium is an essential mineral in the human body, playing a critical role in over 300 enzymatic processes.
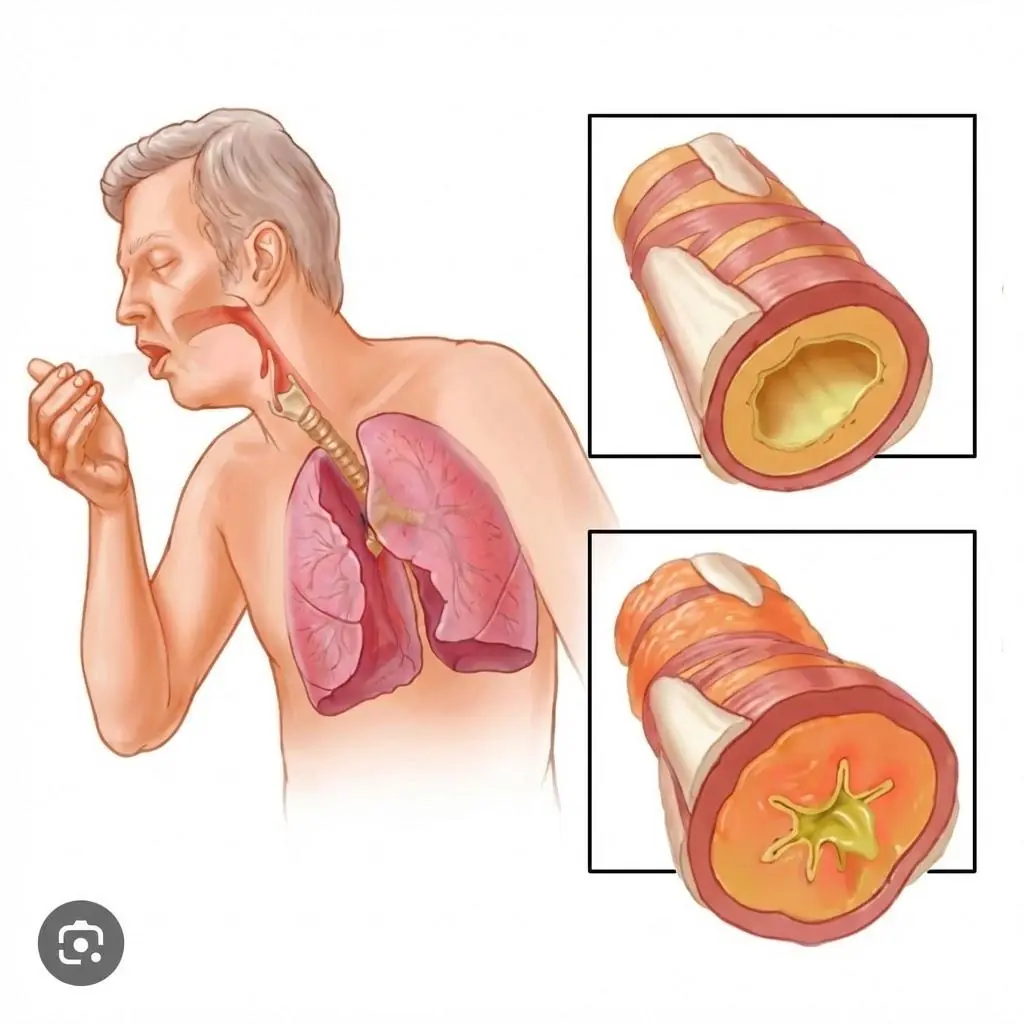
Understanding its possible causes can help individuals seek timely care and prevent more serious complications.
Linh was energetic, bright, and loved by her students.
Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
When they occur, the outcomes are often severe and fast-moving.

If you like to take a nap during the day, then you should definitely know this
He drank water before sleeping… and never woke up. Doctors urge everyone to avoid these 4 drinks at night
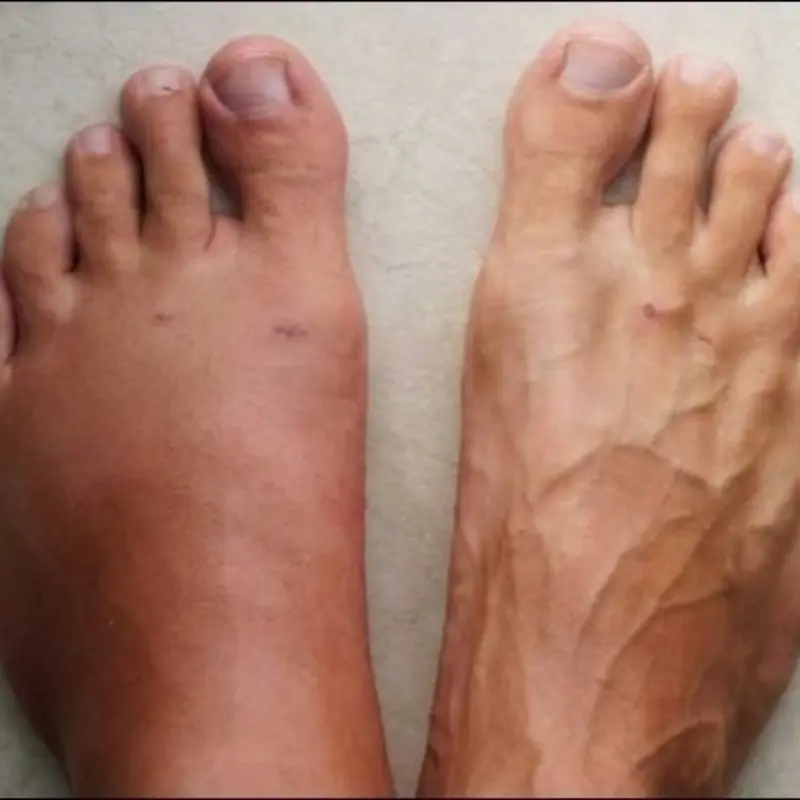
Subtle physical changes can appear weeks before a heart attack strikes.
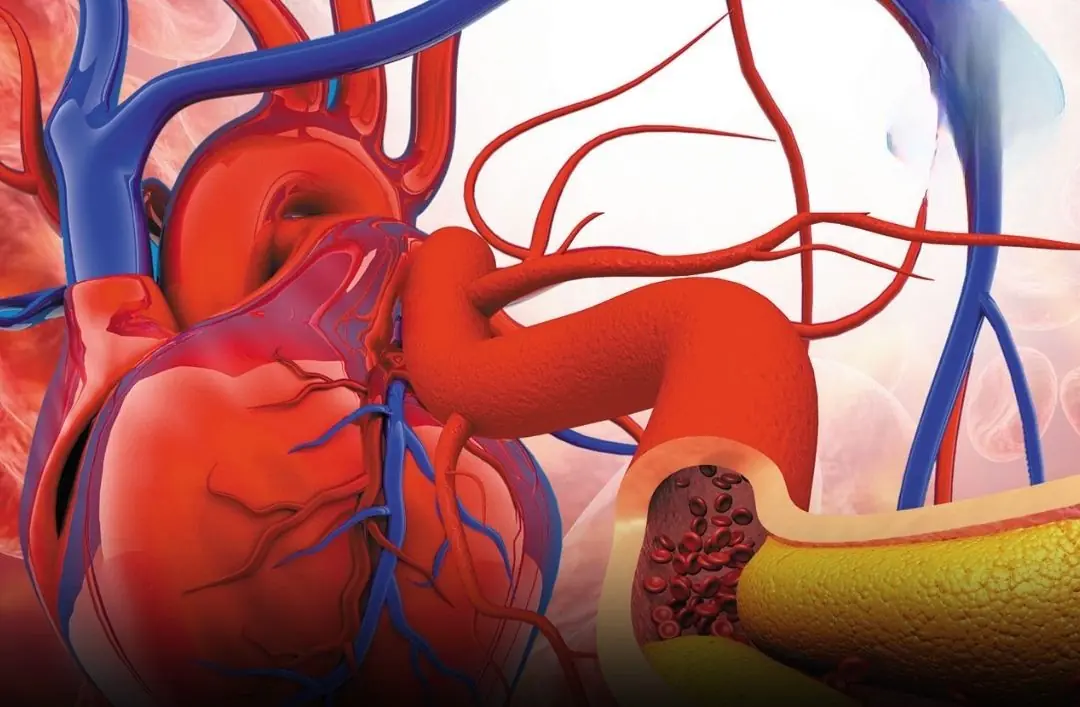
These 3 Morning Mistakes Make Blo:od Pressure & Cholesterol Worse
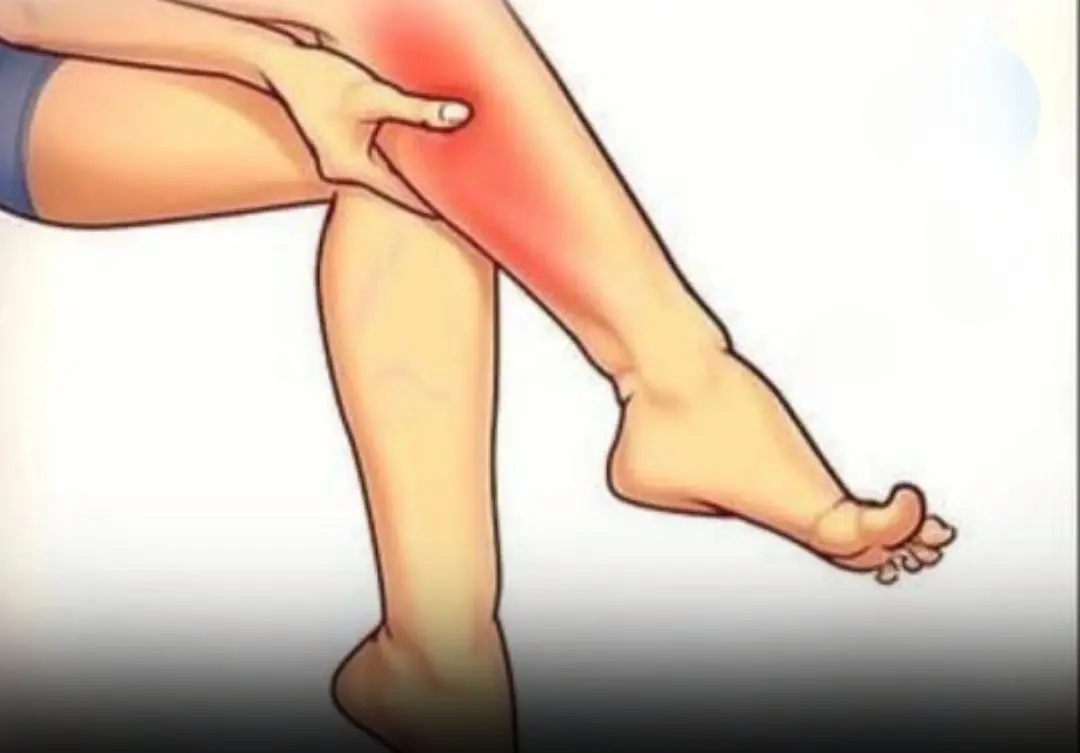
Leg cramps while sleeping? This is how you prevent nighttime calf cramps!
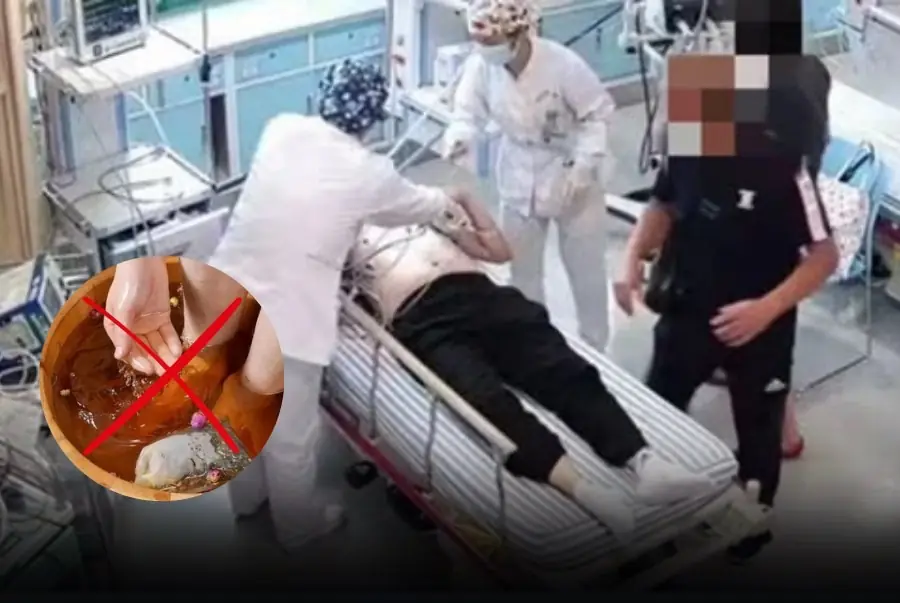
A 65-year-old woman died suddenly at dawn — doctors say her bedtime habits
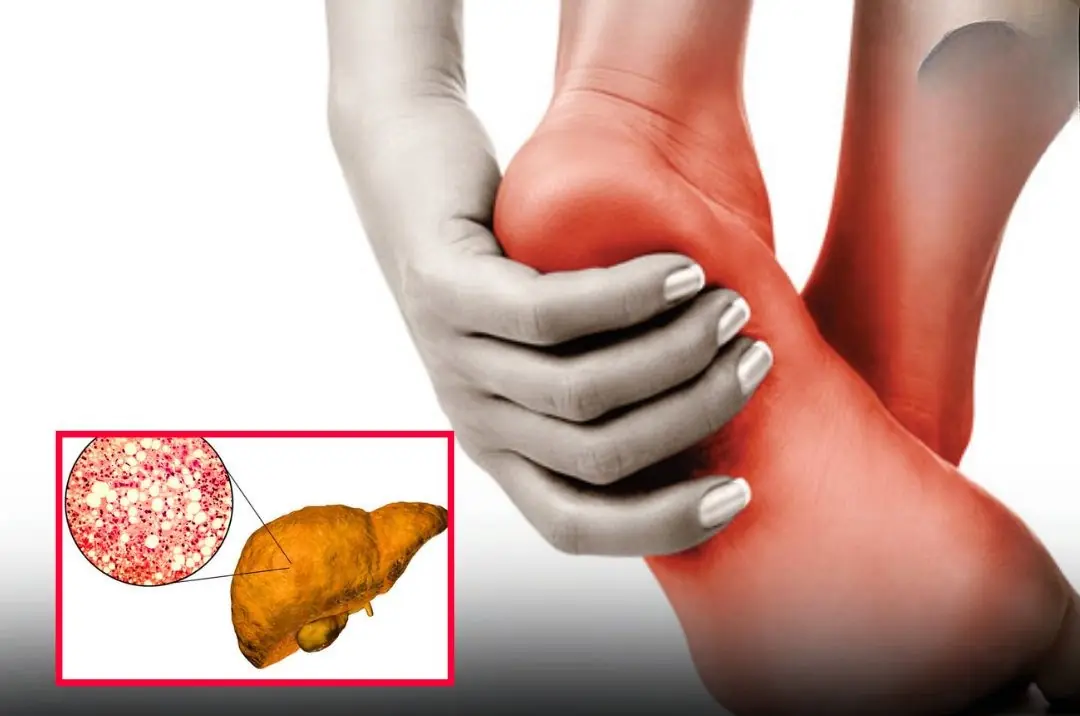
A change in your feet may signal severe fatty liver disease — don’t ignore it

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.
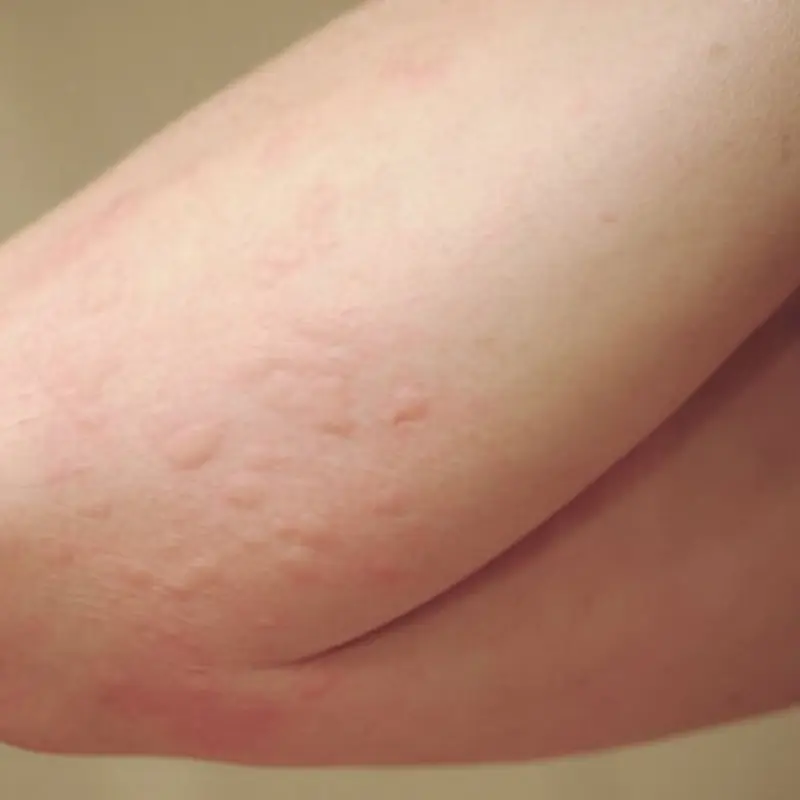
Persistent itching with unusual skin bumps may signal hidden health issues.

Doctors Reveal That Eating Eggs Can Trigger Something Unexpected…
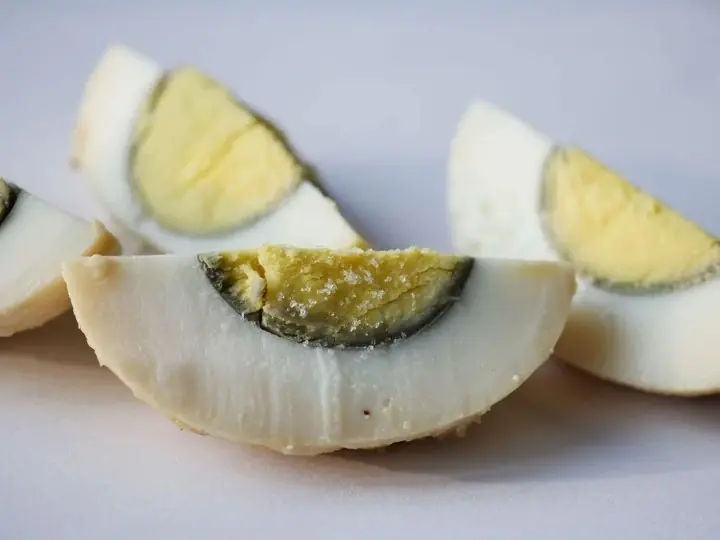

Why hard-boiled eggs get a green ring?
7 silent signs your heart could be in trouble - don't ignore these


The heartbreaking story of a 5-year-old child losing the battle against late-stage cancer has shaken many parents and health professionals.

Golden, cheesy pizza bombs are the irresistible snack everyone wants to try.

Before cancer develops, the hands and feet may exhibit certain warning signs that could indicate an underlying health condition, including cancer.

Japan Considers This the “Strongest Anti-Cancer Food”

Magnesium is an essential mineral in the human body, playing a critical role in over 300 enzymatic processes.

Understanding its possible causes can help individuals seek timely care and prevent more serious complications.

Linh was energetic, bright, and loved by her students.

When love fades, it rarely does so with noise.

Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
When they occur, the outcomes are often severe and fast-moving.

If you like to take a nap during the day, then you should definitely know this

He drank water before sleeping… and never woke up. Doctors urge everyone to avoid these 4 drinks at night

Subtle physical changes can appear weeks before a heart attack strikes.

People who talk behind your back often reveal themselves through the words they use.

These 3 Morning Mistakes Make Blo:od Pressure & Cholesterol Worse

Leg cramps while sleeping? This is how you prevent nighttime calf cramps!

A 65-year-old woman died suddenly at dawn — doctors say her bedtime habits

A change in your feet may signal severe fatty liver disease — don’t ignore it

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.