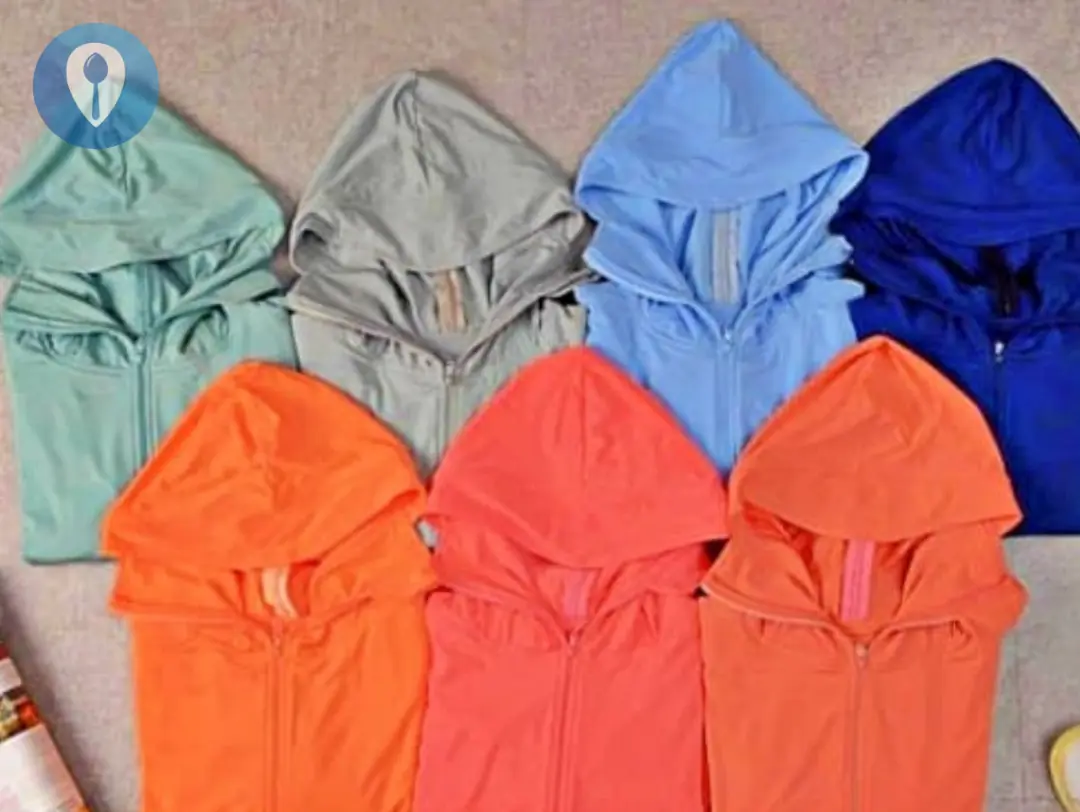
Choosing the right sun-protection shirt goes beyond picking a stylish design. The color and material of your garment are crucial factors that determine how effectively it blocks ultraviolet (UV) radiation and heat. Unfortunately, many people assume that light colors automatically feel cooler and that any UPF-rated fabric will keep them protected. In reality, the science behind color, fiber type, weave density, and specialized coatings is more complex. This article explores which combinations of color and material deliver the best UV-blocking and heat-management performance, highlights common misconceptions, and offers practical guidelines for making an informed choice.
Why Color Matters for UV Blocking and Comfort
Sunlight consists of a spectrum of wavelengths, including UV-A and UV-B rays (which damage skin), visible light (which our eyes perceive), and infrared radiation (which we sense as heat). The color of fabric affects how much of each portion of the spectrum is absorbed, reflected, or transmitted:
-
Dark colors absorb more visible light and infrared radiation, converting that energy into heat at the fabric surface. At the same time, they also absorb a higher proportion of UV rays, preventing them from reaching the skin.
-
Light colors reflect most visible light, making the fabric feel cooler to the touch. However, many light colors—especially pure white—reflect only a modest fraction of UV-A and UV-B, allowing more UV radiation to penetrate thin or loosely woven fabrics.
As a result, a dark-colored shirt often provides superior UV protection, even if it feels warmer when you first touch it outdoors. Conversely, a light-colored shirt may feel cool initially but might expose you to more UV unless it incorporates additional protective features.
Light vs. Dark: The Trade-Off Between Heat and UV Protection
Many people choose a white or pastel sun shirt under the assumption that reflecting visible light equates to overall sun protection. In truth:
-
A white polyester shirt might reflect 80–90% of visible light yet only block 20–30% of UV-B unless it is densely woven or treated with a UV-absorbing finish.
-
A black or navy nylon shirt, even in a lightweight weft, can naturally block 90–95% of UV rays, thanks to the inherent UV absorption properties of its synthetic fibers.
If maximum UV defense is your priority—particularly for activities like hiking, sailing, or gardening—a darker hue in a high-density weave will reduce your skin’s UV exposure more effectively. If thermal comfort is equally important, seek fabrics that combine dark colors with cooling finishes or mesh-ventilated panels that promote airflow.
How Fabric Material and Weave Affect Performance
Beyond color, the type of fiber and how tightly the fabric is woven play a determining role in both UV blocking and heat management:
-
Synthetic fibers (polyester, nylon, acrylic) tend to have smaller, more uniform molecular structures that naturally absorb and scatter UV radiation. These fibers can be engineered into high-density weaves that leave minimal gaps for UV rays to pass through. However, they may trap heat unless engineered with moisture-wicking or phase-change finishes.
-
Natural fibers (cotton, linen, bamboo) offer superior breathability and moisture absorption. A loosely woven cotton shirt feels cool and wicks sweat away from the skin, but the large inter-fibre spaces allow a significant amount of UV to penetrate. Even darker-colored cotton fabrics may only deliver a UPF (Ultraviolet Protection Factor) of 15–20 if loosely woven.
-
Blended fabrics (for example, a 65% polyester/35% cotton blend) strike a balance: polyester provides UV absorption, while cotton improves comfort and moisture management. The overall UV and heat performance depends heavily on the exact blend ratio and weave density.
When shopping, look for fabrics labeled with a specific UPF rating—ideally UPF 30 or higher—with a tight weave. You can often verify weave density by holding the fabric up to bright light: the fewer visible pinholes, the better its UV-blocking capability.
Specialized UV-Protection Technologies
Modern sun shirts often go beyond natural fiber properties and weave density by incorporating advanced treatments:
-
UPF finishes: Chemical treatments (such as those containing titanium dioxide or zinc oxide nanoparticles) bond to fibers to enhance UV reflectance and absorption without significantly affecting breathability.
-
Cooling finishes: Some fabrics are treated with moisture-activated cooling agents that lower the surface temperature when you sweat, offsetting the heat-absorbing nature of dark fibers.
-
Infrared-reflective dyes: These dyes reflect a greater portion of infrared radiation (heat) while still allowing dark colors to block UV effectively, reducing the sensation of heat without diminishing UV protection.
When evaluating these technologies, confirm that the garment still carries an independent UPF certification. Marketing claims alone cannot guarantee real-world performance.
Common Mistakes in Selecting Sun-Protective Shirts
Even experienced outdoor enthusiasts often fall prey to misconceptions:
-
Assuming “lightweight” equals “cool and protective”: Thin fabrics may feel breezy but typically deliver poor UV shielding.
-
Failing to check the UPF rating: A shirt advertised as “UV-protective” might only achieve a UPF of 15 or less, offering minimal real protection.
-
Overlooking fit and ventilation: A shirt that clings to the skin prevents airflow, exacerbating heat buildup. Conversely, excessively loose garments may expose skin through gaps at the shoulders or waist.
-
Ignoring maintenance instructions: Some UV finishes degrade after multiple washes. Failing to follow care labels can drastically reduce UPF performance over time.
Practical Guidelines for Choosing the Best Sun Shirt
To find a sun-protection shirt that balances UV defense and comfort, consider these steps:
-
Check the UPF rating: Aim for UPF 30 or higher (the label should state UPF 30, 50, or 50+).
-
Select a dark hue with cooling features: If UV protection is critical, pick navy, charcoal, or black fabrics with moisture-wicking or infrared-reflective technology.
-
Verify weave density: Hold the fabric up to light; fewer gaps equate to better UV blocking.
-
Consider a synthetic or blended material: Polyester or nylon blends with cotton offer a blend of UV absorption and breathability.
-
Look for mesh panels or vented designs: Strategically placed vents under the arms or on the back allow airflow without compromising coverage.
-
Follow care instructions: Wash according to the label to preserve any UV-protective coatings.
Completing these steps will help you avoid the pitfalls of choosing purely on color or on a “lightweight” claim. You’ll end up with a garment that truly blocks harmful rays and keeps you as cool as possible.
Conclusion
Selecting the optimal sun-protection shirt requires an informed balance between color, material, weave, and advanced textile treatments. While light colors feel cool initially by reflecting visible light, they often underperform in UV resistance unless they carry a certified UPF rating. Dark colors inherently block more UV but can trap heat—unless offset by cooling finishes or infrared-reflective dyes. Ultimately, the best sun shirts combine dark, tightly woven fabrics with moisture-wicking properties, breathable constructions, and reliable UPF certifications. By understanding the science behind color and material and by carefully reviewing garment specs, you’ll ensure maximum protection against UV rays and a more comfortable experience under the sun.