Save a ton of money on electricity
1. Understanding the Key Features
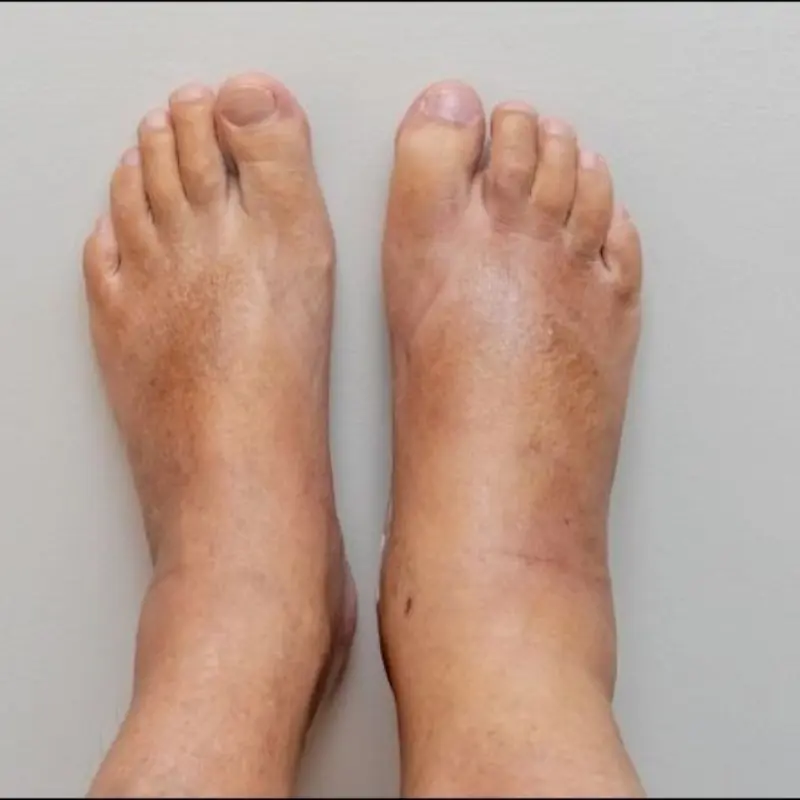
Refrigerators are designed with various controls to regulate temperature and airflow. Two key features highlighted in the image are:
-
Temperature Control Knob:
- This knob allows users to set the cooling intensity within the refrigerator. It usually has settings ranging from "Min" to "Max" or a numeric scale.
- Setting the knob to the appropriate level ensures that the refrigerator maintains the ideal temperature for food preservation without overcooling, which wastes energy.
-
Air Circulation Slider:
- Some refrigerators have an air circulation or vent control slider that regulates the airflow between the freezer and refrigerator compartments.
- Adjusting this slider can balance the cooling between the two sections, ensuring efficient operation based on your storage needs.
2. How These Features Impact Energy Usage
The temperature control knob and air circulation slider directly affect the refrigerator's energy consumption. Here’s how:
-
Overcooling Wastes Energy: Setting the temperature too low causes the compressor to work harder, consuming more electricity. This not only increases your energy bill but may also freeze and spoil fresh produce stored in the fridge compartment.
-
Inefficient Airflow Causes Imbalances: Poor airflow between the freezer and refrigerator sections can lead to uneven cooling. Items in one section may spoil faster, while others freeze unnecessarily, requiring the appliance to work harder.
By optimizing these settings, you can prevent overcooling and ensure even temperature distribution, reducing energy consumption.
3. Ideal Refrigerator Settings for Energy Efficiency
To maximize efficiency and reduce electricity bills, follow these recommended settings:
-
Set the Correct Temperature:
- Refrigerator compartment: 37°F to 40°F (3°C to 5°C) is optimal for preserving food without overcooling.
- Freezer compartment: 0°F (-18°C) is ideal for frozen foods.
- Avoid setting the temperature too low unless absolutely necessary.
-
Adjust the Airflow Slider:
- If your refrigerator is heavily loaded with fresh produce, direct more airflow to the refrigerator compartment.
- For extended freezer use, adjust the slider to favor the freezer section.
-
Use the "Energy-Saving" Mode (if available):
- Some refrigerators have a dedicated energy-saving mode or Eco setting. Activating this feature reduces cooling intensity during periods of low usage, such as overnight.
4. Additional Tips to Reduce Refrigerator Energy Consumption
In addition to optimizing the temperature control knob and airflow slider, consider the following tips:
-
Keep the Refrigerator Full but Not Overcrowded:
- A well-stocked refrigerator retains cold air better, reducing the need for the compressor to work harder. However, avoid overcrowding, as this obstructs airflow.
-
Check the Door Seal:
- Ensure the rubber gasket around the door is intact and forms a tight seal. Leaks can cause cold air to escape, increasing energy usage.
-
Allow Hot Food to Cool Before Storing:
- Placing hot food directly in the refrigerator raises the internal temperature, forcing the compressor to consume more energy.
-
Clean the Coils Regularly:
- Dust and debris on the refrigerator's condenser coils reduce efficiency. Clean them at least twice a year.
-
Defrost Regularly (for Manual Defrost Models):
- Ice buildup in the freezer reduces cooling efficiency. Regular defrosting prevents this issue.
-
Place the Refrigerator in a Cool Location:
- Avoid placing the appliance near heat sources like ovens or in direct sunlight, as this makes it work harder to maintain the desired temperature
News in the same category
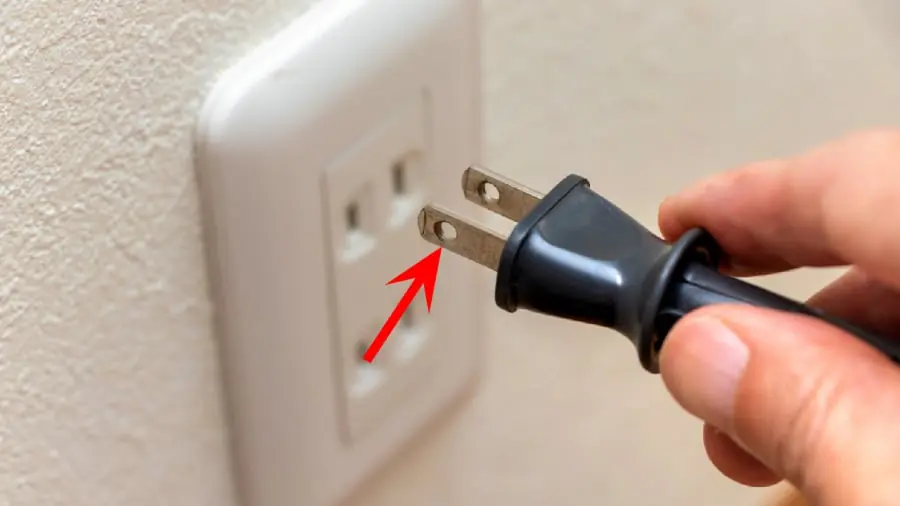


The Special Purpose of the Two Small Holes on Flat Plug Prongs That Many People Don’t Know
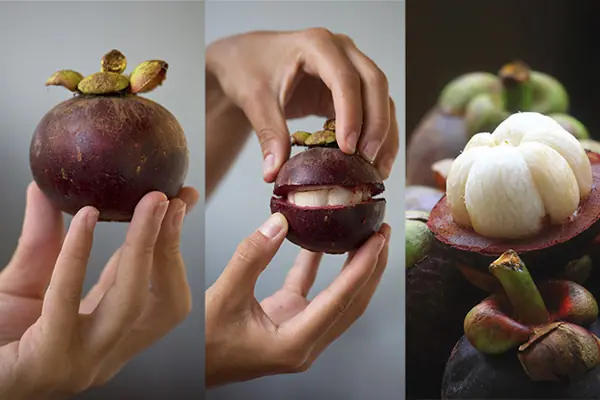

Here's how to choose delicious, sweet mangosteens – all 10 of them are perfect

A 111-year-old man eats these two foods every day—and they’re incredibly cheap at local markets

How to Quickly Eliminate Bed Bugs, Cockroaches, Fruit Flies, and Other Insects from Your Home

Mosquitoes are terrified of this leaf: Place a handful in your home and not a single one will dare to buzz around

Why do people put garlic at the head of the bed before going to sleep? The reason may surprise you.

Snakes are af.raid of these 5 plants - Plant them around your house to repel snakes and protect your family

90% of women don’t know this trick: Add this one thing to the pan and you can fry “everything” without worrying about oil splattering!

When Buying Bananas, Just Say These 3 Words — Sellers Will Think You’re an Expert and Won’t Dare to Cheat You

Stop Storing Ginger in the Fridge! Here’s How to Keep It Fresh for Up to 6 Months

Thought It Was Just Kitchen Waste, Lemon Peels Turn Out to Be a “Hidden Treasure” With 5 Little-Known Uses

Stop washing clothes the old way! Don’t just add detergent—try this quick hack and your clothes will come out like new.

Expert reveals 'military sleep method' that helps you fall asleep in just two minutes
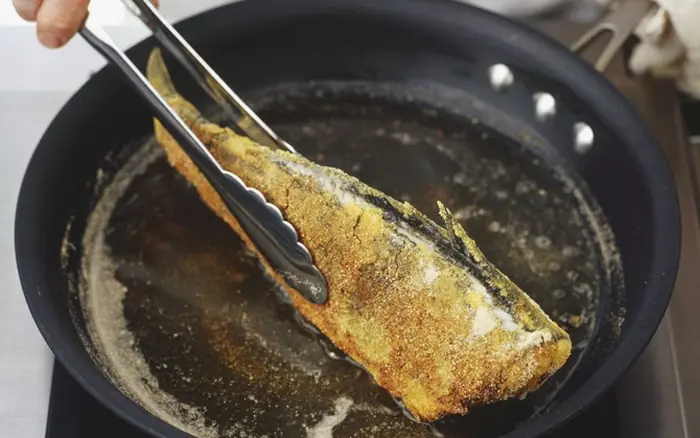

Don’t Fry Fish with Just Oil: Add These 3 Ingredients for Golden, Crispy Fish with No Oil Splatter

Warning for Anyone Using an Air Fryer: There’s One Essential Part You Must Clean—but It’s Often Overlooked
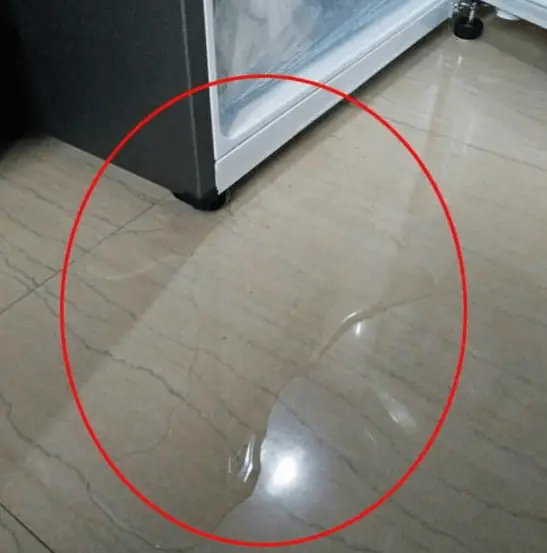

Fridge leaking water: Don't rush to call a technician, just do this to keep your fridge running smoothly without spending money

7 Power-Hungry Home Appliances: Unplugging Them Can Save Electricity—but Also Shorten Their Lifespan
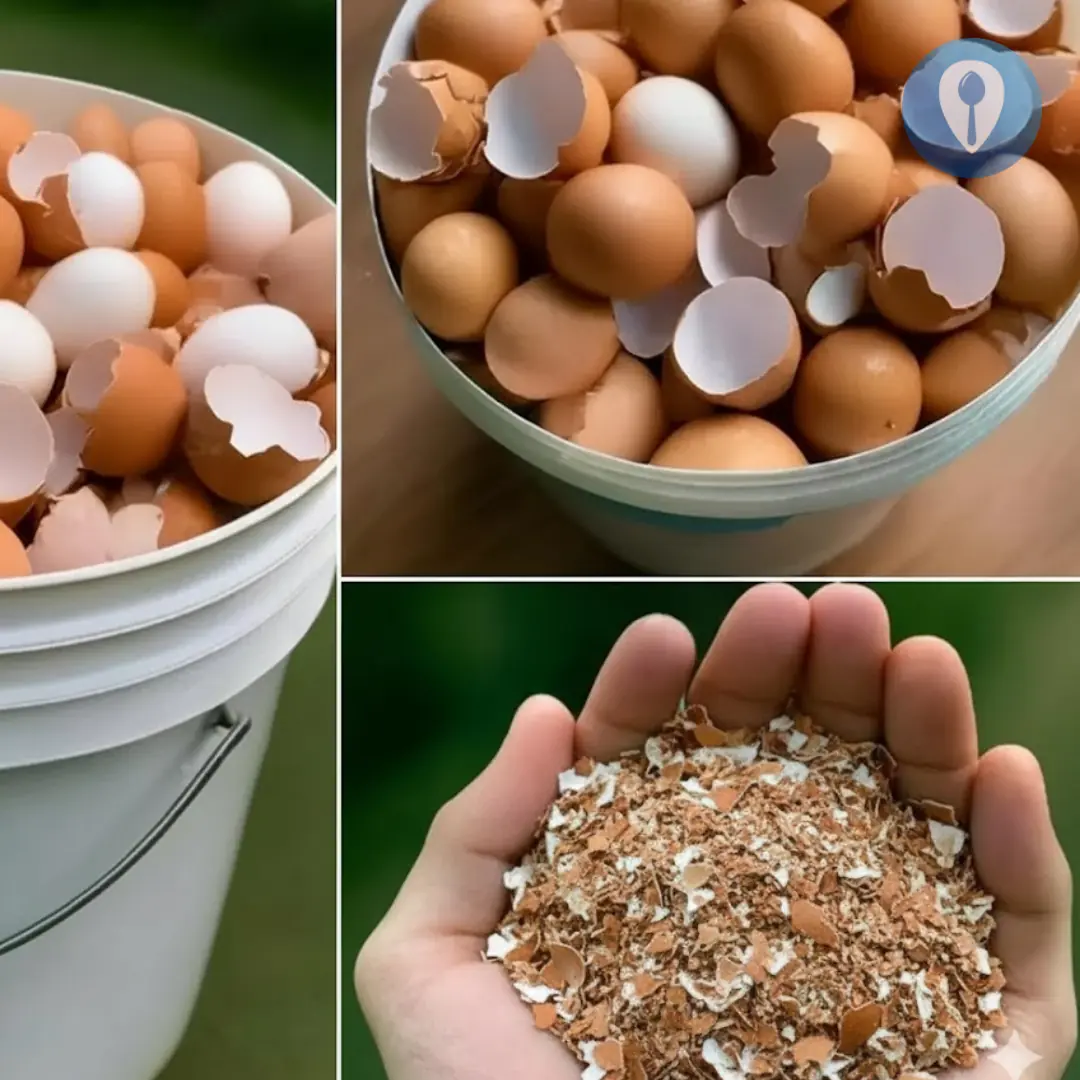

Boil eggshells and say goodbye to the …

Instead of using steel wool, this is the proper way to clean stainless-steel pots and pans to help extend their “lifespan”—a tip many people don’t know.
News Post
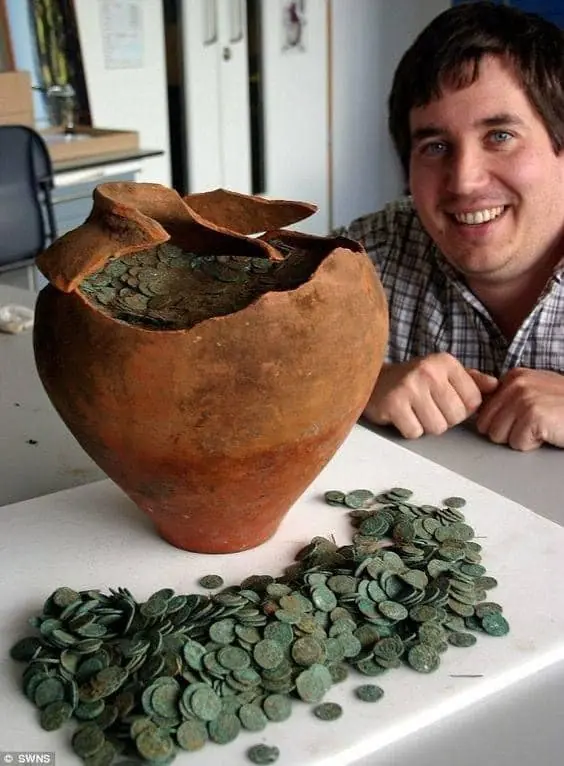

Buried Treasure Fills in Ancient Roman Puzzle

Blueberry Breakfast Quesadilla

The Flight That Celebrated New Year… Twice!

Over 60? 10 Early Dementia Warning Signs You Must NEVER Ignore (Catch Them Before It’s Too Late)
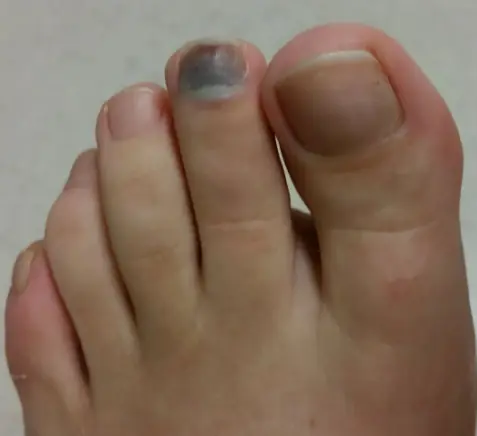
What Causes a Toenail To Turn Black?

Jjajangmyeon – Korean Black Bean Noodles

What To Know and Do About Pain Under Your Left Rib Cage

Understanding the Relationship Between Breast Size and Hormonal Health

Clove Water Sitz Baths for Women: A Gentle Guide to Hygiene and Comfort

Beef, Broccoli & Mushroom Rice Bowl
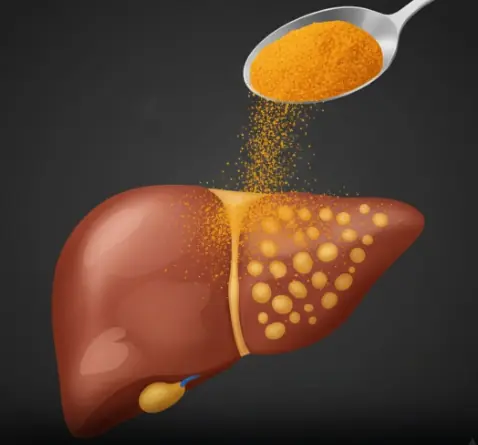
1 teaspoon a day melts away fatty liver naturally
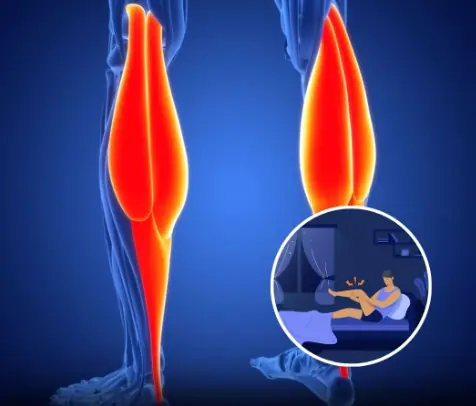
Why Your Legs Cramp At Night And How To Stop It From Happening

Stop pouring hot water down the sink — here’s why!
How to treat nerve pain in the foot, toes & legs

5 foods you should never keep overnight

Crispy Shrimp Rice Balls

Ebi Fry – Japanese Crispy Fried Shrimp

The Special Purpose of the Two Small Holes on Flat Plug Prongs That Many People Don’t Know

Roasted Chicken Leg with Gravy, Mashed Potatoes & Vegetables