5 Taboos When Eating Brown Rice
Eating brown rice this way, many people "bring trouble upon themselves" without realizing it.

Here are 5 taboos when eating brown rice that you need to be aware of to ensure good health and maximize nutrient absorption:
Avoid Eating Undercooked Brown Rice
Brown rice contains more fiber and a tougher bran layer than white rice. Undercooked or raw brown rice can cause digestive issues, leading to bloating, gas, and constipation. The tough bran layer can irritate the stomach lining, causing gastritis or peptic ulcers. Inadequately cooked brown rice reduces the absorption of vitamins and minerals.
It’s recommended to soak brown rice for 4-6 hours or overnight to soften it, making it easier to cook and digest. Cook it with just enough water to ensure the grains are soft and fully cooked. Chewing thoroughly also helps aid digestion.
Do Not Eat Too Much Brown Rice
Brown rice is high in fiber and phytic acid. Overeating it can cause indigestion, hinder mineral absorption, and lead to other health issues. The high fiber content can cause bloating, especially for those with weak digestive systems. Phytic acid in brown rice binds to minerals like iron, zinc, calcium, and magnesium, reducing their absorption. Excessive consumption may also increase the risk of gastrointestinal issues, kidney stones, and thyroid problems due to impaired iodine absorption.
Avoid Combining Brown Rice with Certain Foods
Combining brown rice with certain foods can cause indigestion, reduce nutrient absorption, and even lead to adverse reactions. For example, combining it with milk, acidic fruits (like oranges, tangerines, pineapples), or foods high in tannins (such as tea and coffee) can cause bloating and indigestion. Additionally, calcium in milk and acids in fruits can interfere with the absorption of iron and zinc from brown rice. Brown rice should not be eaten with foods high in oxalates (like spinach) as this may increase the risk of kidney stones.
Do Not Replace White Rice Completely with Brown Rice
While white rice loses some nutrients during processing, it still provides energy and essential vitamins and minerals. White rice offers some important nutrients, and eliminating it entirely from your diet could lead to nutritional deficiencies. A balanced and diverse diet is recommended. Consuming only brown rice may result in a deficiency of nutrients found in other grains.
Avoid Eating Brown Rice If You Have Certain Digestive Disorders
Brown rice is high in fiber, which can be beneficial for many people, but for those with certain digestive conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) or Crohn’s disease, the high fiber content can cause discomfort, bloating, or worsening symptoms. If you suffer from these conditions, it's advisable to limit or avoid brown rice and opt for more easily digestible grains like white rice or rice that has been well-cooked. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making any significant changes to your diet, especially if you have a sensitive digestive system.
News in the same category


People Who Eat Sweet Potatoes for Breakfast Daily Notice These Changes

Study reveals what really happens to your body if you go in sauna directly after working out

Why are the toilets on the train connected directly to the tracks?

A Flower Once Thought Useless Turns Out to Be a Fragrant, Delicious Dish—Now Going Viral
These are the consequences of wearing used…
If you often notice ringing in your ears, this might be a sign that you will suffer from...

Many people don’t know what its purpose is used for
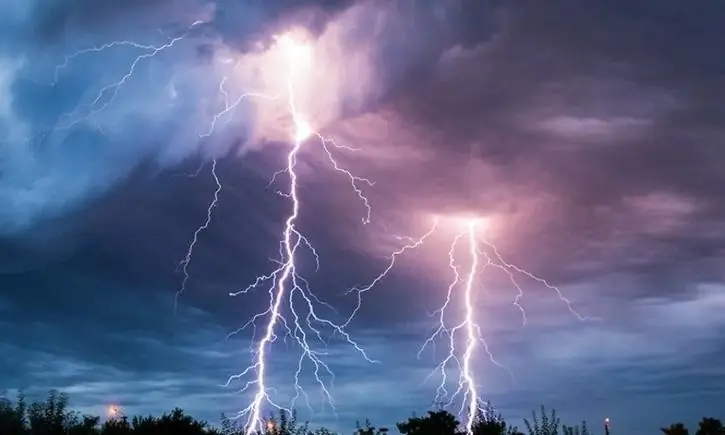

Why should you avoid showering, washing dishes, and doing laundry during a thunderstorm?

Calling all sweet potato fans!

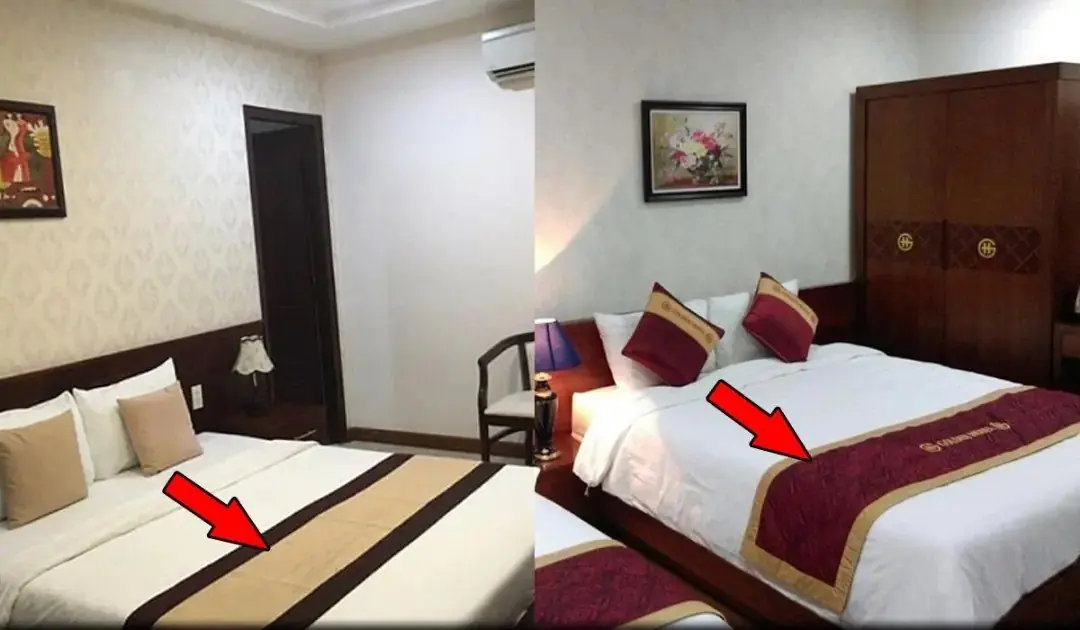
Ever Wondered Why Hotels Put a Cloth Across the Bed? Here’s the Answer

Your Air Conditioner Has a Built-In Way to Indicate Low Refrigerant — Many People Never Notice It

Your Phone Has a Small Setting That Makes Charging Feel Much Faster — Without Harming the Device

Trying to Save Money, Many People Accidentally Bring Serious Danger Into Their Homes

Eating Ginger Without Removing the Peel: Is It Really Harmful or Just a Common Misunderstanding?

Unlock the mystical power of an antique relic

Why are people with M-shaped hands considered special?

How long can cooking oil be stored after opening? How dangerous is it to consume expired oil?

Many people don't realize just how nutritious this vegetable is

Pouring hot water down the kitchen sink may seem helpful, but it actually poses two major risks many people don’t know about
News Post
6 foods that silently drain calcium from the body, the more you eat, the weaker your bones become

90% of women don’t know this trick: Add this one thing to the pan and you can fry “everything” without worrying about oil splattering!
Top Hospitals Issue Stark Warning: This Common Meat May Be “Feeding” Can.cer — Just 50 Grams a Day Raises De.ath Risk by 18%

Black Beans and Black Sesame: The Ancient Pair That “Cleans by Day, Restores by Night” — Yet Most People Use It Wrong

When Buying Bananas, Just Say These 3 Words — Sellers Will Think You’re an Expert and Won’t Dare to Cheat You
The Real Causes of Constant Phlegm and Mucus in Throat — And How to Get Rid of It

3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead
Why you keep waking up with dry mouth—and what it may be telling you

So this is what it does, here is the answer

If You Keep Waking Up at 3AM, The Universe Might Be Trying to Tell You Something

These sudden purple patches on my arms won’t stop appearing, and my doctor is booked until January. What’s happening?

The Hidden Meaning Behind Thumb Rings for Women vs. Men
The Best Foods to Cleanse and Prevent Clogged Arteries

The Ultimate Guide to Cloves: Benefits, Uses, and How They Work

Top 10 Foods to Control Diabetes

90% of Cerebral Infarction Patients Did These 3 Things in the 3 Days Before a Stroke — Chances Are You’re Doing the Second One Right Now

PAN-SEARED WHITE FISH WITH GARLIC CHILI BUTTER
🩺 If Your Kidneys Are in Danger, Your Body Will Warn You With These 8 Signs

You might be eating these every day — and not know the dang:ers
