Health 17/07/2025 10:11
Couple suffers heart and liver d.a.m.age... after eating white mushrooms

Multiple organ damage after eating wild mushrooms
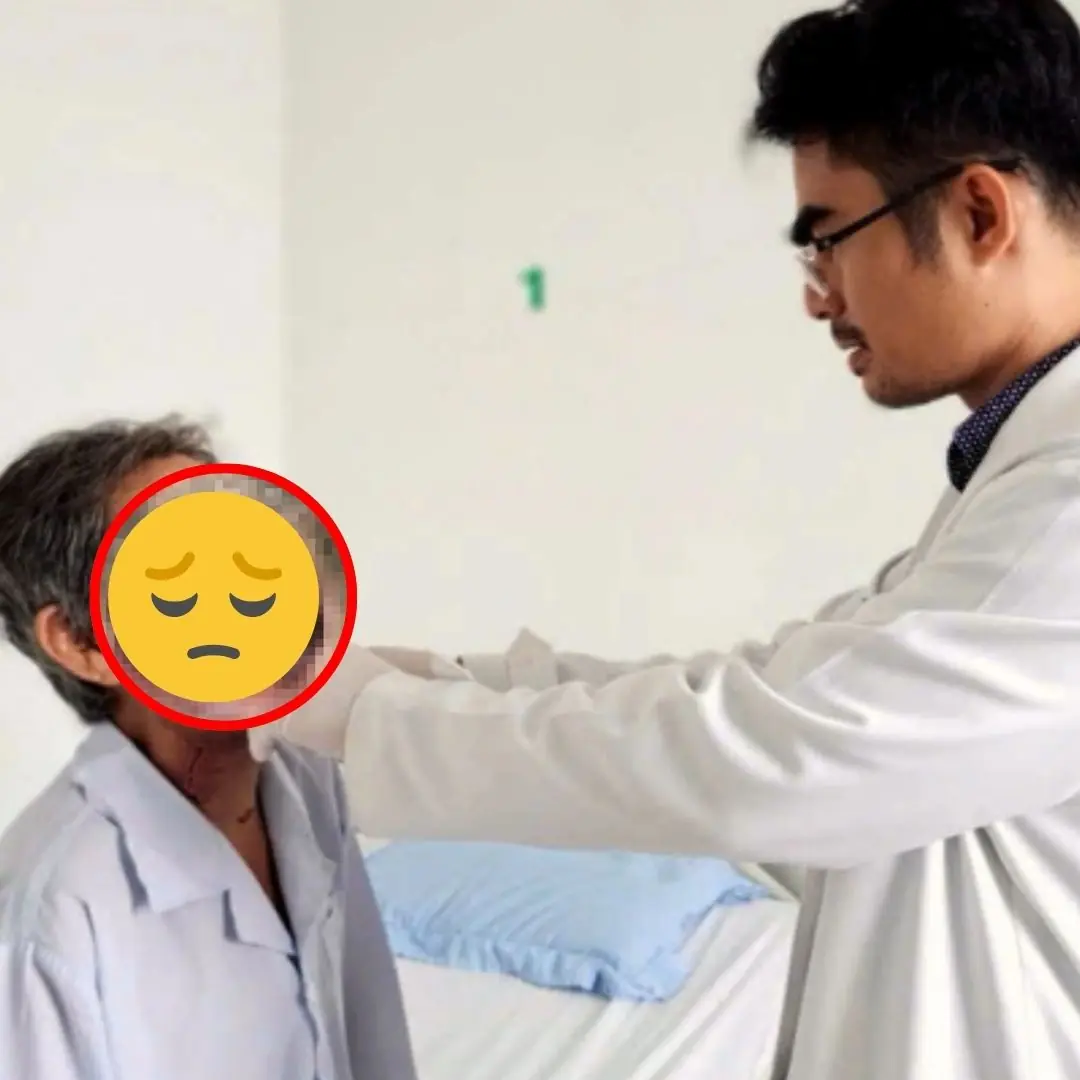
On April 18, the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital informed about 2 cases of critical poisoning from wild mushrooms.
The 18-year-old wife and 21-year-old husband were transferred from Lai Chau General Hospital to Bach Mai Hospital with the diagnosis: Mushroom poisoning causing acute liver failure, blood clotting disorders, heart damage...
The patient's family said that on the afternoon of April 10, the young couple went to the forest to pick mushrooms to eat. This type of mushroom is white, has a round head, and a long stem. About 12 hours after eating the mushrooms, both husband and wife experienced digestive symptoms, including abdominal pain, loose stools, and frequent vomiting.
Both were taken to the emergency room, but their condition worsened so they were transferred to Bach Mai Hospital.
Doctor Nguyen Manh Chien - Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital said that the 2 patients are currently in a deep coma.
Tests showed that the patient had multiple organ damage and failure, irritation of the digestive tract, hepatitis, acute liver failure, hepatic coma, acute renal failure, myocardial damage, severe blood clotting disorders, and a very high risk of death.

The two patients were actively treated by doctors, with plasma exchange, continuous blood filtration, antidotes, resuscitation, etc., but their condition was still very serious.
Slow-poisoning mushrooms: Extremely dangerous
According to Dr. Nguyen Trung Nguyen - Director of the Poison Control Center, Bach Mai Hospital, in Vietnam there are many types of poisonous mushrooms, but they can be classified into 2 groups: The first group is the group that causes slow poisoning, the second group is the group that causes fast poisoning.
The group that causes slow poisoning is the type of mushroom that causes poisoning that manifests late (more than 6 hours after eating), is the most dangerous and often causes death.
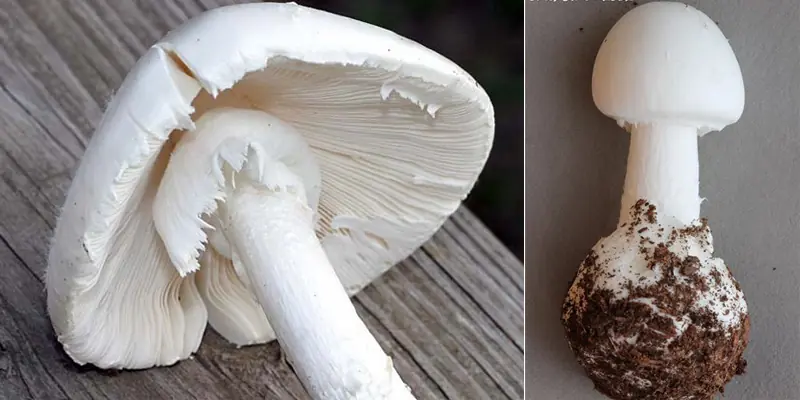
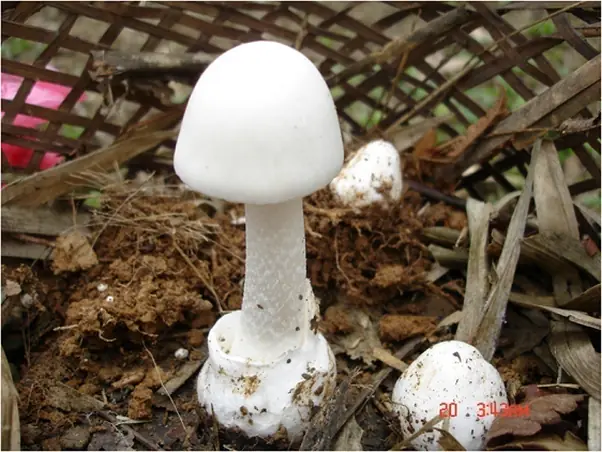
In Vietnam, there are recorded white poisonous mushrooms (Amanita verna) and white poisonous cone mushrooms (Amanita virosa), which are eye-catching, white, young, and look very delicious.
"However, the toxin of these mushrooms is amatoxin, which damages the intestines, liver, kidneys, heart, and other organs," said Dr. Nguyen.
When eating this type of mushroom, poisoning often occurs slowly, at least 6 hours after eating, symptoms appear, and the poisoning usually progresses in 3 stages:
Stage 1: This is the incubation period, lasting from 6-10 hours, when symptoms of abdominal pain, nausea, and acute diarrhea appear many times. This stage lasts 1-2 days.
Stage 2: Digestive symptoms subside, making it easy for patients and inexperienced doctors to misunderstand that they have recovered, but the liver begins to be damaged. This stage lasts for the next 1-2 days.
Stage 3: From about the third day onwards, the patient shows signs of hepatitis, liver failure, kidney failure, blood clotting disorders, jaundice, bleeding, mental stimulation leading to coma, and even death.
"The mortality rate of poisoning from this type of mushroom is estimated by the Poison Control Center to be about 50%, including deaths at the grassroots level and at home," said Dr. Nguyen.

According to this expert, when there are signs of poisoning, that is, more than 6 hours after eating, the poisonous mushroom has passed through the stomach and into the intestines, and even absorbed most of it into the body. Initial emergency measures will no longer be effective.
Patients need to be given emergency care and intensive treatment immediately at a hospital or medical facility with good conditions for anti-poisoning and emergency resuscitation, because the treatment is extremely complicated, requires a lot of effort, resources, and is expensive.
The two cases of patients mentioned above ate mushrooms that caused late poisoning.
Meanwhile, mushrooms that cause early poisoning usually cause poisoning within 6 hours after eating. This group has more types of mushrooms, often with bright colors or unattractive colors.
With this group, poisoning often causes abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, and may have neurological, psychiatric, cardiovascular symptoms... but can be treated and detoxified immediately at the district hospital.
When suspected of eating poisonous mushrooms, if conditions permit and the patient is still conscious (just finished eating), vomiting can be induced to remove the mushrooms from the body."
In case the patient has diarrhea and vomits a lot, the patient can be given fluids to rehydrate and replenish salts. However, the patient still needs to be taken to the nearest medical facility for examination, assessment and emergency treatment by doctors.
"To prevent mushroom poisoning, people should absolutely not pick wild mushrooms to eat (except wood ear mushrooms), because distinguishing between poisonous and non-poisonous mushrooms is very difficult, even for experts is not easy," Dr. Nguyen advised.
News in the same category


Health Warning! Peeing in the shower can severely harm your bladder and pelvic health
Top 7 Foods To Protect Your Bladder — Plus 7 You’d Better Avoid
From a 22-Year-Old's End-Stage Kid.ney Failure: A Wake-Up Call from Your Body’s Warning Signs
Drinking Plain Water Is Healthier Than Eating These 3 Foods in Summer
Cervical Spondylosis — A Common Cause of Neck P.a.in
Stage 4 Can.cer at Age 28: Ignoring 3 Warning Signs Almost Cost Her Life
Caught Early, Treated Better: 5 Warning Signs of Lung Cancer You Must Know
7 Kinds of Pain That Shouldn't Be Ignored

Know About 6 Super-Foods For Osteporosis
Why your va.g.ina smells like fish and how to solve it

Eating One Banana a Day Provides 5 Surprising Health Benefits
Don’t Ignore These 2 Warning Spots
If you wake up in the morning and see your body has these 2 characteristics, be careful, your liver is on the "brink" of failure

Doctors nod in approval: 5 cheap but extremely "high-quality" drinks in preventing stroke

A common mushroom turns out to be the "queen of immunity", rich in 18 types of amino acids and can prevent many diseases
5 Things That Put You at Greater Risk for Developing Varicose Veins
Tired of Poor Circulation and Varicose Veins? Try These 6 Effective Tips!

Papaya Leaves: A Valuable Medicinal Herb
News Post

He Ignored the Signs, Thinking It Was a Ca.n.ker Sor.e—Now His T.o.n.gue Is Gone!
Health 17/07/2025 11:14
First Aid for Jellyfish Stings: What Science Says You Should (and Shouldn’t) Do
Tips 17/07/2025 09:31

Pouring Hot Vinegar Into the Toilet May Seem Wasteful
Tips 16/07/2025 23:42

Health Warning! Peeing in the shower can severely harm your bladder and pelvic health
Health 16/07/2025 23:36

Experts Reveal: The Real Carb Bomb Isn’t White Rice
Facts 16/07/2025 23:29

Top 7 Foods To Protect Your Bladder — Plus 7 You’d Better Avoid
Health 16/07/2025 23:22

Helped Uncle Treat Can.cer but Received a Mysterious Bag in Return
Facts 16/07/2025 23:04

Woman drank 8 limes daily to detox—paid the price for trusting social media advice
Facts 16/07/2025 23:00

Is Eating Soft-Boiled Eggs More Beneficial Than Fully Cooked Eggs?
Facts 16/07/2025 22:53

From a 22-Year-Old's End-Stage Kid.ney Failure: A Wake-Up Call from Your Body’s Warning Signs
Health 16/07/2025 21:35

10 Juicing Mistakes to Avoid at Home: Boost Your Health the Right Way
Facts 16/07/2025 11:45

Why do hotels usually let guests check in at 2pm and check out at 12pm?
Facts 16/07/2025 10:08

No Fridge? No Problem! 14 Foods That Stay Fresh Without It
Tips 16/07/2025 09:04

Drinking Perilla Leaf and Ginger Tea Is Better Than Any Tonic
Facts 16/07/2025 01:29

Drinking Plain Water Is Healthier Than Eating These 3 Foods in Summer
Health 16/07/2025 00:40

Can you spot the two ch.il.dren hidden in the picture?
Relax 15/07/2025 23:29

Can the emergency exit door open while flying? — Little-known fact
Facts 15/07/2025 23:21

Cervical Spondylosis — A Common Cause of Neck P.a.in
Health 15/07/2025 23:12

Stage 4 Can.cer at Age 28: Ignoring 3 Warning Signs Almost Cost Her Life
Health 15/07/2025 17:43