
A leap forward in medicine. Good news for everyone. Read now
Breakthrough Discovery: Scientists Find a Way to Transform Cancer Cells Back to Normal
For decades, cancer treatment has focused on one main goal: destroy the cancer cells. Chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery are all designed to kill or remove abnormal cells as aggressively as possible. While these methods have saved millions of lives, they often come with severe side effects, long recovery times, and the constant fear of relapse.
Now, a new scientific breakthrough is shifting that narrative.
Instead of killing cancer cells, researchers have discovered a method that may reprogram cancer cells and guide them back to a normal, healthy state. If proven safe and effective in humans, this approach could redefine how cancer is treated in the future.
What Makes Cancer Cells Different?
Cancer cells are not foreign invaders. They are originally normal cells that lost control over growth, division, and repair. Genetic mutations disrupt the signals that tell cells when to stop multiplying, when to repair DNA, or when to self-destruct.
Traditional treatments aim to eliminate these cells. The new approach asks a different question:
What if cancer cells could be corrected instead of destroyed?
The Core of the Breakthrough
Scientists studying cellular behavior discovered that certain cancer cells still retain dormant regulatory pathways—mechanisms that once kept them functioning normally. By activating or restoring these pathways, researchers were able to force cancer cells to stop behaving like cancer.
In laboratory studies, malignant cells exposed to specific molecular signals began to:
-
Slow uncontrolled growth
-
Regain normal structure
-
Resume healthy cellular communication
-
Lose their ability to invade surrounding tissue
This process does not erase the cell—it re-educates it.
Why This Approach Is Revolutionary
Transforming cancer cells instead of killing them could reduce many of the complications seen in conventional therapy.
Potential benefits include:
-
Less damage to healthy tissue
-
Reduced inflammation
-
Fewer severe side effects
-
Lower risk of treatment resistance
-
Improved quality of life for patients
Cancer treatments often fail because cancer cells adapt and become resistant. Reprogramming them may bypass this problem entirely.
The Role of the Immune System
Another key element of this discovery involves the immune system. Cancer cells often evade immune detection by disguising themselves. When transformed back into normal-like cells, they lose this invisibility cloak.
This allows the immune system to:
-
Recognize abnormal cells more effectively
-
Prevent future malignant transformation
-
Maintain long-term surveillance
Instead of fighting a war, the body may simply restore balance.
Is This a Cure for Cancer?
It is critical to be clear: this is not yet a cure.
Most findings so far come from laboratory and early-stage studies. Human trials are still required to determine:
-
Safety
-
Effectiveness across cancer types
-
Long-term outcomes
-
Possible risks or unintended effects
However, experts agree this discovery represents a major conceptual shift in cancer research.
What This Means for the Future
Cancer may not be a single disease but a collection of cellular miscommunications. This breakthrough supports the idea that cancer is not always irreversible.
Future treatment strategies may include:
-
Precision cell reprogramming
-
Personalized molecular therapy
-
Combination approaches with immunotherapy
-
Early intervention to prevent malignancy
Instead of destroying the body to save it, medicine may learn how to teach cells to heal themselves.
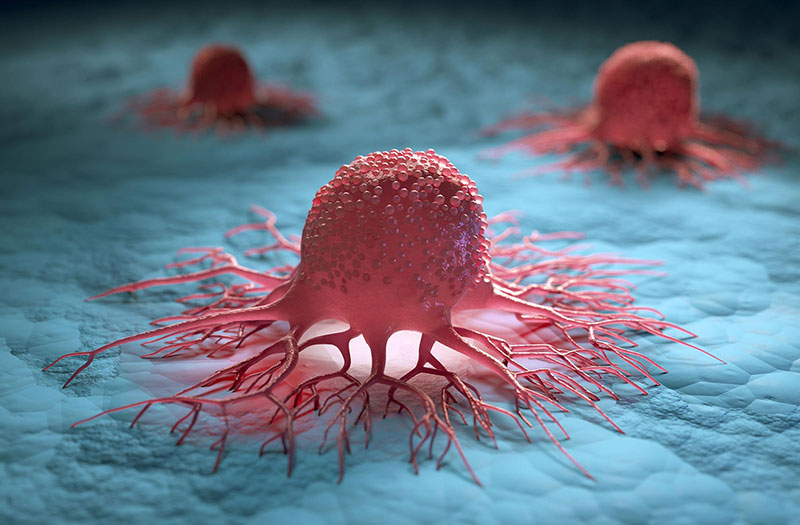
A New Chapter in Cancer Research
This discovery offers hope—not false hope, but scientifically grounded optimism. It challenges long-held assumptions and opens doors to safer, smarter therapies.
Cancer treatment may be moving away from brute force and toward biological intelligence.
And that could change everything.
News in the same category

7 Foods To Eat And 7 Το Avoid For Bladder Health

Longevity May Depend on Age 69: If You Can Still Do These 5 Things Easily, You’re Likely to Live to 90

Some selfish and unhealthy habits from a husband can directly increase the risk of cer.vical can.cer in their wife.
The Foot Symptom That Signals the Damage May Be Irreversible

Deputy Director of Thai Hospital Warns: 5 Foods That Can Lead to Kidney Failure When Eaten in Excess
There is no medicine as benign as the substances in food.
Waking up to these 7 signs may mean your body is silently feeding can.cer cells.

4 best vegetables to help prevent can.cer
8 signs of kid.ney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis
7 Simple Ways to Check If Your He.art Is Healthy

Over 40% of Can.cers Are Preventable: Oncology Doctors Reveal the Daily Habits They Trust Most

U.S. Doctor Recommends 8 “Food-as-Medicine” Ingredients That Lower Cholesterol and Help Prevent Heart Disease and Can.cer

Midnight Phone Reach Leaves Woman Paralyzed on One Side: Doctors Urge the Public Not to Ignore Early Warning Signs
This Food May Help “Slow Down” Can.cer Growth — It’s Hidden in Daily Meals, Yet Many People Don’t Eat Enough of It

Woman Paralyzed on One Side After Turning Over to Grab Her Phone at Night: Don’t Ignore These Warning Signs
A Husband and Wife Were Both Diagnosed With Li.ver Can.cer
The More You Eat This Type of Meat, the Greater the Danger: Over 2,800 People Linked to Bra.in Damage and High Blo.od Pressure

A Man Eats the Same Thing Every Morning—His Doctor Exclaims: “You’re the Healthiest Patient I’ve Ever Seen”
News Post

More People Are Developing Kidney Failure; Doctor Warns of 4 “Tox.ic Drinks” Behind the Surge: “Cut These Down Immediately”

A low price tag isn’t always a good deal—don’t be too quick to buy

7 Foods To Eat And 7 Το Avoid For Bladder Health

Longevity May Depend on Age 69: If You Can Still Do These 5 Things Easily, You’re Likely to Live to 90

Some selfish and unhealthy habits from a husband can directly increase the risk of cer.vical can.cer in their wife.

Mother-in-law came to ask for money with a key to our apartment, but she didn’t expect to find my husband

The Foot Symptom That Signals the Damage May Be Irreversible

Condolences to those who are using these 4 types of electric kettles

A Mother’s Battle: Standing Up for My Children Against Family Betrayal

Deputy Director of Thai Hospital Warns: 5 Foods That Can Lead to Kidney Failure When Eaten in Excess

Mix cloves, honey, and cinnamon and you will thank me! This is my grandmother's secret...

There is no medicine as benign as the substances in food.

Waking up to these 7 signs may mean your body is silently feeding can.cer cells.

4 best vegetables to help prevent can.cer

Boiling Water the Wrong Way? Experts Warn: These 3 Common Habits May Increase Cancer Risk for the Whole Family

8 signs of kid.ney failure that if ignored may require lifelong dialysis

🍗🍝 Ultimate Creamy Pasta with Grilled Chicken & Veggies 🥦

Chicken with Braised Tomatoes and Burrata Ingredients
