Can.cer Cells Love These 3 Flavors the Most — Many People Are Shocked to Realize They Eat Them Every Day
Can.cer Cells Love These 3 Flavors the Most — Many People Are Shocked to Realize They Eat Them Every Day
There are many differences between people who develop cancer and those who remain healthy — including their eating habits.
The saying “disease comes from the mouth” is especially true when it comes to cancer. Numerous studies have shown that diet is closely linked to the development of cancer cells. To reduce your risk, besides maintaining a healthy lifestyle, you should pay close attention to the flavors that cancer cells “love” the most, as listed below.
Cancer cells love rich, greasy flavors from high-fat foods
Fried chicken, grilled meat, French fries… these high-fat foods are hard to resist, but they are also favorites of cancer cells.
A study published in May 2024 in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) by the research team of Academician Tong Erwei from Sun Yat-sen University (China) found that a high-fat diet can increase the risk of cancer, especially breast cancer and melanoma.
Specifically, when the body consumes excessive fat, the gut microbiota changes and releases large amounts of leucine — an amino acid that can stimulate immunosuppressive cells. This weakens the immune system and promotes inflammation and tumor growth.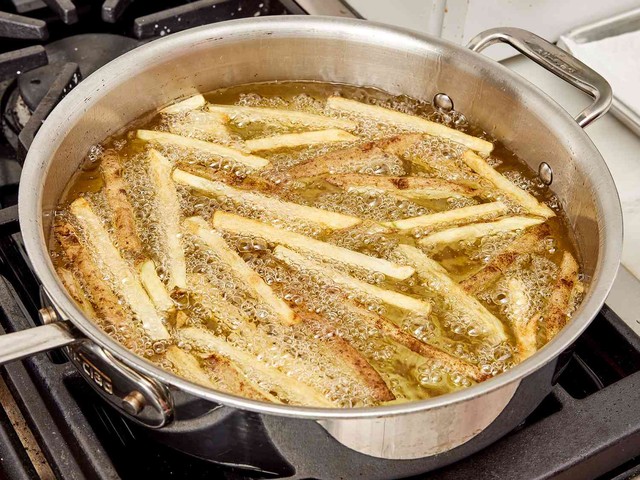
Cancer cells love intensely sweet flavors from excessive sugar
Soft drinks, milk tea, cakes, and desserts are common in daily life, especially among young people. However, consuming too much sugar can significantly increase the risk of many types of cancer.
A U.S. study conducted in 2020 on more than 100,000 people found that those who consumed high amounts of sugar had a significantly higher risk of cancer, particularly breast cancer, compared to those with low sugar intake. In addition, a Harvard University study published in Current Developments in Nutrition in 2022 showed that women who drank more than one sugar-sweetened beverage per day had a 78% higher risk of liver cancer compared to those who rarely consumed such drinks.
The reason is that excessive sugar intake can lead to insulin resistance, increased oxidative stress, hormonal imbalance, and weakened immunity. It also promotes weight gain and inflammation — all of which contribute to the development of cancer cells.
Cancer cells love strong salty flavors from excessive salt intake
Many studies have shown that a high-salt diet is associated with various cancers, especially those affecting the digestive system. Excessive salt intake can cause chronic inflammation and cellular damage, increasing the risk of genetic mutations that lead to cancer. It can also weaken the immune system, creating an environment favorable for cancer cell growth.
Pickled vegetables, salted fish, and smoked meats offer strong flavors but carry hidden cancer risks, particularly gastric cancer. The Gastric Cancer Risk Management Guidelines released by the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association in 2023 pointed out that excessive salt intake can damage the stomach lining, promote genetic mutations, and increase the risk of stomach cancer. An analysis of 26 global studies found that people with high salt consumption had a 25% higher risk of gastric cancer compared to those with low salt intake. Asians are at particularly high risk due to traditionally salty diets.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Chinese Dietary Guidelines (2022), daily salt intake should not exceed 5 grams to reduce health risks. In reality, most people consume nearly twice this amount.
Dietary recommendations to reduce cancer risk
Experts from the Chinese Anti-Cancer Association recommend the following seven dietary guidelines to help prevent cancer:
-
Increase whole grain intake: Rich in fiber and phenolic compounds that help reduce the risk of colorectal, pancreatic, and breast cancers.
-
Prioritize unsaturated fats: From fish, olive oil, and nuts to reduce inflammation and cancer risk.
-
Choose high-quality protein: Such as lean meat, eggs, low-fat dairy, and soy instead of processed meats.
-
Eat plenty of vegetables and fruits: At least two-thirds of daily meals to provide antioxidants and fiber.
-
Drink green tea: Contains polyphenols that help reduce cancer risk.
-
Limit alcohol consumption: According to the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC), more than 740,000 cancer cases worldwide in 2020 were linked to alcohol.
-
Avoid fried, grilled, and charred foods: Opt for steaming, boiling, or stewing to reduce the formation of carcinogenic compounds.
News in the same category


3 Vegetables Known as “Natural Li.ver Tonics,” Widely Sold in Local Markets
3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase a Wife’s Risk of Cervical Can.cer: Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Two Fruits That Can.cer Cells “Love”: Read This to Know What to Avoid

Pine Cone Syrup for Beginners: Natural Benefits, How to Make It, and Practical Uses

Doctors Warn: 2 Winter Bathing Mistakes That Increase the Risk of Headache and Stroke

How Did Song Meiling Live to 106 After a Can.cer Diagnosis at 40? Her Diet May Explain Why
Why do some men grow this nail long?
Doctors Warn: 5 Warning Signs the Body May Send Before a Stroke

Female Student Hospitalized With Severe Kidney Infection After a Common Bathroom Habit

Turns out this is what costs us more electricity than anything else

Behind her battle with a rare disease at a young age was a harmful habit many unknowingly practice every day

32 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore
5 Early Signs of Thyroid Can.cer That Are Easy to Recognize

Three Unusual Neck Signs That May Signal a Serious Health Risk
What Causes a Fishy Vaginal Odor and How You Can Get Rid of It Safely

If You Spot These Tiny Red Marks on Your Arms or Hands, Doctors Urge You to Pay Attention

Getting up to pee often in the night could be a symptom linked to...

A Simple “Finger Test” at Home: Can It Really Detect Early Signs of Lu.ng Cancer?
News Post

If These 4 Foods at Home Start Sprouting, Don’t Throw Them Away: They’re Not To.xic—They’re Even More Nutritious!

Never Smoked but Still Get Lu.ng Can.cer? Doctors Say the Cause Comes from One Thing Almost Everyone Is Exposed To — Especially Asian Women

3 Vegetables Known as “Natural Li.ver Tonics,” Widely Sold in Local Markets

3 Selfish Habits of Husbands That Increase a Wife’s Risk of Cervical Can.cer: Stop Them Now Before They Harm the Whole Family

Two Fruits That Can.cer Cells “Love”: Read This to Know What to Avoid

Pine Cone Syrup for Beginners: Natural Benefits, How to Make It, and Practical Uses

Doctors Warn: 2 Winter Bathing Mistakes That Increase the Risk of Headache and Stroke

Goodbye fleas, ants, and cockroaches with this home remedy

How Did Song Meiling Live to 106 After a Can.cer Diagnosis at 40? Her Diet May Explain Why

Why do some men grow this nail long?

Doctors Warn: 5 Warning Signs the Body May Send Before a Stroke

Female Student Hospitalized With Severe Kidney Infection After a Common Bathroom Habit

Turns out this is what costs us more electricity than anything else

3 Easiest Ways to Get Rid of Mice in Your House

Behind her battle with a rare disease at a young age was a harmful habit many unknowingly practice every day

32 Warning Signs of Magnesium Deficiency You Shouldn’t Ignore

5 Early Signs of Thyroid Can.cer That Are Easy to Recognize

Three Unusual Neck Signs That May Signal a Serious Health Risk
