If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things
If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things
Stomach cancer is often called a “silent disease” because its early symptoms can be vague, mild, or easily mistaken for common digestive
problems. As a result, many cases are only diagnosed at an advanced stage, when treatment options are more limited and outcomes are
less favorable.
Doctors emphasize that paying attention to persistent symptoms after meals can make a critical difference. While these signs do not
automatically mean cancer, they may indicate underlying stomach disorders that require medical evaluation. In some cases, an early
endoscopy can detect problems long before they become life-threatening.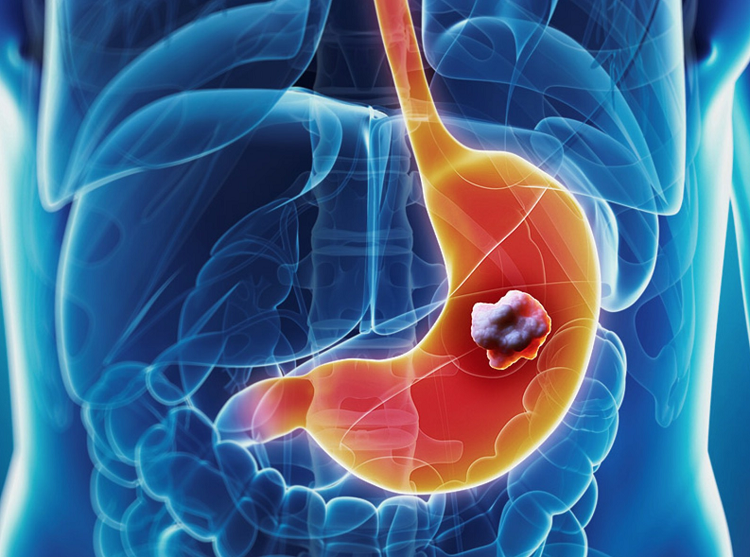
In its early stages, stomach cancer may cause little to no discomfort. When symptoms do appear, they often resemble:
Indigestion
Acid reflux
Mild gastritis
Because these conditions are common, many people delay seeing a doctor. By the time symptoms become severe, the disease may already be
advanced. This is why doctors stress the importance of recognizing warning signs early, especially when they occur repeatedly after eating.
Feeling full very quickly, even after eating only a small portion, can be an early warning sign. This sensation, known as early satiety, may occur
when the stomach lining is irritated or when its ability to expand is reduced.
If this feeling persists over weeks or months and is not related to dieting or lifestyle changes, doctors recommend further evaluation.
Occasional indigestion is normal, but frequent or persistent discomfort after meals is not. Symptoms may include:
Burning or aching pain in the upper abdomen
Pressure or heaviness after eating
Discomfort that does not improve with antacids
When indigestion becomes chronic, especially in people over 40 or those with risk factors, doctors often advise endoscopic examination.
Regular nausea after eating, with or without vomiting, may indicate irritation or blockage within the stomach. In more serious cases, vomiting
may occur shortly after meals or contain traces of blood.
Even mild but persistent nausea should not be ignored if it occurs frequently after eating.
A noticeable decrease in appetite after meals—especially when accompanied by unintentional weight loss—is a red flag. When the stomach
is not functioning properly, the body may subconsciously avoid eating due to discomfort.
Doctors consider unexplained weight loss one of the most important warning signs that warrants immediate medical attention.
Occasional bloating is common, but constant bloating or a heavy sensation after meals that does not resolve may suggest delayed
stomach emptying or irritation of the stomach lining.
If bloating persists despite dietary changes, further investigation may be necessary.
An endoscopy allows doctors to visually examine the stomach lining and detect:
Inflammation
Ulcers
Precancerous changes
Early-stage cancer
Doctors may recommend early endoscopy if:
Symptoms persist for more than 2–3 weeks
Symptoms worsen over time
There is a family history of stomach cancer
The patient is over a certain age or has known risk factors
Early detection dramatically improves treatment outcomes.
Certain groups are at higher risk and should be particularly attentive to symptoms:
People with chronic gastritis or H. pylori infection
Individuals with a family history of stomach cancer
Smokers or heavy alcohol consumers
People with long-term digestive disorders
For these individuals, doctors may recommend screening even before symptoms become severe.
Not every digestive issue is serious, but persistent after-meal symptoms should never be ignored. Stomach cancer is often detected late
precisely because early signs are subtle and dismissed as routine indigestion.
Listening to your body, tracking symptoms, and seeking medical advice early can save lives. If you experience ongoing discomfort after meals,
consult a healthcare professional. An early endoscopy is not something to fear - it can be a powerful tool for reassurance, early treatment, and long-term health.
Early attention can make all the difference.

If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things

When to eat sweet potatoes: 4 times that make a real difference

6 situations where eggs may not be suitable for everyone
Thy.roid no.dules on the rise: Doctors advise limiting certain foods

How to Know if You Have Neuropathy in Your Feet
4 Common Morning Habits That May Increase Stroke Risk — and Should Be Avoided at Any Age
Doctors warn five post-meal symptoms may signal stomach cancer early.

Scratched cookware could silently add thousands of microplastics to meals.

Drooling While You Sleep? Here Are 6 Possible Causes

How carrot juice supports skin health and eye function

Surprising benefits of dates most people overlook
Kidney Health Alert: Key Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention
Why kidney problems are appearing before age 30: 2 habits doctors warn against

Support liver health: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits to include daily
Mr. Tran Vu, 56 years old, living in China, has been diagnosed with diabetes for more than ten years.

Most people feel unsettled at the thought of snakes wandering too close to their balcony, garden, or home.

Her secrets to a long and healthy life have garnered widespread interest, blending a disciplined lifestyle with a meticulous diet.
The benefits of eggs are sometimes overshadowed by mainstream media attention to their potential drawbacks.

If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things

When to eat sweet potatoes: 4 times that make a real difference

6 situations where eggs may not be suitable for everyone

Thy.roid no.dules on the rise: Doctors advise limiting certain foods

How to Know if You Have Neuropathy in Your Feet

4 Common Morning Habits That May Increase Stroke Risk — and Should Be Avoided at Any Age
Doctors warn five post-meal symptoms may signal stomach cancer early.

Scratched cookware could silently add thousands of microplastics to meals.

Drooling While You Sleep? Here Are 6 Possible Causes


How carrot juice supports skin health and eye function

Surprising benefits of dates most people overlook

Kidney Health Alert: Key Warning Signs That Require Immediate Attention

Why kidney problems are appearing before age 30: 2 habits doctors warn against

Support liver health: 4 vegetables and 2 fruits to include daily

These 5 plants in your garden could make it more appealing to snakes

Mr. Tran Vu, 56 years old, living in China, has been diagnosed with diabetes for more than ten years.

Most people feel unsettled at the thought of snakes wandering too close to their balcony, garden, or home.

Her secrets to a long and healthy life have garnered widespread interest, blending a disciplined lifestyle with a meticulous diet.