
Fatty liver disease diet: Crucial foods you should avoid to slash your risk of symptoms
Fatty Liver Disease Diet: Crucial Foods You Should Avoid to Reduce Symptoms
Fatty liver disease is a growing health concern worldwide, affecting millions of people due to poor diet, lack of exercise, obesity, and excessive alcohol consumption. While the condition often develops silently, what you eat plays a decisive role in whether the disease improves or worsens. Health experts agree that avoiding certain foods can significantly reduce symptoms and protect liver function.
Why Diet Matters in Fatty Liver Disease
Fatty liver disease occurs when excess fat builds up in liver cells, interfering with the liver’s ability to function properly. Over time, this can lead to inflammation, liver damage, and even cirrhosis if left unmanaged. One of the most effective ways to control the condition—especially in its early stages—is through dietary changes.
1. Sugary Foods and Drinks Are a Major Trigger
Foods high in added sugars are among the biggest contributors to fatty liver disease. Sugary soft drinks, fruit juices with added sugar, sweets, cakes, and desserts increase insulin resistance and encourage fat accumulation in the liver. Fructose, in particular, is processed almost entirely by the liver and can rapidly worsen fat buildup.
Cutting back on sugar has been shown to lower liver fat and improve liver enzyme levels.
2. Alcohol Can Severely Damage the Liver
Whether fatty liver disease is alcohol-related or not, drinking alcohol places additional strain on the liver. Alcohol promotes inflammation and accelerates liver damage, increasing the risk of fibrosis and cirrhosis.
Doctors strongly advise people with fatty liver disease to avoid or completely stop alcohol consumption to prevent disease progression.
3. Saturated Fats and Processed Meats Increase Liver Fat
Foods high in saturated fat—such as sausages, bacon, fast food, fried foods, butter, and fatty cuts of red meat—can raise “bad” cholesterol levels and increase fat storage in the liver. These foods also promote inflammation, making liver recovery more difficult.
Replacing them with lean proteins and healthy fats can significantly benefit liver health.
4. Refined Carbohydrates Can Worsen Symptoms
Refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, pastries, and sugary cereals cause rapid spikes in blood sugar. This forces the liver to convert excess glucose into fat, worsening fatty liver disease over time.
Health specialists recommend choosing whole grains instead, which are digested more slowly and support better blood sugar control.
5. Long-Term Dietary Changes Can Improve Liver Health

Research suggests that fatty liver disease—particularly in its early stages—can be reversed with consistent lifestyle changes. A diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats, combined with regular physical activity and weight management, can reduce liver fat, lower inflammation, and improve overall liver function.
Conclusion
Fatty liver disease does not have a single cure, but diet remains one of the most powerful tools for managing and improving the condition. Avoiding sugary foods, alcohol, processed meats, refined carbohydrates, and unhealthy fats can dramatically reduce symptoms and slow disease progression. Making informed food choices today can protect your liver and improve long-term health.
News in the same category

This is how my grandmother treated varicose ve.ins… with just 3 kitchen ingredients

You must know these 5 things

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Two Eggs a Day?

Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutrition Facts (Evidence Based)

When you see these 4 conditions while walking, be alert for diabetes
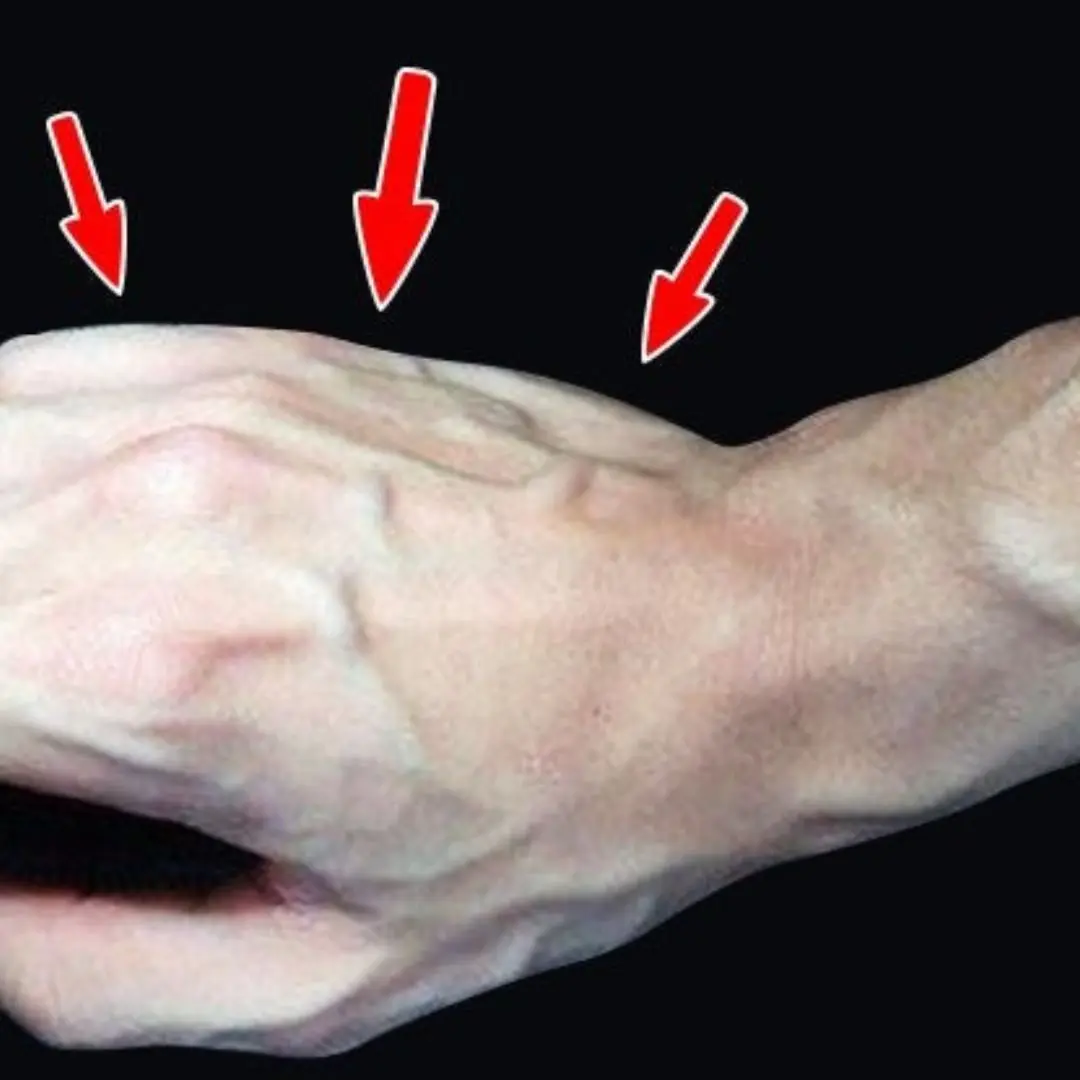
Bulging Veins Aren’t Always Harmless — Here’s What You Need to Know

Clove Water: The Hidden Power in the Kitchen

Never shower at this time of day after 70 – Here’s why doctors warn it could be dan.gerous
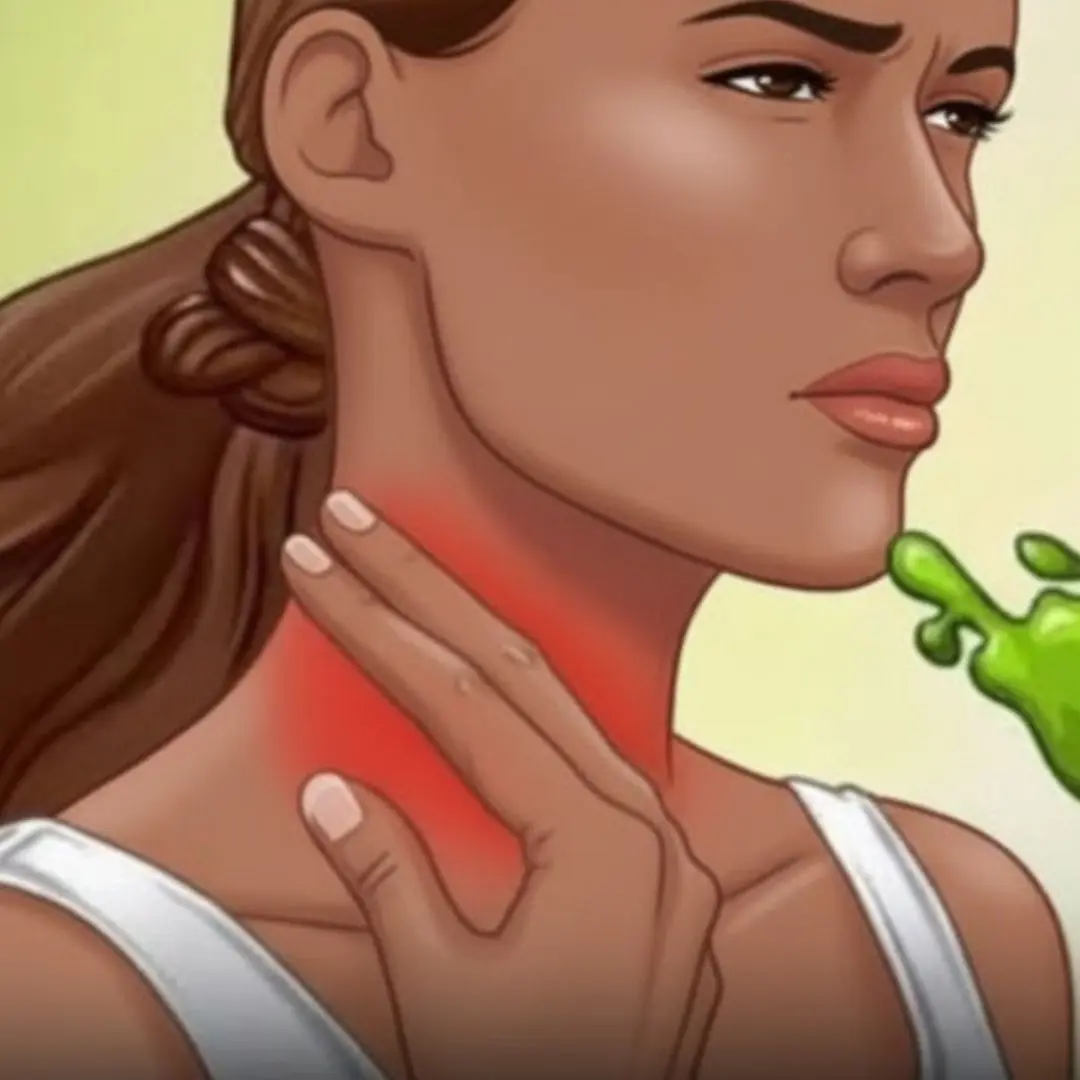
Why your throat keeps filling with mucus - the real causes revealed
Your body will warn you of these 7 signs
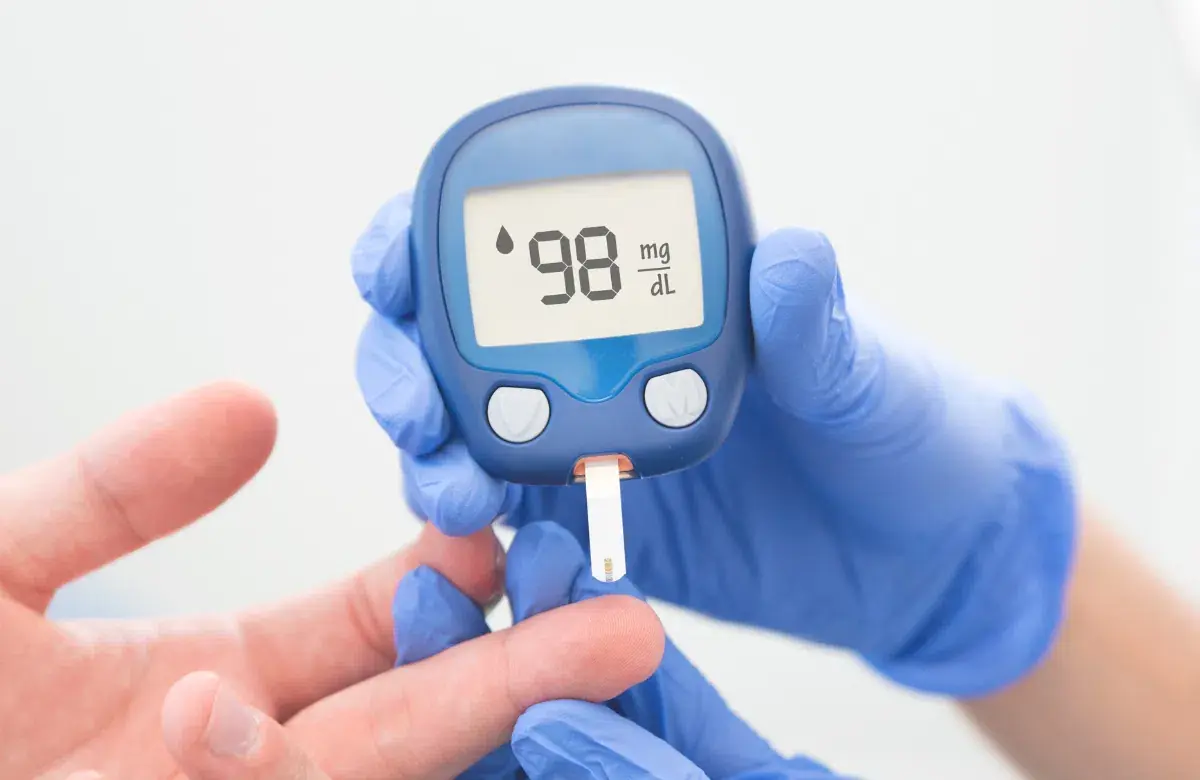
When the body shows 5 se.rious symptoms: What it may signal about advanced dia.betes

Why salmon is no longer the health food we thought it was?

Taro Root: The Ancient Superfood Transforming Health and Sustainability

Eating chicken eggs is harmful to these 5 groups of people: Stay away!
8 Signs You Have Low Blo:od Oxygen Levels

Stretch your ring finger with your thumb and hold it for a few seconds. You'll love the reason!
8 Powerful Foods That May Help Fight Can:cer Naturally

Washing dishes this way is no different from “taking poi.son”: 4 wrong habits many families are making
News Post

Breakthrough Discovery: PARP1 Enzyme Could Revolutionize the Fight Against Aging

This is how my grandmother treated varicose ve.ins… with just 3 kitchen ingredients

You must know these 5 things

What Happens to Your Body When You Eat Two Eggs a Day?

Proven Health Benefits of Celery & Nutrition Facts (Evidence Based)

When you see these 4 conditions while walking, be alert for diabetes

Slow Cooker Tomato Tortellini Soup with Ground Beef

Bulging Veins Aren’t Always Harmless — Here’s What You Need to Know

Clove Water: The Hidden Power in the Kitchen

Refreshing Cherry Cheesecake Parfait

Never shower at this time of day after 70 – Here’s why doctors warn it could be dan.gerous

Why your throat keeps filling with mucus - the real causes revealed

Your body will warn you of these 7 signs

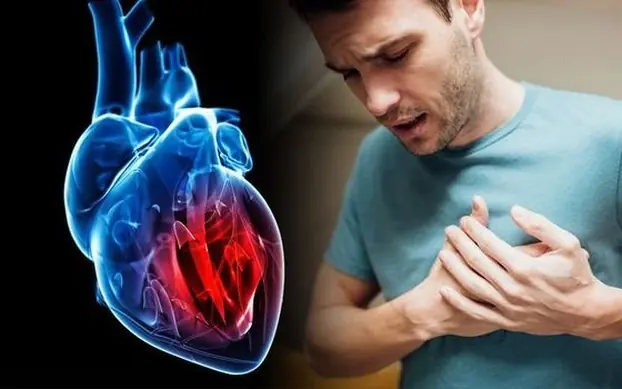
Could sleeping with a fan on cause heart attacks? Understanding the potential heart health dangers

When the body shows 5 se.rious symptoms: What it may signal about advanced dia.betes

What happens to the soul when the body is cremated?

Why salmon is no longer the health food we thought it was?

Taro Root: The Ancient Superfood Transforming Health and Sustainability
