6 foods that silently drain calcium from your body
6 foods that silently drain calcium from your body

Sweet potatoes look harmless. Cozy. Healthy-core. Gym-girl approved.
But real talk: this root vegetable has layers. Eat it right, it’s a glow-up food. Eat it wrong, it can low-key mess with digestion, blood sugar, or
even nutrient balance.
Before loading another plate, here are 13 important facts about sweet potatoes that most people never talk about.
Yes, sweet potatoes are carbs - but they’re complex carbs, meaning they digest slower and provide steadier energy than white bread or
sugary snacks.
What makes them special:
High in fiber
Rich in antioxidants
Naturally sweet without added sugar
That said, “healthy” doesn’t mean unlimited. Portion size still matters.
Orange, purple, white - these aren’t just aesthetic choices.
Orange sweet potatoes → high in beta-carotene (vitamin A power)
Purple sweet potatoes → loaded with anthocyanins (anti-aging, anti-inflammatory vibes)
White sweet potatoes → milder sweetness, lower glycemic impact
Different color = different benefits. Rotate them instead of sticking to one type.
Sweet potatoes have a moderate to high glycemic index, especially when:
Overcooked
Mashed
Eaten alone without protein or fat
If blood sugar balance matters, pair sweet potatoes with:
Eggs
Fish
Yogurt
Nuts or olive oil
Context matters more than the food itself.
How sweet potatoes are cooked can upgrade or downgrade their benefits.
Best options:
Steamed
Boiled
Baked with skin on
Not-so-great:
Deep-fried
Loaded with sugar or syrup
Frying = higher calories, oxidized fats, and lost nutrients. Not the move.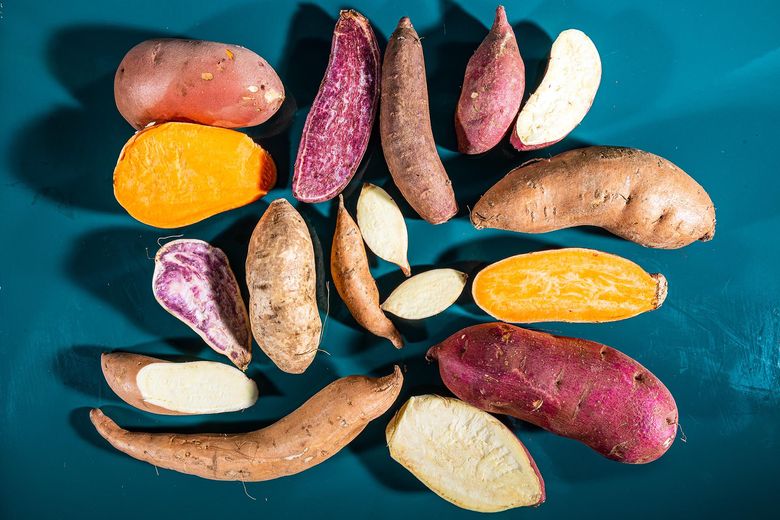
One medium orange sweet potato can provide over 400% of daily vitamin A needs.
Amazing for:
Eye health
Skin glow
Immune support
But too much vitamin A long-term (especially if combined with supplements) can cause imbalance. Balance is key.
Sweet potatoes are high in:
Fiber
Resistant starch
Great for gut health - until it’s too much.
Overdoing it may cause:
Bloating
Gas
Stomach discomfort
If digestion feels off, reduce portion size or cook them more thoroughly.
Sweet potatoes contain goitrogens (mild ones), which may interfere with iodine uptake if eaten excessively and raw.
Good news:
Cooking reduces this effect
Normal portions are generally fine
If thyroid health is a concern, variety in vegetables is safer than relying on one food.
They’re filling, fiber-rich, and satisfying. That’s the win.
But here’s the plot twist:
Large portions = calorie overload
“Healthy” doesn’t mean zero-calorie
Weight goals depend on how much and how often, not just what food it is.
Thanks to antioxidants like:
Beta-carotene
Anthocyanins
Vitamin C
Sweet potatoes may help:
Reduce inflammation
Support joint health
Improve recovery
Especially helpful for active lifestyles or stress-heavy routines.
The fiber feeds good gut bacteria, which affects:
Digestion
Mood
Immunity
But again - start slow if not used to high-fiber foods. Gut health is a marathon, not a sprint.
Sweet potatoes are naturally gluten-free, making them great for people avoiding gluten.
Just don’t confuse gluten-free with low-carb. They still count as carbs and should be treated like one nutritionally.
The skin contains:
Extra fiber
Antioxidants
Micronutrients
As long as they’re washed properly, eating the skin = more benefits, less waste.
When sweet potatoes work best:
Pre-workout (energy boost)
Post-workout (glycogen refill)
Lunch (sustained energy)
Less ideal:
Late-night overeating
Paired with sugary sauces
Food timing doesn’t have to be strict - just intentional.
Sweet potatoes are not the villain. They’re also not magic.
They can:
Support health
Boost energy
Improve digestion
Or:
Spike blood sugar
Cause bloating
Stall progress
It all comes down to portion, preparation, and balance.
So yeah 0 don’t eat sweet potatoes blindly. Eat them smart.

6 foods that silently drain calcium from your body
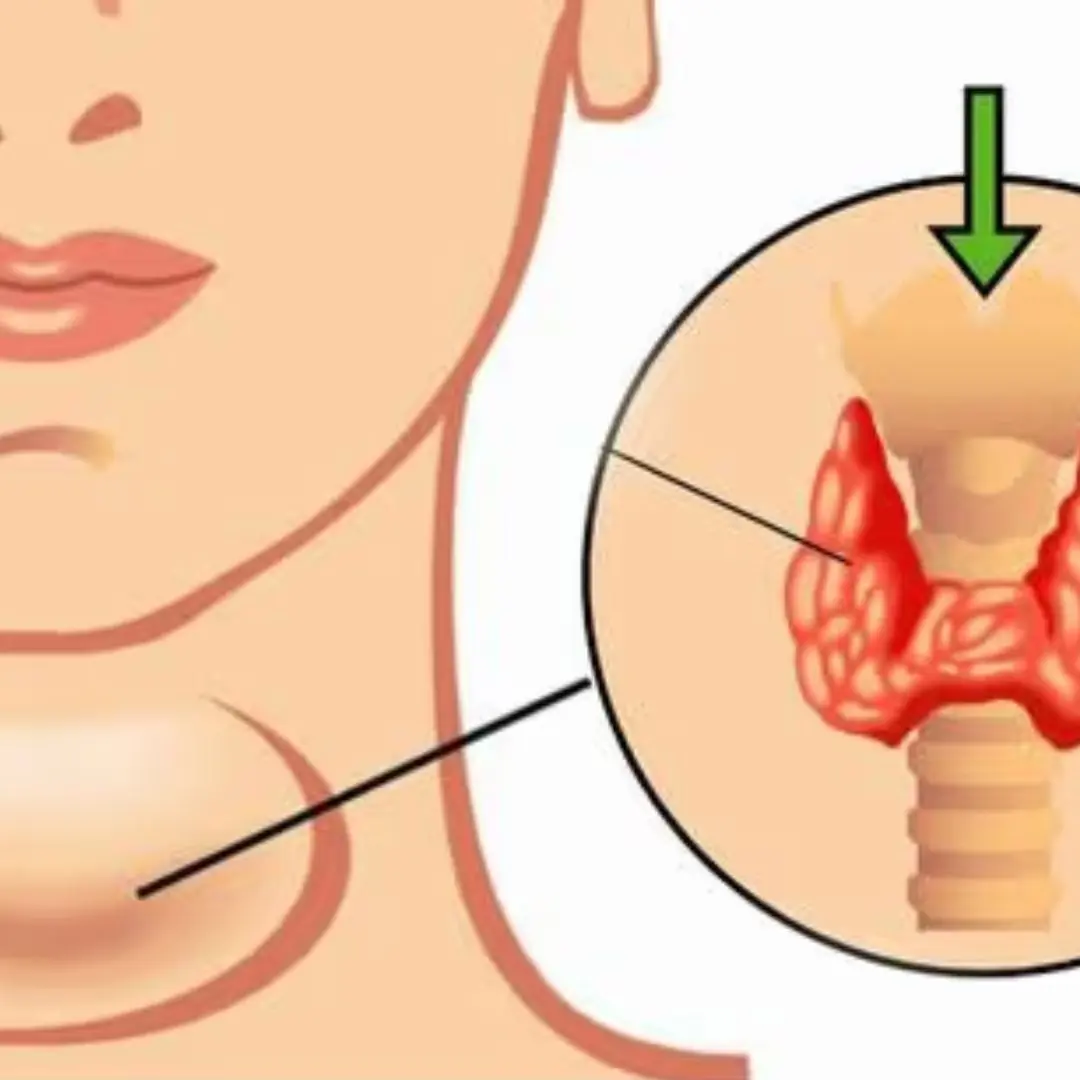
Thy.r.o.id can.cer warning: 7 early body changes, and the first 3 are surprisingly common
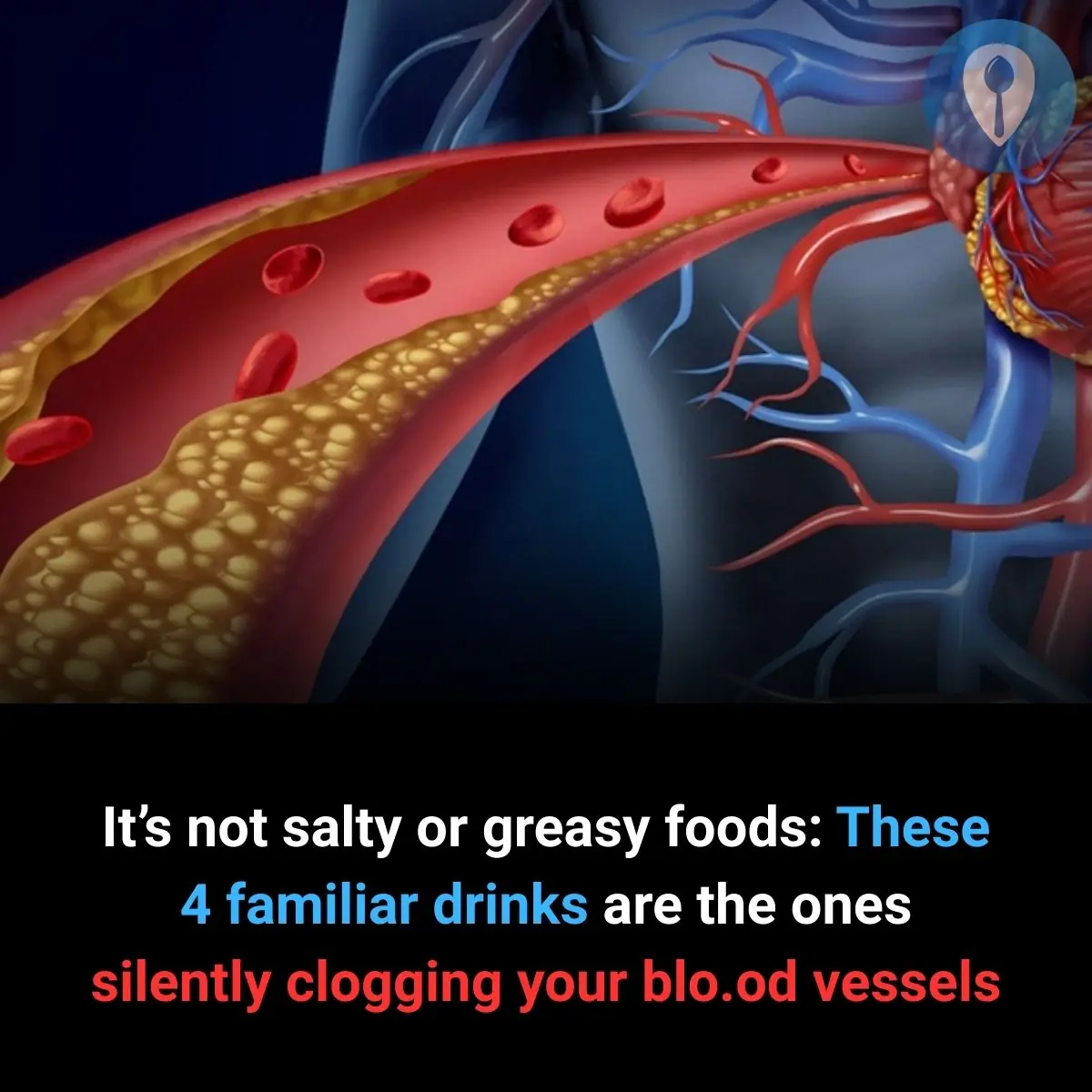
It’s not salty foods or fatty meals—everyday familiar drinks are quietly “eroding” your blood vessels.
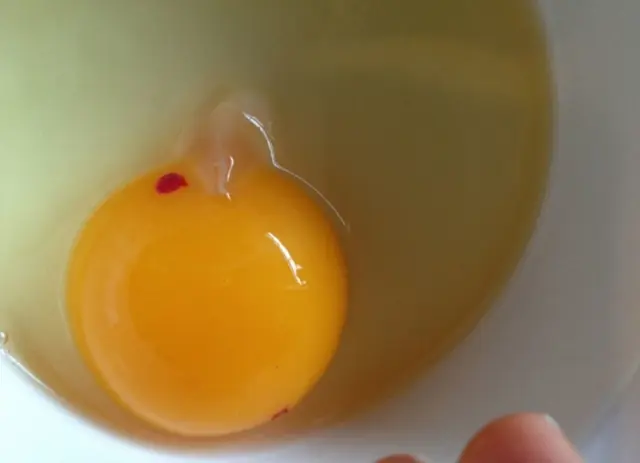

These are eggs that do not meet quality and food safety standards.

5 early clinical indicators of cer.vical can.cer
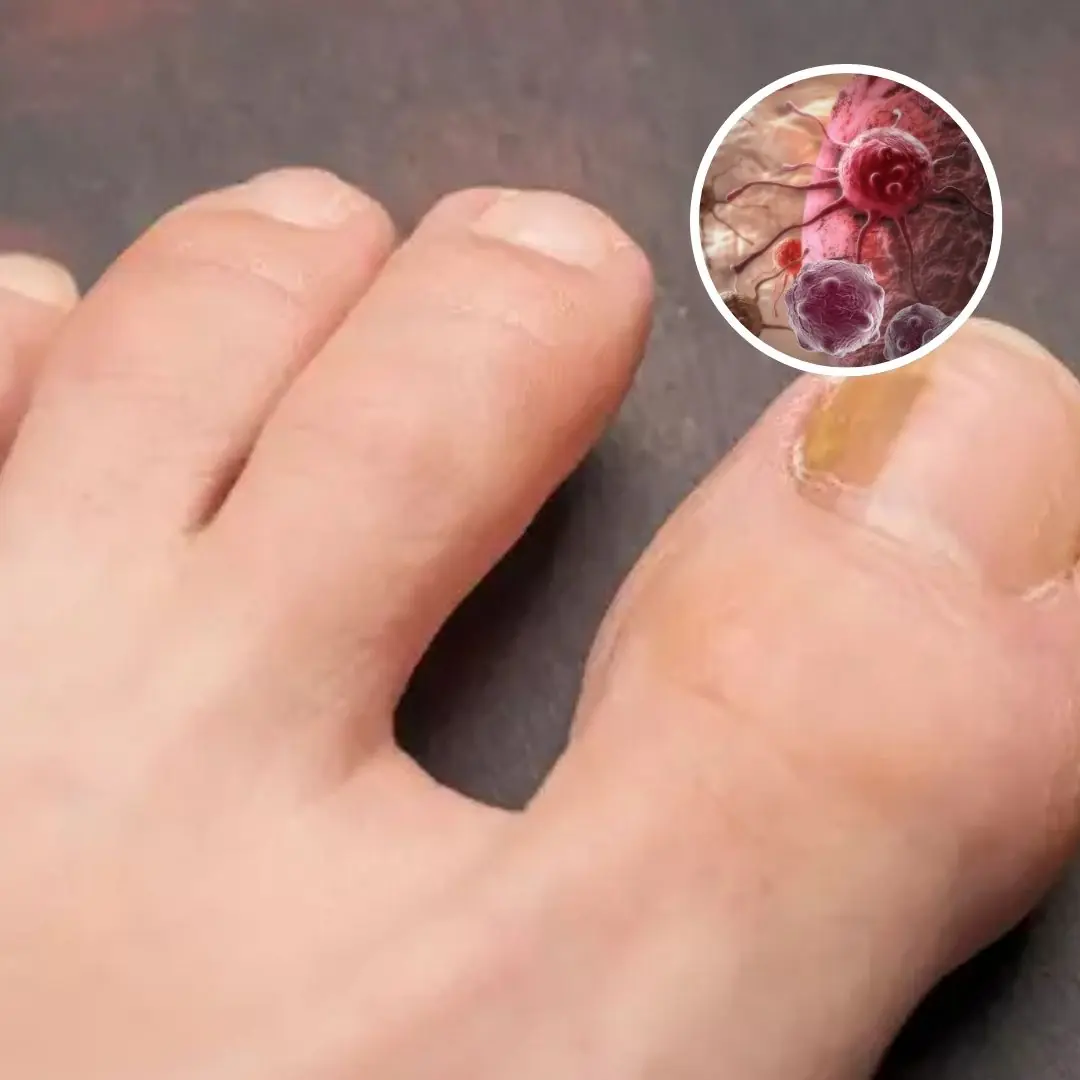
Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails
Doctors warn: The body may signal a str.oke 15 minutes before it happens - act fast

4 finger changes that may indicate lung can.cer
Experts issue warning for cancer symptom that can appear on pillows in the morning

Hand-related warning signs associated with advanced liver dis.ease
Spleen Cancer: A Rare But Dangerous Disease - You Need To Know!

🥬 Eat More Celery: A Simple Superfood with Powerful Health Benefits
It was an ordinary evening for Mr. Nguyen, a 40-year-old office worker in good health—or so he thought.
Ginger is one of the most widely used and beloved ingredients in kitchens around the world.

Have you ever been woken up in the middle of the night by a strong cramp in your leg that felt as if it was going to tear your muscle apart?

When Gerry Cannon invited me to co-author his forthcoming book

Scientists have developed an AI system that reads tiny electromagnetic shifts in the ground before earthquakes.

Gyan Mudra, an elegant hand gesture with deep roots in yoga, has been treasured for centuries for its ability to calm the mind and sharpen focus.
Have you ever stopped to wonder whether your body might be signaling a problem long before a blood test confirms it?
Have you ever jolted awake in the middle of the night with a mouth so dry it feels like it’s coated in dust?

6 foods that silently drain calcium from your body
The Technology No One Else Can Build

Strawberry Cheesecake Cupcakes

Thy.r.o.id can.cer warning: 7 early body changes, and the first 3 are surprisingly common

It’s not salty foods or fatty meals—everyday familiar drinks are quietly “eroding” your blood vessels.

These are eggs that do not meet quality and food safety standards.

What are those “Small bags” on the wall really?

The real reason hotels use white bed linens

5 early clinical indicators of cer.vical can.cer

Doctors warn of little-known cancer symptom you can see on your toenails

Doctors warn: The body may signal a str.oke 15 minutes before it happens - act fast

Woman who died and came back to life after stroke reveals exactly what she saw

4 finger changes that may indicate lung can.cer

Experts issue warning for cancer symptom that can appear on pillows in the morning

Hand-related warning signs associated with advanced liver dis.ease

The hidden reason you should stop charging your phone to 100%

Spleen Cancer: A Rare But Dangerous Disease - You Need To Know!

🥬 Eat More Celery: A Simple Superfood with Powerful Health Benefits

It was an ordinary evening for Mr. Nguyen, a 40-year-old office worker in good health—or so he thought.

Ginger is one of the most widely used and beloved ingredients in kitchens around the world.