
Things to keep in mind when eating jellyfish to avoid food poisoning

Jellyfish are soft-bodied mollusks, an abundant food source from the sea, and are easily prepared into delicious dishes enjoyed by many.
Jellyfish are abundant in Vietnam and have high nutritional value. 100g of jellyfish contains 12.3g of protein, 0.1g of fat, 3.9g of sugar, 182mg of calcium, 9.5mg of iron, and 132mg of iodine.
Jellyfish are high in protein and antioxidants, and especially rich in omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, as well as polyphenols, which help reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease. Polyphenols, in particular, promote brain function and help prevent several chronic diseases, including cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer.
Things to keep in mind when eating jellyfish.
There are many different types of jellyfish, but not all are edible. Jellyfish that are consumed as food are not poisonous. However, if not prepared properly, jellyfish can cause poisoning. Caution is also needed during consumption as it can cause allergic reactions and anaphylactic shock, affecting health.
If you've never eaten jellyfish before, start with small amounts. If you don't experience any adverse reactions, you can then eat more to prevent potential allergies. When eating, ensure you follow food safety rules and only consume properly processed jellyfish; do not eat raw sea jellyfish.
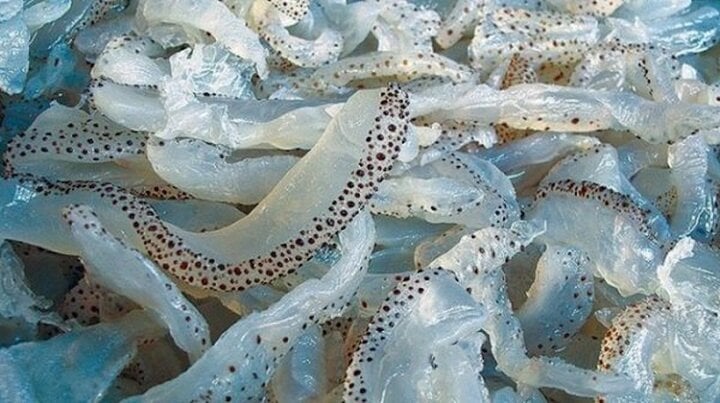

Jellyfish are delicious, but children under 8 years old should not eat them.
To ensure public health and prevent food poisoning from jellyfish during the summer, the Food Safety Department advises people not to consume fresh (unprocessed) jellyfish as food, especially in raw salads, and particularly not to feed jellyfish (including processed jellyfish) to children. Only properly processed jellyfish should be consumed.
Fresh jellyfish must be soaked three times in a brine and alum solution until the jellyfish meat turns a light red or light yellow color before it can be used for cooking.
It's best to avoid eating too much jellyfish to prevent the risk of excess aluminum in the body, because many people may use alum to soak jellyfish during preparation. This is a chemical compound commonly known as aluminum potassium sulfate, sometimes used as a food preservative.
Although aluminum is permitted in food, consuming large amounts can lead to excessively high levels of aluminum, potentially contributing to Alzheimer's disease and inflammatory bowel disease.
Who should not eat jellyfish?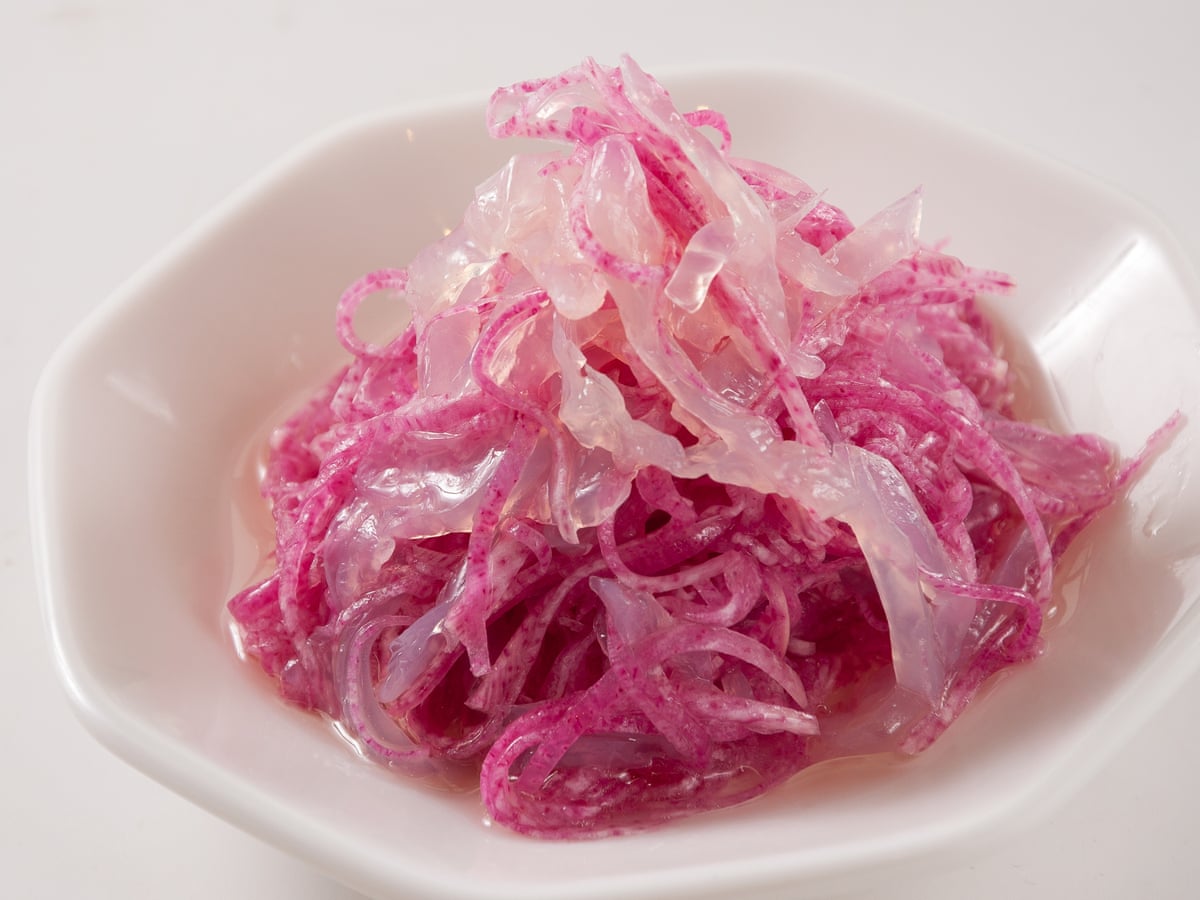
Although jellyfish is a nutritious, cooling, and healthy food, the following groups of people need to be cautious when eating it, even if it has been processed or cooked:
- People with a history of seafood allergies
- People who have recently recovered from illness
- People who are experiencing physical weakness.
- People with a history of previous food poisoning.
In particular, children under 8 years old should not eat jellyfish because their immune systems are still weak, and they are at a higher risk of allergies or food poisoning.
News in the same category

Why Are My Veins Suddenly Bulging and Visible?

7 Health Problems Linked to Not Drinking Enough Water
3 pain areas on the body that could signal early-stage can:cer: don't delay, or it could spread

6 Surprising Reasons Women Should Eat Dates More Often

Two vegetables considered “natural remedies” for headaches—eat them and sleep soundly through the night
The 4 earliest warning signs the body sends as a “cry for help” for cerv.ical can.cer—sadly, many women overlook them
More and more people are developing kid.ney failure. U.S. experts warn: Eating too much of these 4 foods is especially harmful to the kid.neys and should be limited immediately
4 Foods to Eat on an Empty Stomach in the Morning That May Support Digestion and Long-Term Health
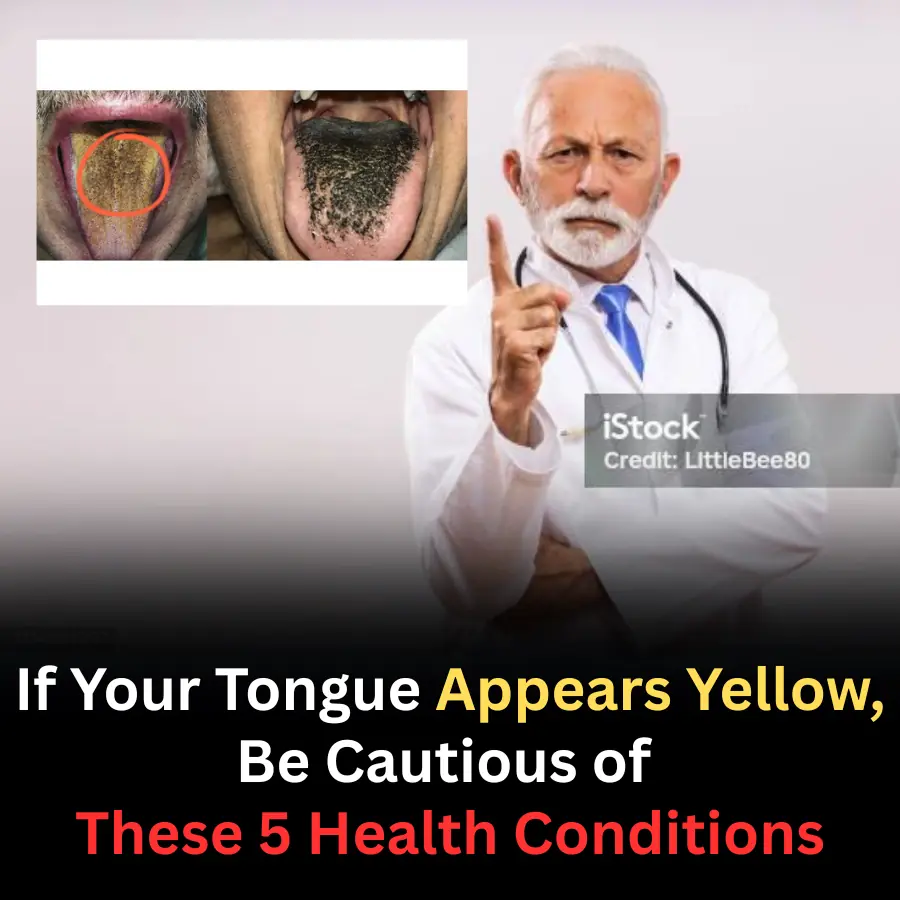
Yellow Tongue: A Small Sign That May Signal Serious Health Problems
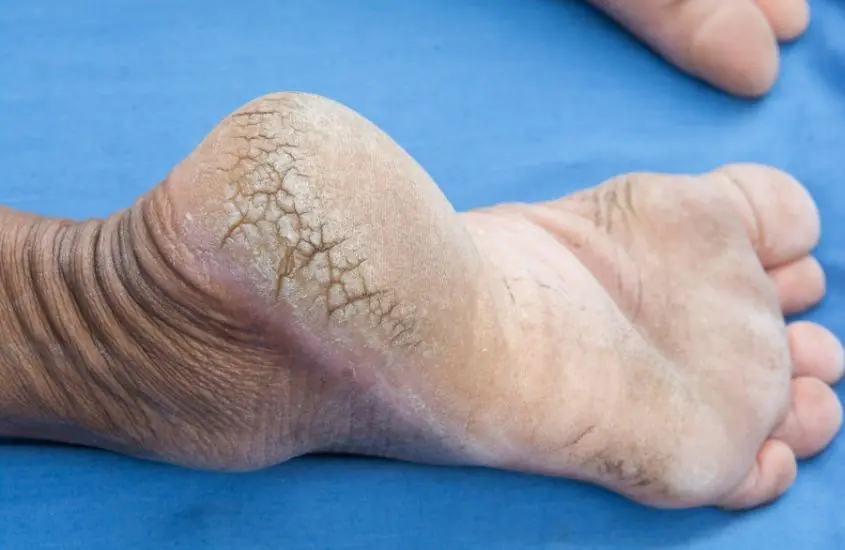
Pharmacist shares major wa:rning sign in heels of foot that could be symptom of serious condition
Cancer May Be Silent at First: 8 Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore When Using the Toilet
Breakthrough: Scientists discover a way to turn can.cer cells back into normal cells

American Nutrition Experts Praise Avocados as a Top Heart-Healthy Fruit
Why Your Throat Feels Mucusy: The Real Reasons Behind That Sticky Sensation

Does Reheating Rice Cause Cancer? What You Should Really Know
Losing Both Kidneys Before 30: A Wake-Up Call About Kidney Health

An Overlooked Flower That Supports Liver and Kidney Health
News Post

How to Effectively Remove Black Mold Spots from Household Items

Colorful Quinoa Power Bowl

Eating a boiled egg every morning: The surprising effects on your body

Why Are My Veins Suddenly Bulging and Visible?

7 Health Problems Linked to Not Drinking Enough Water

3 pain areas on the body that could signal early-stage can:cer: don't delay, or it could spread

6 Surprising Reasons Women Should Eat Dates More Often

Many people cook rice every day—but still get it wrong: 4 simple tips for tastier rice and better digestion

Two vegetables considered “natural remedies” for headaches—eat them and sleep soundly through the night

The 4 earliest warning signs the body sends as a “cry for help” for cerv.ical can.cer—sadly, many women overlook them

More and more people are developing kid.ney failure. U.S. experts warn: Eating too much of these 4 foods is especially harmful to the kid.neys and should be limited immediately

4 Foods to Eat on an Empty Stomach in the Morning That May Support Digestion and Long-Term Health

Just follow these 4 steps and pork will always turn out tender, juicy, and never tough

Yellow Tongue: A Small Sign That May Signal Serious Health Problems

Pharmacist shares major wa:rning sign in heels of foot that could be symptom of serious condition

5 Common Drinking-Water Mistakes That Can Damage Your Liver and Kidneys

Cancer May Be Silent at First: 8 Warning Signs You Should Never Ignore When Using the Toilet

Mix White Salt With Fabric Softener: A Simple Household Trick That Saves Money and Solves Multiple Problems
