More and more people are developing kid.ney failure. U.S. experts warn: Eating too much of these 4 foods is especially harmful to the kid.neys and should be limited immediately
Kidney failure is becoming an increasingly concerning health issue.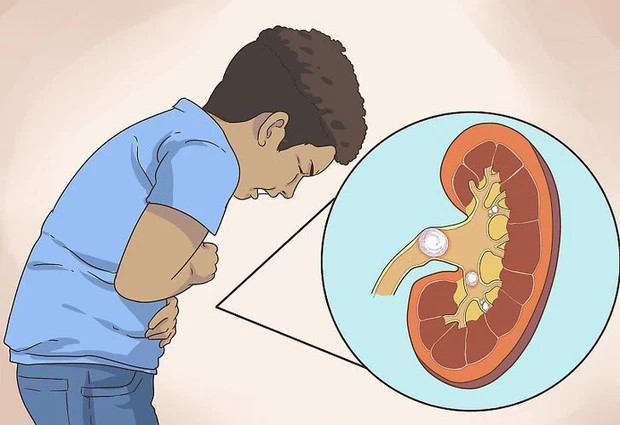
According to experts, unhealthy eating habits are one of the major factors that damage the kidneys. Many common foods and beverages can overload the kidneys, increasing the risk of declining kidney function if consumed frequently and over long periods.
Drinking large amounts of dark-colored carbonated soft drinks
Soft drinks, especially dark-colored sodas, often contain high levels of artificial phosphorus. According to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), phosphorus is an essential mineral that helps maintain strong bones. In people with healthy kidneys, excess phosphorus from food can usually be excreted efficiently.
However, American nutrition expert Catalina Ruz Gatica warns that artificial phosphorus is absorbed more quickly and places greater strain on the kidneys than naturally occurring phosphorus in foods. She notes that nutritionists advise limiting these drinks not only because of their phosphorus content, but also because they are high in added sugars, which increase the risk of metabolic disorders and long-term kidney damage.
To protect kidney function and overall health, experts recommend avoiding or strictly limiting dark sodas and choosing healthier beverages such as plain water or unsweetened drinks.
Consuming too many frozen ready-made meals
Frozen ready meals are a convenient option for many households because they are pre-cooked, packaged, and frozen, requiring only reheating in a microwave or oven.
However, according to Catalina Ruz Gatica, a single serving of these meals often contains more than 1,000 mg of sodium. Meanwhile, the American Heart Association recommends that adults consume no more than 2,300 mg of sodium per day, ideally limiting intake to 1,500 mg to reduce the risk of heart disease and high blood pressure.
Controlling sodium intake is crucial for kidney health. Long-term excessive sodium consumption raises blood pressure and increases filtration pressure in the kidneys, forcing them to work harder and accelerating the risk of kidney failure.
Eating too much fast food
According to Catalina Ruz Gatica, a kidney-friendly diet should prioritize fruits, vegetables, complex carbohydrates, and lean protein sources. In contrast, fast food is typically high in sodium, refined carbohydrates, saturated fats, and preservatives, while lacking essential nutrients that help protect and maintain kidney function.
When sodium intake is high, the kidneys must constantly work to eliminate the excess. Over time, this contributes to high blood pressure—one of the leading causes of chronic kidney disease. Preservatives commonly found in fast food have also been linked to declining kidney function when consumed regularly in large amounts.
“Although convenient and widely available, frequent fast-food consumption can place significant strain on the kidneys and negatively affect long-term health,” Ruz Gatica explains.
Eating too much red meat
Protein is essential for building and repairing body tissues. However, excessive protein intake—especially from animal sources—can put considerable stress on the kidneys. “When you consume a lot of animal protein, the body produces higher levels of acid in the blood, and the kidneys must work harder to remove it. Eating meat in moderation is therefore important for protecting kidney health,” says Catalina Ruz Gatica.
In addition, the saturated fat and cholesterol in red meat can raise cholesterol levels, increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease and kidney function decline. This does not mean meat must be completely eliminated, but daily red meat intake should be carefully controlled to maintain overall health.