
Discover the Plant That Can Purify Your Blood, Renew Your Skin, and Cleanse Your Organs — But Only If You Use It This Way
It’s as if your body is quietly asking for a break — not another diet, not another supplement, but something deeper.

Magnesium is one of the most essential minerals in the human body, yet it is often overlooked. It plays a critical role in more than 300 enzymatic and biochemical reactions, influencing nearly every major system, including the nervous system, muscles, bones, immune function, and metabolism.
Adequate magnesium levels are necessary for maintaining strong bones, balanced blood sugar, stable mood, and healthy digestion. Unfortunately, modern diets, chronic stress, poor sleep, and certain medications have made magnesium deficiency increasingly common.
This article explains how magnesium works in the body, how it can help manage several common health issues, and the proper ways to take magnesium safely and effectively.
Magnesium is essential for bone formation and maintenance. It works closely with calcium and vitamin D to regulate bone mineralization and maintain bone density. Without enough magnesium, calcium cannot be properly absorbed or directed into bones, which may lead to calcium buildup in soft tissues and joints instead.
Long-term magnesium deficiency has been linked to:
Reduced bone density
Increased fracture risk
Chronic bone and joint pain
Accelerated bone loss, especially in older adults
Recommended forms: Magnesium glycinate or magnesium citrate, both of which are well absorbed and gentle on the stomach
Suggested dosage: 300–400 mg per day for adults
Best combination: Take magnesium alongside vitamin D and an appropriate amount of calcium for optimal bone support
Dietary sources: Pumpkin seeds, sunflower seeds, almonds, cashews, spinach, Swiss chard, and whole grains
Important note: Avoid excessive calcium intake without magnesium, as this may increase the risk of calcium deposits in joints and arteries.

Magnesium plays a crucial role in insulin function and glucose metabolism. It helps insulin transport glucose into cells and supports normal insulin sensitivity. Research has consistently shown that people with low magnesium levels are at a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In individuals with diabetes, magnesium deficiency is common and may contribute to:
Poor blood sugar control
Increased insulin resistance
Higher risk of complications
Recommended forms: Magnesium taurate or magnesium chloride
(Magnesium taurate is particularly beneficial because taurine supports insulin function and cardiovascular health.)
Suggested dosage: 250–350 mg daily
Best timing: Take magnesium after meals to help stabilize blood sugar levels
Dietary sources: Dark chocolate (in moderation), black beans, lentils, quinoa, brown rice, and leafy greens
Important note: If you are taking diabetes medications, consult your healthcare provider before supplementing with magnesium to avoid potential low blood sugar episodes.
Magnesium is often referred to as a “calming mineral” because of its powerful effects on the nervous system. It helps regulate neurotransmitters such as serotonin and GABA, which influence mood, relaxation, and stress response.
Low magnesium levels have been associated with:
Increased anxiety and irritability
Poor stress tolerance
Sleep disturbances
Depressive symptoms
Recommended form: Magnesium L-threonate, which crosses the blood-brain barrier effectively
Suggested dosage: 200–400 mg per day
Best timing: In the evening or before bedtime to promote relaxation and better sleep
Lifestyle support: Pair magnesium intake with stress-reduction practices such as meditation, breathing exercises, or gentle stretching
Important note: Excessive caffeine and alcohol intake can deplete magnesium levels and reduce its calming effects.

Magnesium also plays a role in digestive health by relaxing smooth muscles in the intestinal tract and drawing water into the bowels. This softens stools and supports regular bowel movements, making magnesium particularly helpful for occasional constipation.
Recommended forms: Magnesium citrate or magnesium oxide
Suggested dosage: 400–500 mg at night, as needed
Best approach: Start with a lower dose to assess tolerance and increase gradually if necessary
Dietary support: Drink plenty of water and consume fiber-rich foods such as vegetables, oats, and prunes
Precaution: Magnesium laxatives should not be used daily or long-term without medical supervision.
Magnesium deficiency can present in subtle ways. Common symptoms include:
Muscle cramps or spasms
Fatigue or weakness
Headaches or migraines
Insomnia
Tingling or numbness
Anxiety or mood swings
Irregular heartbeat
If you experience several of these symptoms, a blood test can help confirm whether your magnesium levels are low.

Choose high-quality magnesium supplements with minimal additives
Always consult a healthcare provider before starting supplementation, especially if you are pregnant, breastfeeding, or taking medications
Excess magnesium from supplements may cause diarrhea, nausea, or abdominal cramps
Whenever possible, prioritize magnesium-rich foods as your primary source
Magnesium is a powerful yet often underestimated mineral that supports nearly every aspect of health. From strengthening bones and improving blood sugar control to calming the nervous system and supporting digestion, its benefits are wide-ranging and well-documented.
By ensuring adequate magnesium intake through a balanced diet and carefully chosen supplements when needed, you can support long-term health, reduce discomfort, and improve overall quality of life. Magnesium may not be a miracle cure, but it is undeniably a cornerstone of optimal health and vitality.
Taking care of your magnesium levels today is an investment in your well-being for years to come.

It’s as if your body is quietly asking for a break — not another diet, not another supplement, but something deeper.
8 Best Anti-Cancer Foods You Should Add to Your Diet

When sinus pressure builds, your head feels heavy, your nose refuses to drain, and even simple breathing can feel exhausting.

Romantic relationships are full of ups and downs, but one timeless truth remains: love thrives on simple moments and deep emotional bonds.

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.



Vicks VapoRub is one of the most popular ointments in the world, widely known for relieving nasal congestion, colds, and muscle pain.

This soothing herbal infusion helps promote healthier vision
Mini-str.oke in your 40s and later: The warning sign many people ignore
Signs That May Indicate Kidney Damage
2 Warning Signs Your Liver May Be Failing — Don’t Ignore Them

Who Should Avoid Eating Oysters? 6 At-Risk Groups
Why Am I Feeling Pain on the Left Side of My Body?

The Bedtime Trick Everyone’s Talking About: Why Banana Tea Works
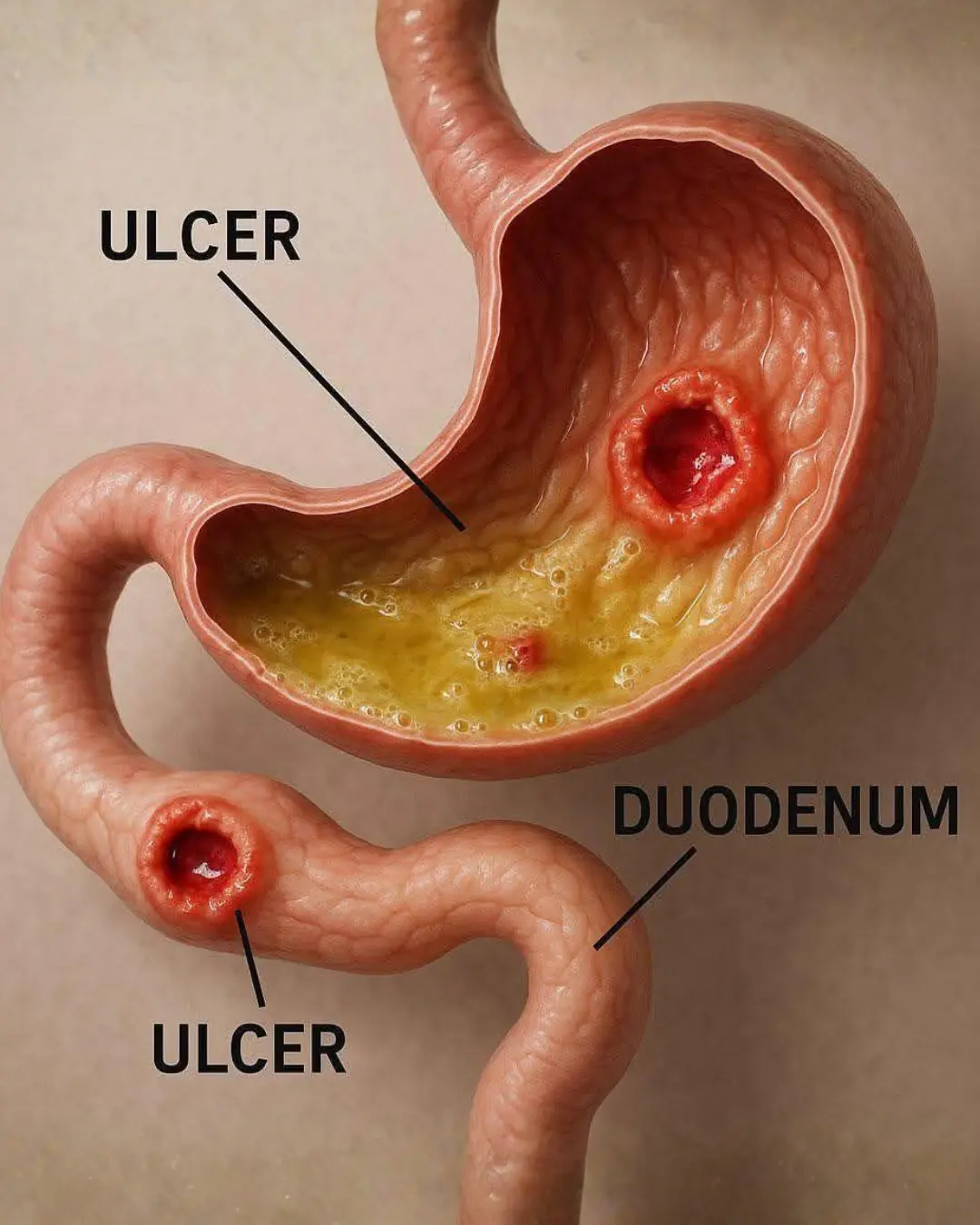
Stop Eating These Foods If You Want Your Ulcer to Heal

Carob (Ceratonia siliqua) Explained: Health Advantages and Easy DIY Applications

Common Milkweed (Asclepias syriaca) Explained: Health Advantages, Nutritional Insights, and Important Risks to Know
6 night-time warning signs of dia.betes you shouldn't ignore!
A Pharmacist Shares a Warning Sign in Your Heel That Could Be a Symptom of a Serious Condition

Once Ignored, Now Celebrated: The Wild-Growing Vegetable Being Called a “Miracle Herb” for Health

It’s as if your body is quietly asking for a break — not another diet, not another supplement, but something deeper.

Cats are curious, independent creatures—and while that’s part of their charm, it can also be the source of stress when one suddenly disappears.

8 Best Anti-Cancer Foods You Should Add to Your Diet

When sinus pressure builds, your head feels heavy, your nose refuses to drain, and even simple breathing can feel exhausting.

Romantic relationships are full of ups and downs, but one timeless truth remains: love thrives on simple moments and deep emotional bonds.

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.



Vicks VapoRub is one of the most popular ointments in the world, widely known for relieving nasal congestion, colds, and muscle pain.

This soothing herbal infusion helps promote healthier vision

A powerful 2-ingredient solution that beats bleach at removing grout mold

Mini-str.oke in your 40s and later: The warning sign many people ignore

Signs That May Indicate Kidney Damage

2 Warning Signs Your Liver May Be Failing — Don’t Ignore Them

Who Should Avoid Eating Oysters? 6 At-Risk Groups

Why Am I Feeling Pain on the Left Side of My Body?

The Bedtime Trick Everyone’s Talking About: Why Banana Tea Works

Stop Eating These Foods If You Want Your Ulcer to Heal

Carob (Ceratonia siliqua) Explained: Health Advantages and Easy DIY Applications