Waking up in the middle of the night with sudden, painful leg cramps is an experience many people know all too well. These cramps often strike without warning, tightening the calf, foot, or thigh muscles and forcing sufferers to sit up or stretch in pain. While nighttime leg cramps are common, health experts say they are not something that should be ignored—especially when they occur frequently or worsen over time.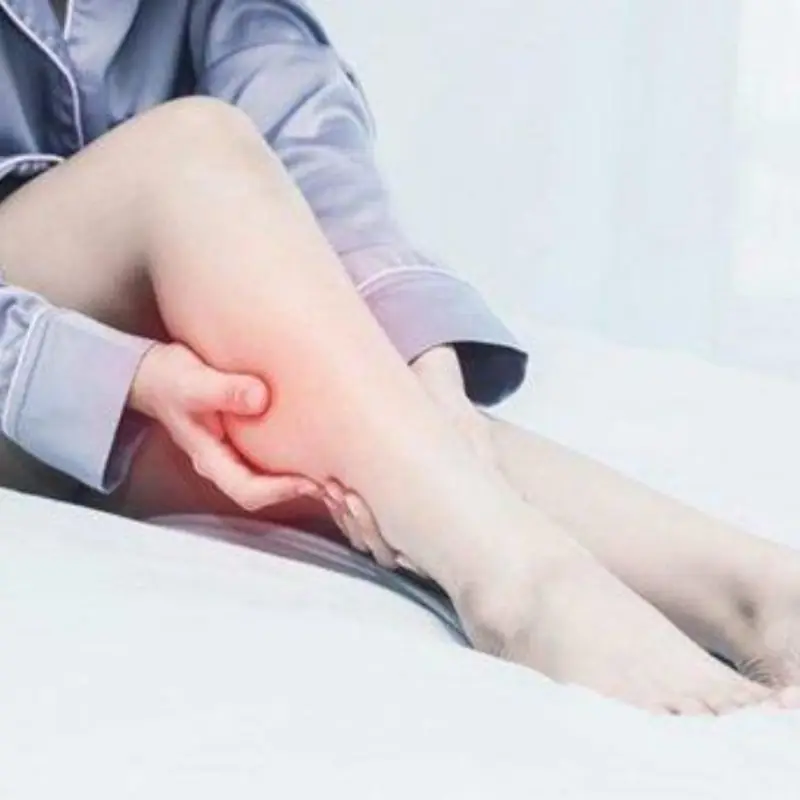
Nighttime leg cramps, also known as nocturnal leg cramps, are involuntary muscle contractions that typically happen during sleep or periods of rest. Unlike restless leg syndrome, which causes an urge to move the legs, cramps are characterized by sharp pain and muscle stiffness that can last from seconds to several minutes. In some cases, soreness may linger into the next day.
According to health professionals, one of the most common contributors to leg cramps at night is muscle fatigue. People who stand for long hours, exercise intensely, or remain physically inactive for extended periods may place extra strain on their muscles. This strain can disrupt normal muscle function and make cramps more likely during rest.
Dehydration and mineral imbalance are also frequently cited causes. Muscles rely on electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium, calcium, and sodium to contract and relax properly. When these minerals are out of balance—due to poor diet, excessive sweating, or inadequate fluid intake—muscle spasms can occur more easily at night. Older adults are particularly vulnerable, as the body’s ability to regulate fluids and minerals declines with age.
Health experts also point to poor blood circulation as a contributing factor. When circulation to the legs is reduced, muscles may not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, increasing the likelihood of cramping. Conditions such as peripheral artery disease, diabetes, or prolonged sitting can interfere with blood flow and trigger nighttime discomfort.
Another factor often overlooked is nerve-related issues. Compression or irritation of nerves in the lower back or spine may send abnormal signals to the leg muscles, causing sudden contractions. This is why some people with lower back problems or spinal conditions experience recurring leg cramps at night.
Certain medications may also play a role. Diuretics, cholesterol-lowering drugs, blood pressure medications, and some asthma treatments can affect fluid balance or muscle function. Health experts recommend reviewing medications with a doctor if leg cramps begin after starting a new prescription.
So how can nighttime leg cramps be prevented? Health professionals emphasize that simple lifestyle changes often make a big difference. Staying well-hydrated throughout the day, especially in hot weather or after exercise, is essential. Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins helps ensure adequate intake of key minerals.
Stretching before bed is another highly recommended strategy. Gentle calf and hamstring stretches can relax muscles and reduce nighttime spasms. Experts also advise maintaining proper sleep posture and avoiding tightly tucked blankets that may keep the feet pointed downward, which can shorten calf muscles and increase cramp risk.
For those who sit or stand for long periods, regular movement during the day improves circulation. Light walking, ankle rotations, or leg elevation can help reduce muscle tension before bedtime. In some cases, applying a warm compress or taking a warm shower before sleep may relax muscles and prevent cramps.
Health experts caution that while most leg cramps are harmless, persistent or severe cramps may signal an underlying health issue. If cramps are accompanied by swelling, numbness, weakness, or changes in skin color, medical evaluation is important. Chronic cramps may also warrant blood tests to check for electrolyte imbalances or circulation problems.
In conclusion, leg cramps at night are common but not inevitable. Health experts agree that understanding the causes—whether related to muscle fatigue, hydration, circulation, or nerve function—is the first step toward relief. With proper hydration, nutrition, movement, and stretching, many people can significantly reduce nighttime cramps and enjoy more restful sleep. When cramps persist despite these measures, seeking medical advice can help uncover and address the root cause, ensuring both comfort and long-term health.