
Doctors Explain What Eating Boiled Eggs Every Morning Does to Your Body
A daily boiled egg may bring surprising benefits—and a few cautions.
Needing to use the bathroom shortly after eating is something many people experience from time to time. But if it happens almost every
time you eat, it can feel confusing - or even concerning. Is it normal? Is something wrong with digestion? Or is the body simply doing what
it’s designed to do?
In most cases, this pattern has a logical explanation. Below is a clear, in-depth look at why the urge to poop right after meals happens,
when it’s considered normal, and when it might be worth paying closer attention.
The most frequent explanation is something called the gastrocolic reflex.
This is a natural reaction in which:
Eating stretches the stomach
The digestive system sends signals to the colon
The colon contracts to make room for incoming food
As a result, waste that’s already in the colon is pushed toward the rectum - creating the urge to poop.
For some people, this reflex is stronger and faster, which is why the need can feel almost immediate.
This is especially common:
In the morning
After large meals
After warm or fatty foods
In healthy individuals, this response is normal and not harmful.
A common misconception is that food is moving straight through the body in minutes. In reality:
Digestion takes many hours
The bowel movement after eating is usually waste from earlier meals
The new meal simply triggers the colon to empty what’s already there.
So even if the timing feels instant, digestion itself is not unusually fast.
Certain foods can stimulate bowel activity more strongly, especially in sensitive digestive systems.
Common triggers include:
Fatty or greasy foods
Spicy foods
Coffee and caffeine
Dairy (for lactose intolerance)
Artificial sweeteners
If the urge consistently follows specific foods, it may indicate a mild food intolerance or sensitivity, rather than a serious condition.
Keeping a simple food-and-symptom journal can help identify patterns.
The gut and brain are closely connected through the nervous system. Emotional states can directly affect digestion.
Stress or anxiety can:
Increase gut motility
Heighten awareness of bodily sensations
Make the gastrocolic reflex feel more urgent
People who are frequently tense, rushed, or anxious may notice stronger digestive reactions after meals—even when eating the same foods as
others.
For some individuals, frequent post-meal bowel movements are associated with Irritable Bowel Syndrome, particularly IBS with diarrhea
(IBS-D).
Common IBS-related signs include:
Urgent need to poop after eating
Abdominal cramping
Bloating
Relief after a bowel movement
IBS does not damage the digestive tract, but it can significantly affect quality of life. Symptoms often fluctuate with stress, diet, and routine.
While usually harmless, frequent post-meal bowel movements may deserve attention if they are accompanied by:
Persistent diarrhea
Blood in the stool
Unexplained weight loss
Severe or worsening pain
Nighttime bowel movements
These symptoms are not typical of a normal gastrocolic reflex and should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
If the pattern is uncomfortable or disruptive, small adjustments can help:
Eat smaller, slower meals
Reduce trigger foods
Manage stress before eating
Stay hydrated
Maintain consistent meal times
For many people, simply slowing down and being mindful while eating reduces digestive urgency.
Needing to poop shortly after eating is often a sign of a responsive and active digestive system, not a problem. The body is coordinating
digestion efficiently, clearing space as new food arrives.
However, digestion should feel manageable - not distressing. Paying attention to patterns, triggers, and overall comfort helps determine
whether the behavior is simply normal physiology or something worth exploring further.
In most cases, the answer isn’t alarming. It’s just the gut doing its job promptly and efficiently.

A daily boiled egg may bring surprising benefits—and a few cautions.

Six natural drinks that may help you fall asleep faster and sleep deeper.

The fastest way to lose peace is to fight what you cannot control. Choose calm instead

5 types of meat that require extra caution, even sellers tend to avoid them

Japanese honeysuckle: Health benefits and easy homemade remedies
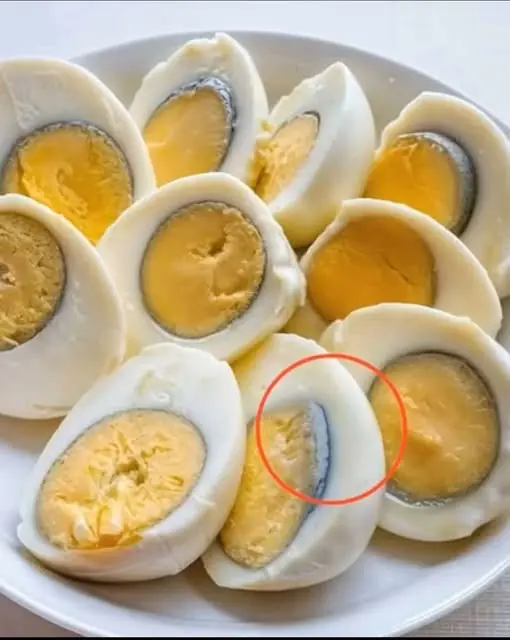

If you are one of those people who prefer their eggs hard-boiled, you have certainly noticed that green color ring around the yolk.
New research is shedding light on a startling consequence of chronic sleep loss:
3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead

Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a frequent complication that arises in individuals with diabetes.
Sugar is everywhere in modern diets—from obvious sources like desserts to hidden ones like salad dressings, breads, sauces, and even “healthy” snacks.
Three urine warning signs you should never ignore for kidney health
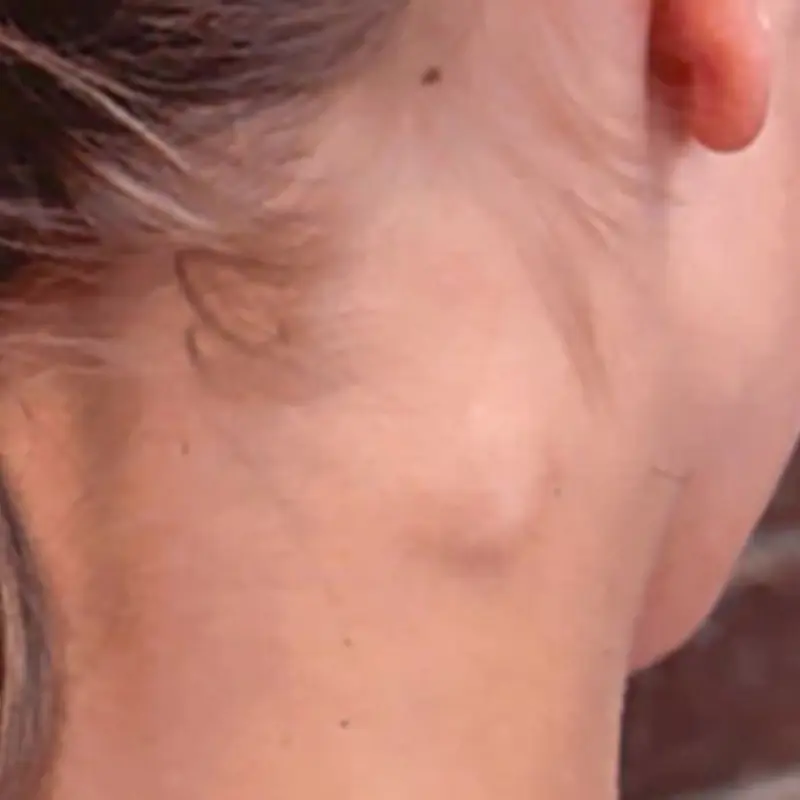

Three neck changes that should never be ignored, doctors warn
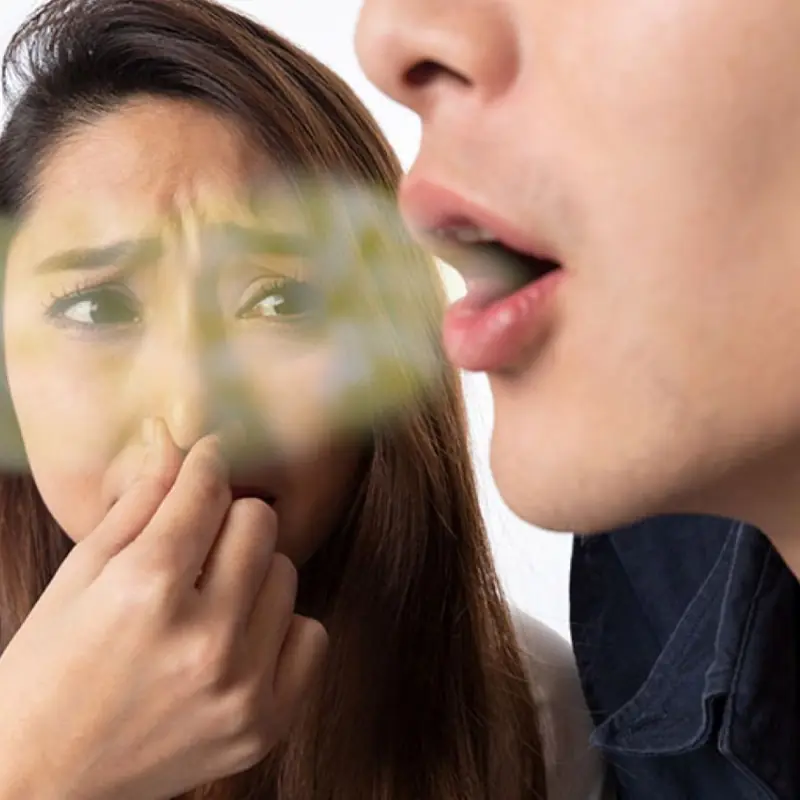

Unusual body odors may be an early warning sign of liver trouble

6 Surprising Health Benefits of Sleeping in a Cold Room (And Why You Might Skip the Fan)
4 Common Morning Mistakes That Could Put You at Higher Risk of Stroke

This leafy green is redefining nutrition and fine dining worldwide
Eating leftovers from the fridge, 50-year-old man di.es: 5 foods you should never keep overnight, if left over, throw it away
The body often shows five important warning signs up to three months before a heart attack, but they are frequently overlooked
3 Pain Areas on the Body That Could Signal Early - Stage Canc:er

In fact, countless women do it every day without realizing the hidden risks.

5 powerful plants that help fight formaldehyde and purify indoor air

Your phone’s volume buttons do more than you realize: 6 hidden tricks


A daily boiled egg may bring surprising benefits—and a few cautions.



Six natural drinks that may help you fall asleep faster and sleep deeper.

No matter where you are in life - these 4 things shouldn’t stay in your home for long

The fastest way to lose peace is to fight what you cannot control. Choose calm instead

Why sleeping on the floor is a common choice in Japan and what motivates this habit?

4 great reasons to place an onion in the corner of your room

5 types of meat that require extra caution, even sellers tend to avoid them

Japanese honeysuckle: Health benefits and easy homemade remedies

7 smells snakes can’t stand that help keep them away from your home

If you are one of those people who prefer their eggs hard-boiled, you have certainly noticed that green color ring around the yolk.

The journey to finding and keeping love can feel magical —

New research is shedding light on a startling consequence of chronic sleep loss:

3 Signs Your Parent May Be Nearing the End of Life — How to Prepare for What’s Ahead

Neuropathy, or nerve damage, is a frequent complication that arises in individuals with diabetes.