Can.cer remains one of the most feared diseases worldwide, affecting millions of people each year across all age groups. One of the biggest
challenges in fighting cancer is that it often develops silently. While many people associate cancer with severe pain or obvious physical
symptoms, the reality is that early-stage cancer frequently presents with subtle changes that are easy to overlook or dismiss.
Early detection plays a critical role in successful treatment. When cancer is identified in its initial stages, treatment options are often more
effective, recovery outcomes are better, and survival rates increase significantly. Medical experts consistently emphasize the importance of
paying close attention to your body and responding promptly to unusual or persistent symptoms.
Below are 20 early warning signs of cancer that should never be ignored, followed by practical steps you can take to reduce your overall
cancer risk.
20 Early Signs of Can.cer to Watch For
1. Unexplained Weight Loss
Sudden and unintentional weight loss - typically more than 5% of body weight within a short period — may be an early indicator of cancer.
This symptom is commonly associated with cancers of the pancreas, stomach, lungs, and esophagus.
Watch for: Rapid weight loss without changes in diet, exercise, or lifestyle.
2. Persistent Fatigue
Ongoing fatigue that does not improve with rest can signal an underlying medical condition, including cancer. This type of fatigue is deeper
than normal tiredness and may interfere with daily activities.
Watch for: Constant exhaustion that persists despite adequate sleep and rest.
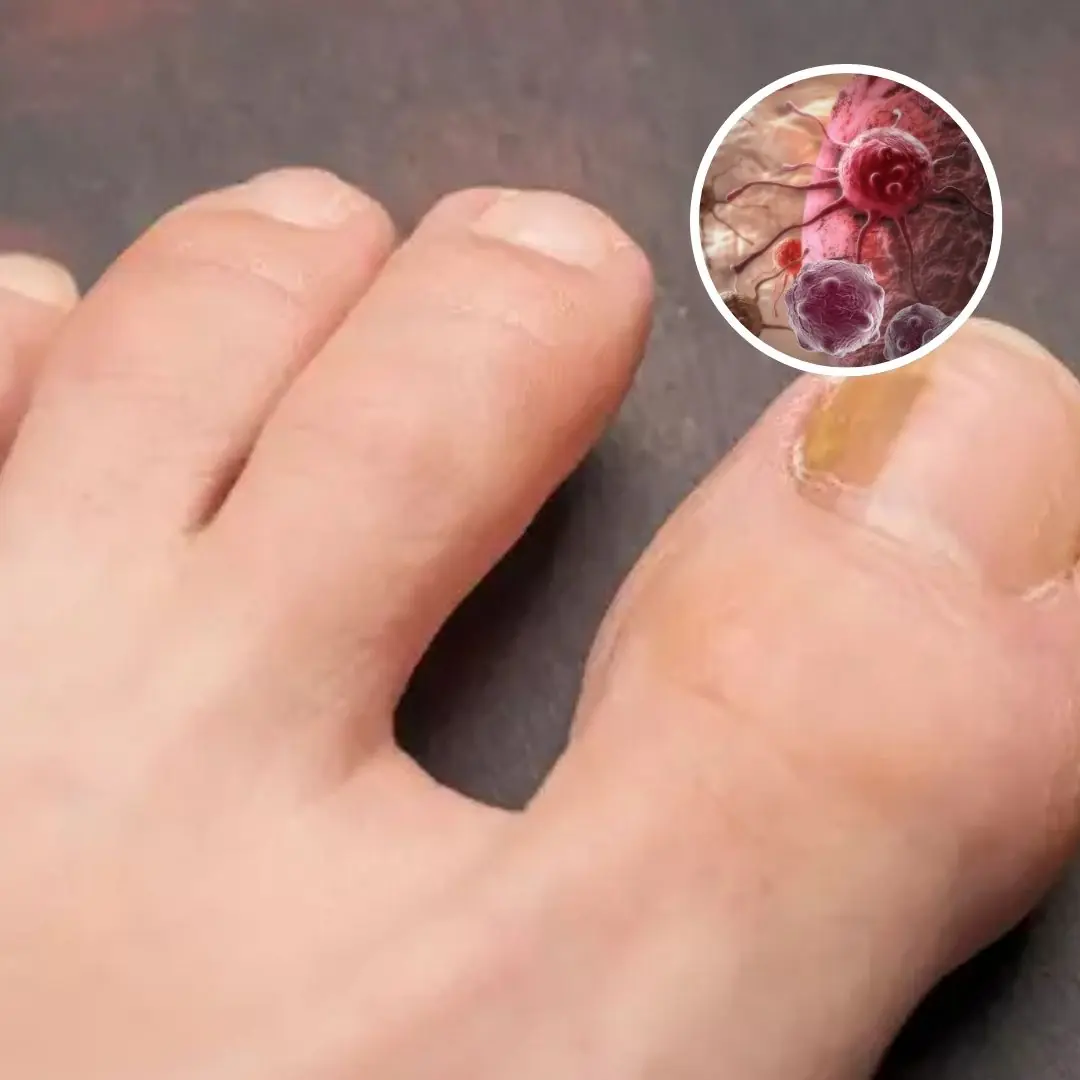
3. Changes in Skin Appearance
Skin changes can indicate several types of cancer, particularly skin cancer. New moles, changes in existing moles, or sores that do not heal
should be evaluated promptly.
Watch for: Irregular borders, changes in color, asymmetry, or unexplained skin growths.
4. Persistent Cough or Hoarseness
A cough that lasts for weeks or hoarseness that does not resolve may be linked to lung or throat cancer.
Watch for: Coughing up blood, chest discomfort, or difficulty breathing.
5. Ongoing Abdominal Pain or Digestive Issues
Chronic abdominal discomfort, bloating, or digestive disturbances may be linked to cancers of the colon, pancreas, stomach, or ovaries.
Watch for: Persistent pain or changes in bowel habits that do not resolve.
6. Difficulty Swallowing
Progressive difficulty swallowing, also known as dysphagia, can be an early sign of cancers affecting the esophagus or throat.
Watch for: Sensation of food getting stuck or pain while swallowing.
7. Persistent or Unexplained Fever
A fever that lasts for weeks without a clear cause may be associated with blood-related cancers such as leukemia or lymphoma.
Watch for: Ongoing fever accompanied by night sweats or unexplained weight loss.
8. Unexplained Bleeding
Unexpected bleeding is always a reason for medical evaluation and may signal cancer depending on the source.
Watch for: Blood in stool or urine, coughing up blood, or abnormal vaginal bleeding.
9. Changes in Bowel Habits
Long-term changes in bowel movements, including constipation, diarrhea, or changes in stool shape, may indicate colorectal cancer.
Watch for: Symptoms lasting longer than a few weeks or blood in stool.
10. Lumps or Swelling
A new lump or swelling anywhere in the body - particularly in the neck, breast, armpit, or groin - should be checked by a healthcare professional.
Watch for: Hard, painless, or enlarging lumps.
11. Painful Urination or Blood in Urine
These symptoms may indicate bladder or kidney cancer and should never be ignored.
Watch for: Persistent urinary discomfort or visible blood in urine.
12. Shortness of Breath
Sudden or unexplained breathing difficulties can be associated with lung cancer or other serious conditions.
Watch for: Breathlessness at rest or wheezing without exertion.
13. Persistent Back Pain
Chronic back pain that does not improve with rest or treatment may be linked to cancers affecting the pancreas, spine, or colon.
Watch for: Severe pain that worsens over time or radiates to other areas.
14. Loss of Appetite
A persistent lack of appetite, especially when combined with weight loss, can indicate cancers of the digestive system.
Watch for: Feeling full quickly or complete loss of interest in food.
15. Ongoing Nausea or Vomiting
Chronic nausea or vomiting not related to infection or food poisoning may be associated with gastrointestinal cancers.
Watch for: Symptoms that persist despite treatment or lifestyle changes.
16. Unexplained Muscle or Joint Pain
Persistent pain in muscles or joints without injury may be linked to bone cancer or cancers that have spread to the bones.
Watch for: Pain that does not respond to standard treatments.
17. Night Sweats
Severe night sweats that soak bedding, especially without fever or infection, may signal lymphoma.
Watch for: Recurrent sweating that disrupts sleep.
18. Changes in Breast Tissue or Nipple Discharge
Any changes in breast shape, texture, or discharge should be evaluated promptly.
Watch for: Lumps, skin dimpling, redness, or unusual nipple discharge.
19. White Patches or Sores in the Mouth
Persistent mouth sores or white patches may indicate oral or throat cancer.
Watch for: Lesions that do not heal or bleed easily.
20. Chronic Indigestion or Heartburn
Ongoing indigestion or acid reflux that worsens over time may be linked to stomach or esophageal cancer.
Watch for: Difficulty swallowing or persistent chest discomfort.
How to Lower Your Risk of Cancer
While not all cancers can be prevented, many risk factors are influenced by lifestyle choices. Making healthier decisions can significantly
reduce your risk and improve overall well-being.
1. Maintain a Balanced, Nutritious Diet
A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins provides essential nutrients and antioxidants that protect cells from damage.
Key habits:
-
Increase fruit and vegetable intake
-
Limit red and processed meats
-
Choose whole grains over refined carbohydrates
-
Stay well hydrated
2. Exercise Regularly
Physical activity helps regulate hormones, maintain a healthy weight, and boost immune function — all of which lower cancer risk.
Goal: At least 30 minutes of moderate activity most days of the week.
3. Avoid Smoking and Limit Alcohol
Tobacco use remains one of the leading causes of preventable cancer. Alcohol consumption also increases cancer risk in a dose-dependent manner.
Best practices:
-
Quit smoking entirely
-
Limit alcohol intake
4. Protect Your Skin From Sun Exposure
Excessive UV exposure is the primary cause of skin cancer.
Protective steps:
-
Use broad-spectrum sunscreen
-
Avoid peak sun hours
-
Wear protective clothing
5. Get Vaccinated
Certain cancers are caused by viral infections that can be prevented through vaccination.
-
HPV vaccine: Helps prevent cervical and other HPV-related cancers
-
Hepatitis B vaccine: Reduces risk of liver cancer
6. Attend Regular Health Screenings
Routine screenings can detect cancer early, when treatment is most effective.
Common screenings include:
-
Mammograms
-
Pap tests
-
Colonoscopies
-
Skin examinations
7. Manage Stress and Prioritize Mental Health
Chronic stress contributes to inflammation and hormonal imbalance, both of which may increase cancer risk.
Helpful strategies:
-
Mindfulness practices
-
Adequate sleep
-
Emotional support
8. Reduce Exposure to Environmental Toxins
Limiting contact with harmful chemicals and pollutants can further reduce cancer risk.
Suggestions:
-
Avoid secondhand smoke
-
Use safer household products
-
Improve indoor air quality
Conclusion
Although cancer cannot always be prevented, many steps can be taken to significantly reduce risk. Paying attention to early warning signs,
maintaining a healthy lifestyle, attending regular screenings, and seeking medical advice when something feels wrong can make a life-saving
difference.
The most powerful approach to cancer is awareness, prevention, and early action. Listening to your body and prioritizing health today can
lead to a longer, healthier future.