
5 diseases that can cause stomach pain after eating - What your body may be trying to tell you?

Experiencing stomach pain after eating is a common complaint, but it should never be ignored - especially if it happens frequently. While
occasional discomfort may be caused by overeating or eating too quickly, persistent pain after meals can be a warning sign of an
underlying digestive disorder.
Below are five common diseases that can cause stomach pain after eating, how they affect the body, and when it’s time to seek medical
attention.
1. Gastritis (Stomach Lining Inflammation)
Gastritis occurs when the protective lining of the stomach becomes inflamed or eroded.
Why it causes pain after eating
After a meal, the stomach produces acid to digest food. If the stomach lining is inflamed, this acid can irritate the tissue, leading to pain or
burning sensations shortly after eating.
Common symptoms
-
Upper abdominal pain or burning
-
Nausea or vomiting
-
Feeling overly full after small meals
-
Bloating
Common causes
-
Helicobacter pylori infection
-
Long-term use of painkillers (NSAIDs)
-
Excessive alcohol consumption
-
Chronic stress
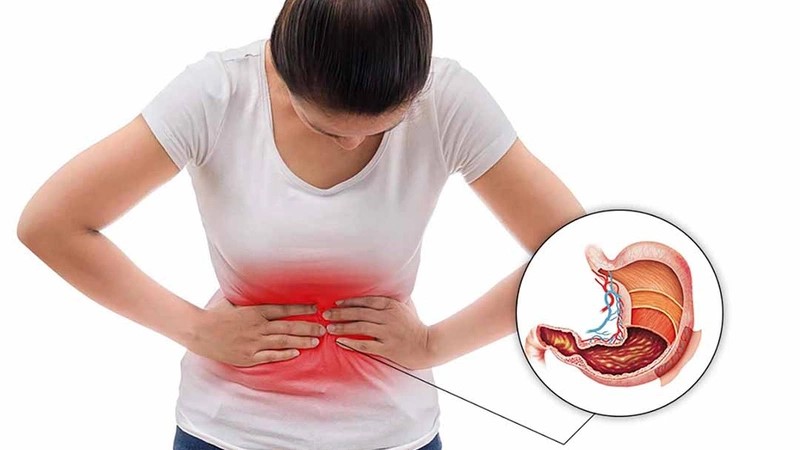
2. Peptic Ulcer Disease
Peptic ulcers are open sores that form in the stomach or the upper part of the small intestine.
Why it causes pain after eating
Food stimulates acid production. When acid comes into contact with an ulcer, it can cause sharp or gnawing pain, often worsening shortly after meals (especially with stomach ulcers).
Common symptoms
-
Burning or stabbing stomach pain
-
Pain that comes and goes
-
Nausea
-
Dark or tarry stools (in severe cases)
Risk factors
-
H. pylori infection
-
Long-term NSAID use
-
Smoking
Untreated ulcers can lead to bleeding or perforation, making early diagnosis essential.
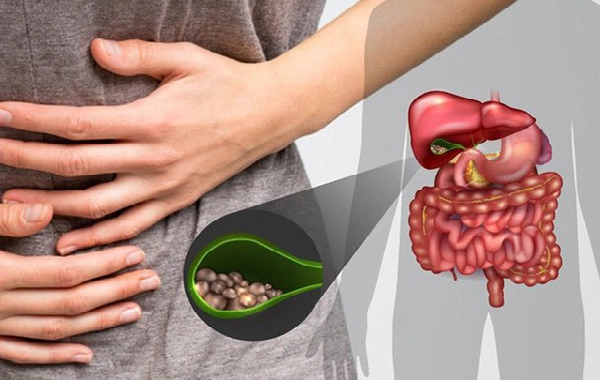
3. Gallbladder Disease (Gallstones or Inflammation)
Gallbladder problems often cause pain after eating, especially after fatty meals.
Why it causes pain after eating
The gallbladder releases bile to help digest fats. If gallstones block bile flow or the gallbladder is inflamed, eating triggers sudden and intense pain.
Common symptoms
-
Pain in the upper right abdomen
-
Pain radiating to the back or right shoulder
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Pain after greasy or heavy meals
Gallbladder pain often appears 30 minutes to a few hours after eating.
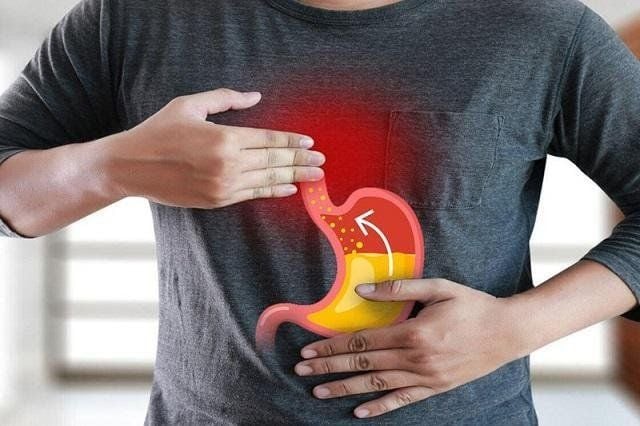
4. Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
GERD occurs when stomach acid flows back into the esophagus.
Why it causes pain after eating
Eating increases stomach pressure. If the lower esophageal sphincter is weak, acid reflux occurs, causing pain and irritation.
Common symptoms
-
Burning pain in the chest or upper abdomen
-
Sour or bitter taste in the mouth
-
Regurgitation
-
Pain that worsens when lying down
Certain foods—such as spicy foods, caffeine, chocolate, and acidic foods—can worsen symptoms.
5. Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
IBS is a functional gastrointestinal disorder affecting how the intestines work.
Why it causes pain after eating
Eating triggers intestinal contractions. In people with IBS, these contractions can be painful due to heightened gut sensitivity.
Common symptoms
-
Cramping or abdominal pain after meals
-
Bloating and gas
-
Diarrhea, constipation, or both
-
Relief after bowel movements
IBS does not cause structural damage but can significantly affect quality of life.
When to Be Concerned
You should see a doctor if stomach pain after eating is:
-
Frequent or worsening
-
Severe or sharp
-
Accompanied by weight loss
-
Associated with vomiting, bleeding, or fever
-
Interfering with daily life
Early diagnosis can prevent complications and improve treatment outcomes.
What You Can Do to Reduce Pain After Eating
-
Eat smaller, more frequent meals
-
Avoid trigger foods (fatty, spicy, acidic)
-
Eat slowly and chew thoroughly
-
Avoid lying down immediately after meals
-
Manage stress levels
-
Stay hydrated
However, lifestyle changes alone are not a substitute for medical evaluation if symptoms persist.
Final Thoughts
Stomach pain after eating is not something to dismiss as “normal.” It is often the body’s way of signaling a digestive disorder that needs attention. Conditions like gastritis, ulcers, gallbladder disease, GERD, and IBS are common—but manageable when diagnosed early.
Listening to your body and seeking timely medical advice can make a significant difference in both comfort and long-term health.
News in the same category


30 Powerful Benefits of Sessile Joyweed (Alternanthera sessilis): A Traditional Plant with Remarkable Potential

Doctors warn: 6 types of food that can promote can.cer growth that people are unaware of

Why shouldn't you set the air conditioner to 26°C at night?

Are feet an "early warning sign" of cervical can:cer? Don't ignore these 4 situations
This is why some people always keep a lemon with them - it may help in unexpected situations

Don’t Ignore These 5 Symptoms at Night That Could Be Linked to Can.cer
Canadian Researchers Discover New Evidence That Vitamin D Shuts Down Cancer Cells
Warning: 6 vegetables that naturally contain to.xins
If you find a “Bleach” patch in your underwear - What it really means?
Lines on your nails could be a hidden health warning: What your body may be telling you?
20 Early Red Flags Your Body Uses to Warn You About Cancer

Why You Should Avoid Using Wet Wipes For Intimate Hygiene: An Expert Sheds Light
Eat 4 foods on an empty stomach in the morning to help clean the intestines, improve digestion, and prevent can.cer

Why should you stop eating tilapia right now? What you need to know before your next meal?
Noticing brown spots in your eyes? These causes may surprise you — and the solutions are simple

This is Why You Always Wake Up in the MIDDLE of the Night
Mini Stroke in People Over 40
Tiny White Pimples on Your Face? Here’s What Causes Them—and How to Get Rid of Them
News Post

Grilled Chicken Rice Bowl with Corn

10 symptoms of dia.betes that may show up in your feet

Loaded Cheesy Bacon Fries

Cheesy Stuffed Beef Buns (Baked Meat & Cheese Rolls)

30 Powerful Benefits of Sessile Joyweed (Alternanthera sessilis): A Traditional Plant with Remarkable Potential

Doctors warn: 6 types of food that can promote can.cer growth that people are unaware of

Why shouldn't you set the air conditioner to 26°C at night?

9 out of 10 people store onions incorrectly: Here's why you shouldn't keep them in the fridge

Smart travel tip: Why you should toss a water bottle under your hotel bed?

Don't throw away your yellowed white shirts - try this soaking method to make them bright and as good as new

Are feet an "early warning sign" of cervical can:cer? Don't ignore these 4 situations

Different Green Juices to Reduce Be.lly Fat

This is why some people always keep a lemon with them - it may help in unexpected situations

Classic Baked Lasagna

Don’t Ignore These 5 Symptoms at Night That Could Be Linked to Can.cer

Canadian Researchers Discover New Evidence That Vitamin D Shuts Down Cancer Cells

Warning: 6 vegetables that naturally contain to.xins

If you find a “Bleach” patch in your underwear - What it really means?
