
Lym.phoma: Quiet Warning Signs That Went Unnoticed Too Long
Lym.phoma: The Early Clues Many People Failed to Recognize in Time
Managing diabetes does not always require complicated systems, restrictive extremes, or expensive
supplements. While medication, regular monitoring, and professional medical supervision remain essential
foundations of care, daily lifestyle habits play a powerful supporting role.
In many cases, consistent, manageable adjustments in nutrition, activity, stress management, and hydration can
significantly improve blood sugar stability and long-term metabolic health.
The key is not perfection. It is sustainability.
Below are five practical, natural strategies that individuals living with diabetes can incorporate into everyday life
to help maintain more stable glucose levels safely and effectively.
Blood glucose levels are directly influenced by what is eaten — and how foods are combined. Carbohydrates
raise blood sugar, but the rate and intensity of that rise depend on their type and the presence of other
nutrients.
To promote steadier glucose levels:
Choose complex carbohydrates such as whole grains, legumes, and non-starchy vegetables
Pair carbohydrates with protein and healthy fats
Limit refined sugar, white bread, pastries, sweetened beverages, and ultra-processed snacks
Protein and healthy fats slow digestion and reduce rapid glucose absorption. For example, instead of eating rice
alone, combining it with lean protein, tofu, eggs, nuts, or yogurt can significantly blunt post-meal spikes.
Portion size also matters. Smaller, evenly spaced meals often result in more stable blood sugar patterns
compared to large, infrequent meals.
Consistency in meal timing can further support insulin efficiency and metabolic rhythm.
Fiber — particularly soluble fiber — plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar. It slows the absorption of
glucose into the bloodstream and improves insulin sensitivity over time.
Fiber-rich foods include:
Leafy greens, broccoli, carrots, and other vegetables
Whole grains such as oats, brown rice, and barley
Legumes including beans, lentils, and chickpeas
Fruits with edible skins, such as apples, pears, and berries
Research consistently shows that higher fiber intake is associated with better glycemic control and reduced
post-meal glucose elevations. Fiber also supports gut microbiome health, which emerging evidence links to
improved metabolic function.
A practical target for many adults is approximately 25–30 grams of fiber per day. Intake should increase
gradually to minimize digestive discomfort.
Physical activity enhances the body’s ability to use glucose effectively. When muscles contract during
movement, they absorb glucose from the bloodstream, lowering blood sugar levels naturally.
Importantly, the intensity of exercise does not need to be extreme to produce benefits.
Effective options include:
Walking for 20–30 minutes, especially after meals
Gentle cycling or swimming
Light resistance training
Stretching, yoga, or tai chi
Even a short walk after eating can significantly reduce post-meal glucose spikes. Over time, consistent
movement improves insulin sensitivity, making blood sugar easier to regulate.
In diabetes management, consistency is more important than intensity. Sustainable daily activity yields stronger
long-term outcomes than sporadic intense workouts.
Stress directly affects blood sugar regulation. When the body experiences stress, it releases hormones such as
cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones signal the liver to release stored glucose into the bloodstream,
potentially raising blood sugar levels — even in the absence of food intake.
Chronic stress and insufficient sleep can contribute to:
Increased insulin resistance
Elevated fasting glucose
Heightened cravings for high-sugar foods
Disrupted appetite regulation
Practical stress-reduction strategies include:
Deep breathing exercises
Mindfulness or meditation
Gentle physical activity
Spending time outdoors
Maintaining structured daily routines
Equally important is sleep. Obtaining 7–8 hours of consistent, quality sleep each night supports hormonal
balance, appetite control, and glucose metabolism.
Improving sleep hygiene — such as limiting screen time before bed and maintaining regular sleep hours — can have measurable metabolic benefits.
Hydration influences blood sugar concentration. When the body is dehydrated, glucose becomes more
concentrated in the bloodstream, potentially leading to higher readings.
Optimal beverage choices include:
Plain water
Unsweetened herbal teas
Warm water with lemon (without added sugar)
Sugary drinks, fruit juices, sweetened coffee beverages, and soda can cause rapid spikes in blood glucose and
should be minimized.
Adequate hydration also supports kidney function, which plays an important role in filtering excess glucose from
the blood.
Regular water intake throughout the day contributes to overall metabolic efficiency and energy balance.
While natural lifestyle strategies are powerful, they do not replace prescribed medications or professional
medical care.
Key reminders include:
Blood sugar responses vary significantly between individuals
Regular glucose monitoring helps identify what works best
Major dietary or exercise changes should be discussed with a healthcare provider
Medication adherence remains essential
Diabetes management is individualized. What stabilizes blood sugar for one person may require adjustment for
another.
Stabilizing blood sugar does not require extreme measures. It often begins with simple, repeatable habits:
Eating balanced meals
Increasing fiber intake
Moving consistently
Managing stress
Staying well hydrated
Over time, small daily decisions compound into meaningful health outcomes. For individuals living with
diabetes, steady routines create protective effects that extend far beyond glucose control — supporting
cardiovascular health, energy levels, and overall well-being.
In many cases, the most powerful medicine is not dramatic. It is consistent.
And it begins with how daily life is structured.

Lym.phoma: The Early Clues Many People Failed to Recognize in Time
Lym.phoma: Early Symptoms Survivors Say They Overlooked Before Diagnosis
Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.
Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.
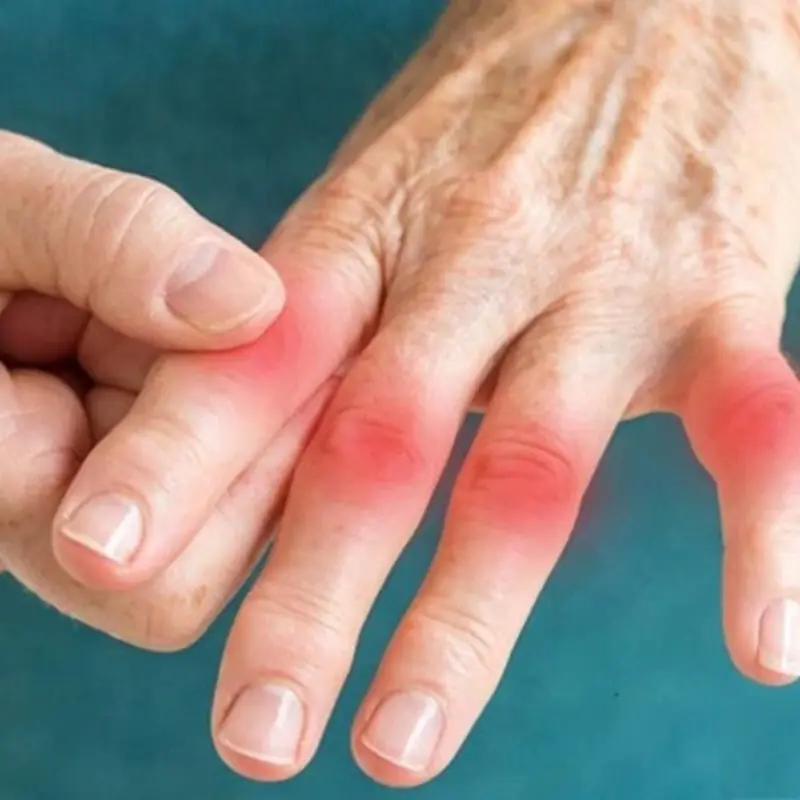
A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.
Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.
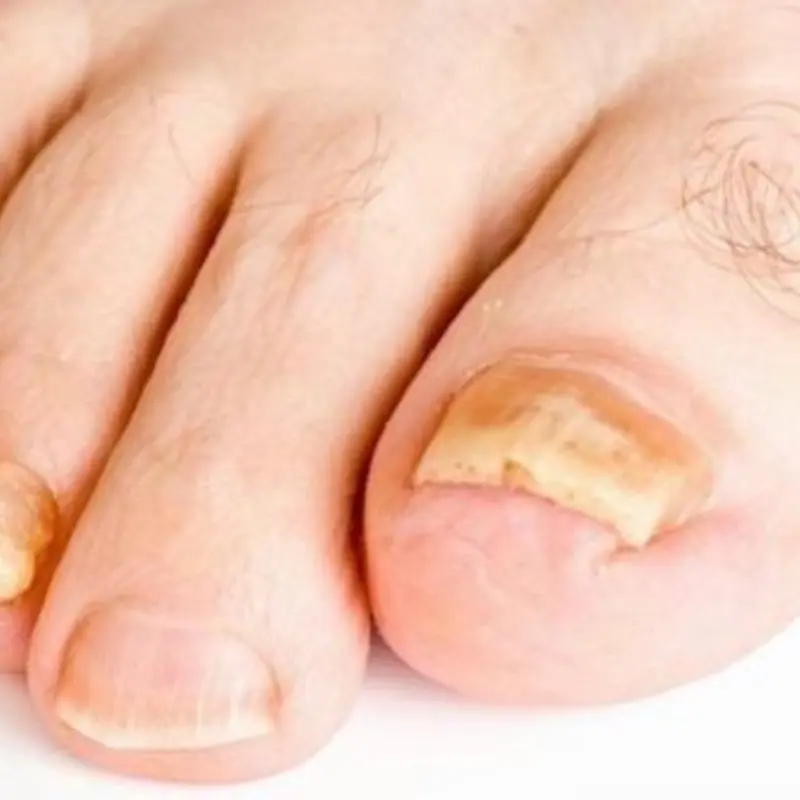
Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.
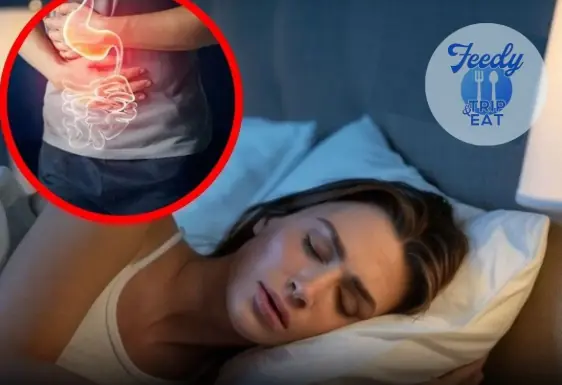
Despite having a full night’s rest, many people still get up feeling sleepy and lacking energy.
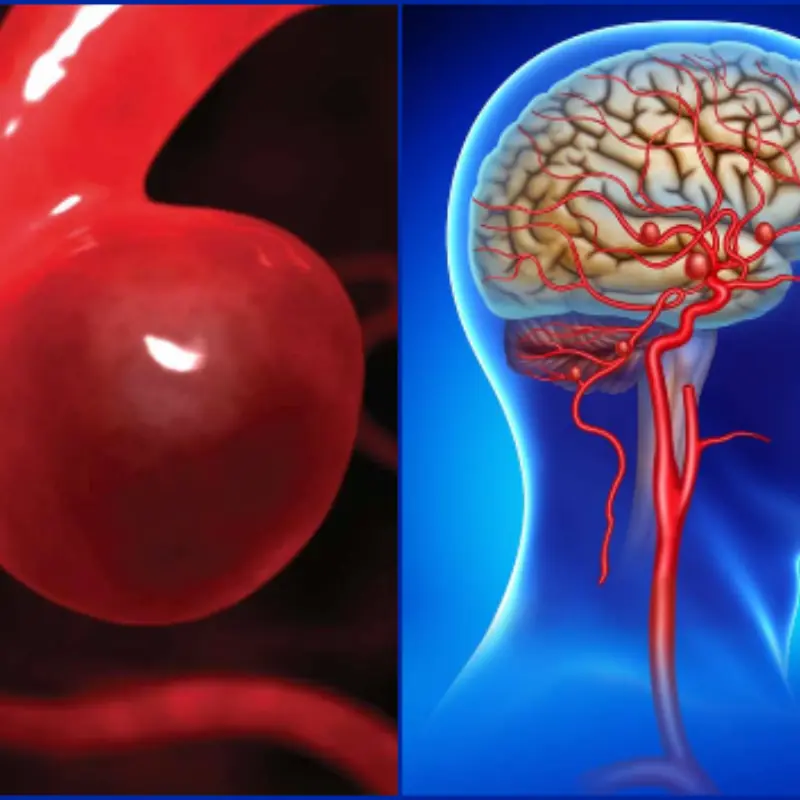
Hidden aneurysm signs can appear suddenly and turn life-threatening.
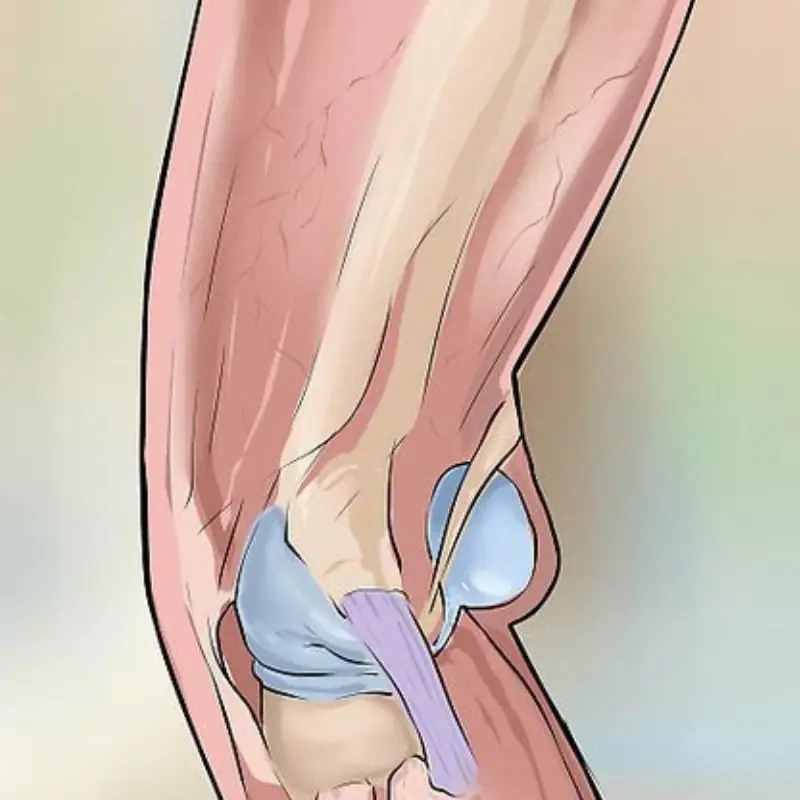
Pain behind the knee may signal hidden health risks—don’t ignore it.

Pay attention to these signs!
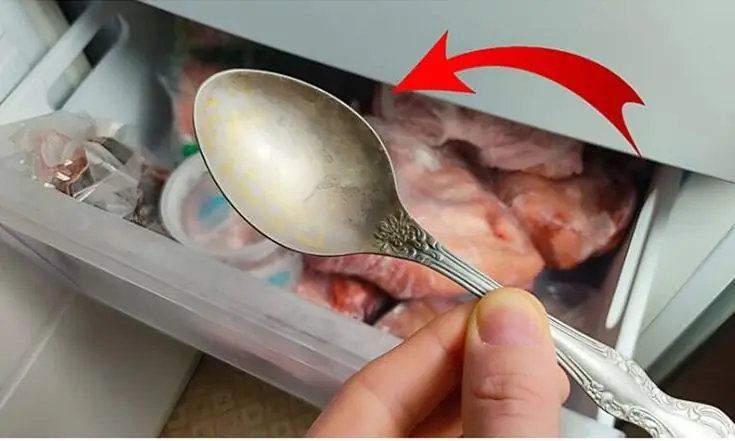
Almost no one knows about it, and it's more useful than you think
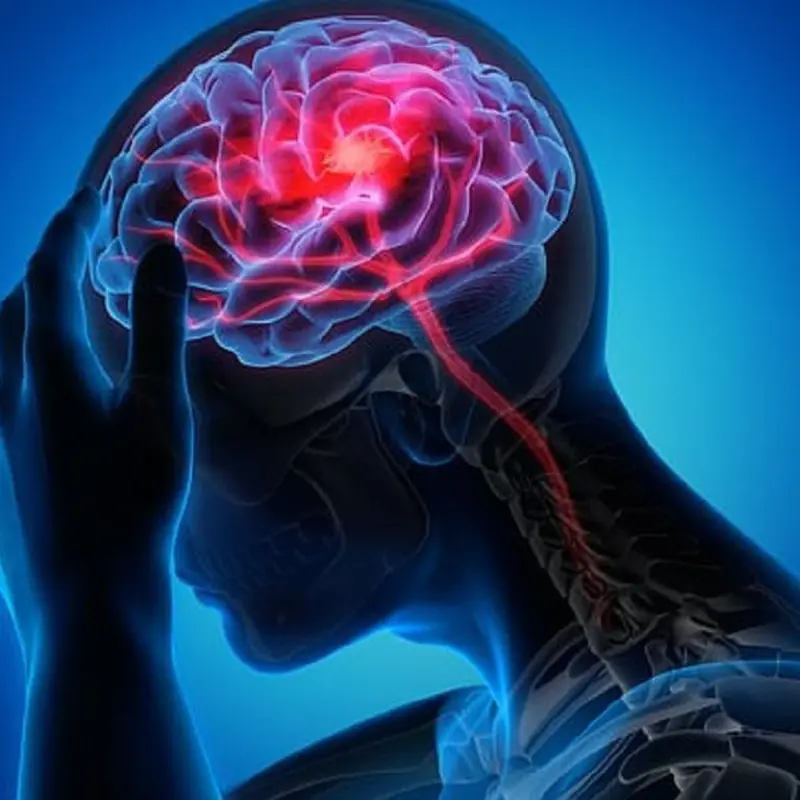
9 subtle warning signs of brain clots that may appear before a stroke
Doctors warn after woman develops sudden kidney failure post-dinner.
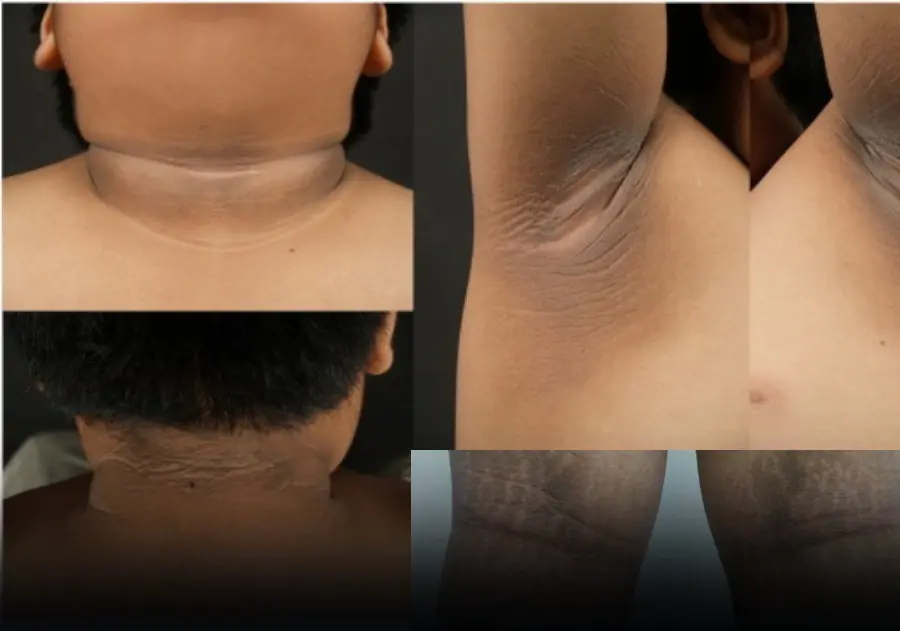
It commonly occurs in healthy people, but in some cases it can be a sign of an underlying disease.

Why You Should Drink Water on an Empty Stomach Immediately After Waking Up
Your eyes can reveal more than you think — even hidden signs of diabetes that often go unnoticed

Lym.phoma: The Early Clues Many People Failed to Recognize in Time

Lym.phoma: Early Symptoms Survivors Say They Overlooked Before Diagnosis

Toothpaste and Salt Combined: Unexpected Benefits You Can Use at Home

The day my ex husband and my new husband sat at the same table changed everything for our kids

Our blended family felt like a competition until we faced a challenge together

I was convinced my son in law did not respect me until i understood his silence

When Our Parents Remarried I Thought I Lost My Place In The Family Until I Found A Brother Instead

Growing up with a half sister i barely knew taught me what family really means

My father in law never thought I was good enough until the day we were stranded together

Living with my in laws felt impossible until we learned to become a real family

My father in law was always quiet around me until I discovered the reason
I thought my mother in law would never accept me until the day she stood up for me

Diabetic neuropathy complications are one of the most common chronic complications of diabetes and also a major cause of diabetic foot disease.

Bathing is a habit that helps clean the body and relax, but we should not always bathe immediately.

The Myth About Fruits Feeding Cancer Cells: A Critical Look at the Claims

Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical cancer in women.

A hidden disease may grow silently — and one habit worsens it.

Garlic has long become an indispensable spice in the family kitchen.

Two small changes in your feet may reveal serious hidden health risks.