A Common Mistake Countless Families Don’t Even Know They’re Making
Using an Electric Kettle the Wrong Way: 6 Common Mistakes That Can Quietly Harm Your Kidneys
Electric kettles are a daily essential in many households. They are fast, convenient, and seem harmless. A press of a button, a few minutes of waiting, and hot water is ready for tea, coffee, instant noodles, or cooking. However, few people realize that how an electric kettle is used can gradually affect kidney health over time.
The kidneys play a critical role in filtering waste, balancing fluids, and regulating minerals in the body. Small, repeated habits that increase toxin intake, mineral overload, or dehydration can quietly place extra strain on these organs. Below are six common electric kettle mistakes that may contribute to kidney stress if they become long-term habits.
1. Reboiling Water Multiple Times
One of the most common mistakes is repeatedly boiling the same water. When water is boiled, some of it evaporates, but minerals such as calcium, magnesium, nitrates, and heavy metals remain. Reboiling concentrates these substances further.
Over time, regularly drinking reboiled water may increase mineral intake beyond what the kidneys comfortably handle. This can raise the risk of kidney stones or worsen existing kidney conditions, especially in people who already have reduced kidney function.
2. Using the Kettle to Boil Anything Other Than Water
Some people use electric kettles to boil instant noodles, eggs, soup, or even herbal mixtures directly inside the kettle. This is a serious misuse. Food residues can react with heat and metal surfaces, releasing unwanted compounds into the water.
Leftover starch, seasoning, or oils can also promote bacterial growth if the kettle is not thoroughly cleaned. Drinking water contaminated with these substances may increase toxin exposure, forcing the kidneys to work harder to filter them out.
3. Rarely Cleaning the Kettle Interior
Mineral scale buildup inside kettles is often ignored because it seems harmless. In reality, limescale indicates a high concentration of minerals that continue to dissolve into boiling water.
Consistently drinking mineral-heavy water can burden the kidneys, especially in individuals prone to kidney stones. In addition, neglected kettles may harbor bacteria or mold, particularly around the lid and spout, increasing the risk of low-grade infections or inflammation.
4. Drinking Very Hot Water Frequently
Drinking water that is extremely hot can irritate the lining of the mouth, throat, and digestive tract. While this may not directly damage the kidneys, it can reduce fluid intake overall because very hot water discourages proper hydration.
Chronic mild dehydration is a known risk factor for kidney damage. When fluid intake is insufficient, the kidneys must concentrate urine more heavily, increasing stress on kidney tissues and raising the risk of stone formation.
5. Using Poor-Quality or Contaminated Water Sources
Boiling water does not remove all harmful substances. Heavy metals, excessive fluoride, and certain chemical residues remain even after boiling. If an electric kettle is consistently used with low-quality tap water or unfiltered sources, these substances may accumulate in the body.
The kidneys are responsible for filtering these toxins. Long-term exposure, even at low levels, can contribute to declining kidney function, particularly in older adults or those with pre-existing health conditions.
6. Replacing Water Only Once a Day
Filling the kettle once in the morning and using the same water all day increases the likelihood of reboiling and concentration of impurities. Stagnant water may also absorb odors, dust, or airborne contaminants, especially if the kettle lid is frequently opened.
Fresh water should be used each time boiling is needed. This simple habit reduces unnecessary mineral buildup and limits the kidneys’ exposure to concentrated substances.
Why the Kidneys Are Especially Vulnerable
Unlike many organs, the kidneys filter the entire blood supply multiple times a day. Even small increases in toxins, minerals, or dehydration can have cumulative effects. Damage often develops silently, without pain or obvious symptoms, until kidney function is significantly reduced.
Fatigue, swelling, changes in urination, or high blood pressure may appear only after long-term stress has already occurred.
Safer Habits for Kidney-Friendly Kettle Use
Protecting kidney health does not require eliminating electric kettles, only using them correctly:
-
Always pour out leftover water after boiling
-
Avoid reboiling previously heated water
-
Use filtered or high-quality water when possible
-
Clean the kettle regularly to remove mineral buildup
-
Use the kettle for water only, never food
-
Allow water to cool slightly before drinking
Final Thought
Electric kettles are not dangerous by nature, but everyday misuse can quietly contribute to kidney strain over time. These effects are subtle, cumulative, and often overlooked because they do not cause immediate discomfort.
Paying attention to small daily habits can make a meaningful difference in long-term kidney health. Sometimes, protecting vital organs starts with something as simple as how water is boiled and consumed.
News in the same category


The real electricity th.ief in your home

Scientists Finally Reveal a Sho:cking Answer to the ’Chicken-or-Egg’ Dilemma

Two-Way Mirrors: The Privacy Risks Most People Don’t See

Put ginger next to your pillow when sleeping: A simple secret for good health and sleep
Why do dogs ba.rk and bi.te some people but not others? There's always a reason!

Packed with powerful nutrients, these 3 humble vegetables are hailed in Japan
The small button on your phone that connects to Wi-Fi automatically: No password needed, no mobile data used — what’s the truth?

Applying Medicated Oil to the Soles Before Sleep: A Traditional Practice with Potential Benefits

When a lizard visits your house that’s a sign...

Even if you remain single forever, never marry a man from these 4 types of families

You Sleep on It Every Night — But Could It Be Exposing You to Toxins?

Out at Night and See This Scene? Don’t Get Closer

The Anti-Can:cer Vegetable Ranked Best in the World by U.S. Experts

3 vegetables that may cause can.cer avoid them now

Applying Toothpaste to Ginger: A Little-Known Household Trick With Surprising Benefits

Remove This One String to Eliminate Fishy Smell — A Simple Cooking Secret Many People Miss

The Plant That Mosquitoes and Snakes Both Avoid — A Natural Protector for Your Home
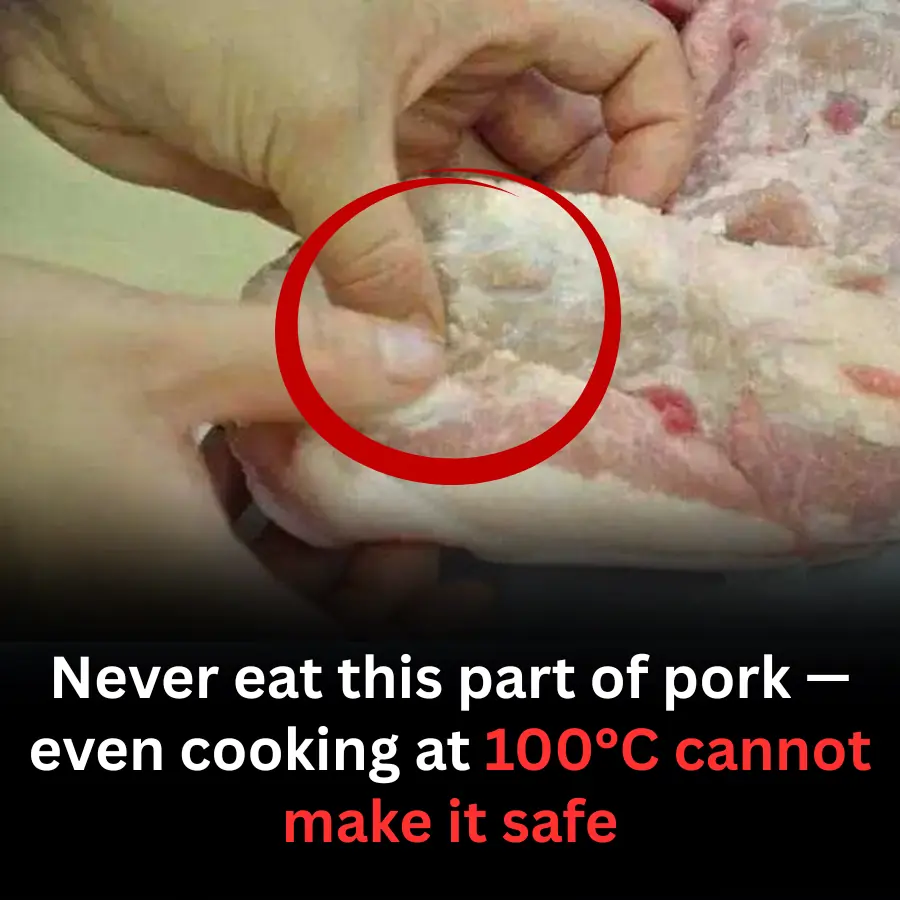
Never Eat This Part of Pork: Even 100°C Heat Cannot Eliminate the Danger
News Post

Eating Taro the Right Way: A Simple Habit That May Support Can:cer Prevention and Overall Health

7 Morning Symptoms Your B.o.dy Might Be Using to Signal Hidden Diabetes
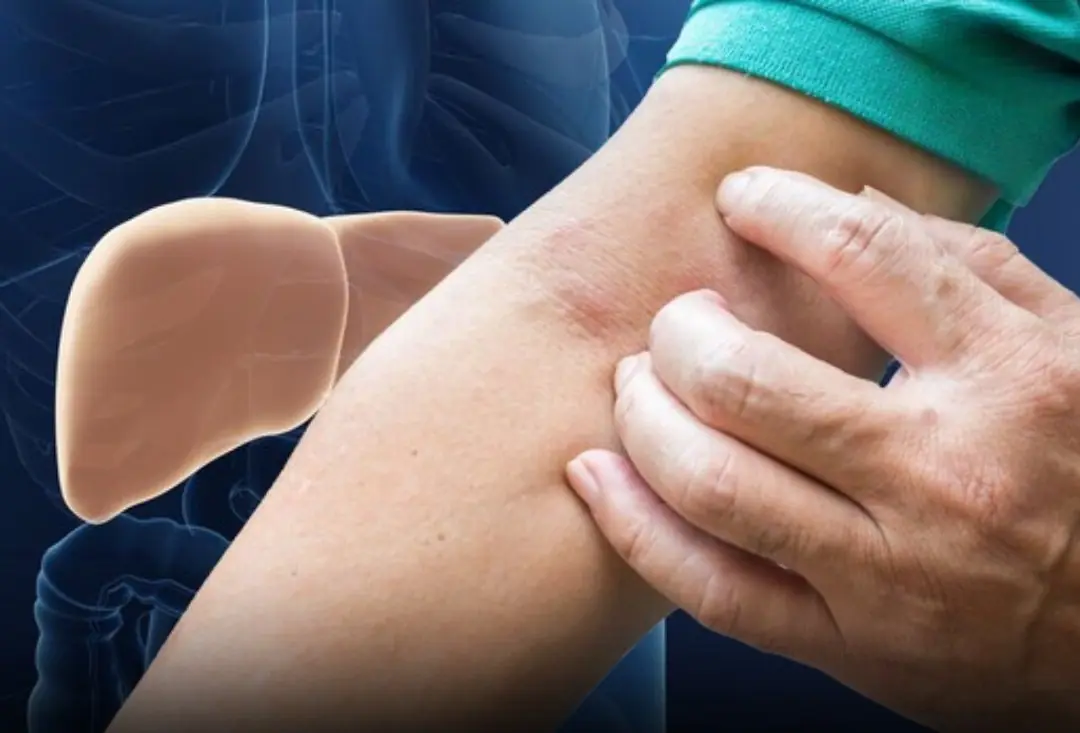
See any of these symptoms? Don’t hesitate — get checked immediately!
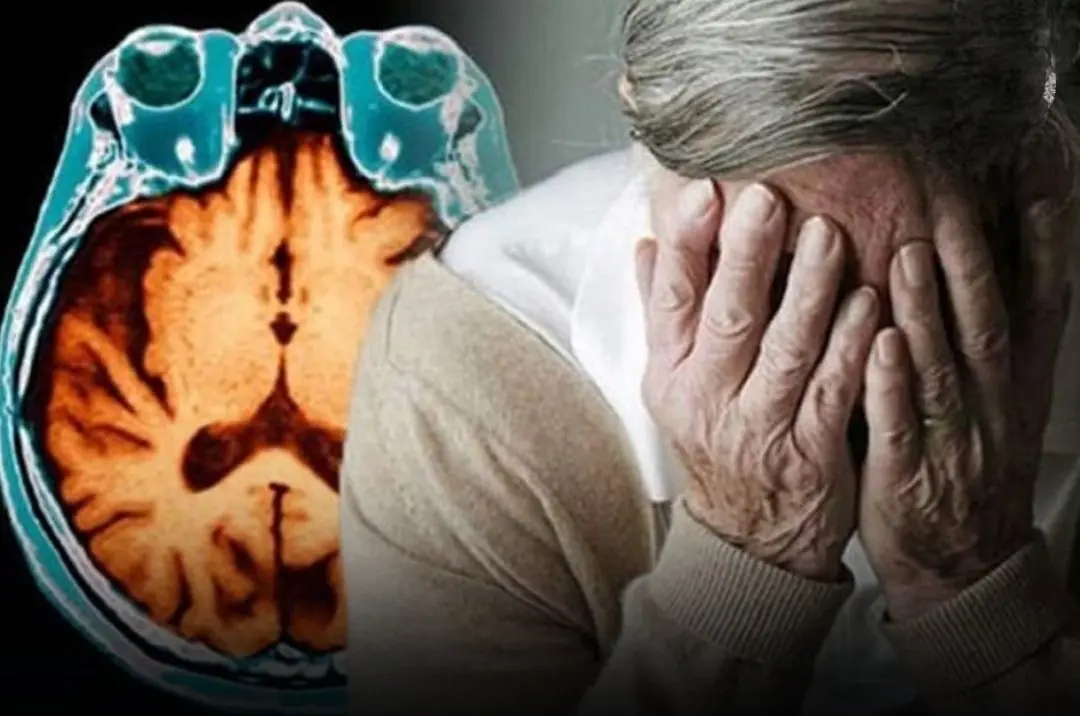
Roughly 15 minutes before a str.ok.e strikes, the body often sends out 4 unmistakable war.ning signs
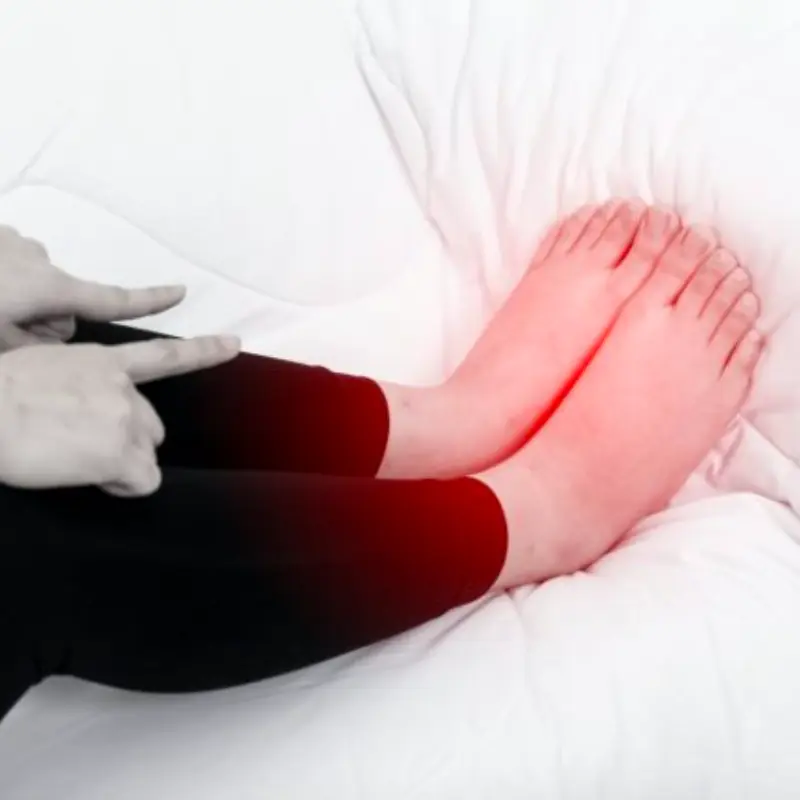
7 Subtle Signs That Your Heart May Be Having Problems – Don’t Ignore These Warnings
Scientists say they found the cellular "mortality timer" that dictates aging
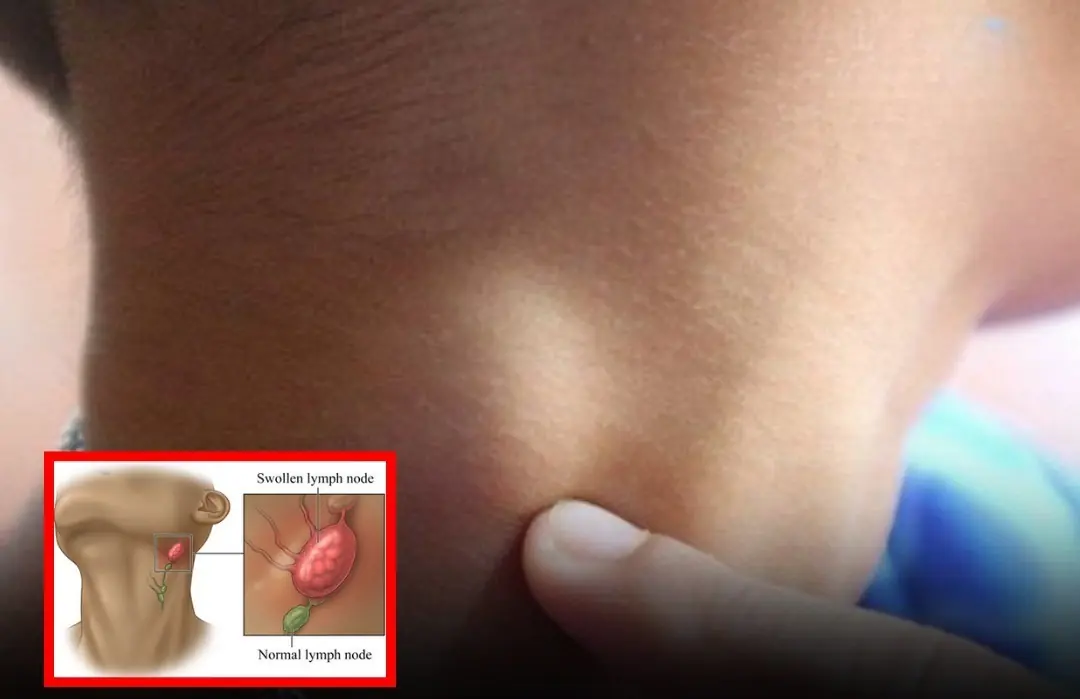
Ne.ck Swe.lling and Lymph No.des: Know When It’s Time to Act

In winter, drying thick clothes is a slow process—and sometimes, they end up smelling bad.

8 signs that you have low blo.od oxygen levels.

Smart tips to get rid of cockroaches and maintain a clean, fresh home
Wake up and see these 10 signs? Be careful - your blo:od sugar could be spiking
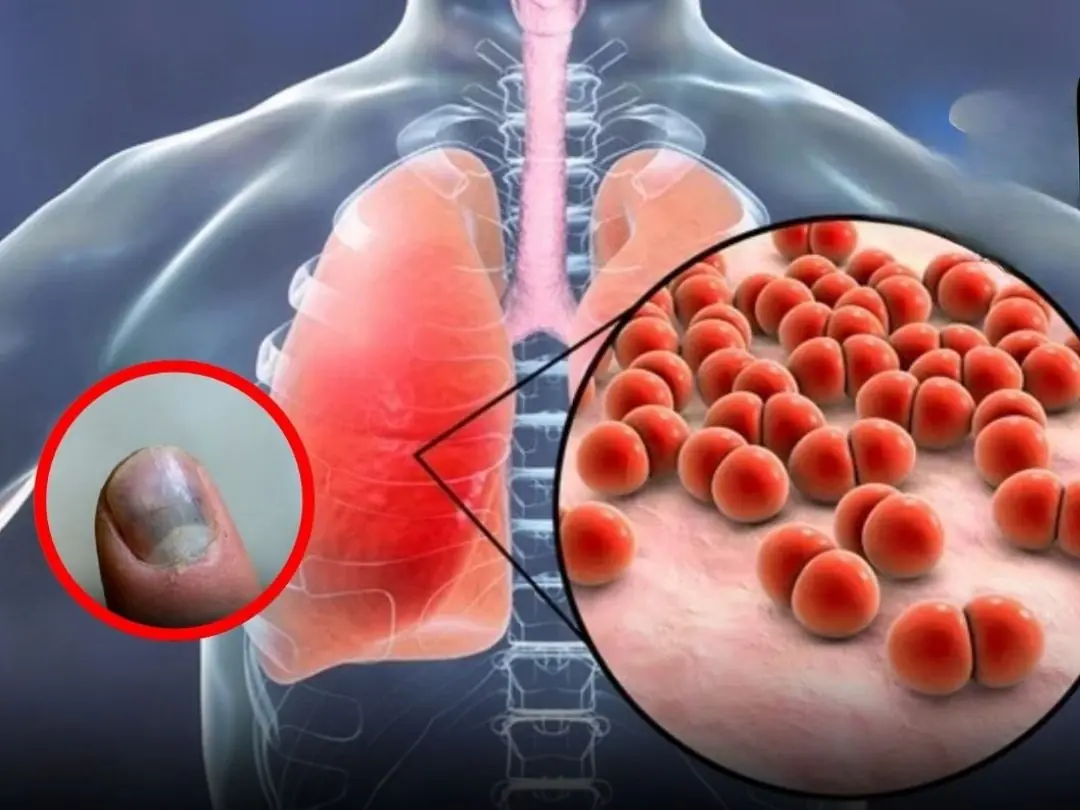
Your Hands Might Be Exposing Serious Lu.ng Trouble Without You Realizing It

This “Anti-Can.cer King” Vegetable Is Tiny But Its Benefits Are Huge

Crispy Buffalo Chicken Bites with Creamy Ranch Dip

Pan-Seared Steak with Creamy Pepper Sauce

Morning sweet potatoes: A simple daily habit that brings major health benefits

Strawberry Basil Citrus Juice (Blush Pink & Aromatic)
The odd lung can:cer symptom you can spot on your fingers – and the 9 other signs you must know