A mortality timer based on nucleolar size triggers
Genome instability is a hallmark of aging, with the highly repetitive ribosomal DNA (rDNA) within the nucleolus being particularly prone to genetic damage. Aging is often accompanied by nucleolar enlargement across diverse organisms, from yeast to mammals. Interestingly, various anti-aging interventions correlate with smaller nucleoli, suggesting a direct link between nucleolar size and lifespan regulation. However, the precise mechanism by which nucleolar expansion drives aging remained unclear—until now.

Nucleolar Size and Aging: A Direct Connection
In a recent study, researchers engineered a system to artificially reduce nucleolar size in budding yeast. Surprisingly, this intervention led to a significant extension of replicative lifespan, even though it did not alter protein synthesis rates or rDNA silencing—two processes closely linked to nucleolar function. Instead, the key determinant of lifespan appeared to be the biophysical properties of the nucleolus and its ability to maintain a selective barrier against unwanted proteins.
As nucleoli expand beyond a critical size threshold, their internal organization is disrupted. This allows proteins that are normally excluded from the nucleolus, such as Rad52, a key homologous recombination repair factor, to infiltrate the nucleolar space. The entry of Rad52 triggers aberrant recombination events within rDNA, leading to heightened genome instability, DNA damage accumulation, and ultimately cellular death. These findings strongly suggest that nucleolar expansion is not just correlated with aging but is sufficient to drive the process.
A ‘Mortality Timer’ for Cells
A particularly intriguing discovery from this research is that nucleolar expansion appears to act as a built-in mortality timer for cells. Once nucleoli surpass a certain size limit, their phase-separated condensate properties weaken, allowing genome-destabilizing events to accelerate. This threshold-dependent disruption provides a mechanistic explanation for why nucleolar size is such a strong predictor of cellular lifespan.
Moreover, these findings align with observations in higher organisms, where nucleolar hypertrophy is often associated with age-related diseases such as cancer and neurodegeneration. This suggests that targeting nucleolar integrity could be a promising strategy for extending lifespan and mitigating age-related genome instability in humans.
Future Implications: Can We Target Nucleolar Expansion?
Given the strong link between nucleolar size and aging, developing interventions to regulate nucleolar expansion could be a novel anti-aging strategy. Potential approaches might include:
- Pharmacological compounds that modulate nucleolar structure and prevent excessive expansion.
- Dietary and metabolic interventions, such as caloric restriction and rapamycin treatment, which have been shown to reduce nucleolar size and extend lifespan.
- Genetic modifications targeting key nucleolar components to maintain their selective permeability and prevent rDNA instability.
By controlling nucleolar expansion, it may be possible to delay aging and improve genome stability, ultimately extending healthy lifespan in various organisms—including humans.
News in the same category
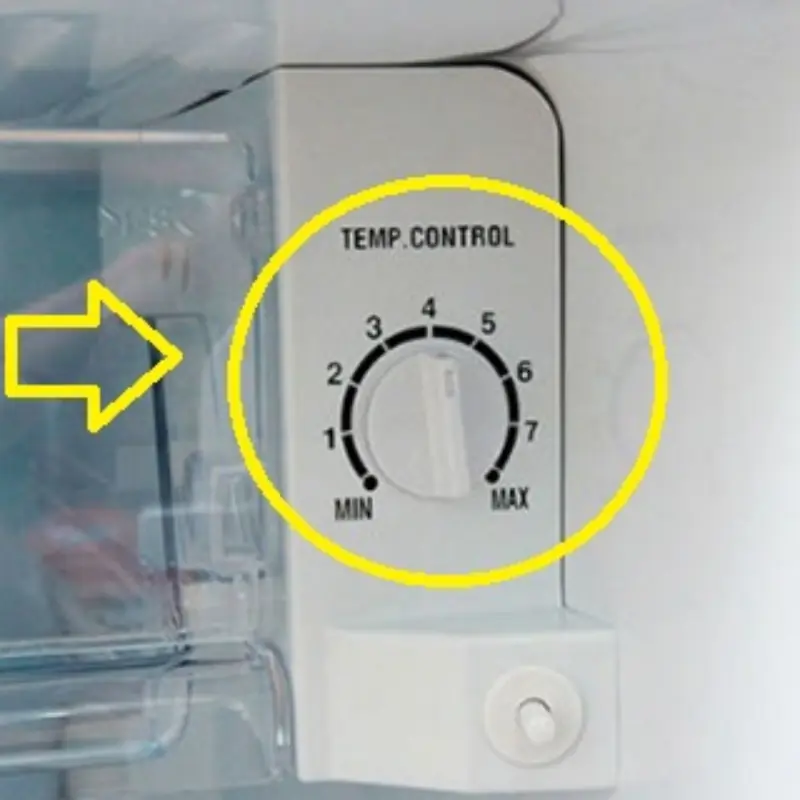


Save a ton of money on electricity

Do not immerse fish directly in water

Unexpected benefits but few people know

4 Clothes-Drying Mistakes That Can Harm Your Health—Common in Humid Weather

What is the effect of squeezing lemon juice into the frying oil before frying?

3 types of sprouted vegetables are very good

Why should you put a cup of salt water at the head of your bed
A mortality timer based on nucleolar size triggers
One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs

Add Fabric Softener to Floor Cleaner! Great Tip You Didn't Know

Use this leaf to wash your hair, hair problems will be solved
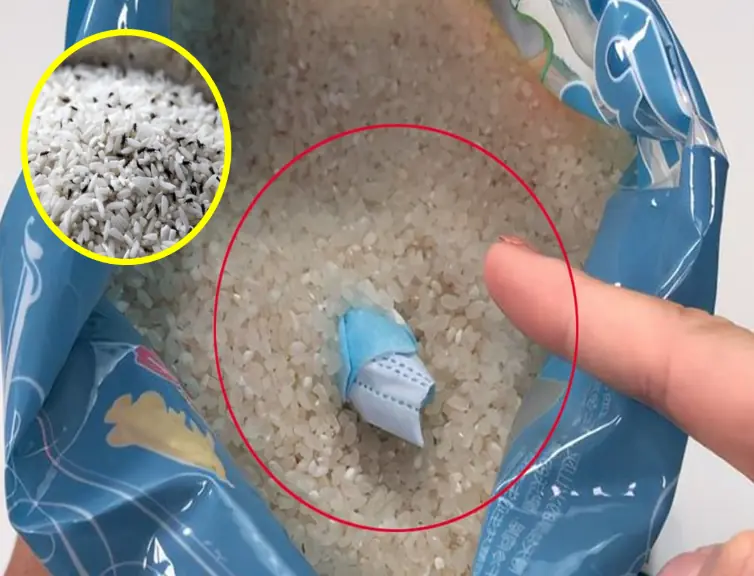

How to Store Rice to Prevent Moths and Mold

Tips for cleaning wooden cu.tting boards quickly and cleanly
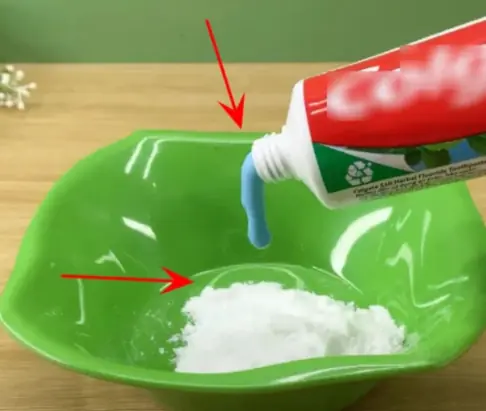

Mix toothpaste with this, clean plaque
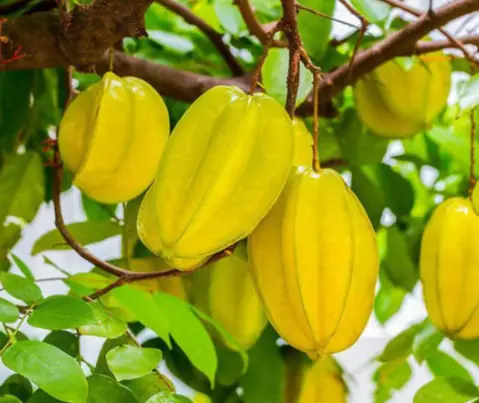

The type of water that star fruit trees like best
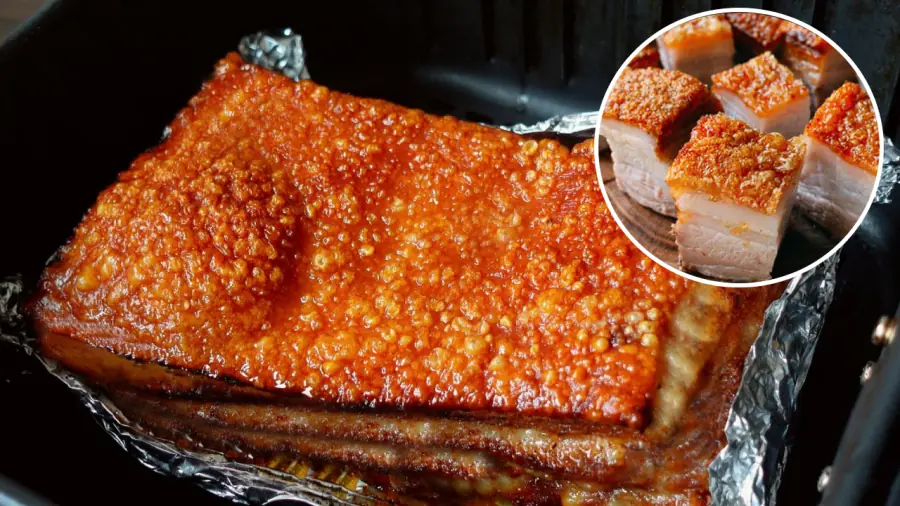

Simple Tips for Making Crispy Roasted Pork with Perfect Crackling

Why you should place peppercorns under your bed?
How to preserve and things you may not know about avocado

When buying melons, just look at this point to know which ones are ripe, sweet, juicy, and safe.
News Post

Refreshing and Healing: How to Make and Use Lemongrass Tea

Quick and Odor-Free Fish Defrosting Tips + 4 Common Mistakes to Avoid

Mullein: Unlocking the Healing Powers of Its Leaves, Flowers, and Roots

Wild Spinach Power: 10 Health Benefits of Lamb’s Quarters You Should Know

Save a ton of money on electricity

Do not immerse fish directly in water
Don't ignore these warning signs
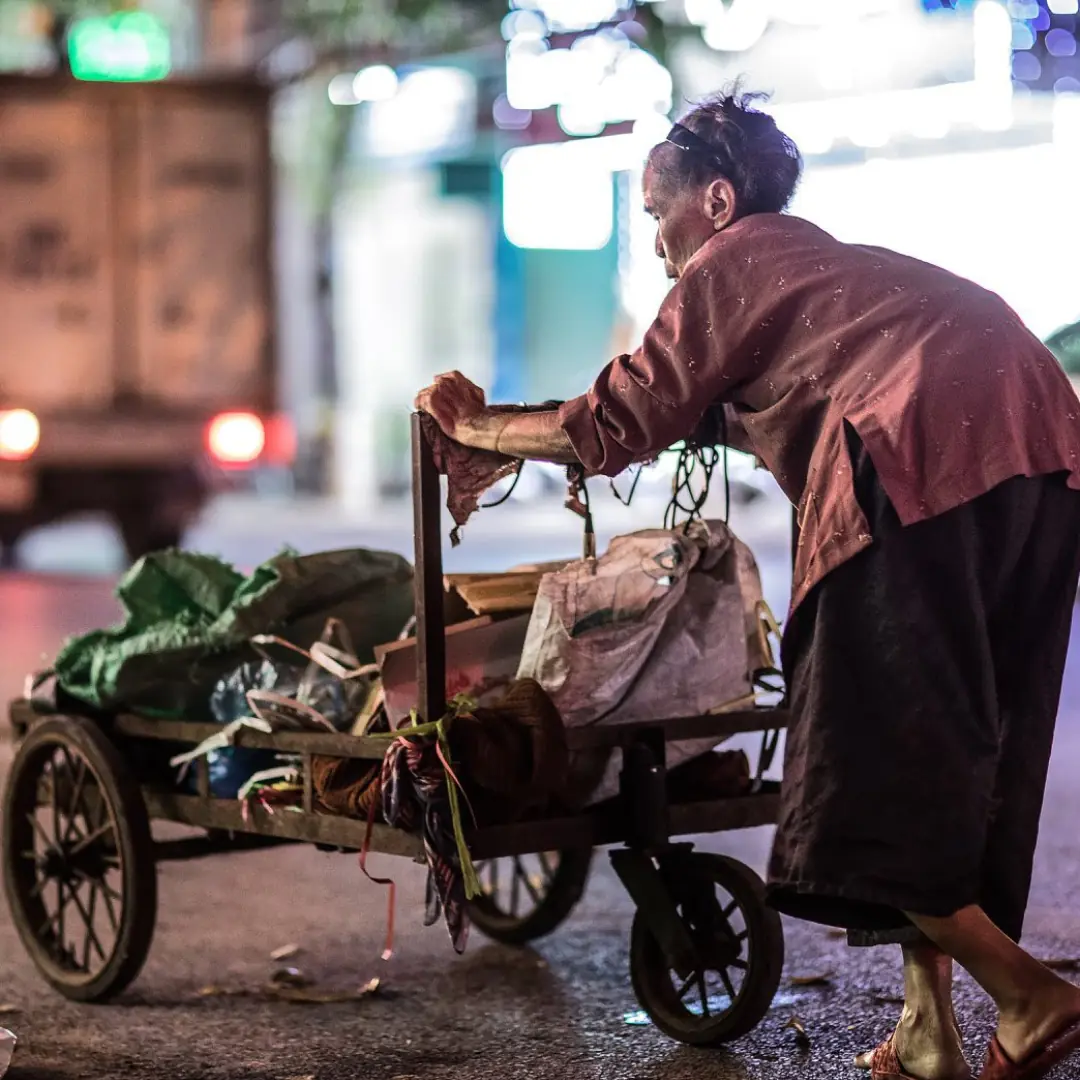

Tears fall over photo series of 83-year-old woman with hunched back struggling to pick up trash at night to raise 2 gran.dch.ildren

Unexpected benefits but few people know

4 Clothes-Drying Mistakes That Can Harm Your Health—Common in Humid Weather

What is the effect of squeezing lemon juice into the frying oil before frying?

3 types of sprouted vegetables are very good

Why should you put a cup of salt water at the head of your bed

One Month Before A Heart Attack, Your Body Will Warn You Of These 7 Signs
Fatty Liver: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment & Home Remedies
Early Signs Your Body is Fighting Cancer
Before can:cer arrive, hands and feet often have these 4 signs

Only women can spot the abnormality in the photo