
From Detox to Heart Health: 10 Reasons Basil Is a Natural Superfood
Often seen as a simple garnish or aromatic addition to meals, basil is far more than a flavorful herb.
Breathing is automatic — but how you breathe matters.
While both the nose and mouth can move air in and out of the lungs, they serve very different physiological functions. Nasal breathing isn’t just a preference — it’s a biologically optimized system designed to filter, humidify, and regulate airflow before it reaches the lungs.
Your nose acts as a multi-layer filtration and conditioning unit.

As air passes through nasal passages, it is:
Mouth breathing bypasses these processes.
While useful during intense exercise or congestion, chronic mouth breathing — especially during sleep — has been associated with:
Nasal breathing also influences diaphragm mechanics.

Breathing through the nose naturally encourages slower, deeper breaths that engage the diaphragm rather than shallow chest breathing. This supports parasympathetic (calming) nervous system activation, promoting relaxation and recovery.
Mouth breathing, in contrast, is often faster and shallower, which may reinforce stress signaling pathways.
Signs of habitual mouth breathing include:
Improving nasal breathing habits can involve:
Over time, many people report improvements in sleep depth, endurance, and baseline calmness when nasal breathing becomes dominant.

Breathing may be automatic…
But optimizing how you breathe can quietly reshape how you sleep, recover, and function daily.

Often seen as a simple garnish or aromatic addition to meals, basil is far more than a flavorful herb.
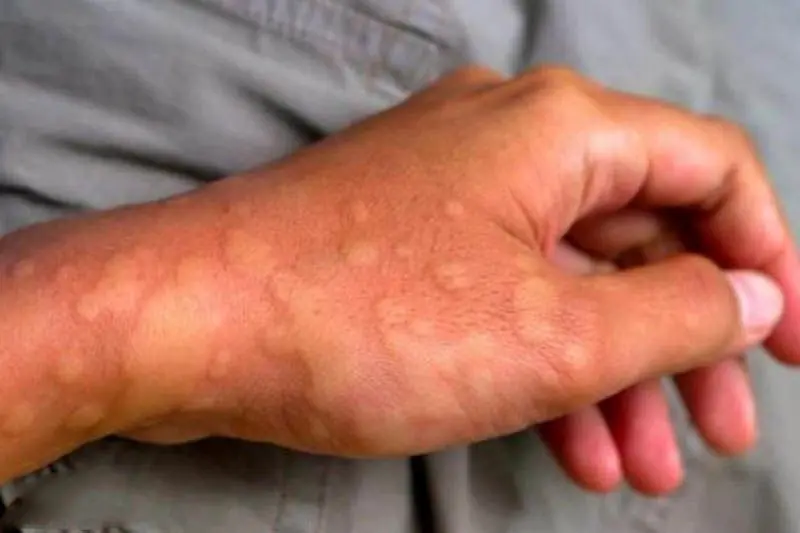
After suffering from prolonged itching, a 37-year-old woman sought specialized medical examination and was diagnosed with infections from five different parasites

Consuming it incorrectly can transform this fruit into a silent threat to the liver.


As healthy living trends continue to grow, coconut water is often viewed as a relatively pure “natural electrolyte drink.”



Chicken gizzards: the overlooked superfood packed with nutrients










Often seen as a simple garnish or aromatic addition to meals, basil is far more than a flavorful herb.

I’m 73 Years Old. I Live Alone, But I Never Feel Lonely. My Top 4 Tips

After suffering from prolonged itching, a 37-year-old woman sought specialized medical examination and was diagnosed with infections from five different parasites

Consuming it incorrectly can transform this fruit into a silent threat to the liver.
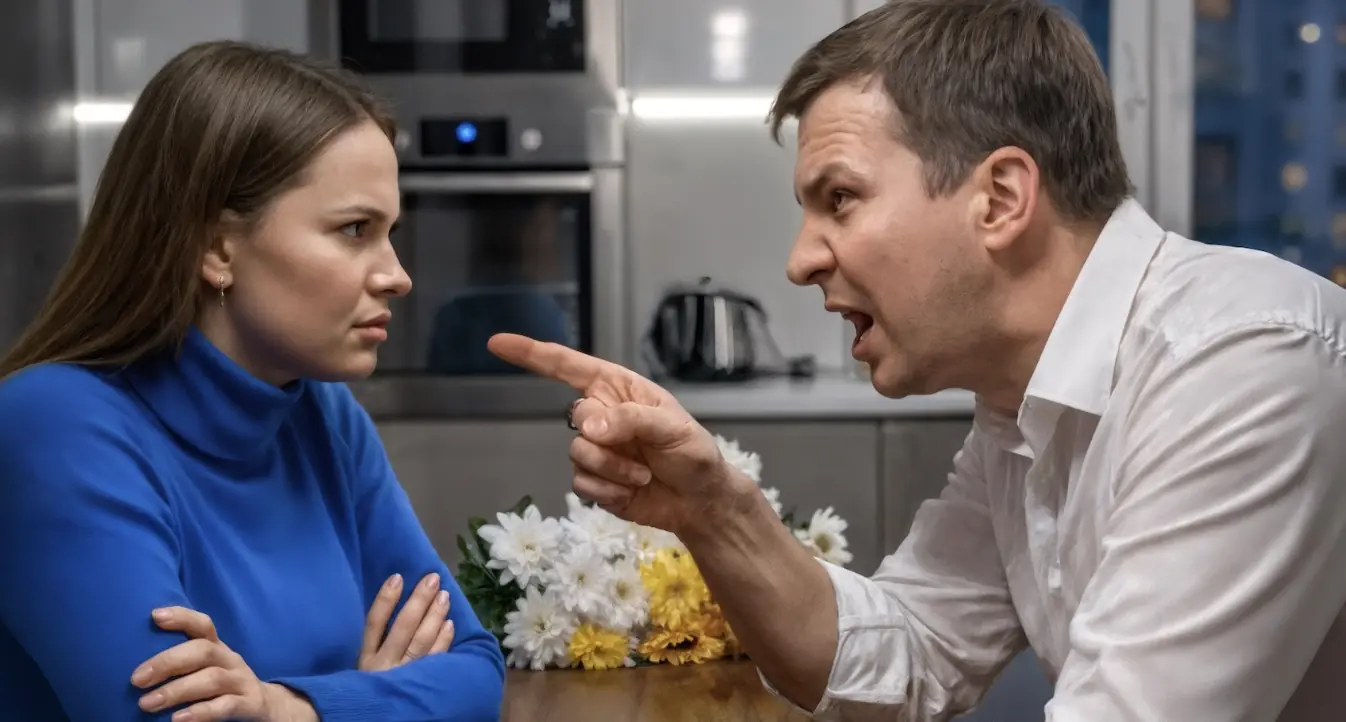

“Who Cares Whose Apartment It Is? I’m the Man — That Means I Run Everything,” the Unemployed Husband Declared
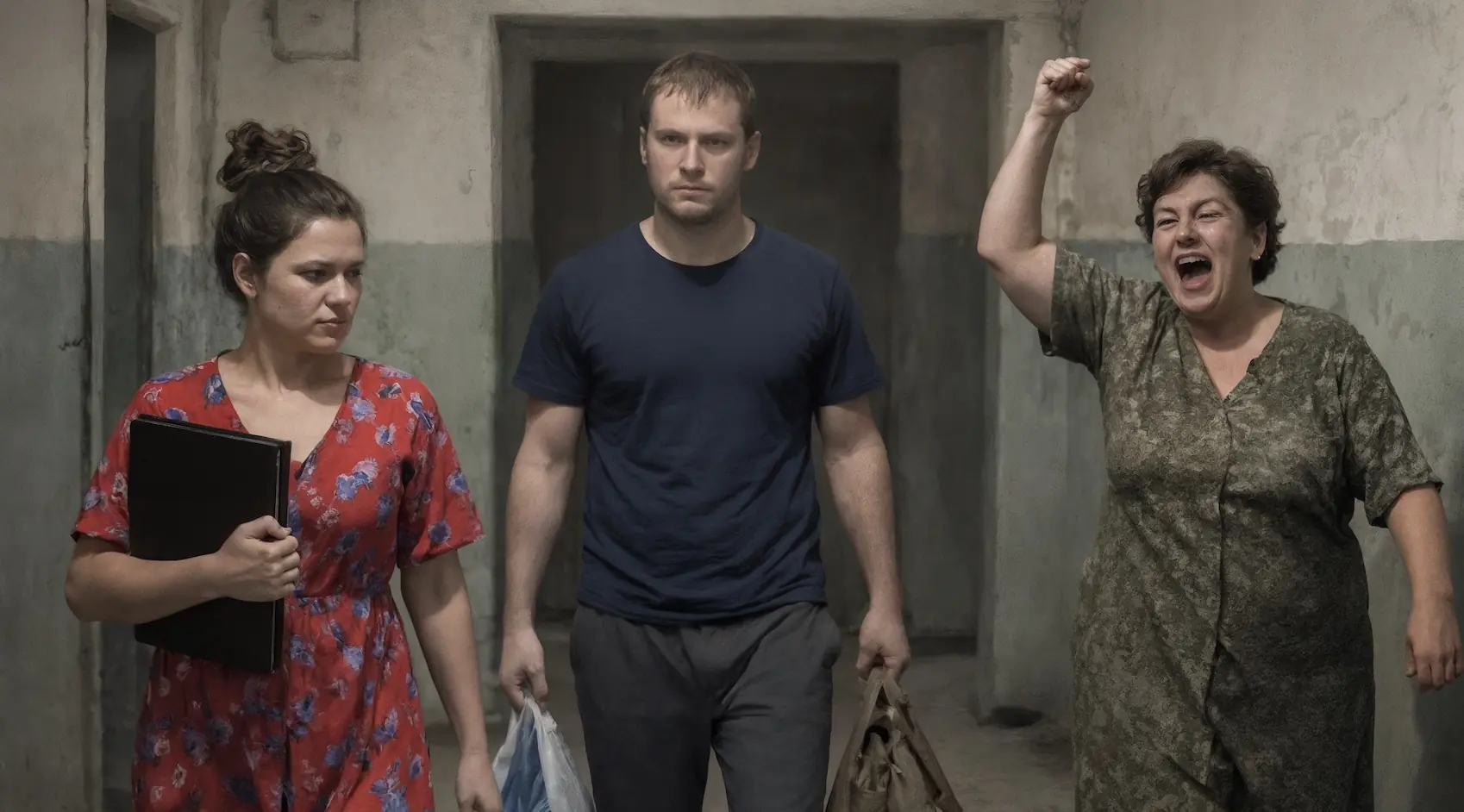

“Now that’s a real man — he squeezed the chicken dry!” the mother-in-law was already celebrating her victory
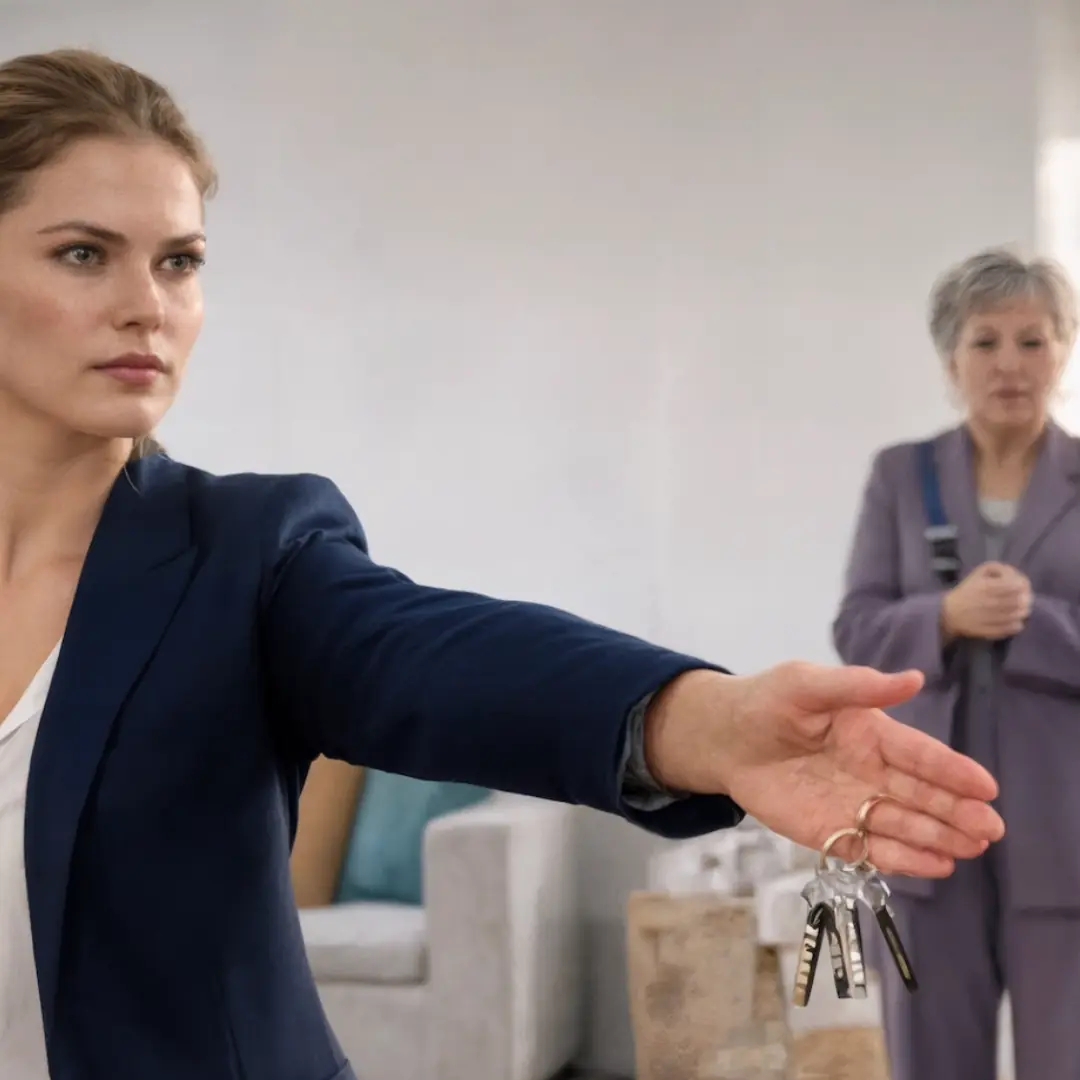

“I’m the one buying the groceries, and this house is“I’m the one buying the groceries, and this house is mine—so pack up and get out.” I cut off my mother-in-law’s little performance mine—so pack up and get out.” I cut off my mother-in-l


“Stop spending money on yourself—our son needs to save up for a car!” my mother-in-law snapped, eyeing my manicure





As healthy living trends continue to grow, coconut water is often viewed as a relatively pure “natural electrolyte drink.”



Chicken gizzards: the overlooked superfood packed with nutrients

