
A Young, Healthy Man Uncovered a Serious Tuber.cu.losis Infection from a Small, Ignored Sign
A 22-Year-Old in Good Health Discovered Severe Tu.bercu.losisfrom a Subtle Warning Sign
Headlines that blame “selfish husbands” oversimplify a complex medical issue. Cervical cancer is primarily caused by persistent infection with high-risk human papillomavirus (HPV) — a very common virus transmitted through intimate skin-to-skin contact.
This is not about blame. It is about understanding shared responsibility in sexual health.
Here are three relationship-related factors that science shows can influence risk.
HPV is extremely common. Most sexually active adults will encounter it at some point.
Key facts:
High-risk HPV strains (especially HPV-16 and HPV-18) are linked to cervical cancer.
Many people with HPV have no symptoms.
The immune system clears most infections within 1–2 years.
Persistent infection is the main risk factor.
Using condoms reduces HPV transmission risk but does not eliminate it entirely because HPV spreads through skin contact.
Vaccination and screening remain the most powerful prevention tools.
The risk of HPV exposure increases with the number of lifetime sexual partners — for both men and women.
If one partner has had multiple previous partners, the probability of prior HPV exposure increases.
Important:
This is about epidemiology, not morality.
HPV can persist silently for years.
Long-term monogamy does not guarantee zero risk if prior exposure occurred.
Open communication and preventive care matter more than stigma.
Smoking weakens the immune system’s ability to clear HPV infections.
Studies show:
Women who smoke have a higher risk of cervical cancer.
Exposure to secondhand smoke may contribute to immune suppression.
If one partner smokes, quitting benefits both individuals’ health — not only regarding cancer risk but also heart and lung health.
Cervical cancer is highly preventable with modern medical care.
Recommended for adolescents and young adults.
Effective against the most dangerous HPV strains.
Can significantly reduce lifetime risk.
Detects precancerous cell changes.
Allows treatment before cancer develops.
Screening saves lives.
Communication between partners.
Routine health check-ups.
Awareness of symptoms.
Early cervical cancer usually has no symptoms.
Later signs may include:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding
Bleeding after intercourse
Pelvic pain
Pain during intimacy
Unusual discharge
Any persistent abnormal symptom should be evaluated.
Cervical cancer does not happen overnight. It develops gradually over years through precancerous changes.
The narrative should not focus on blame but on prevention.
Both partners share responsibility for:
Vaccination
Screening
Smoking cessation
Open health communication
Cervical cancer is primarily linked to persistent high-risk HPV infection.
Certain behaviors can increase exposure risk, but modern prevention methods — especially vaccination and routine screening — are highly effective.
Awareness empowers families. Fear-based headlines do not.

A 22-Year-Old in Good Health Discovered Severe Tu.bercu.losisfrom a Subtle Warning Sign

Tofu Is Healthy, But Certain People May Need to Limit It

Morning Sweet Potatoes: A Small Change That Can Transform Your Health
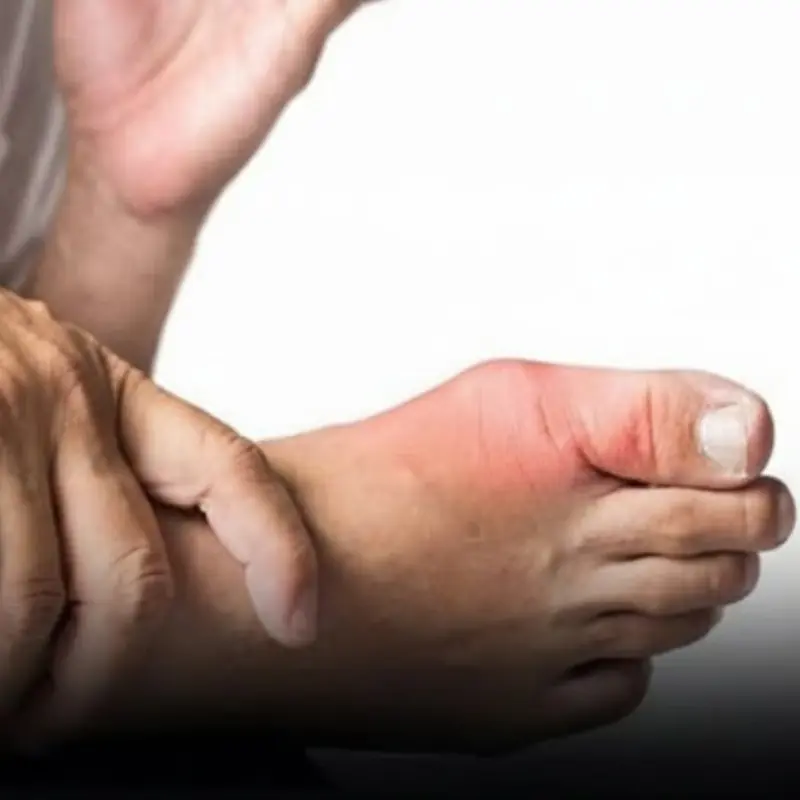
Your feet may reveal early warning signs of hidden diabetes.

Be Alert to Dia.betes If You Experience These 5 Uncommon Symptoms Often
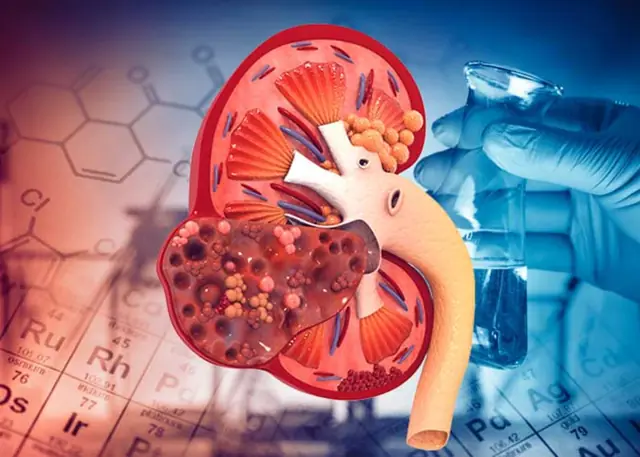
8 Possible Signs of Kidney Fai.lure You Should Not Ignore

Discover Juniper: 20 Impressive Health Benefits and Practical Uses
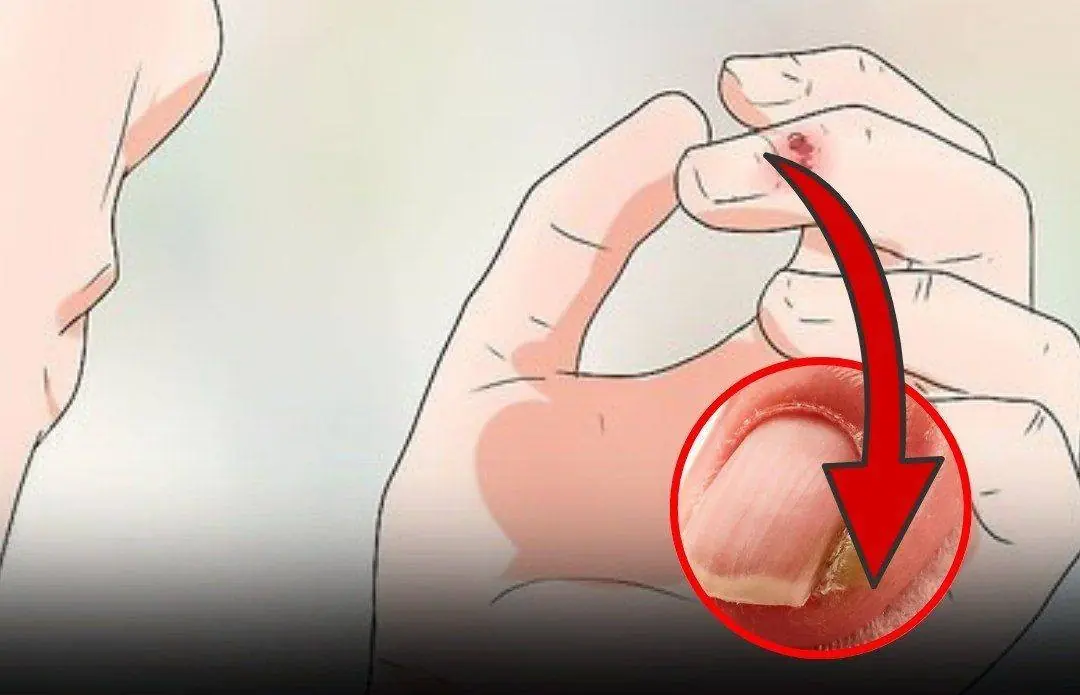
Suffering from Canker Sores? Here Are 3 Powerful Home Treatments You Should Try
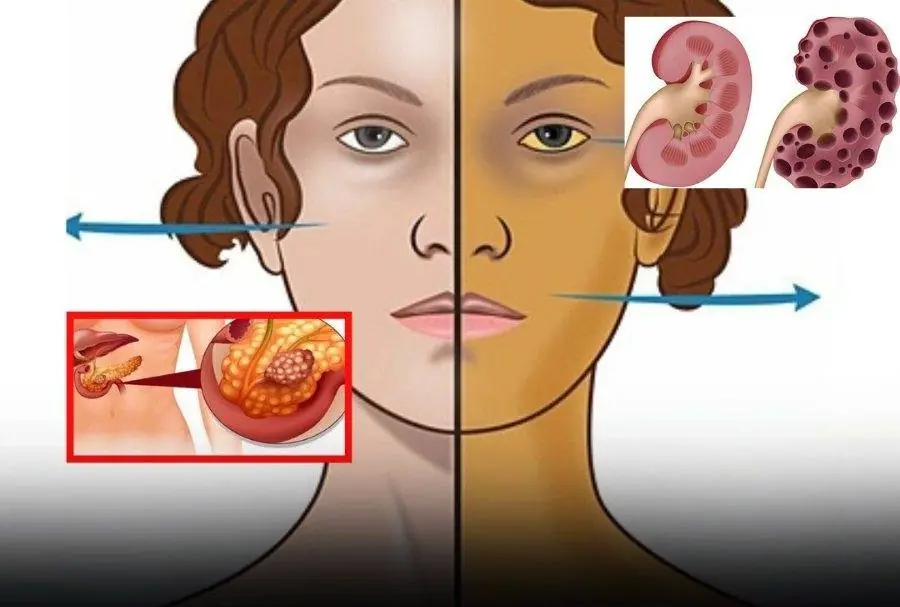
Spot Pancreatic Ca:ncer Early – 11 Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore
Back pain, urinary incontinence, then I'm sorry you have this terrible disease.
Early Signs of Kidney Disease & How to Protect Your Kidneys....
3 common husband behaviors that could raise their wives’ cervical c.an.cer r.isk — don’t ignore the signs
Morning Warning: Spot This Sign When You Wake Up? Don’t Ignore — It May Signal C.a.n.cer
9 Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore
Top Signs of Iron Deficiency and How To Increase Iron Levels In Your Blood

A 58-year-old ate one raw garlic clove every morning for six months — what happened next sho:cked him
10 Early Dementia Signs Your Brain Is Warning You About

10 Early Warning Signs of Breast Can:cer Every Woman Should Be Aware Of

A 22-Year-Old in Good Health Discovered Severe Tu.bercu.losisfrom a Subtle Warning Sign

Tofu Is Healthy, But Certain People May Need to Limit It

Morning Sweet Potatoes: A Small Change That Can Transform Your Health

Okra is nutritious, but not everyone should include it in their diet.

Your feet may reveal early warning signs of hidden diabetes.

The little arrow next to the gas gauge is something most people notice - but never truly understand

Be Alert to Dia.betes If You Experience These 5 Uncommon Symptoms Often

8 Possible Signs of Kidney Fai.lure You Should Not Ignore

Discover Juniper: 20 Impressive Health Benefits and Practical Uses

Suffering from Canker Sores? Here Are 3 Powerful Home Treatments You Should Try

Spot Pancreatic Ca:ncer Early – 11 Warning Signs You Shouldn’t Ignore

Back pain, urinary incontinence, then I'm sorry you have this terrible disease.

Early Signs of Kidney Disease & How to Protect Your Kidneys....

3 common husband behaviors that could raise their wives’ cervical c.an.cer r.isk — don’t ignore the signs

Morning Warning: Spot This Sign When You Wake Up? Don’t Ignore — It May Signal C.a.n.cer

9 Warning Signs of Diabetes You Shouldn’t Ignore

Top Signs of Iron Deficiency and How To Increase Iron Levels In Your Blood

A 58-year-old ate one raw garlic clove every morning for six months — what happened next sho:cked him

10 Early Dementia Signs Your Brain Is Warning You About