
Are Peanuts Always Healthy? Doctors Reveal the Surprising Truth
Health Experts Explain the Potential Risks of Eating Too Many Peanuts

Cloves are small, dark brown flower buds with a powerful aroma and an even more powerful chemical profile. Used for centuries in traditional
medicine systems and global cuisines, cloves are more than just a warming spice. Modern research has begun to explore the biological
mechanisms behind their long-standing reputation for health support.
This guide breaks down what cloves are, how they work in the body, their potential benefits, practical uses, and important safety
considerations.
Cloves come from the dried flower buds of the tree Syzygium aromaticum, native to Indonesia. They are intensely aromatic because they
contain high concentrations of essential oils, particularly eugenol, which is responsible for much of their medicinal activity.
Cloves can be used in several forms:
Whole dried buds
Ground clove powder
Clove essential oil
Clove-infused water or tea
Their flavor is warm, slightly sweet, and spicy, making them popular in both savory and sweet dishes.
The primary bioactive compound in cloves is eugenol, a natural phenolic compound with strong antioxidant and antimicrobial properties.
Other important components include:
Beta-caryophyllene
Tannins
Flavonoids
Triterpenoids
These compounds work together to produce anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant effects.
While cloves are not a cure for disease, research suggests they may support several aspects of health.
Cloves rank extremely high on antioxidant scales compared to many other spices and plant foods. Antioxidants help neutralize free radicals —
unstable molecules that can damage cells and contribute to aging and chronic disease.
Eugenol, in particular, has been shown in laboratory studies to reduce oxidative stress and support cellular protection.
Clove oil has demonstrated strong antimicrobial effects against various bacteria and fungi in laboratory settings.
Historically, cloves were used to preserve food and prevent spoilage due to their antibacterial properties. Today, clove oil is commonly found
in oral care products for its ability to inhibit harmful microbes.
One of the most well-known uses of cloves is for dental pain. Eugenol has mild anesthetic properties, which is why clove oil has been
traditionally applied to relieve toothaches.
In dentistry, eugenol has been used in temporary fillings and dental cements due to its soothing and antimicrobial characteristics.
Cloves may stimulate digestive enzyme secretion, which can help improve digestion and reduce bloating.
In traditional medicine, cloves were often used to relieve indigestion, gas, and nausea. Their warming nature may also support healthy gut
motility.
Chronic inflammation is associated with many long-term health conditions. Some animal and laboratory studies suggest that clove
compounds may reduce inflammatory markers.
While more human research is needed, the anti-inflammatory potential of cloves is one reason they are studied in relation to metabolic and
cardiovascular health.
Preliminary research suggests that clove extracts may influence insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism. Some small studies have observed
modest improvements in blood sugar markers when cloves are included in the diet.
However, cloves should not replace prescribed treatments for diabetes. They may only serve as a supportive dietary component.
Animal studies have shown that eugenol may help reduce oxidative damage in the liver. Because the liver is responsible for detoxification,
antioxidant support can be beneficial.
Human evidence is still limited, so moderation is key.
The effects of cloves primarily stem from eugenol and related phenolic compounds. These molecules:
Neutralize oxidative stress
Interact with inflammatory pathways
Inhibit microbial growth
Modulate certain enzymes
Eugenol can influence cell signaling pathways involved in inflammation and microbial defense. However, these effects are dose-dependent —
higher concentrations do not necessarily mean better outcomes.
Cloves enhance flavor in:
Curries
Stews
Rice dishes
Baked goods
Mulled beverages
Because of their potency, a small amount goes a long way.
Clove tea is made by steeping 2–3 whole cloves in hot water for 5–10 minutes. Some people add cinnamon or ginger for additional warmth.
This preparation is often used for digestion and immune support.
Soaking cloves overnight in water creates a mild infusion. This is consumed in small amounts for general wellness in some traditional
practices.
Clove essential oil must be diluted before applying to the skin. It is sometimes used for:
Toothache relief
Minor fungal issues
Muscle discomfort
Never ingest essential oil directly without medical supervision.
While cloves are safe in culinary amounts, concentrated forms require caution.
High doses of clove oil can be toxic
Excessive consumption may cause digestive irritation
Clove oil may interact with blood-thinning medications
Not recommended for young children without medical advice
Moderation is critical. A typical culinary amount (1–3 cloves per day) is generally safe for most healthy adults.
Cloves are nutrient-dense and bioactive, but no single food can replace a balanced diet. They are best viewed as a supportive component
within a diverse nutritional plan that includes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
Cloves are a small spice with significant biological activity. Their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties have made them
valuable for centuries in both traditional medicine and culinary traditions.
Modern science continues to explore their mechanisms and potential benefits. While they are not a cure-all, cloves can play a meaningful role
in supporting overall wellness when used responsibly and in moderation.
Sometimes, the most powerful ingredients come in the smallest forms.

Health Experts Explain the Potential Risks of Eating Too Many Peanuts

This “Healthy” Daily Food Choice Resulted in Concerning Liver Test Findings
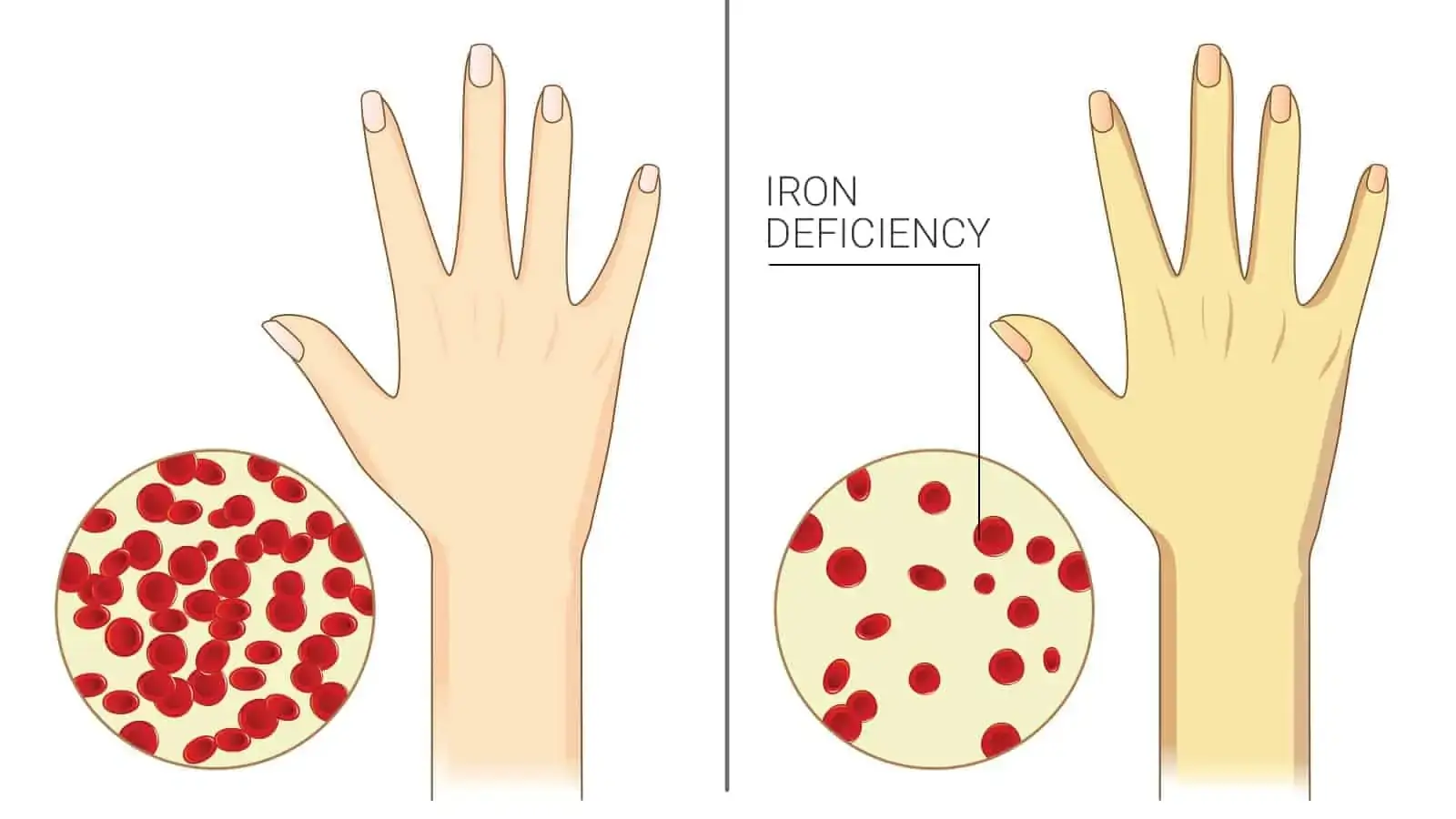
Hidden but Harmful: 7 Signs of Chronic Iron Deficiency Women Often Miss
High Cholesterol Can Show on Your Skin — Here’s What to Watch For
8 overlooked foods that may help fight can.cer cells
Understanding Pancreatic Cancer: Early Warning Signs and Why They Matter





The humble root praised for powerful health-protective nutrients

What drooling in your sleep may reveal about your brain and body

Hidden parasite risks in common foods you may be overlooking

Sweet potatoes or potatoes: which choice is truly healthier?

A go-to option for quick, convenient meals, this type of meat has been classified by the World Health Organization (WHO) as a Group 1 carcinogen

There is a part of the pig that many people avoid or discard, thinking it’s unhealthy—yet it is exceptionally rich in nutrients, especially iron, protein, and vitamins.
Five Foot-Related Changes That May Signal Circulation or Metabolic Health Issues

Why drooling during sleep happens: 6 health conditions to be aware of

Papaya, a delicious tropical fruit, is renowned for its sweet taste and digestive benefits.

Health Experts Explain the Potential Risks of Eating Too Many Peanuts

This “Healthy” Daily Food Choice Resulted in Concerning Liver Test Findings

Hidden but Harmful: 7 Signs of Chronic Iron Deficiency Women Often Miss

Moving to a new city felt scary until we built a home together

High Cholesterol Can Show on Your Skin — Here’s What to Watch For
The surprise that brought our whole family to tears of joy

We didn’t have much, but we had each other

When we faced a health scare, we learned what truly matters

Our family tradition almost ended until we rediscovered why it mattered

I thought we were drifting apart until one honest conversation changed everything

Our small house was crowded, but it was full of love

The year everything went wrong was the year we grew closer than ever

8 overlooked foods that may help fight can.cer cells

We almost gave up on our dream until our family pulled together

Understanding Pancreatic Cancer: Early Warning Signs and Why They Matter




Subtle behavioral shifts can reveal deeper relationship secrets.