Say Goodbye to Swelling …
Say Goodbye to Swelling …
Waking up in the middle of the night with a sudden, sharp pain in your leg is an experience many people know too well. One moment you are asleep, the next you are wide awake, gripping your calf, waiting for the pain to pass.
Nighttime leg cramps are often dismissed as harmless or temporary. People blame stress, overwork, age, or simply “sleeping wrong.” But when these cramps happen frequently, they may be the body’s subtle way of asking for attention.
The body rarely sends signals without a reason. Night cramps are not random. They are messages — quiet ones — and understanding them can make a real difference to long-term health.
Nighttime leg cramps are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions, most commonly affecting the calf, foot, or thigh. They can last from a few seconds to several painful minutes and may leave lingering soreness afterward.
Unlike restless leg syndrome, which causes an urge to move, cramps involve actual muscle tightening and pain.
They often occur during rest or sleep, when the body is supposed to be recovering.
At night, the nervous system shifts into repair mode. Blood circulation slows, muscles relax, and electrolyte balance becomes more noticeable. This is when imbalances or deficiencies tend to show themselves most clearly.
In other words, nighttime is when the body stops compensating — and starts signaling.
One of the most common contributors to leg cramps is an imbalance in key minerals, especially:
Magnesium
Potassium
Calcium
These minerals play a critical role in muscle contraction and relaxation. When levels are low or poorly absorbed, muscles may contract uncontrollably.
Highly processed diets, dehydration, excessive caffeine, and certain medications can all affect mineral balance — often without obvious symptoms during the day.
Night cramps may be the first sign that something is off.
Many people believe dehydration only happens in extreme heat or intense exercise. In reality, mild, chronic dehydration is extremely common.
When the body lacks sufficient fluids:
Electrolyte balance shifts
Muscle fibers become more sensitive
Nerve signals misfire
At night, when fluid intake stops, the effect becomes more noticeable — and cramps appear.
Healthy muscles need a steady supply of oxygen and nutrients. Reduced circulation, especially in the legs, can contribute to nighttime cramping.
Factors that may affect circulation include:
Long periods of sitting or standing
Lack of physical activity
Smoking
Tight clothing
Certain chronic conditions
When blood flow slows at night, muscles that are already under-supplied may respond with painful contractions.
Muscles remember what they endure during the day.
Long hours of:
Standing
Walking on hard surfaces
Wearing unsupportive shoes
Repetitive movements
can leave muscles fatigued and tense. When they finally relax at night, they may seize instead of resting.
Night cramps are sometimes delayed reactions to daytime strain.
Muscle movement is controlled by nerve signals. If nerves are irritated, compressed, or overstimulated, they may send incorrect messages.
This can happen due to:
Spinal posture issues
Vitamin B deficiencies
Prolonged poor sleeping positions
At night, when the nervous system recalibrates, miscommunication can result in sudden muscle tightening.
Blood sugar levels influence nerve and muscle function more than most people realize.
Frequent spikes and crashes — often linked to diets high in refined carbohydrates and sugar — can affect how muscles respond to nerve signals.
Some people notice leg cramps more often when their blood sugar regulation is unstable, especially during long fasting periods at night.
Night cramps are brief. They come and go. And because they don’t usually appear during doctor visits, they are easy to dismiss.
Common thoughts include:
“It’s just age.”
“I must be tired.”
“It’s nothing serious.”
But repetition is the key signal. Occasional cramps are normal. Frequent cramps are information.
In many cases, the body is not signaling danger — it is signaling imbalance.
That imbalance may involve:
Hydration
Nutrition
Movement patterns
Recovery time
Nervous system stress
Listening early allows small corrections instead of larger interventions later.
Without making medical claims, many people find relief by focusing on fundamentals:
Drinking adequate water throughout the day
Stretching calves and feet before sleep
Improving sleep posture
Reducing excessive caffeine and alcohol
Eating more whole, mineral-rich foods
Moving regularly during the day
These changes support the body’s natural regulation systems.
If leg cramps are:
Frequent
Severe
Increasing over time
Accompanied by swelling, numbness, or weakness
they should not be ignored. A medical professional can help rule out underlying conditions and provide proper guidance.
Seeking advice is not overreacting — it is proactive care.
Nighttime leg cramps are uncomfortable, disruptive, and easy to brush off. But pain, even brief pain, exists for a reason.
The body does not speak in words. It speaks in sensations.
When cramps repeat, they are not trying to ruin sleep — they are trying to be heard.
Listen early. Adjust gently. And give the body what it has been quietly asking for.

Say Goodbye to Swelling …
Understanding Mucus in the Throat: Causes You Might Not Expect

Here are 3 dishes you should add to your daily menu
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical can.cer in women

3 fruits that fight liver fat, regulate sugar and cholesterol
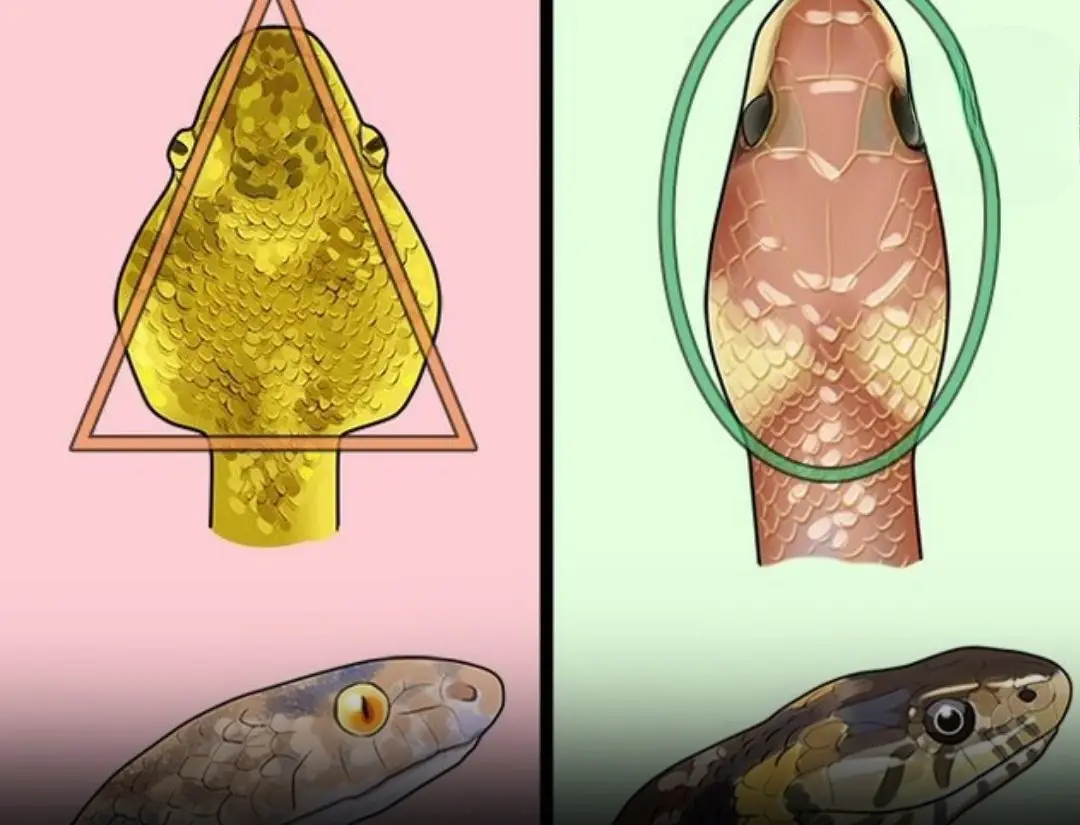
Snake bite emergency: The FIRST things you must do to stay alive!

These 3 Vegetables May Raise Ca:ncer Risk

Reducing These Foods May Be a Key Step in Protecting Your Health, Doctors Say
Be sure to watch for these signs.
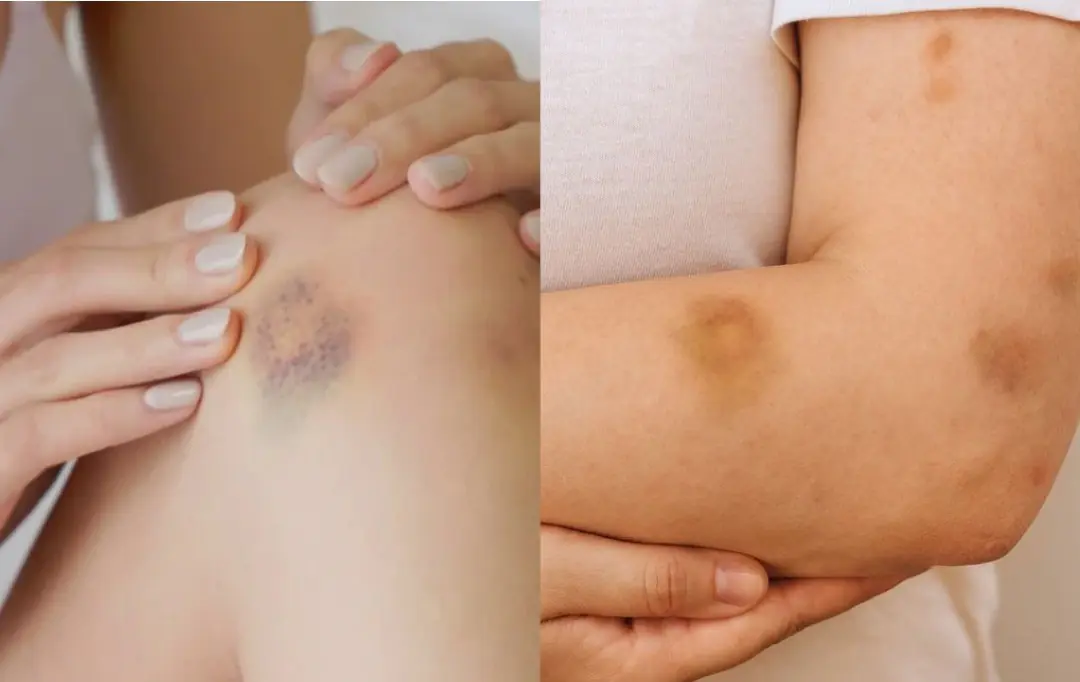
BE CAREFUL, if you get these bruises on your body, here’s what it means....
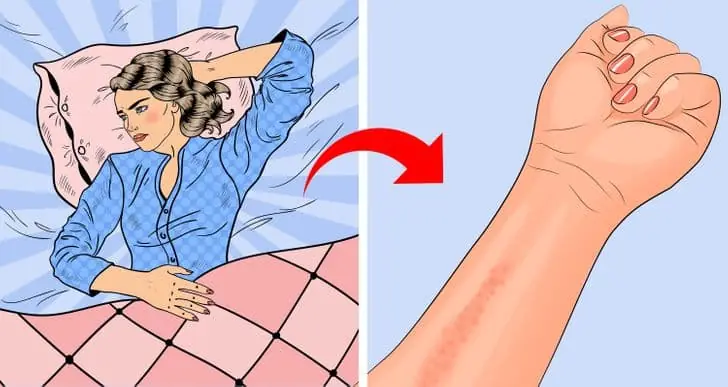
Do you sleep on your side? Here's the powerful effect one simple change can have on your body
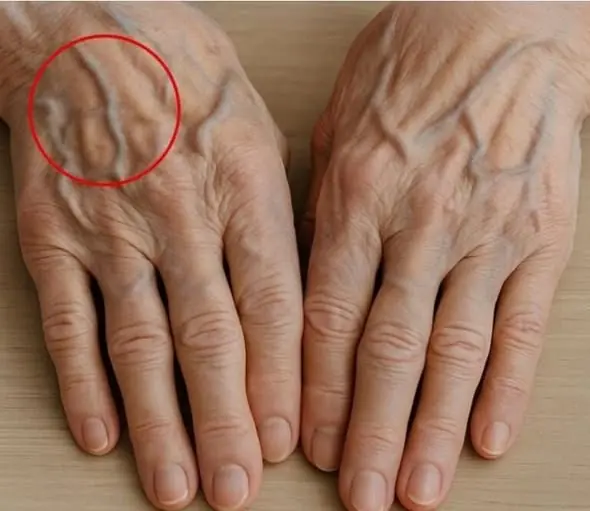
If you see someone with bulging v.e.i.ns, you must tell them these things
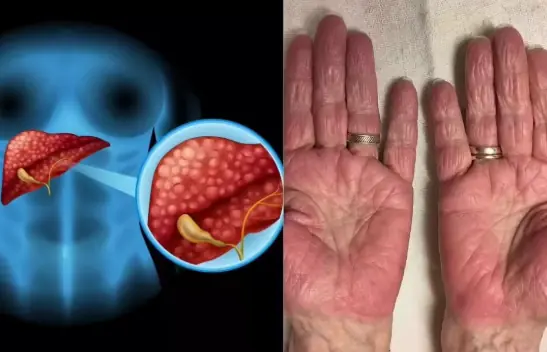
Your liver is one of the most vital organs in your body — a silent workhorse that supports hundreds of biochemical processes essential for survival.
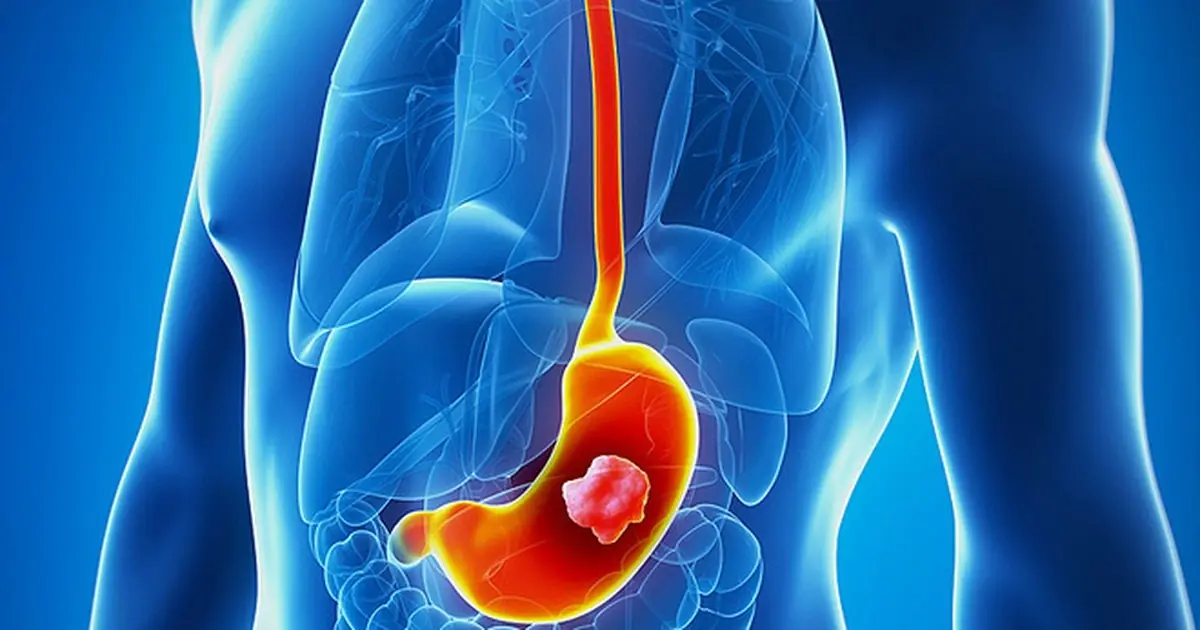
Why stomach can.cer is often diagnosed late and 5 after-meal signs doctors say to check early?
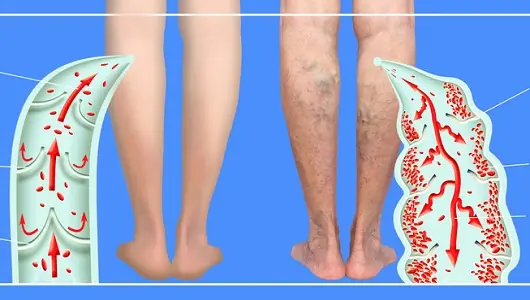
If You Have Poor Circulation, Cold Feet or Varicose Veins, Start Doing these 6 Things

When to eat sweet potatoes: 4 times that make a real difference

6 situations where eggs may not be suitable for everyone
Thy.roid no.dules on the rise: Doctors advise limiting certain foods

How to Know if You Have Neuropathy in Your Feet

Say Goodbye to Swelling …

Understanding Mucus in the Throat: Causes You Might Not Expect

Here are 3 dishes you should add to your daily menu

Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical can.cer in women

3 fruits that fight liver fat, regulate sugar and cholesterol

Snake bite emergency: The FIRST things you must do to stay alive!

These 3 Vegetables May Raise Ca:ncer Risk

Reducing These Foods May Be a Key Step in Protecting Your Health, Doctors Say

Be sure to watch for these signs.

BE CAREFUL, if you get these bruises on your body, here’s what it means....

Words matter most in grief: four things never to say at a funeral

Psychologists explain why infidelity peaks at certain life stages.

Experts say showering together may affect health, boundaries, and balance.

Do you sleep on your side? Here's the powerful effect one simple change can have on your body

If you see someone with bulging v.e.i.ns, you must tell them these things

Your liver is one of the most vital organs in your body — a silent workhorse that supports hundreds of biochemical processes essential for survival.

Statues of gods featured prominently throughout the ancient world, but many of those that are best known from literary evidence have never been found.

When someone in the family pas:ses away, never wear 3 types of shirts at a funeral

Why stomach can.cer is often diagnosed late and 5 after-meal signs doctors say to check early?