What if sea water wasn't salty?

Water is known as the source of life, and we need to consume a significant amount of it every day. The unfortunate reality is that while there is a vast amount of water on Earth, about 71% of its surface is covered by the salty water of the seas.
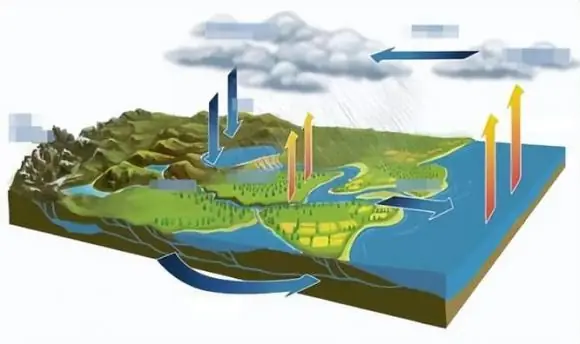
Why is seawater salty? The answer is that seawater contains a large amount of salt, which partly comes from minerals in the sea bed and is also closely related to the Earth's water cycle.
Specifically, the sun’s energy can cause surface water to evaporate, forming water vapor that moves into the atmosphere. When water vapor condenses under suitable conditions, it returns to Earth's surface as rain or snow. A large amount of salt on land gets dissolved and flows back into the ocean through various waterways. Since evaporation in the ocean does not remove salt, the salt continues to accumulate over time, increasing the salinity of seawater.
In other words, the high salinity of seawater is actually the result of Earth's evolution over billions of years. So, what would happen if all the seawater on Earth turned into fresh water? To this question, the first thought many people might have is, "Wouldn't we lose seafood?"
In fact, if such a thing were to happen, it would indeed mean no more seafood to eat. Over the long course of evolution, marine organisms have completely adapted to the high salinity of seawater. If it became fresh water, it would be disastrous for them. However, the mass extinction of marine life would only be the beginning.
What you need to know is that about 70% of the oxygen in Earth's atmosphere comes from algae in the oceans. If all the seawater turned into fresh water, these algae would not be able to survive, and the "raw materials" for oxygen production would disappear. The carbon dioxide that algae process comes from many sources, including the respiration of organisms on Earth, microbial decomposition, volcanic activity, and human activities that continuously generate carbon dioxide.
In this scenario, the oxygen supply in Earth's atmosphere would significantly decrease, while carbon dioxide would continue to accumulate. Since carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas, its large buildup would enhance the greenhouse effect, raising Earth's average temperature and increasing ocean evaporation.
Compared to fresh water, salty seawater is less prone to evaporation. This is because a large amount of dissolved salt in seawater increases the attraction between water molecules, slowing evaporation. If all the seawater on Earth became fresh water, the rate of ocean evaporation would be much higher than it is with salty seas.
Importantly, water vapor itself is also a greenhouse gas. As evaporation increases, the water vapor content in the atmosphere would rise, further amplifying the greenhouse effect and raising temperatures even more. This increased evaporation would send more water vapor into the atmosphere, creating a positive feedback loop that would continuously drive temperatures higher.
It is not difficult to imagine that under such conditions, even Earth's land biosphere would suffer severe devastation. Many species would go extinct, and humans would not be able to survive on their own.
Of course, this is just a hypothesis. In reality, seawater suddenly turning into fresh water is impossible, so there’s no need to worry. Over billions of years of evolution, Earth has developed a delicate and stable natural balance. Ocean salinity, climate changes, and ecosystem functioning are all parts of this long-term balance.
Because Earth's natural environment is fragile and delicate, we should cherish our planet, use resources wisely, and protect ecosystems, avoiding excessive human intervention. While seawater won’t turn into fresh water overnight, real issues like climate change and ocean pollution deserve our attention. Only by respecting and protecting nature can this blue planet continue to benefit all of us, including humans.
Of course, the temperature increase would not go on indefinitely. Essentially, the rise in temperature caused by the greenhouse effect happens because greenhouse gases "trap" more heat from the sun, and eventually, the Earth would receive less heat from the sun. In general, the amount of heat is finite, so once temperatures rise to a certain point, they would stabilize. Nevertheless, the Earth's average temperature would still be much higher than today, possibly exceeding current levels by 10°C or more.
This isn’t the end of the story. You must understand that one of the driving forces behind many ocean currents is the salinity difference in seawater. If all seawater turned fresh, this driving force would disappear. In such circumstances, many ocean currents would weaken or even collapse, eliminating a key "regulator" of the global climate system. As a result, the global climate system would descend into chaos, with extreme weather events (such as heatwaves, cold spells, droughts, or heavy rainfall) becoming more frequent. The number of catastrophic storms would also significantly increase.
News in the same category


At the market, if you see these 4 types of vegetables, don’t hesitate—buy them immediately

Flip the Bottle: The Simple Trick to Tell Real Honey From Fake—Experts Warn Shoppers to Stop Buying Blindly

Why You Should Never Place the Head of Your Bed Toward These Two Directions: Feng Shui Experts Call It a Major Prosperity Taboo

Shower First or Wash Hair First? Doctors Warn: The Wrong Order May Trigger Dangerous Health Risks

Surprising Nutrition Insight: 4 Sprouted Foods That Become Even Healthier — Not Toxic

Doctors Warn: Going to Bed Too Early May Be Harmful for Seniors — People Over 65 Should Sleep at This Recommended Time

Experts Warn: 4 Fruits Most Commonly Sprayed With Pesticides — Shoppers Should Avoid Buying Them Hastily
The finger you cut first might say more about you than you think

If Your Parent Shows These 3 Signs, They May Be Nearing the End of Life. Prepare Yourself for What’s to Come

When a Wife’s Intuition Speaks: Signs Your Husband May Be Having an Affair
The Story of Two Exhausted Surgeons After a 32-Hour Operation: A Symbol of Sacrifice in Medicine

When Someone Close to You Passes Away, Never Throw Out These 4 Important Items

Ancient Wisdom Explains: “Don’t Buy Pork Neck, Don’t Buy Crucian Carp”—The Real Reasons Revealed Today

A Simple Method Keeps Rice Fresh for One Year Without Worms or Weevils — Many People Regret Not Learning It Sooner

Charging Your Phone to 100% and Unplugging It Is a Common Mistake: Experts Share the Correct Method to Double Battery Lifespan

The “Miracle Herb” Chinese Locals Praise: Abundant on Roadsides but Often Feared and Overlooked

Papaya Flowers Soaked in Honey: Highly Nutritious but Strictly Unsafe for These 4 Groups, Doctors Warn

3 everyday foods that can explode while cooking — one nearly disfigured a young woman
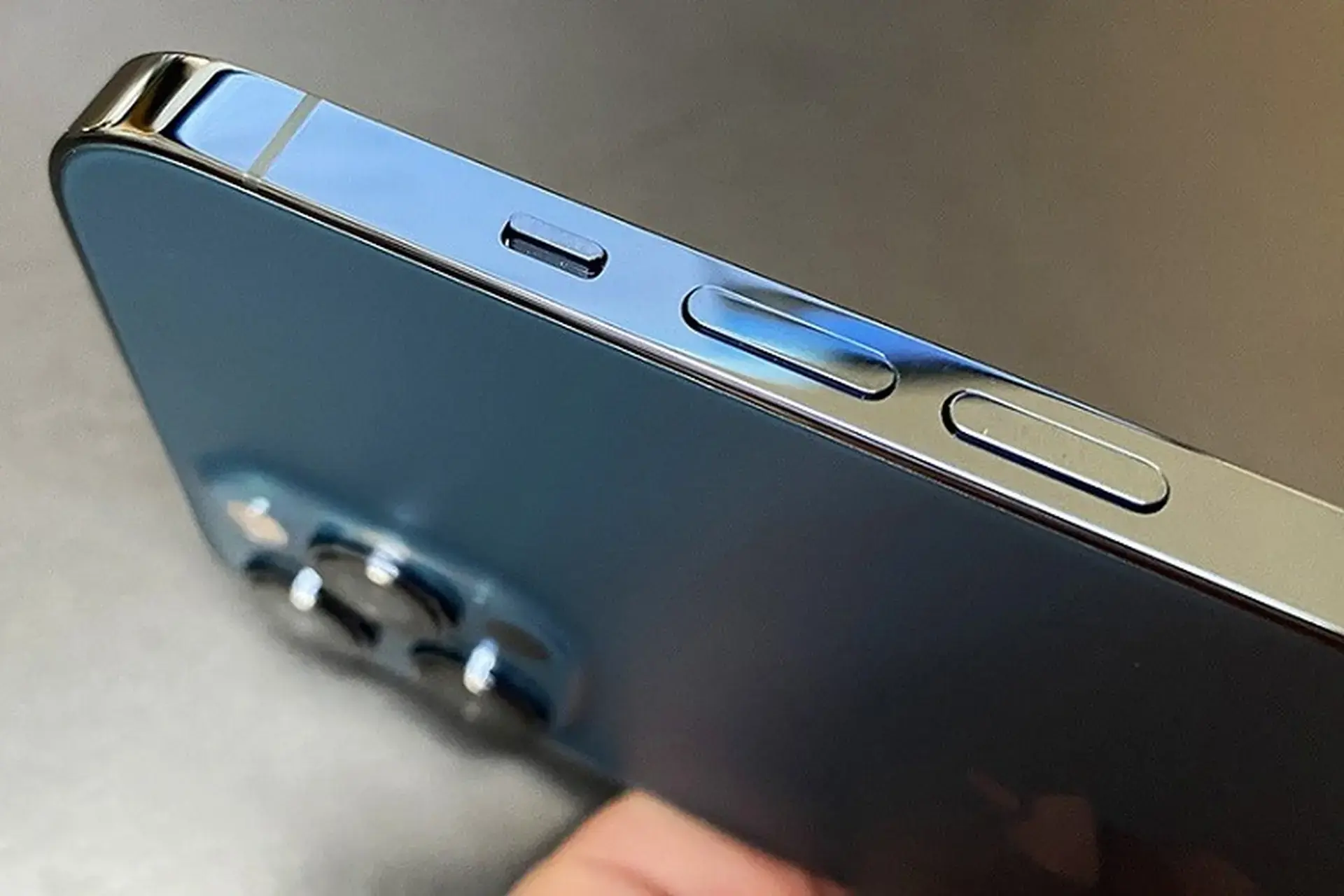

The Volume Button on Your Phone Has More Power Than You Think — Here Are 3 Useful Functions Most People Miss
News Post
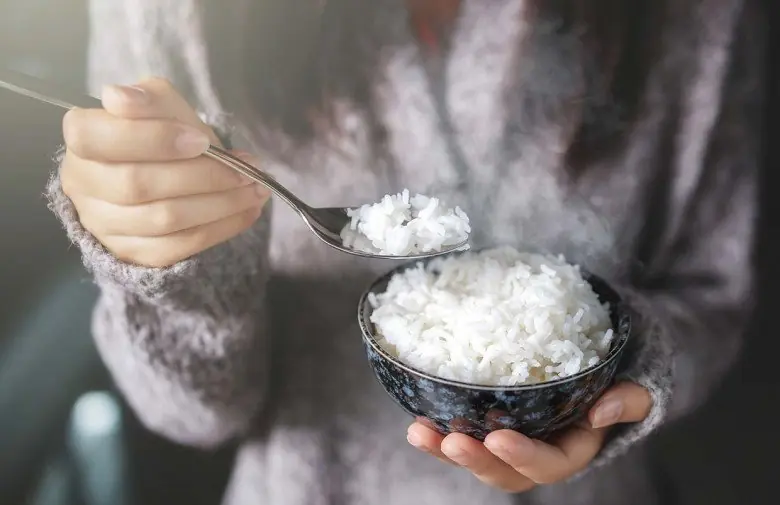

More and more people are dy.ing from diabetes. Doctors warn: In cold weather, it’s better to eat plain white rice than to keep doing these 4 things

7 signs that you should stop drinking coffee

This One Superfood Could Tackle Major Health Issues—Here’s What You Need To Know
How to Treat H. Pylori (Helicobacter Pylori) Naturally Without Antibiotics

Depressing find at the bottom of the Mariana Trench is a warning to the world
From Causes to Cures: Everything You Need to Know About Fatty Liver

Electrical devices to unplug during storms, thunder, and lightning

4 Clear Signs That Appear 15 Minutes Before a Stroke: Call for Immediate Help

4 warning signs from the appendix, do not ignore!

8 Unusual Signs That May Indicate Cervical Can.cer
7 Powerful Exercises to Relieve Heel Pain and Treat Plantar Fasciitis Naturally
Scientists May Have Actually Found One Of The Causes Of Autism

Don’t go to sleep without taking this — 1 cup before bed clears excess sugar

3 Ways to Stop Acid Reflux Naturally
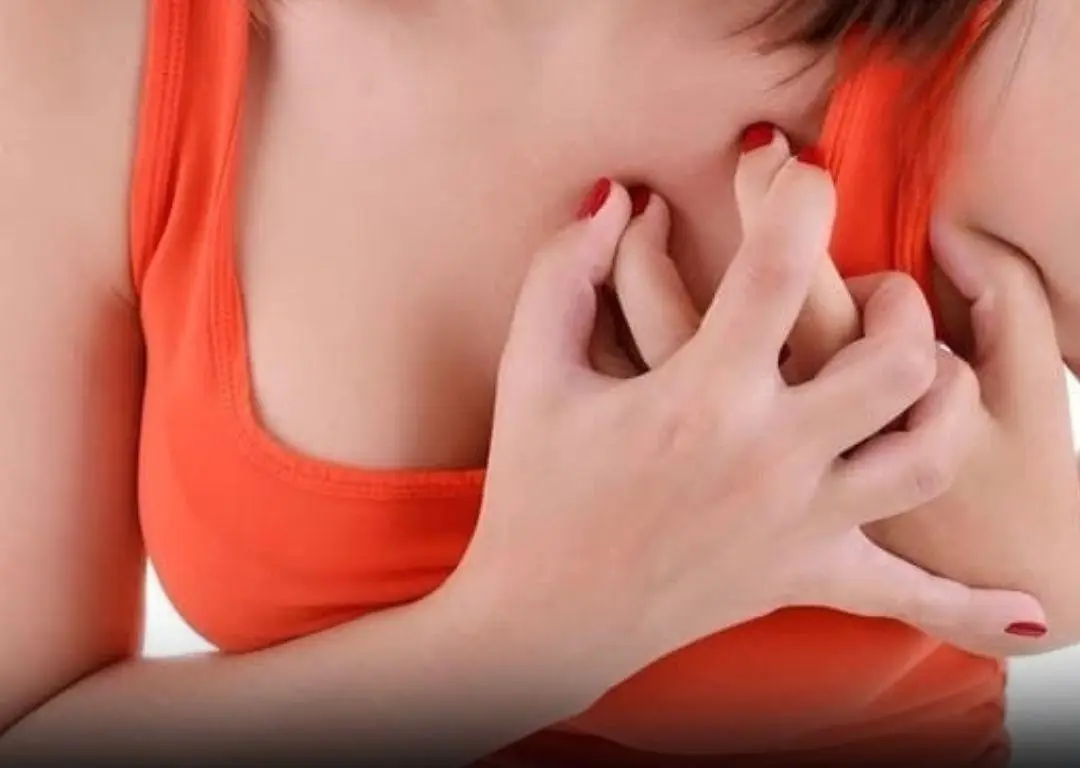

The Reason You May Get Random Stabbing Pai:ns in Your Chest Explained

Nose Picking What This Taboo Habit Really Reveals About Us
Those Mysterious Leg Bruises? They Might Indicate Dang.erous Diseases

What does this gesture signify?
Early Cervical Cancer Clues? Don’t Ignore These 4 Foot Warning Signs