He Ignored the Itching, Thinking It Was an Allergy — Until Doctors Found the Real Cause
He Ignored the Itching, Thinking It Was an Allergy—Until Doctors Found the Real Cause.
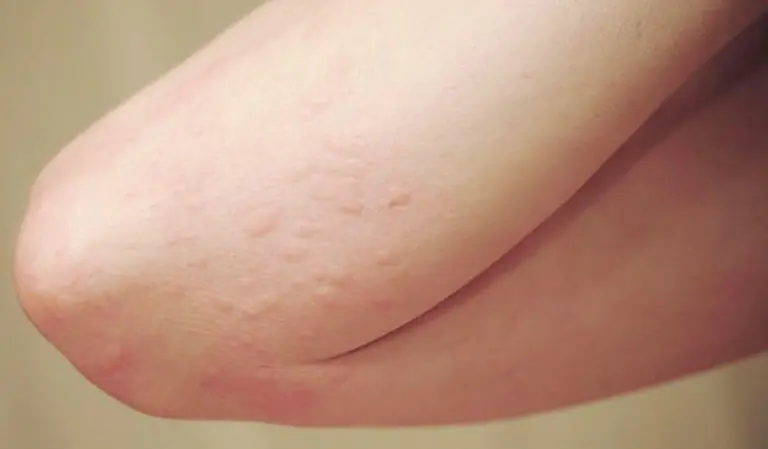
Almost everyone has experienced it: tiny bumps rising on your skin out of nowhere. You’re not cold. Nothing touched you. Yet suddenly, your arms or legs are covered in goosebumps.
So why does this happen?
While goosebumps are often linked to cold weather or strong emotions, they can also appear without an obvious trigger. The explanation lies deep within your nervous system—and your evolutionary past.
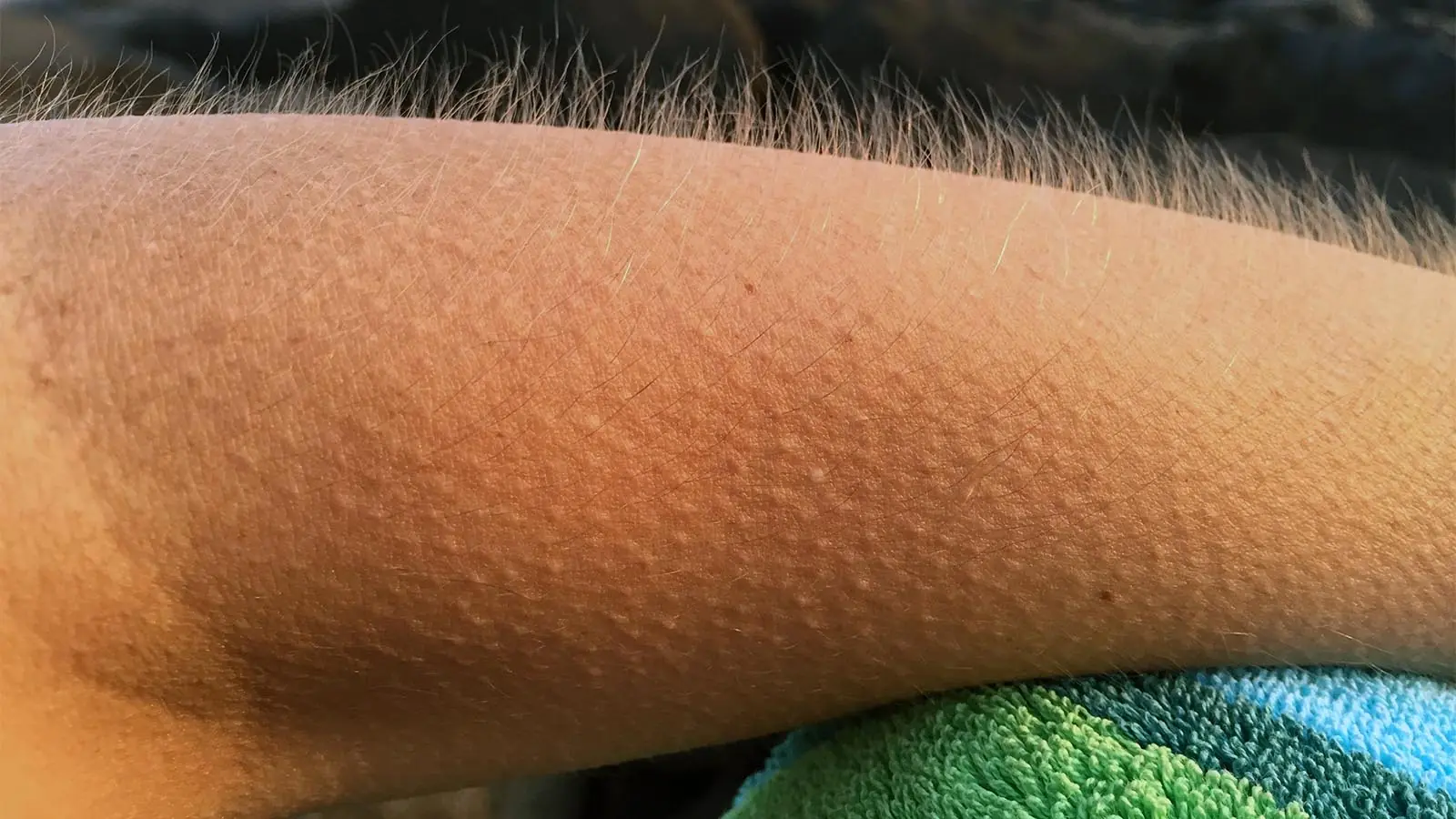

Goosebumps, medically known as piloerection, occur when tiny muscles at the base of your hair follicles contract. This causes the hairs to stand upright and the surrounding skin to form small bumps.
This reaction is completely involuntary. You don’t control it. Your body does.
Goosebumps are a leftover survival mechanism from our ancestors.
When early humans (and animals) felt cold or threatened, raising body hair helped in two ways:
It trapped air to keep the body warm
It made the body appear larger and more intimidating to predators
Although humans no longer rely on body hair for survival, the reflex still exists. Your nervous system hasn’t forgotten it.
Goosebumps are controlled by the autonomic nervous system, which also regulates breathing, heart rate, and digestion.
This system reacts automatically to perceived changes in your environment or internal state. Even subtle signals—many of which you don’t consciously notice—can trigger goosebumps.
That’s why they sometimes seem to appear “for no reason.”
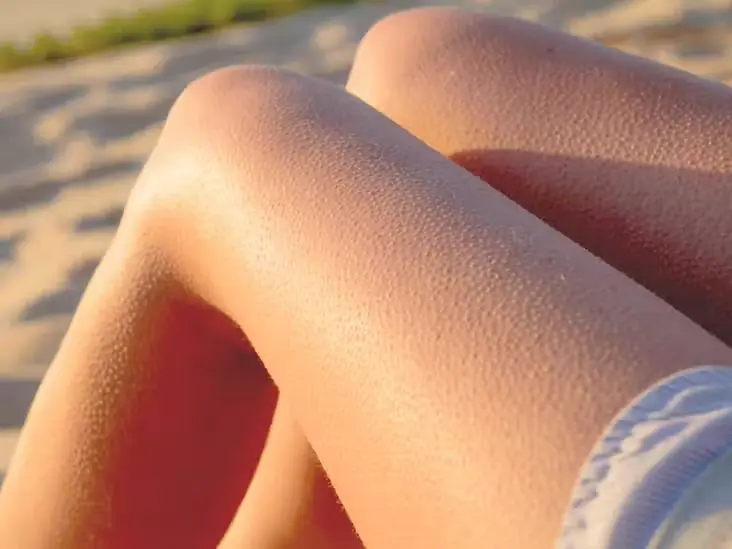

Even when you think nothing is happening, your body may be reacting to:
Music, memories, or thoughts can briefly activate emotional centers in the brain, especially those linked to awe, nostalgia, or fear.
A slight drop in skin temperature—caused by airflow, sweat evaporation, or changes in blood flow—can be enough.
Adrenaline surges, even small ones, can activate the muscles responsible for goosebumps.
Your body may enter a mild “alert mode” without you realizing it.
Certain sounds, visuals, or textures can trigger a response, even subconsciously.
Goosebumps during music or emotional moments are especially fascinating.
Studies suggest that emotionally powerful experiences activate the brain’s reward system, releasing dopamine. This intense emotional processing can stimulate the same nervous pathways involved in survival reflexes.
In short, your body reacts to emotional intensity as if something important is happening.
In most cases, goosebumps are completely normal.
However, frequent goosebumps accompanied by other symptoms—such as dizziness, irregular heartbeat, or unexplained anxiety—may be linked to nervous system sensitivity or stress-related conditions.
On their own, though, random goosebumps are rarely a cause for concern.
Many people notice goosebumps when they’re relaxed or doing nothing.
This is because your nervous system is more noticeable when external distractions are reduced. Subtle internal signals—normally ignored—become more apparent when the body is still.
Goosebumps are a reminder that your body is constantly monitoring and responding to the world, even when you aren’t aware of it.
They reflect:
A highly sensitive nervous system
Deep emotional processing
Ancient biological programming still at work
Your body doesn’t always need a clear reason to react. Sometimes, it’s simply doing what it was designed to do.

Getting goosebumps “for no reason” isn’t strange—it’s human.
They are harmless signals from your nervous system, shaped by evolution, emotion, and subtle environmental changes. Most of the time, they mean nothing more than your body briefly responding to something you didn’t consciously notice.
The next time goosebumps appear out of nowhere, remember:
your body is listening, even when you aren’t.

He Ignored the Itching, Thinking It Was an Allergy—Until Doctors Found the Real Cause.

Many people eat lettuce the wrong way without realizing they belong to a group that should avoid it.
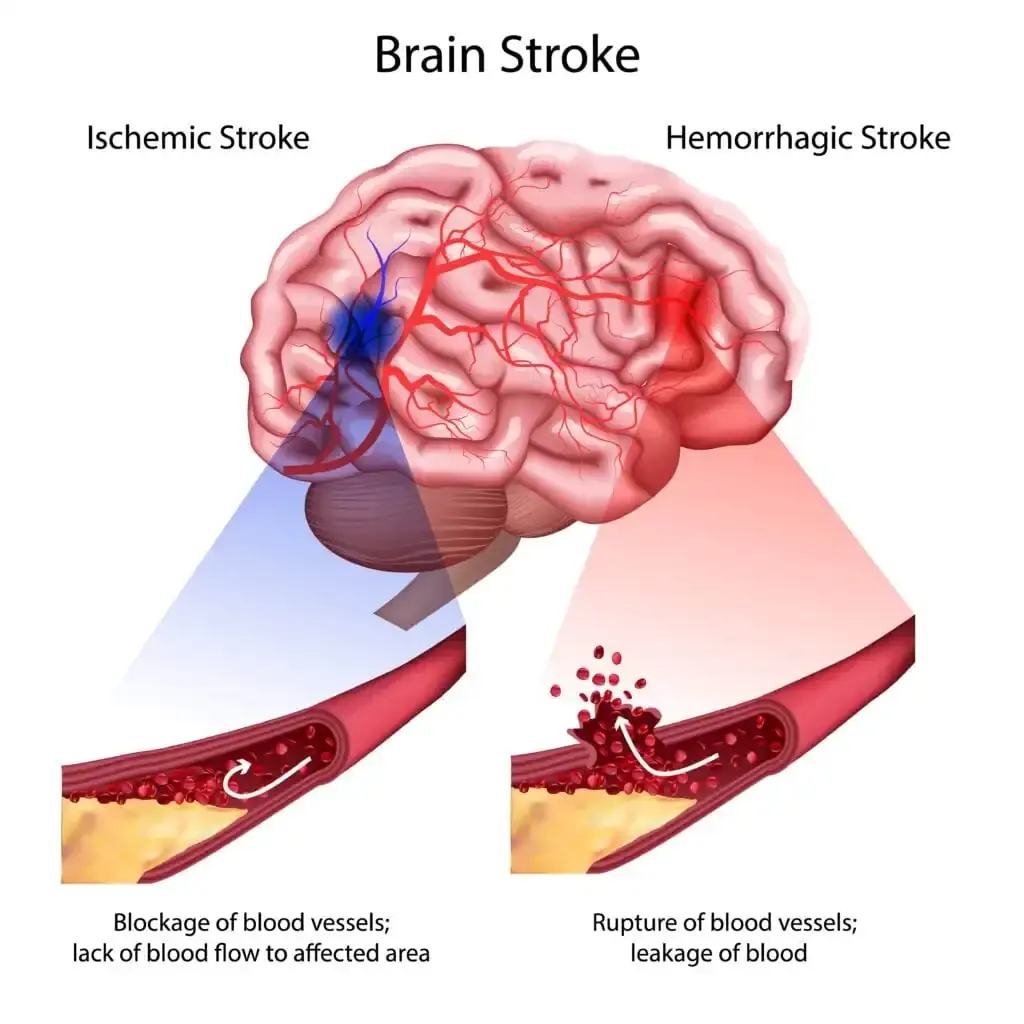
3 Stroke Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention
Your diet matters: 8 everyday foods linked to cancer prevention
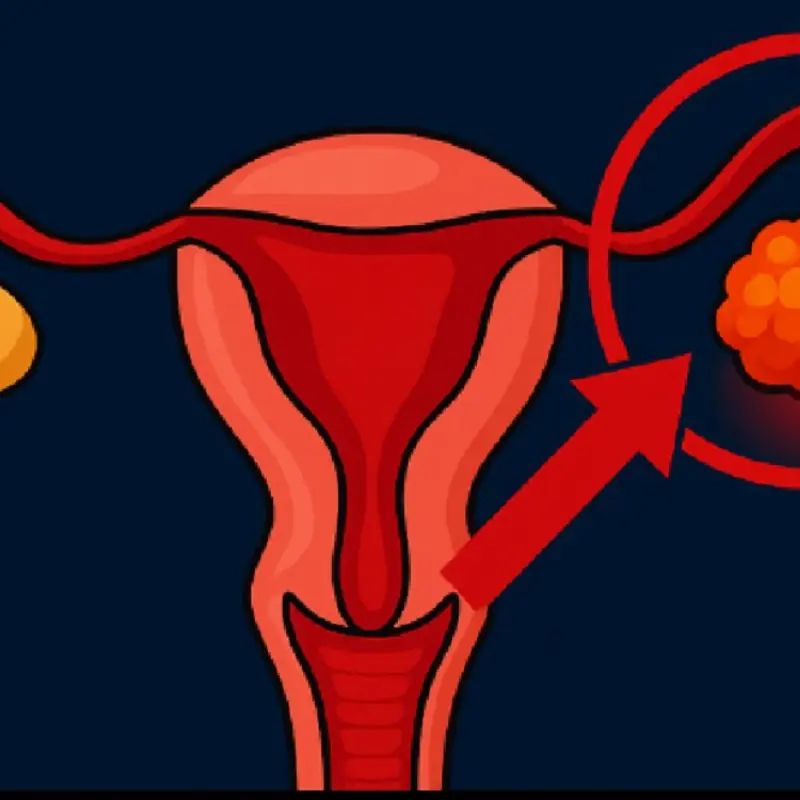
Ovarian cancer often shows subtle early signs that many women ignore.
A young groom’s death raises urgent questions about food safety and health.
Persistent ear ringing can signal deeper health issues you should not ignore.

Boiled eggs may look simple, but their health effects surprise many.
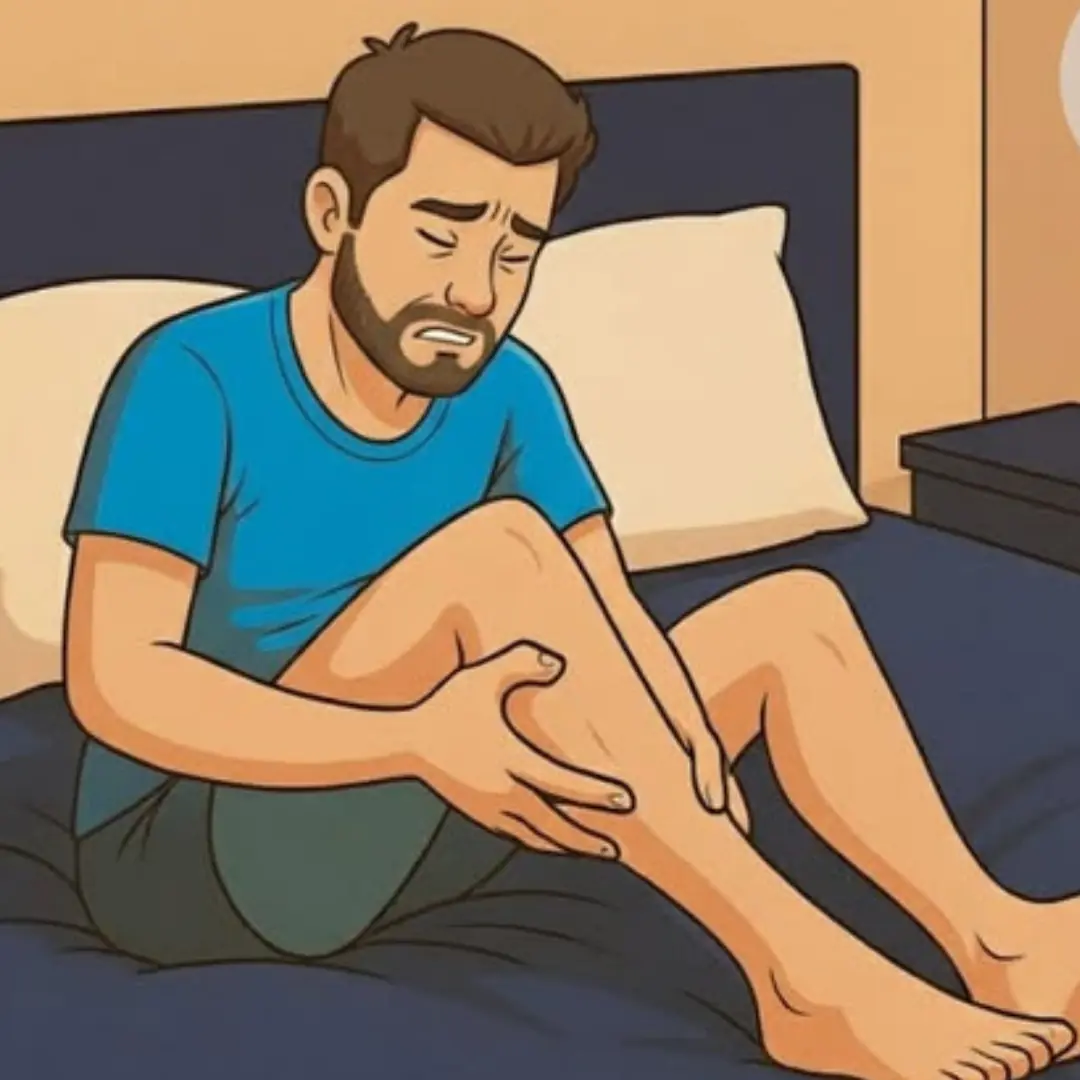

Nighttime Leg Cramps Could Be Telling You Something Important

The combination of garlic and lemon, often simmered into a drinkable liquid, appears repeatedly in folk medicine across cultures, from Southeast Asia to Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean.
What Causes a Sour Vaginal Smell? 4 Possible Reasons

But this wholesome reputation hides an uncomfortable truth.

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries
3 Nighttime Warning Signs That May Signal Can:cer Developing in Your Body
7 Serious Warning Signs of Stomach Can.cer in Its Later Stages

65-year-old m.an pa.ssed a.way at 11pm: Doctor w.arns no matter how thirsty you are, don't drink these 4 types of water before bed
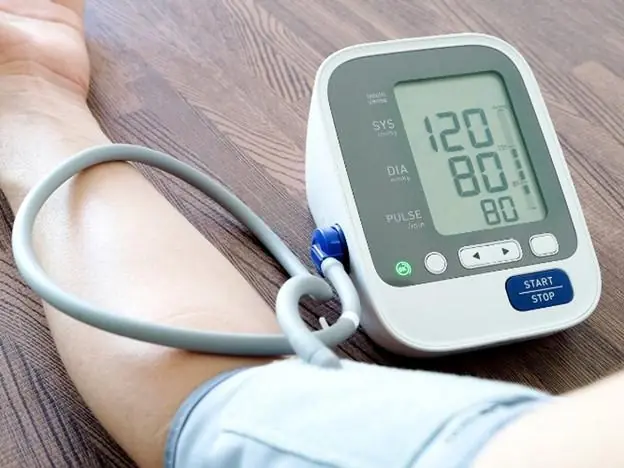
For decades, 120/80 mmHg has been stamped into public consciousness as the gold standard for “normal” blood pressure.

If your body suddenly jolts awake while you're sleeping, could it be that your brain is worried you're sleeping too soundly and wants to wake you up?
Chronic kidney disease is often called a “silent killer” because it progresses quietly.

Here are 7 golden rules for handling marital conflicts:

He Ignored the Itching, Thinking It Was an Allergy—Until Doctors Found the Real Cause.

Many people eat lettuce the wrong way without realizing they belong to a group that should avoid it.

3 Stroke Symptoms That Require Immediate Attention

Happy marriages share a hidden key—many fulfilled women have it in common.

Not everyone who enters your life brings positive value.

Your diet matters: 8 everyday foods linked to cancer prevention

Ovarian cancer often shows subtle early signs that many women ignore.

A young groom’s death raises urgent questions about food safety and health.

Persistent ear ringing can signal deeper health issues you should not ignore.

Boiled eggs may look simple, but their health effects surprise many.

The Surprising Reason We Can’t Sleep Without a Blanket

Nighttime Leg Cramps Could Be Telling You Something Important

Psychologically speaking, there are a few reasons why a woman might…

The combination of garlic and lemon, often simmered into a drinkable liquid, appears repeatedly in folk medicine across cultures, from Southeast Asia to Eastern Europe and the Mediterranean.

What Causes a Sour Vaginal Smell? 4 Possible Reasons

But this wholesome reputation hides an uncomfortable truth.

Doctors Warn: This Common Way of Eating Boiled Eggs Can Clog Your Arteries