
3 inti.mate habits of husbands that may increase wives ri.sk of cer.vical can.cer
Cer.vical can.cer remains one of the leading cancers affecting women worldwide, but it is also one of the most preventable forms of can.cer, thanks to early detection through regular screening (Pap smears) and the availability of the HPV vaccine. However, despite preventive measures, certain behaviors can still increase a woman’s ri.sk of developing cer.vical can.cer. Interestingly, some of these ri.sk factors are linked to inti.mate habits that involve the husband. While it may be difficult to acknowledge, there are behaviors that men may not realize could affect their partner’s health, especially when it comes to cer.vical can.cer.
In this article, we will discuss three inti.mate habits of husbands that can inadvertently increase the ri.sk of cer.vical can.cer in wives and the necessary steps to stop these habits before it’s too late. Understanding these factors is vital for both partners, as cer.vical can.cer prevention is a shared responsibility.
1. Smoking: A Habit That Can Affect Both Partners
While smoking is often seen as a personal habit, it has far-reaching consequences for both the smoker and their partner. For women, particularly those in intimate relationships with smokers, the ri.sk of developing cervical cancer can be significantly higher. In fact, secondhand smoke can increase a woman’s chances of contracting human papillomavirus (HPV), a virus that is the primary cause of cer.vical can.cer.
How Smoking Increases Cer.vical Can.cer Ri.sk:
-
Weakened Immune System: Smoking weakens the immune system, making it more difficult for the body to clear the HPV virus from the cervix. HPV is typically cleared by the immune system within a couple of years, but smoking hampers this process, leaving women more vulnerable to persistent HPV infections, which can lead to cer.vical can.cer.
-
Direct Exposure to Carcinogens: Smokers inhale ha.rmful chemicals that can cause direct dam.age to the cells in the cervix, increasing the likelihood of abnormal cell changes. These changes, if not detected early, can eventually progress into can.cer.
-
Secondhand Smoke: Even if a woman is not a smoker herself, exposure to secondhand smoke can still increase her ri.sk of developing cer.vical can.cer. Studies have shown that women who live with a smoker or are regularly exposed to secondhand smoke are at an increased risk of contracting HPV and developing cer.vical can.cer.
What Husbands Can Do:
To reduce the ri.sk, husbands should consider quitting smoking or at least avoiding smoking around their wives. If quitting is challenging, there are many resources available, such as nicotine replacement therapies or counseling, that can help smokers successfully quit. Additionally, creating a smoke-free environment for both partners is essential in preventing secondhand smoke exposure.
2. Multiple Sexual Partners or Unprotected Sex: The Role of HPV Transmission
Another intimate habit that can increase the ri.sk of cervical cancer is a high number of se.xual partners or engaging in unprotected s.ex. Human papillomavirus (HPV), the leading cause of cer.vical can.cer, is transmitted through se.xual contact. Men, often without realizing it, may unknowingly carry the virus, putting their wives or partners at greater risk of HPV infection.
How Se.xual Behavior Affects Cer.vical Can.cer Ri.sk:
-
Increased Exposure to HPV: Having multiple se.xual partners or unprotected s.ex increases the chances of being exposed to different strains of HPV. Some strains of HPV are more likely to cause persistent infections that can lead to cer.vical can.cer. Women who have a partner with multiple se.xual partners are at an even higher ri.sk, especially if the husband is not monogamous or has engaged in ri.sky se.xual behaviors in the past.
-
Lack of Protection: Unprotected s.ex increases the likelihood of contracting HPV and other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) that can further da.mage cer.vical cells. Condoms, while not offering 100% protection against HPV, can significantly reduce the ri.sk of transmission, especially if used consistently.
What Husbands Can Do:
-
Get Vaccinated: Husbands should consider getting the HPV vaccine, especially if they are young or haven't been vaccinated yet. The vaccine is not just for women; it can protect both men and women from several strains of the virus, reducing the ri.sk of transmission to their partners.
-
Practice Safe S.ex: Using condoms during sex, even in long-term monogamous relationships, can reduce the transmission of HPV and other s.exually transmitted infections. This simple practice can significantly protect your wife from potential health risks.
-
Be Monogamous: Committing to a monogamous relationship with one sexual partner can significantly reduce the ri.sk of HPV transmission. If a man has had multiple partners, it’s essential to discuss this openly with his wife and take extra precautions to ensure safety.
3. Poor Hygiene and Lack of Se.xual Health Awareness
Poor hygiene practices or a lack of attention to se.xual health can also increase a woman's ri.sk of cervical can.cer. While hygiene might not seem like a direct factor in cervical cancer, the health and cleanliness of intimate areas are crucial for overall reproductive health. Additionally, some men may be unaware of the importance of se.xual health and hygiene, contributing to the spread of infections that can lead to cer.vical can.cer.
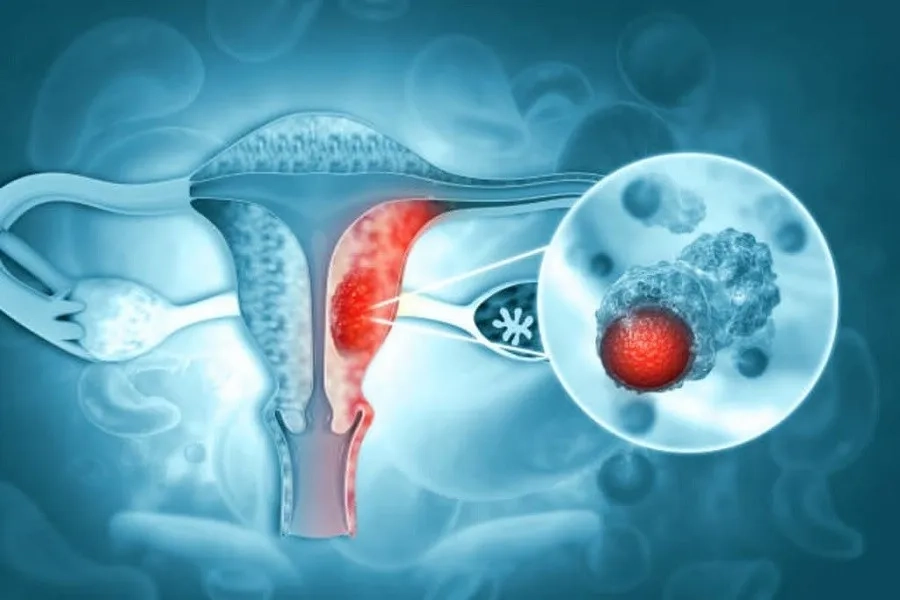
How Poor Hygiene Affects Cer.vical Can.cer Ri.sk:
-
Bacterial Infections: Poor hygiene can lead to the development of bacterial infections in the genital area, which can increase the likelihood of HPV infection or other infections that damage the cervix over time. These infections can cause inflammation in the cervix, making it more susceptible to can.cerous changes.
-
HPV and Other Infections: Poor hygiene practices, such as failing to clean the genital area after s.ex, can also increase the chances of contracting HPV or other se.xually transmitted infections. These infections can irritate the cervix and lead to abnormal cell changes.
What Husbands Can Do:
-
Maintain Good Hygiene: Good personal hygiene is crucial for both men and women. This includes regular washing of the genital area, particularly after se.xual activity. Husbands should maintain proper hygiene and encourage their wives to do the same.
-
Be Mindful of Se.xual Health: Husbands should be aware of their own sexual health and get regular check-ups to prevent the spread of infections. If either partner has any symptoms of STIs, such as unusual discharge or discomfort, it’s essential to seek medical attention promptly.
-
Open Communication: Discussing se.xual health openly with a partner is key to preventing the spread of infections. Regular check-ups, open communication about se.xual health, and mutual care can help reduce the risk of cer.vical can.cer.
Conclusion: How to Protect Your Wife’s Health
The intimate habits of husbands can unknowingly impact their wives’ health, especially when it comes to the risk of cer.vical can.cer. Smoking, high-risk se.xual behavior, and poor hygiene practices can all contribute to an increased risk of contracting HPV and other infections that can lead to cervical cancer. However, by practicing safe s.ex, quitting smoking, maintaining good hygiene, and being aware of se.xual health, husbands can take significant steps to reduce these ri.sks and protect their wives from cer.vical can.cer.
Open communication and a commitment to maintaining a healthy lifestyle are essential in preventing cer.vical can.cer. Taking responsibility for one’s actions and understanding how they can impact a partner’s health is crucial in building a supportive and healthy relationship. By following these practices, you can help ensure a long, healthy life for both you and your partner.
News in the same category


What causes limb twitching while sleeping?
5 Subtle Signs of Thyroid Cancer — Know Them Early to Stay Safe

70-year-old man drinks lemon water to treat high blo.od pressure for 2 years, faces unexpected outcome
Research suggests a link between blo.od type and stomach can.cer risk

These 3 vegetables have a high risk of causing can.cer. Know early to avoid them and tell your loved ones!

These 5 people should absolutely avoid eating jackfruit, no matter how much they crave it
Tiny Red Dots on Your Skin — Causes, Meanings, and When to Worry
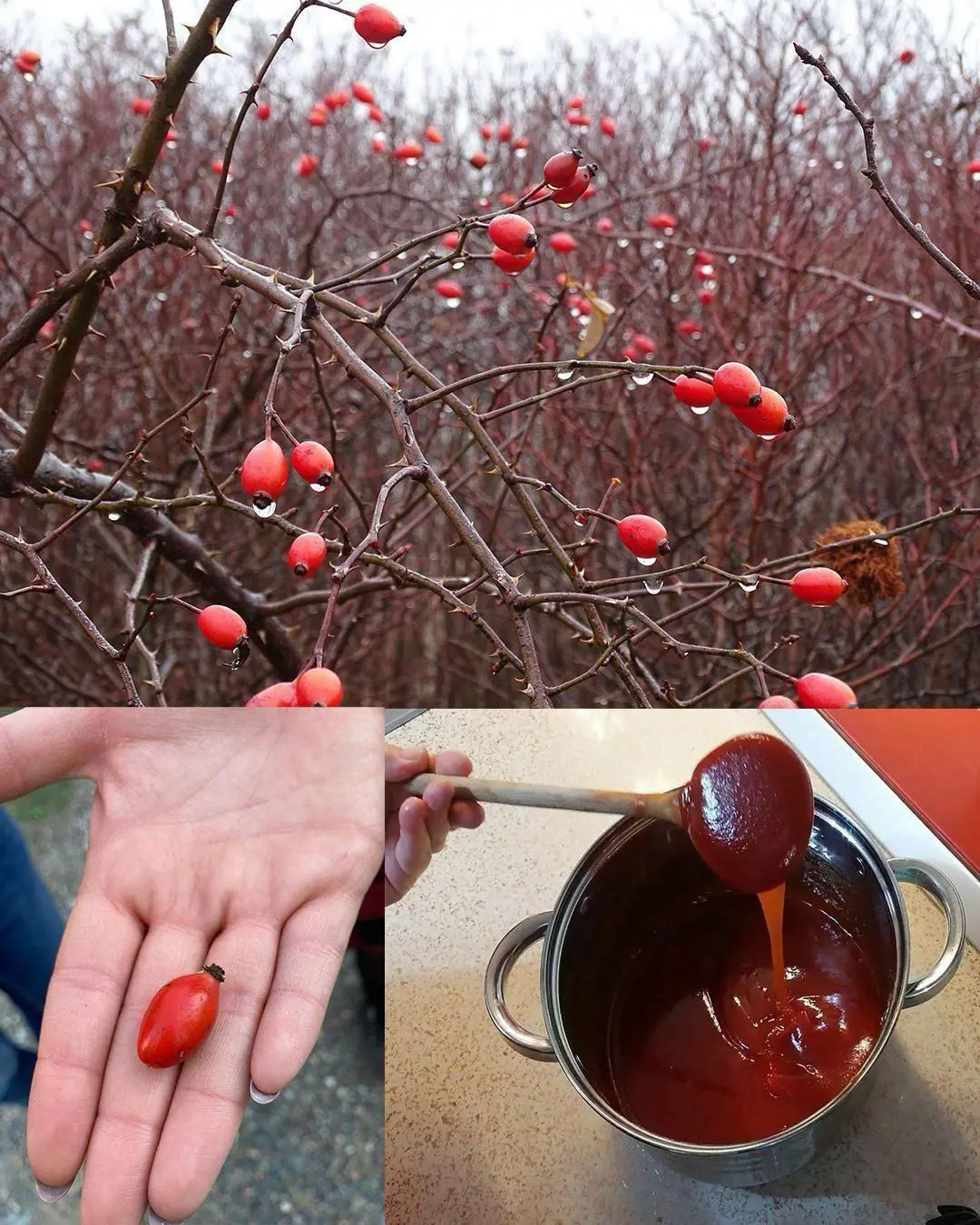

The Hidden Power of Dog Rose (Rosa canina): 10 Surprising Health Benefits and How to Use It

90% of people sleep in the wrong position without realizing it: Sleeping on this side is actually a “lifesaver” for the body
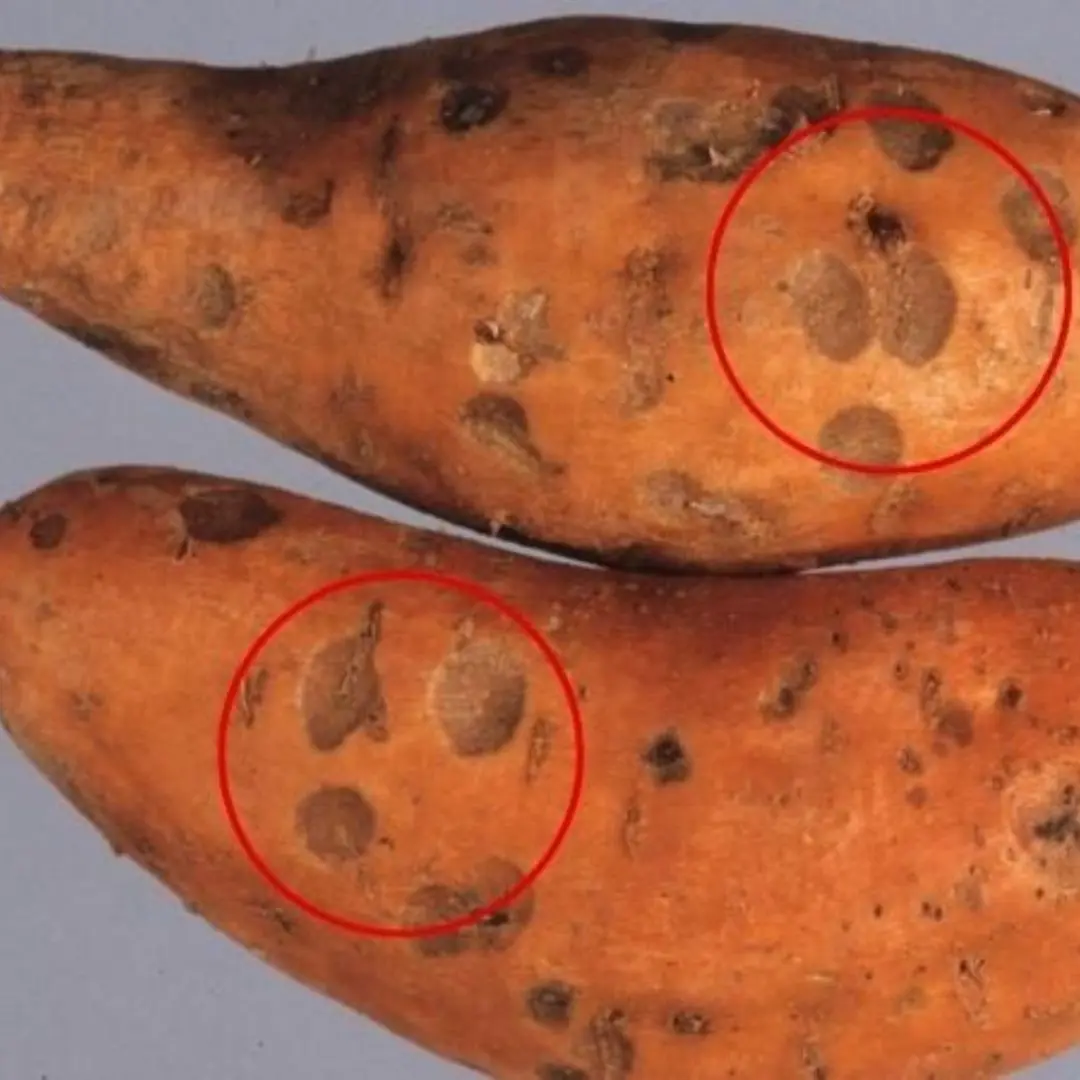

Doctors Warn: 3 Foods That Severely Damage Your Liver
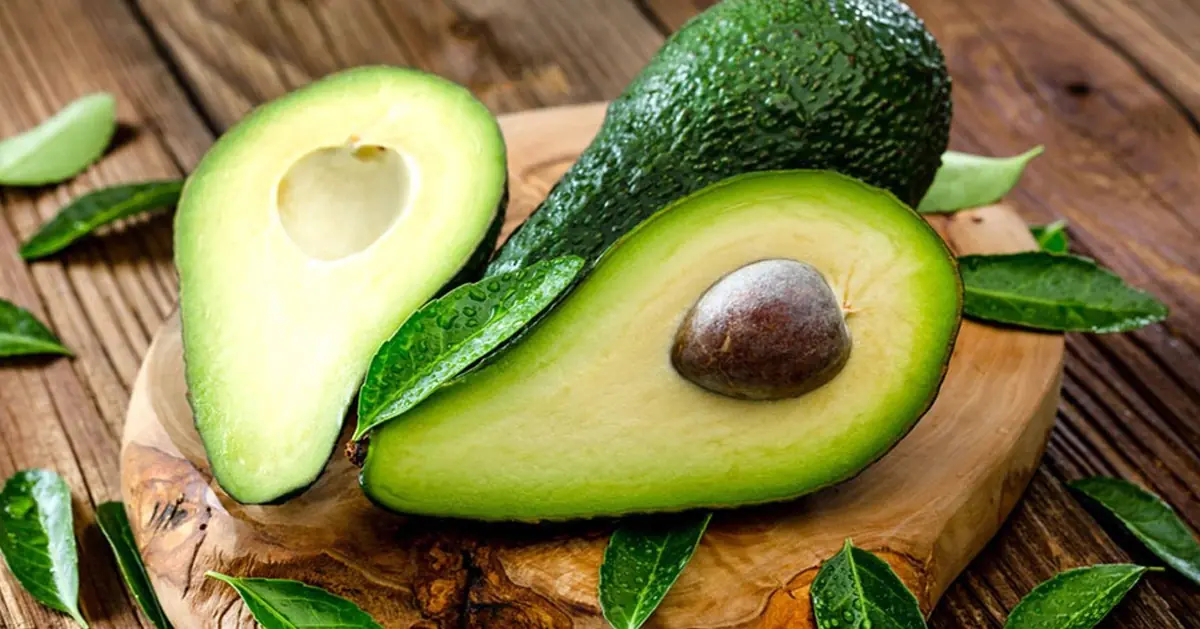

5 groups of people who should avoid avocado, no matter how much they crave it
5 Signs of Bone C.a.ncer - Doctor's Warning

A young woman nearly had her face disfigured while cooking, warning about 3 foods that can easily “expl.ode” and require caution
Look at your nails to predict your health. If your nails have these 3 points, see a doctor immediately before you re.gret it
Kidney failure doesn’t happen overnight: 8 signs that demand immediate attention
What could happen to your body if you sleep without a pillow?
Cancer cells love these 3 flavors the most many people are shocked to realize they eat them every single day
5 signs of healthy kidneys and how to recognize them
News Post

Breakfast Plate with Pancakes, Fried Egg & Avocado

Simple hack to remove mold from bathroom grout using just 2 common ingredients - Better than bleach!

5 Habits That Lead to Diabetes in the Future

What causes limb twitching while sleeping?

Why are buttons on men’s and women’s shirts always on opposite sides?

Smart people unplug the TV when checking into a hotel - Knowing why you will do it immediately

Tropical Berry Fizz Smoothie

5 Subtle Signs of Thyroid Cancer — Know Them Early to Stay Safe

70-year-old man drinks lemon water to treat high blo.od pressure for 2 years, faces unexpected outcome

Research suggests a link between blo.od type and stomach can.cer risk

These 3 vegetables have a high risk of causing can.cer. Know early to avoid them and tell your loved ones!

These 5 people should absolutely avoid eating jackfruit, no matter how much they crave it

Tiny Red Dots on Your Skin — Causes, Meanings, and When to Worry

Grilled Chicken & Pineapple Salad with Avocado

Don’t Throw Away Lemon Peels: Smart, Natural Ways to Clean and Freshen Your Home

Grilled Herb Chicken with Fresh Vegetable Salad

Strawberry Piña Colada with Malibu Frosting

The Hidden Power of Dog Rose (Rosa canina): 10 Surprising Health Benefits and How to Use It
