
5 groups of people who should absolutely NOT eat chocolate – the 3rd group will surprise you!

Chocolate is not just a type of food—it’s also a common ingredient in various cakes, snacks, and flavorings. To understand who should avoid eating chocolate and why, Long Chau Pharmacy invites you to read the following article.
Is eating chocolate good for you?
Before learning about who should avoid chocolate, it's important to understand whether chocolate is actually beneficial for your health. Chocolate is mainly made from cacao beans, along with other ingredients such as milk, additives, and sugar to create various flavors.
According to many nutrition experts and research studies, consuming chocolate at the right time, in the right way, and by the right individuals can bring many health benefits. When used properly, chocolate can provide numerous advantages:
Reduces the risk of heart disease
Research by renowned scientists shows that eating chocolate or consuming foods with a high cocoa content in moderate amounts can reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease by up to 35%. Moreover, dark chocolate with at least 70% cocoa supports better blood flow and helps prevent blood clot formation.
Lowers bad cholesterol levels
As you may know, high cholesterol is a major cause of cardiovascular issues, especially fatty blood and atherosclerosis. Regularly eating or using chocolate can reduce bad cholesterol (LDL) by up to 5% after 4–5 weeks.
Reduces the risk of diabetes
Studies show that cocoa in chocolate can stimulate the production of more insulin, helping to prevent diabetes. This benefit is most effective when you consume dark chocolate with more than 70% cocoa, and with low sugar and fat content.
Reduces stress
Another benefit of eating chocolate is its ability to reduce stress and promote relaxation. Surveys indicate that people who eat chocolate regularly are 10% less likely to suffer from depression compared to those who don’t.
Supports weight loss
Many believe that chocolate causes weight gain and that those trying to lose weight should avoid it. However, the opposite may be true. Eating moderate amounts of dark chocolate (70–85% cocoa) can stimulate the body’s hormone production, provide fiber, and increase satiety—thereby reducing food intake during meals.
Health Risks of Eating Too Much Chocolate

Despite its many benefits, chocolate should be consumed in moderation. It's also crucial to understand who should avoid it to prevent potential harm.
Obesity
Consuming large amounts of chocolate regularly—especially milk chocolate or varieties high in sugar—can greatly increase the risk of obesity.
Diabetes
While moderate chocolate intake can help prevent diabetes, overconsumption can raise blood sugar levels due to its high sugar and fat content, potentially accelerating the onset of diabetes.
Insomnia
Chocolate contains caffeine, like coffee. Eating it at night or before bed can cause sleeplessness and restlessness, leading to fatigue and moodiness the next morning.
Digestive Issues
Health experts note that eating large amounts of chocolate frequently can disrupt the digestive system. Common symptoms include bloating and indigestion, as chocolate increases stomach acid levels. Long-term overconsumption may even lead to acid reflux.
Who Should Not Eat Chocolate?
As you’ve seen, chocolate has both benefits and downsides. For certain individuals, chocolate should be strictly limited—or avoided entirely—to protect their health.
People with heart valve issues or atherosclerosis
Although chocolate is generally heart-friendly, it's not suitable for everyone. In these cases, frequent or high-fat chocolate consumption can reduce heart efficiency and increase the risk of complications. Individuals with valve problems may experience rapid heartbeat, fatigue, or dizziness after eating chocolate.
People with diabetes
Those with type 1 or type 2 diabetes should avoid eating too much chocolate. Sugary and fatty types like milk chocolate or white chocolate can spike blood sugar quickly, making it harder for insulin to regulate. If consumed, it should be in the form of dark, sugar-free chocolate and only in small amounts. People at risk of diabetes should also limit their intake.
People who are overweight or obese
Most health and nutrition experts advise overweight individuals to avoid chocolate. Its high sugar, fat, and cholesterol content contributes to rapid weight gain. However, dark chocolate with high cocoa content and low sugar can be consumed in small amounts (10–20g per serving) to curb appetite and promote satiety.
Children under 3 years old
Young children should not consume chocolate, as their digestive and excretory systems are still developing. Chocolate can cause digestive issues, restlessness, sleep disturbances, or hyperactivity in toddlers.
Breastfeeding women
Since chocolate is unsuitable for young children, it’s also best avoided by breastfeeding mothers. Compounds in chocolate can be transferred to the baby through breast milk, causing similar effects like insomnia and indigestion.
Final Notes
In summary, individuals who should not consume chocolate must be particularly cautious. It is best for them to avoid it completely to safeguard their health. For others, daily intake should not exceed 50 grams to prevent any negative impact on the body.
News in the same category

People with blue ve.ins should pay attention to this

5 Foods That Can Increase Ca.n.c.er Risk – Should Be Limited In Daily Meals

3 types of fruit that can.cer cells love

6 Subtle Changes That May Signal the Early Stages of Colo.rectal Can.cer

7 Common Vegetables That Can Cause Kid.ney Stones
Why Can Young People Still Suffer Strokes and Sudden Death? 5 Dangerous Habits You Need to Quit Immediately

5 Delicious Foods Once Misunderstood as Har.mful
Spleen Cancer: A Rare But Dangerous Disease – You Need To Know!

Achy Mornings? Here’s What Your Body’s Trying to Tell You — And How to Fix It
5 Pancreatic Can.cer Symptoms Often Mistaken for Sto.mach Issues
5 Types of Drinks That Can Harm Your Liv.er and Kid.neys at Night
Suffering from Canker Sores? Here Are 3 Powerful Home Treatments You Should Try
When Fat Invades and Des.troys the Liv.er, the Body Swells in 5 Areas

3 “Golden” Foods That Help Women During Menopause

4 Clear Warning Signs of Stro.ke

6 Bodily Changes That Are “SOS Signals” From Your Kid.neys Before Can.cer

Your Body Might Be Low on Zinc — Here Are 6 Signs to Watch For

Woman gets brain infection after eating refrigerated watermelon
News Post

Bitter mouth in the early morning - a silent sign of a serious illness?

A Wild-Growing Vegetable Once Ignored Is Now Highly Sought After

A Little-Known Leaf That Can Be Eaten Fresh or Brewed as Tea

This Vegetable Contains 60 Times More Vitamin K Than Duck Eggs

5 Types of Vegetables Rich in Natural Collagen

People with blue ve.ins should pay attention to this

How Sleeping After 11 PM Can Damage Your Body – Expert-Backed Insights

5 Foods That Can Increase Ca.n.c.er Risk – Should Be Limited In Daily Meals

3 types of fruit that can.cer cells love

Mistake #5: Almost everyone makes it—but few actually notice

A familiar vegetable ranked among the cleanest by the U.S

The royal-class meat highly praised in the U.S

This pot of stew has never been left on fire for 50 years — the reason behind it will surprise you!

Tips to Skim Excess Fat from Greasy Soup

6 Subtle Changes That May Signal the Early Stages of Colo.rectal Can.cer

Onions Aren’t Just for Cooking: 5 Surprising Hacks

No Matter How Tight Money Is, Eat These 3 Types of Meat as Little as Possible
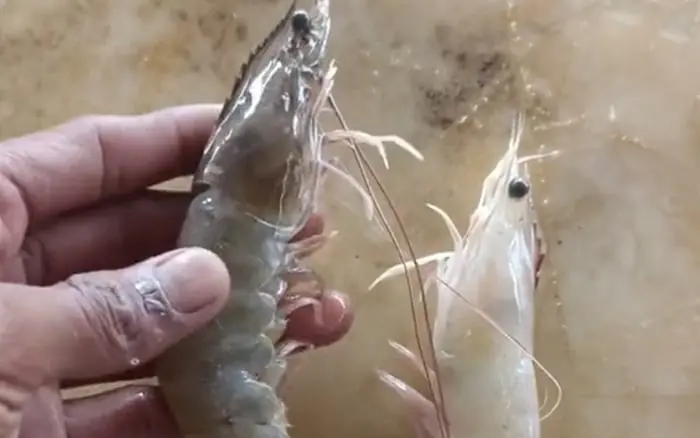

Want to Know If a Shrimp Is Farm-Raised or Wild-Caught?
