Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
A sudden, sharp pain.
A calf muscle that tightens like a knot.
Sleep instantly shattered.
If you’ve ever woken up in the middle of the night with intense leg cramps, you know how frightening—and painful—they can be. For many people, these cramps feel random and unavoidable. But doctors say nighttime leg cramps are rarely “mysterious.” They are often the body’s way of signaling an underlying imbalance or habit that can be corrected.
Here’s what causes leg cramps at night—and how to stop the pain before it starts.
Night leg cramps are sudden, involuntary muscle contractions, most commonly affecting the calf, foot, or thigh. They can last from a few seconds to several minutes and often leave lingering soreness afterward.
Unlike restless leg syndrome, cramps are painful, forceful, and localized, not just uncomfortable sensations.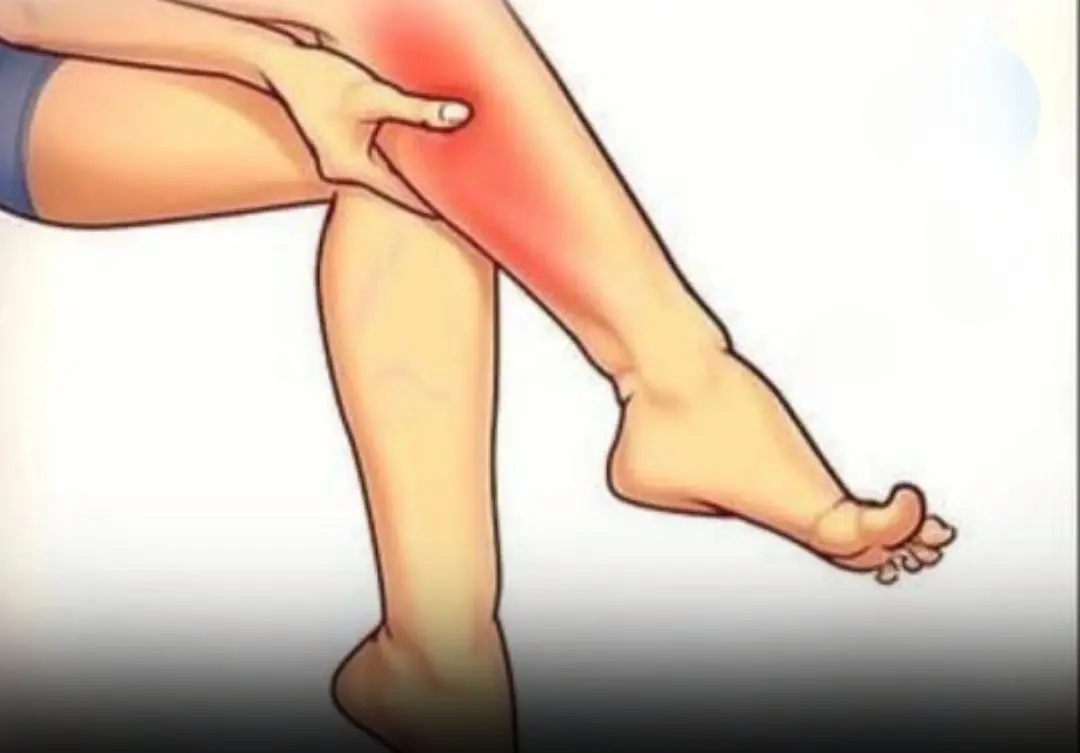
They happen most often at night because:
Muscles relax during sleep
Blood circulation slows
Electrolyte shifts become more noticeable
One of the top triggers is not drinking enough fluids during the day.
When the body is dehydrated:
Electrolytes like sodium, potassium, and magnesium fall out of balance
Muscles become more excitable
Nerves fire abnormally, triggering cramps
Many people assume dehydration only happens in hot weather, but air conditioning, caffeine, and low water intake can quietly dry the body out year-round.
Low levels of certain minerals are strongly linked to leg cramps, especially:
Magnesium – helps muscles relax
Potassium – supports muscle contraction and nerve signaling
Calcium – regulates muscle movement
Deficiencies may come from poor diet, excessive sweating, certain medications, or digestive absorption issues.
If you sit for long hours, especially with legs bent:
Blood flow to the lower limbs decreases
Muscles receive less oxygen
Nerve signaling becomes disrupted
At night, when circulation naturally slows, these muscles are more likely to spasm.

Both extremes can cause cramps.
Overuse: Intense exercise, standing all day, or repetitive movements
Underuse: Weak, deconditioned muscles from inactivity
In both cases, muscle fibers fatigue and misfire during rest.
Certain positions—especially pointing the toes downward or sleeping with heavy blankets pressing on the feet—can shorten calf muscles overnight.
This increases the chance of sudden tightening when the muscle shifts.
Night cramps are more common in people with:
Diabetes
Peripheral artery disease
Nerve compression
Kidney or liver conditions
Some medications—such as diuretics, statins, and blood pressure drugs—can also increase cramp risk by altering fluid and mineral balance.
If a cramp strikes in the middle of the night:
Stretch immediately – flex the foot upward, pulling toes toward the knee
Massage the muscle firmly
Stand and walk if possible
Apply warmth to relax tight fibers
Avoid forceful jerking, which can worsen pain or cause strain.
Drink water throughout the day—not just before bed. Avoid excessive caffeine or alcohol, which increase fluid loss.
Gentle calf and hamstring stretches for 5–10 minutes before bed can significantly reduce cramp frequency.
Include foods rich in:
Magnesium (leafy greens, nuts, seeds)
Potassium (bananas, avocados, beans)
Calcium (dairy, fortified alternatives)
Always consult a doctor before taking supplements.
Move regularly during the day. Simple leg movements, walking, or ankle rotations help maintain blood flow.
Keep feet in a neutral position. If needed, loosen heavy bedding or use a pillow to support the feet.
Occasional cramps are common.
But frequent or worsening cramps may require medical evaluation, especially if accompanied by:
Swelling or redness
Numbness or weakness
Skin discoloration
Persistent pain during the day
These may signal circulatory, nerve, or metabolic problems that need treatment.
Leg cramps aren’t just painful interruptions.
They’re often signals—small warnings before bigger problems develop.
By understanding what causes them and making simple changes, many people can dramatically reduce—or completely eliminate—nighttime leg cramps.
Better sleep often starts with listening to what your muscles are trying to say.

Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
When they occur, the outcomes are often severe and fast-moving.

If you like to take a nap during the day, then you should definitely know this
He drank water before sleeping… and never woke up. Doctors urge everyone to avoid these 4 drinks at night
Subtle physical changes can appear weeks before a heart attack strikes.
These 3 Morning Mistakes Make Blo:od Pressure & Cholesterol Worse
A 65-year-old woman died suddenly at dawn — doctors say her bedtime habits
A change in your feet may signal severe fatty liver disease — don’t ignore it

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.
Persistent itching with unusual skin bumps may signal hidden health issues.

Doctors Reveal That Eating Eggs Can Trigger Something Unexpected…

Why hard-boiled eggs get a green ring?
7 silent signs your heart could be in trouble - don't ignore these

Lines like these on your nails may be a strong warning that...

These 5 Vegetables Can Contain Hidden Worms — Be Careful When Eating Them Raw
Noticing Red Dots Like These? Your Body Could Be Sending a Warning
Why Your Throat Feels Mucusy: The Real Reasons Behind That Sticky Sensation

Why Eating Tilapia May Be More Harmful Than You Think

Health Expert Reveals 30 - Second Hand Test That Could Uncover a Hidden Brain Condition
When they occur, the outcomes are often severe and fast-moving.

If you like to take a nap during the day, then you should definitely know this

He drank water before sleeping… and never woke up. Doctors urge everyone to avoid these 4 drinks at night

Subtle physical changes can appear weeks before a heart attack strikes.

People who talk behind your back often reveal themselves through the words they use.

These 3 Morning Mistakes Make Blo:od Pressure & Cholesterol Worse

A 65-year-old woman died suddenly at dawn — doctors say her bedtime habits

A change in your feet may signal severe fatty liver disease — don’t ignore it

A single morning habit. One overlooked warning. And a medical emergency that changed everything.

Affectionate gestures after closeness often reveal a husband’s true feelings.

Persistent itching with unusual skin bumps may signal hidden health issues.

Small habits that quietly drain passion and intimacy in relationships.

Doctors Reveal That Eating Eggs Can Trigger Something Unexpected…
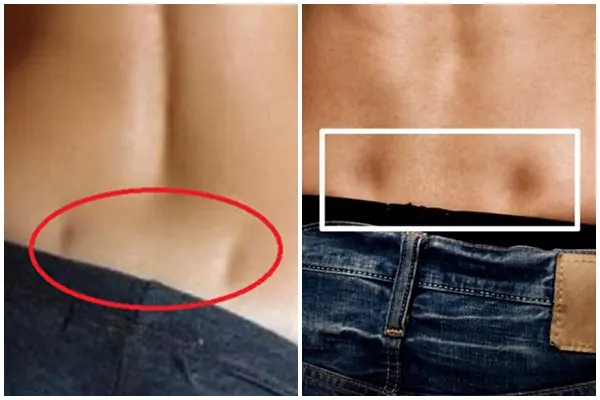

If You Have These Two Small Dimples on Your Lower Back, They May Reveal Something Fascinating

Why Do Japanese People Avoid Eye Contact for Too Long? It’s Not What You Think

On trains or in crowded places, the silence of the Japanese people intrigues many tourists. What is the real reason behind it?

How often should underwear be changed for good hygiene?
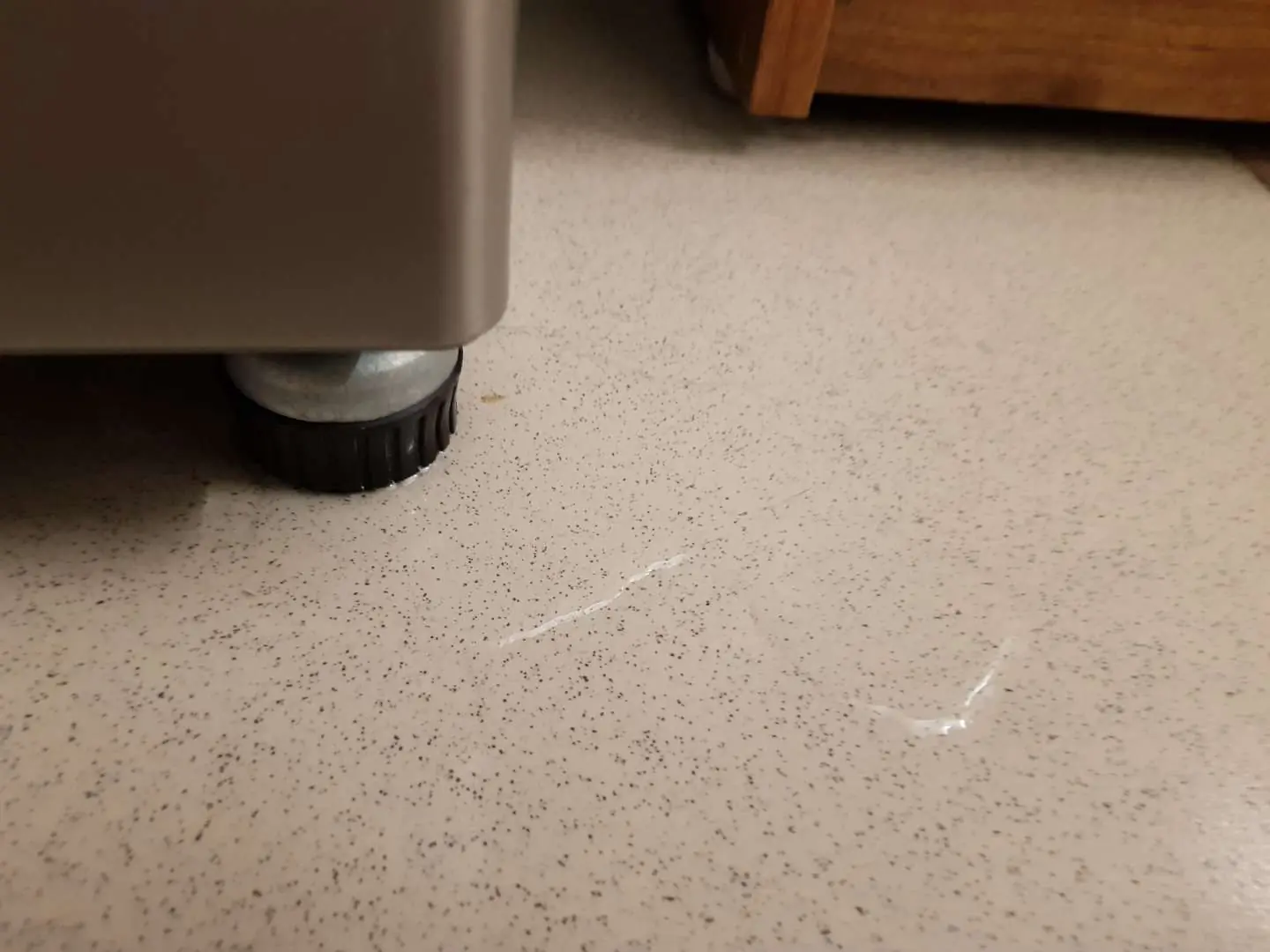

How to Fix a Leaking Refrigerator: Easy Solutions and Maintenance Tips