Why Your Throat Feels Sticky: The Real Causes of Mucus
Why Your Throat Feels Sticky: The Real Causes of Mucus
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects millions of children and adults around the world.
Characterized by differences in social interaction, communication, and patterns of behavior, autism exists on a broad spectrum, with each
individual experiencing it in a unique way. Despite decades of scientific investigation, the underlying causes of autism have remained only
partially understood.
Researchers agree that autism does not stem from a single cause. Instead, it appears to arise from a complex interaction of genetic,
biological, and environmental factors, many of which begin influencing development long before birth. Recently, however, a new line of
research has offered valuable insight into how autism may begin during early brain development, bringing scientists closer to understanding
one of its possible biological foundations.
This article explores recent research findings, what they suggest about autism’s origins, and how these discoveries may shape future
diagnosis, intervention, and support.
Autism has long challenged researchers because of its diversity. Some individuals require substantial daily support, while others live
independently with minimal assistance. This wide variation makes it difficult to identify a single biological pathway responsible for ASD.
For many years, scientists have suspected a strong genetic component, supported by family and twin studies. At the same time,
environmental influences - such as prenatal health, maternal stress, infections, or exposure to certain substances—have also been examined.
However, no single factor has been able to fully explain how autism develops.
Most experts now believe autism arises from multiple factors acting together, especially during critical periods of early brain development.
Understanding exactly how and when these factors interact has remained one of the most important challenges in neuroscience.
Recent studies have shed new light on how autism may begin during early prenatal brain development. According to this research, certain
genetic variations may affect how the brain’s neural networks form during the earliest stages of pregnancy.
Rather than focusing on autism as something that emerges later in childhood, this work suggests that subtle changes in brain wiring may
occur long before behavioral signs appear. These early changes may influence how brain regions responsible for communication, social
interaction, and sensory processing develop.
Researchers have identified specific genetic mutations that appear to influence how neurons form, migrate, and connect during early
development. These mutations may alter communication between brain cells, leading to differences in how information is processed.
Such differences do not necessarily indicate damage but rather atypical development, which aligns with the concept of autism as a
neurodevelopmental difference rather than a single pathological condition.
One of the most significant findings highlights the first trimester of pregnancy as a critical window for brain development. During this time,
the foundations for regions involved in social behavior, language, and cognition are established.
Disruptions during this sensitive period - whether genetic or biological may influence how these brain systems mature, potentially
contributing to traits associated with autism later in life.
Another important discovery involves proteins that guide neural growth and connectivity. In embryos with certain genetic risk factors, these
proteins may not be produced or regulated correctly.
Because these proteins play a crucial role in building communication pathways in the brain, altered production could affect how neural circuits
form and function, leading to long-term developmental differences.
While no single study can fully explain autism, this research provides an important piece of the larger puzzle. It helps clarify when and where
autism-related differences may begin, offering several promising directions for future research.
Greater understanding of early brain development could eventually lead to improved screening methods that identify autism-related risk
factors earlier than ever before. Earlier identification does not mean labeling or limiting a child, but rather providing support sooner, when
the brain is most adaptable.
By understanding the biological pathways involved in early brain development, researchers may be able to design interventions that support
healthy neural communication. These approaches would focus on supporting development, not changing who a person is.
This research reinforces the idea that autism is not a single condition but a spectrum shaped by many influences. Identifying biological
differences helps explain why individuals with autism can have very different strengths, challenges, and needs.
Despite this progress, autism remains a deeply complex condition. No single cause applies to everyone on the spectrum, and future research
will need to explore how genetics, environment, and early development interact over time.
What this research does offer is hope and clarity - hope for earlier support, better understanding, and more personalized approaches to care,
and clarity about the importance of early brain development in shaping lifelong outcomes.
Scientific progress goes hand in hand with social responsibility. Alongside research, society plays a crucial role in creating inclusive
environments where individuals with autism can thrive.
Ways to contribute include:
Supporting reputable autism research organizations
Promoting awareness and acceptance
Encouraging inclusive education and workplaces
Offering understanding and support to families
The discovery of potential links between early brain development and autism represents a meaningful step forward in understanding ASD.
While it does not provide all the answers, it deepens our understanding of autism as a natural variation in human development shaped by
biology and experience.
As research continues to evolve, so too does the opportunity to provide better support, earlier guidance, and a more inclusive society for
individuals on the autism spectrum. Knowledge alone is powerful - but when paired with empathy and action, it has the potential to change
lives.

Why Your Throat Feels Sticky: The Real Causes of Mucus

Fa.tty liver explained: Causes, symptoms and effective treatment options
Doctors Issue Warning: These 4 Morning Symptoms May Signal Lung Cancer Is Advancing

Why You Often Need to Poop Right After Eating — Explained by Doctors

Doctors identify the blo.od type linked to the lowest can.cer risk

An overlooked vegetable packed with nutrients and remarkably high in calcium
This natural drink may help ease mucus, cough and sinus discomfort
How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat

Eating walnuts regularly can bring a wide range of health benefits

You don’t need to believe in magic drinks to enjoy beet juice.


These foods were found to benefit not only cardiovascular health but also provide clear advantages for the nervous system and cognitive function.
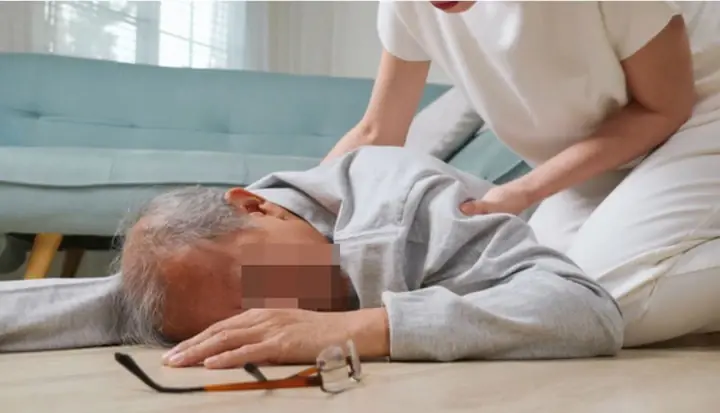
A single rushed movement after waking up can trigger a stroke.
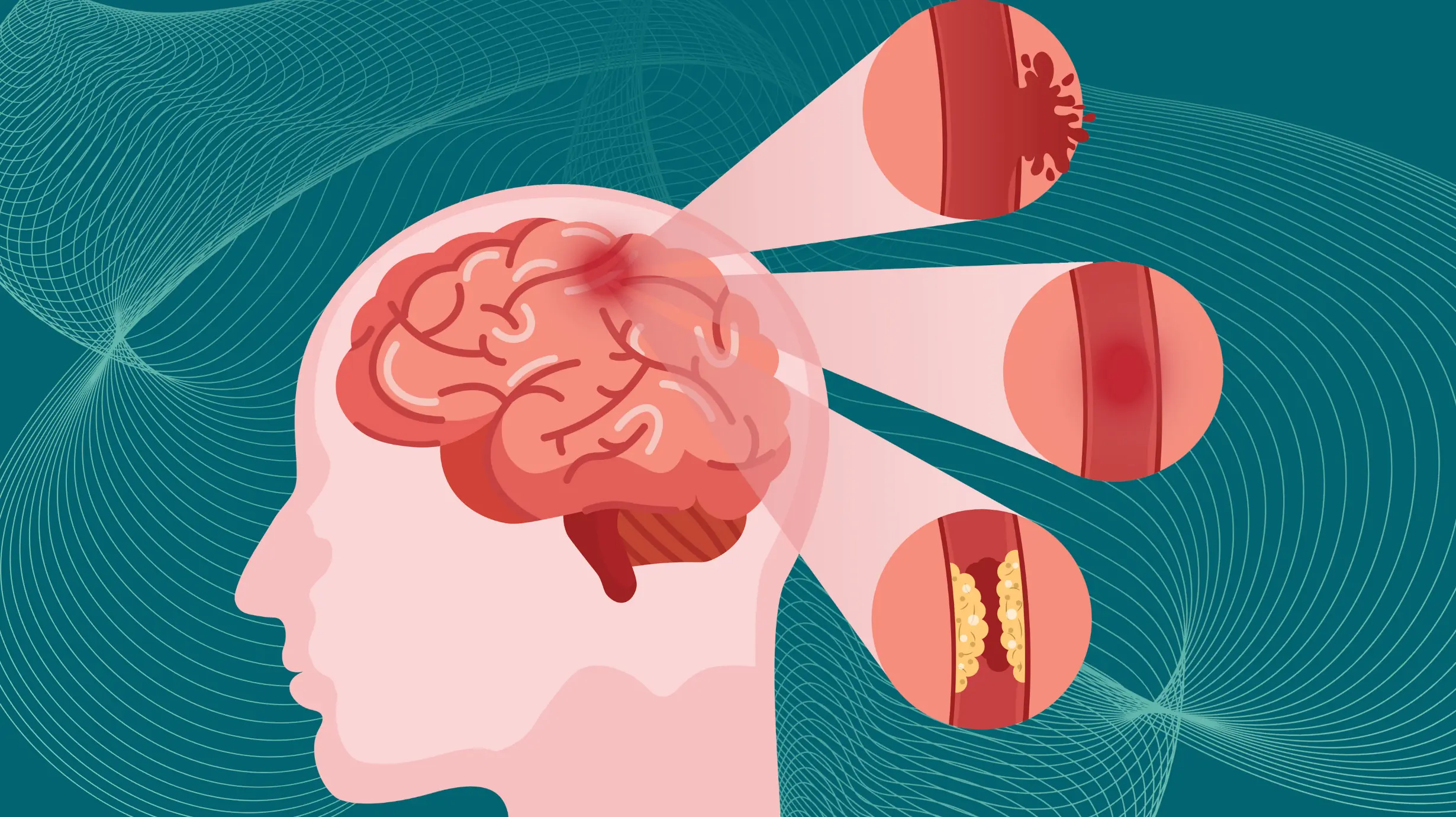
Preventing Stroke At Any Age: 3 “Don’ts” After Meals — And 4 “Don’t” Before Bed

Nighttime leg cramps may signal dehydration or hidden health issues.
Say Goodbye to Swelling …
Understanding Mucus in the Throat: Causes You Might Not Expect
Some unhealthy habits during intimacy may be a hidden cause of cervical can.cer in women

Why Your Throat Feels Sticky: The Real Causes of Mucus

Fa.tty liver explained: Causes, symptoms and effective treatment options

Doctors Issue Warning: These 4 Morning Symptoms May Signal Lung Cancer Is Advancing

Why You Often Need to Poop Right After Eating — Explained by Doctors

Doctors identify the blo.od type linked to the lowest can.cer risk

An overlooked vegetable packed with nutrients and remarkably high in calcium

This natural drink may help ease mucus, cough and sinus discomfort

How to get rid of phlegm and mucus in your chest and throat

A creamy, healthy burrito that’s quick to make and impossible to resist.

Eating walnuts regularly can bring a wide range of health benefits

You don’t need to believe in magic drinks to enjoy beet juice.

After a period of use, showerheads often get clogged due to mineral deposits sticking inside, causing uneven water flow.

Here’s a surprisingly simple household trick to sharpen your old, dull scissors without any special tools.


These foods were found to benefit not only cardiovascular health but also provide clear advantages for the nervous system and cognitive function.

A single rushed movement after waking up can trigger a stroke.
Your sleeping posture may reveal more about your future than you think.

Preventing Stroke At Any Age: 3 “Don’ts” After Meals — And 4 “Don’t” Before Bed

Certain everyday phrases may quietly signal emotional or physical infidelity.